Changes in Volatile and Non-Volatile Flavor Chemicals of “Valencia” Orange Juice over the Harvest Seasons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Fruit and Juice Preparation
2.2. General Fruit and Juice Features
2.3. Sugar and Acid Analyses
2.4. Limonoid Analysis
2.5. Volatile Analysis
2.6. Pectin and PME
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Fruit and Juice Features
| Attribute | Content/value in 2007 | Content/value in 2012 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | |
| fruit weight (g·fruit−1) | 105 b a | 108 ab | 111 a | 107 b | 144 b | 148 ab | 153 a | 146 b |
| peel oil (g·100·g−1) | 0.024 b | 0.025 b | 0.035 a | 0.025 b | ||||
| insoluble solids (g·100·g−1) | 1.5 b | 1.4 b | 1.4 b | 1.8 a | ||||
| pectin (GAb, mg·g−1) | 0.037 b | 0.095 b | 0.285 a | 0.310 a | 0.46 b | 0.52 ab | 0.53 ab | 0.56 a |
| PME c activity (µmol·min−1·mL−1) | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.31 | ||||
| juice color number | 39.5 a | 39.7 a | 38.5 b | 38.8 b | ||||
| juice content (mL·100·g−1) | 53 a | 49 b | 50 b | 46 c | 57 a | 55 b | 55 b | 49 c |
| titratable acidity (TA, g·100·g−1) | 0.82 a | 0.68 b | 0.57 c | 0.43 d | 1.07 a | 0.93 b | 0.74 c | 0.68 d |
| citric acid (g·100·g−1) | 1.06 a | 0.80 b | 0.62 c | 0.62 c | ||||
| malic acid (g·100·g−1) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | ||||
| soluble solids content (SSC, g·100·g−1) | 10.7 ab | 10.1 b | 10.6 ab | 11.0 a | 12.1 c | 12.7 b | 13.2 ab | 13.6 a |
| sucrose (g·100·g−1) | 4.9 b | 5.2 ab | 5.5 a | 5.6 a | 4.8 c | 5.1 bc | 5.9 b | 6.6 a |
| glucose (g·100·g−1) | 1.9 a | 1.9 a | 2.0 a | 2.0 a | 3.7 ab | 3.3 b | 3.5 ab | 4.0 a |
| fructose (g·100·g−1) | 1.9 a | 2.0 a | 2.0 a | 2.0 a | 3.2 b | 3.1 b | 3.0 b | 3.7 a |
| SSC/TA ratio | 13.2 d | 15.1 c | 18.6 b | 25.8 a | 11 d | 14 c | 18 b | 20 a |
| limonin (µg·g−1) | 0.90 a | 0.78 ab | 0.67 bc | 0.52 c | 5.6 a | 3.9 b | 2.5 c | 2.4 c |
| nomilin (µg·g−1) | 0.22 ab | 0.30 a | 0.12 b | 0.06 b | 1.9 a | 1.5 b | 1.3 b | 0.9 c |
3.2. Sugars and Acids
3.3. Limonoids
3.4. Pectin and PME Activity
3.5. Volatiles

| Compound | Oder Description a | Threshold in OJ Matrix (µg·mL−1) b | Concentration (µg·mL−1) by DHS in 2007 | Concentration (µg·mL−1) by HS-SPME in 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group c | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Group c | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | |||||||||||
| d-limonene | Citrus, lemon, minty | 13.3 | C1 | 58 | b d | 90 | b | 336 | a | 302 | a | C2 | 224 | c | 217 | c | 298 | a | 248 | b |
| myrcene | Mossy, musty, geranium | 0.5 | C1 | 0 | b | 0 | b | 2.64 | a | 2.53 | a | C2 | 0.86 | c | 0.78 | c | 1.42 | a | 1.15 | b |
| α-pinene | Resin, pine tree, ethereal | 2.0 | C1 | 0.1 | b | 0.15 | b | 0.83 | a | 0.79 | a | C2 | 0.38 | c | 0.32 | c | 0.66 | a | 0.53 | b |
| γ-terpinene | Sweet, citrus | 2.1 e | A5 | 0.0038 | b | 0.0010 | c | 0.0049 | ab | 0.0060 | a | |||||||||
| valencene | Lemon, floral | 10.5 | B2 | 2.71 | a | 2.59 | a | 2.46 | a | 2.49 | a | A1 | 2.1 | c | 2.5 | bc | 2.8 | b | 3.3 | a |
| linalool | Floral, fruity, sweet | 0.1 | C1 | 1.66 | c | 2.1 | b | 3.15 | a | 2.9 | a | C1 | 0.17 | b | 0.12 | b | 1.05 | a | 0.20 | b |
| α-terpineol | Lemon, minty, piney | 9.1 | A7 | 0.94 | a | 0.8 | b | 0.76 | b | 0.99 | a | A5 | 0.15 | ab | 0.14 | b | 0.17 | a | 0.20 | a |
| nootkatone | Grapefruit, green | 3.1 | C3 | 0.080 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.03 | |||||||||||||
| geranial | Citrus, minty, green | 0.7 | C1 | 0.031 | c | 0.022 | c | 0.042 | a | 0.036 | b | |||||||||
| neral | Citrus, lemon, minty | 0.7 | C1 | tr | b | tr | b | 0.0033 | a | tr | b | |||||||||
| β-sinensal | orange, fruity | 0.004 f | C4 | 0.0023 | c | 0.0030 | c | 0.0083 | a | 0.0061 | b | |||||||||
| acetaldehyde | Fresh, fruity, solvent | 0.3 | C4 | 4.9 | a | 8.1 | a | 7.2 | a | 7.8 | a | B1 | 4.1 | a | 3.7 | a | 2.2 | b | 1.6 | b |
| hexanal | Grassy, green, soapy | 0.09 | A5 | 0.04 | b | 0.02 | c | 0.04 | b | 0.07 | a | C1 | 0.000 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.00 | ||||
