Multi-Sip Time–Intensity Evaluation of Retronasal Aroma after Swallowing Oolong Tea Beverage
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Measurement of Temporal Changes in Sensory Attributes
1.2. Multi-Sip Sensory Evaluation
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