| (Z)-3-hexenal | Green, grassy | 0.02 | A3 | 0.019 | b | 0.017 | b | 0.016 | b | 0.047 | a | |||||||||
| octanal | Floral, citrus, green | 0.1 | C1 | 0 | b | 0.04 | b | 0.53 | a | 0.05 | b | C2 | 0.12 | b | 0.10 | b | 0.21 | a | 0.12 | b |
| nonanal | Citrus, floral, soapy | 0.2 | C1 | 0.004 | b | 0.006 | b | 0.017 | a | 0.006 | b | |||||||||
| decanal | Citrus, fatty, green | 0.1 | C1 | 0.05 | c | 0.05 | c | 0.26 | a | 0.01 | b | C1 | 0.143 | c | 0.180 | b | 0.287 | a | 0.257 | ab |
| (E,E)-2,4-decadienal | Fatty, waxy, green | 0.004 | A1 | 0.027 | b | 0.033 | c | 0.061 | b | 0.079 | a | |||||||||
| ethyl acetate | Fruity, solvent | 11.0 | B4 | 3.86 | a | 3.27 | b | 3.43 | b | 3.02 | c | A2 | 0.24 | b | 0.25 | b | 0.26 | b | 0.49 | a |
| ethyl butanoate | Fruity, pineapple | 0.005 | C3 | 0.06 | b | 0.86 | a | 0.09 | a | 0.08 | a | A7 | 0.90 | ab | 0.89 | b | 0.77 | b | 1.21 | a |
| methyl butanoate | Fruity, stawberry | 0.4 | C1 | 0.01 | b | 0.02 | ab | 0.04 | a | 0.03 | ab | A5 | 0.014 | 0.007 | 0.019 | 0.025 | ||||
| ethyl 2-methylbutanoate | Fruity | 0.0002 | A6 | 0.025 | tr | tr | 0.038 | |||||||||||||
| ethyl 3-hydroxyhexanoate | Citrus | 10.2 | A4 | 0.325 | 0.155 | 0.183 | 0.197 | |||||||||||||

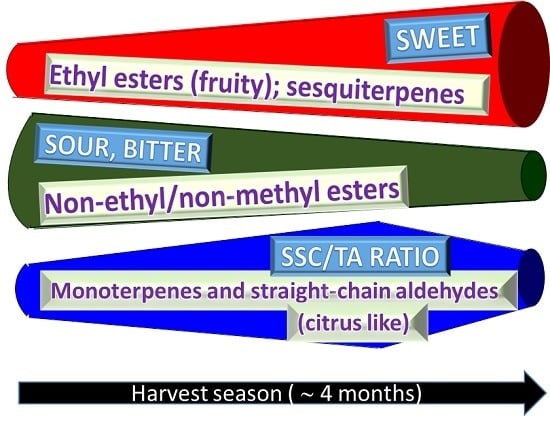
3.6. Overall Flavor Quality


4. Conclusions
5. Disclaimer
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimball, D.; Parish, M.E.; Braddock, R. Oranges and tangerines. In Processing Fruits: Science and Technology; Barrett, D.M., Somogyi, L.P., Ramaswamy, H.S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 617–638. [Google Scholar]
- Soule, J.; Grierson, W.; Blair, J. Quality tests for citrus fruits; University of Florida, Cooperative Extention Service: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1967; p. 315. [Google Scholar]
- Ritenour, M.A. Orange. In The Commercial Storage of Fruits, Vegetables, and Florist and Nursery Stocks; Agriculture Handbook, No. 66; Gross, K., Wang, C.Y., Saltveit, M., Eds.; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. Available online: http://www.ba.ars.usda.gov/hb66/orange.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Models for seasonal changes in °Brix and ratio of citrus fruit juice. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 1990, 103, 251–255. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, V.; Hasegawa, S.; Bennett, R.; Echols, L. Limonin and limonoids: Chemistry, biochemistry, and juice bitterness. In Citrus Nutrition and Quality; Nagy, S., Attaway, J.A., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, S.; Miyake, M. Biochemistry and biological functions of citrus limonoids. Food Rev. Int. 1996, 12, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, E.; Bai, J.; Plotto, A.; Ritenour, M. Citrus fruit quality assessment: Producer and consumer perspectives. Stewart Postharvest Rev. 2014, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Dagulo, L.; Danyluk, M.D.; Spann, T.M.; Valim, M.F.; Goodrich-Schneider, R.; Sims, C.; Rouseff, R. Chemical characterization of orange juice from trees infected with citrus greening (Huanglongbing). J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C199–C207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Cacho, P.R.; Rouseff, R.L. Fresh squeezed orange juice odor: A review. Critical Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotto, A.; Margaría, C.A.; Goodner, K.L.; Baldwin, E.A. Odour and flavour thresholds for key aroma components in an orange juice matrix: Esters and miscellaneous compounds. Flavour Fragr. J. 2008, 23, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotto, A.; Margaría, C.A.; Goodner, K.L.; Goodrich, R.; Baldwin, E.A. Odour and flavour thresholds for key aroma components in an orange juice matrix: Terpenes and aldehydes. Flavour Fragr. J. 2004, 19, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.E. Fruit II. In Volatile Compounds in Foods and Beverages; Maarse, H., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 305–327. [Google Scholar]
- González-Mas, M.C.; Rambla, J.L.; Alamar, M.C.; Gutiérrez, A.; Granell, A. Comparative analysis of the volatile fraction of fruit juice from different Citrus species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cameron, R.G.; Baker, R.A.; Grohmann, K. Multiple forms of pectinmethylesterase from citrus peel and their effects on juice cloud stability. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brat, P.; Rega, B.; Alter, P.; Reynes, M.; Brillouet, J.-M. Distribution of volatile compounds in the pulp, cloud, and serum of freshly squeezed orange juice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3442–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, T.; Kawashima, K.; Friedel, P.K.; Pope, L.E.; Gianturco, M.A. Distribution of volatile compounds between the pulp and serum of some fruit juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1974, 22, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwald, T.R. Current epidemiological understanding of citrus huanglongbing. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010, 48, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, E.; Plotto, A.; Manthey, J.; McCollum, G.; Bai, J.; Irey, M.; Cameron, R.; Luzio, G. Effect of Liberibacter infection (Huanglongbing disease) of citrus on orange fruit physiology and fruit/fruit juice quality: Chemical and physical analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotto, A.; Baldwin, E.; McCollum, G.; Manthey, J.; Narciso, J.; Irey, M. Effect of Liberibacter infection (Huanglongbing or “Greening” disease) of citrus on orange juice flavor quality by sensory evaluation. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, S220–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Hartung, J.S.; Levy, L. Quantitative real-time PCR for detection and identification of Candidatus Liberibacter species associated with citrus huanglongbing. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 66, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Baldwin, E.; Liao, H.-L.; Zhao, W.; Kostenyuk, I.; Burns, J.; Irey, M. Extraction of DNA from orange juice, and detection of bacterium Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus by real-time PCR. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9339–9346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Baldwin, E.A.; Bai, J.; Plotto, A.; Irey, M.S. Method for Assessing Juice/Cider Quality and/or Safety. U.S. Patent 20150093755 A1, 2 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, E.A.; Bai, J.; Plotto, A.; Cameron, R.; Luzio, G.; Narciso, J.; Manthey, J.; Widmer, W.; Ford, B.L. Effect of extraction method on quality of orange juice: Hand-squeezed, commercial-fresh squeezed and processed. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2029–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, W.C.; Veldhuis, M.K. Rapid estimation of recoverable oil in citrus juices by bromate titration. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1966, 49, 628–633. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Manthey, J.A.; Ford, B.L.; Luzio, G.; Cameron, R.G.; Narciso, J.; Baldwin, E.A. Effect of extraction, pasteurization and cold storage on flavonoids and other secondary metabolites in fresh orange juice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthey, J.A. Differences in secondary metabolites in leaves from orange (Citrus sinensis L.) trees affected with greening disease (Huanglongbing) (HLB). Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 2008, 121, 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, S.; Bennett, R.D.; Herman, Z.; Fong, C.H.; Ou, P. Limonoid glucosides in citrus. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 1717–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, H.; Fong, C.H.; Berhow, M.; Hasegawa, S. Thin-layer and high-performance liquid chromatographic analyses of limonoids and limonoid glucosides in Citrus seeds. J. Chromatogr. A 1993, 639, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Baldwin, E.; Stover, E.; Driggers, R.; Hearn, J. Volatile Profile Comparison of USDA Sweet Orange-Like Hybrids Versus "Hamlin" and "Ambersweet". Hort Sci. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. United States Standards for Grades of Orange Juice; USDA-AMS: Washington, DC, USA, 1983; p. 15.
- Rich, T.F. Orange stripper essence and stripper oil having high ratios of more desirable to less desirable flavor compounds. U.S. Patent No. 4,973,485, 27 November 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, T.G.; Klieber, A.; Sedgley, M. The relationship between oil gland and fruit development in Washington navel orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck). Ann. Bot. 2001, 88, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, G.W. A brief history of the lysigenous gland hypothesis. Bot. Re. 1999, 65, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, R.F. Frozen Concentrated Orange Juice from Florida Oranges; Univ. Fla. IFAS Extension: Gainsville, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, R.L.D. Selected studies of consumer preferences for canned orange juices. Proc. Fla. State Hortic. Soc. 1952, 65, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, E.A. Citrus fruit. In Biochemistry of Fruit Ripening; Seymour, G.B., Taylor, J.E., Tucker, G.A., Eds.; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 107–149. [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria, E.; Valich, J. Carbohydrate and enzyme distribution in protoplasts from valencia orange juice sacs. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruemmer, J.H. Terminal oxidase activity during ripening of Hamlin orange. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 2901–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagni, D.G.; Maier, V.P.; Turnbaugh, J.G. Effect of neodiosmin on threshold and bitterness of limonin in water and orange juice. J. Food Sci. 1976, 41, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.L.; Nisperos, M.O. Changes in the chemical constituents of New Zealand grapefruit during maturation. Food Chem. 1983, 11, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, D. Factors affecting the rate of maturation of citrus fruits. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 1984, 97, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Dea, S.; Plotto, A.; Manthey, J.A.; Raithore, S.; Irey, M.; Baldwin, E. Interactions and thresholds of limonin and nomilin in bitterness perception in orange juice and other matrices. J. Sens. Stud. 2013, 28, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A.; Gomez-Carneros, C. Bitter taste, phytonutrients, and the consumer: A review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rouseff, R. Bitterness in food products: An overview. In Bitterness in Foods and Beverages. Developments in Food Science; Rouoseff, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 25, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, R.A.; Cameron, R.G. Clouds of citrus juices and juice drinks. Food Technol. 1999, 53, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Galant, A.L.; Widmer, W.W.; Luzio, G.A.; Cameron, R.G. Characterization of molecular structural changes in pectin during juice cloud destabilization in frozen concentrated orange juice. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.R.; Singh, R.K.; Handa, A.K. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1997, 37, 47. [PubMed]
- Sinclair, W.B.; Jolliffe, V.A. Pectic substances of Valencia oranges at different stages of maturity. J. Food Sci. 1961, 26, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, A.H.; Atkins, C.D.; Moore., E.L. The occurrence and evaluation of pectin in component parts of Valencia oranges during maturation. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 1962, 75, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Rouse, A.; Moore, E. Effect of maturity, variety and processing on color, cloud, pectin and water-insoluble solids of orange juice. II. Pectin and water-insoluble solids. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 1975, 88, 342–345. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, R.G.; Baker, R.A.; Buslig, B.S.; Grohmann, K. Effect of juice extractor settings on juice cloud stability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 2865–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versteeg, C.; Rombouts, F.; Spaansen, C.; Pilnik, W. Thermostability and orange juice cloud destabilizing properties of multiple pectinesterases from orange. J. Food Sci. 1980, 45, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon-Asa, L.; Shalit, M.; Frydman, A.; Bar, E.; Holland, D.; Or, E.; Lavi, U.; Lewinsohn, E.; Eyal, Y. Citrus fruit flavor and aroma biosynthesis: Isolation, functional characterization, and developmental regulation of Cstps1, a key gene in the production of the sesquiterpene aroma compound valencene. Plant J. 2003, 36, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Plotto, A.; Baldwin, E.A.; Bai, J.; Huang, M.; Yu, Y.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Gmitter, F.G. Proteomic and metabolomic analyses provide insight into production of volatile and non-volatile flavor components in mandarin hybrid fruit. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Hagenmaier, R.D.; Baldwin, E.A. Volatile response of four apple varieties with different coatings during marketing at room temperature. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7660–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, Y.; Tsuda, A.; Bai, J.; Fujishita, N.; Chachin, K. Characteristic pattern of aroma ester formation from banana, melon and strawberry with reference to the substrate specificity of ester synthetase and alcohol contents in pulp. J. Jpn. Food Sci. Technol. 1992, 39, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, C.; Peters, J.S.; Tieman, D.M.; Tiznado, M.E.; Handa, A.K. Pectin methylesterase regulates methanol and ethanol accumulation in ripening tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) fruit. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 4293–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekwilder, J.; Alvarez-Huerta, M.; Neef, E.; Verstappen, F.W.A.; Bouwmeester, H.J.; Aharoni, A. Functional Characterization of Enzymes Forming Volatile Esters from Strawberry and Banana. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1865–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, K. Green leaf volatiles: Hydroperoxide lyase pathway of oxylipin metabolism. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Baldwin, E.A.; Imahori, Y.; Kostenyuk, I.; Burns, J.; Brecht, J.K. Chilling and heating may regulate C6 volatile aroma production by different mechanisms in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2011, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Baldwin, E.A.; Plotto, A.; Luo, W.; Raithore, S.; Yu, Z.; Bai, J. Effect of methyl salicylate and methyl jasmonate pre-treatment on the volatile profile in tomato fruit subjected to chilling temperature. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 108, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, S.G.; Leach, D.; Nonhebel, H.; Lusunzi, I. Biochemical pathways for the formation of esters in ripening fruit. In Flavour Science. Recent Developments; Taylor, A.J., Mottram, D.S., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1997; pp. 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán, G.; Bejaoui, M.A.; Jimenez, A.; Sanchez-Ortiz, A. Ethanol in olive Fruit. Changes during ripening. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5309–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrı́guez-Concepción, M.; Boronat, A. Elucidation of the methylerythritol phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria and plastids. A metabolic milestone achieved through genomics. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kealey, K.; Kinsella, J.; Nagy, S. Orange juice quality with an emphasis on flavor components. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1979, 11, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alférez, F.; Burns, J.K. Postharvest peel pitting at non-chilling temperatures in grapefruit is promoted by changes from low to high relative humidity during storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 32, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Xie, B.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G.; Yao, X.L.; Pan, S.Y. Characterization of aroma active compounds in fruit juice and peel oil of Jinchen sweet orange fruit (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) by GC-MS and GC-O. Molecules 2008, 13, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.M.; Dennison, R.A.; Dougherty, R.H.; Shaw, P.E. Flavor and odor thresholds in water of selected orange juice components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Plotto, A.; Baldwin, E.A.; Reyes-De-Corcuera, J.I.; Gmitter, F.G., Jr. Aroma characterization of tangerine hybrids by gas-chromatography–olfactometry and sensory evaluation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arctander, S. Perfume and Flavor Chemicals (Aroma Chemicals); Vol. I; Published by the Author: Montclair, NJ, USA, 1969; p. 332. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz Perez-Cacho, P.; Mahattanatawee, K.; Smoot, J.M.; Rouseff, R. Identification of sulfur volatiles in canned orange juices lacking orange flavor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5761–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausch, B.J.; Lorjaroenphon, Y.; Cadwallader, K.R. Flavor chemistry of lemon-lime carbonated beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazemore, R.; Rouseff, R.; Naim, M. Linalool in orange juice: Origin and thermal stability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisperos-Carriedo, M.O.; Shaw, P.E. Comparison of volatile flavor components in fresh and processed orange juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleva-Toledo, E.; Naim, M.; Zehavi, U.; Rouseff, R. Formation of α-terpineol in Citrus Juices, Model and Buffer Solutions. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshonas, M.G.; Shaw, P.E. Isolation of trans, trans-2,4-decadienal and intermedeol from cold-pressed citrus oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1979, 27, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selli, S.; Cabaroglu, T.; Canbas, A. Volatile flavour components of orange juice obtained from the cv. Kozan of Turkey. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2004, 17, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, E.A.; Goodner, K.; Plotto, A. Interaction of volatiles, sugars, and acids on perception of tomato aroma and flavor descriptors. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, S294–S307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, J.; Baldwin, E.A.; McCollum, G.; Plotto, A.; Manthey, J.A.; Widmer, W.W.; Luzio, G.; Cameron, R. Changes in Volatile and Non-Volatile Flavor Chemicals of “Valencia” Orange Juice over the Harvest Seasons. Foods 2016, 5, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods5010004
Bai J, Baldwin EA, McCollum G, Plotto A, Manthey JA, Widmer WW, Luzio G, Cameron R. Changes in Volatile and Non-Volatile Flavor Chemicals of “Valencia” Orange Juice over the Harvest Seasons. Foods. 2016; 5(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods5010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Jinhe, Elizabeth A. Baldwin, Greg McCollum, Anne Plotto, John A. Manthey, Wilbur W. Widmer, Gary Luzio, and Randall Cameron. 2016. "Changes in Volatile and Non-Volatile Flavor Chemicals of “Valencia” Orange Juice over the Harvest Seasons" Foods 5, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods5010004
APA StyleBai, J., Baldwin, E. A., McCollum, G., Plotto, A., Manthey, J. A., Widmer, W. W., Luzio, G., & Cameron, R. (2016). Changes in Volatile and Non-Volatile Flavor Chemicals of “Valencia” Orange Juice over the Harvest Seasons. Foods, 5(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods5010004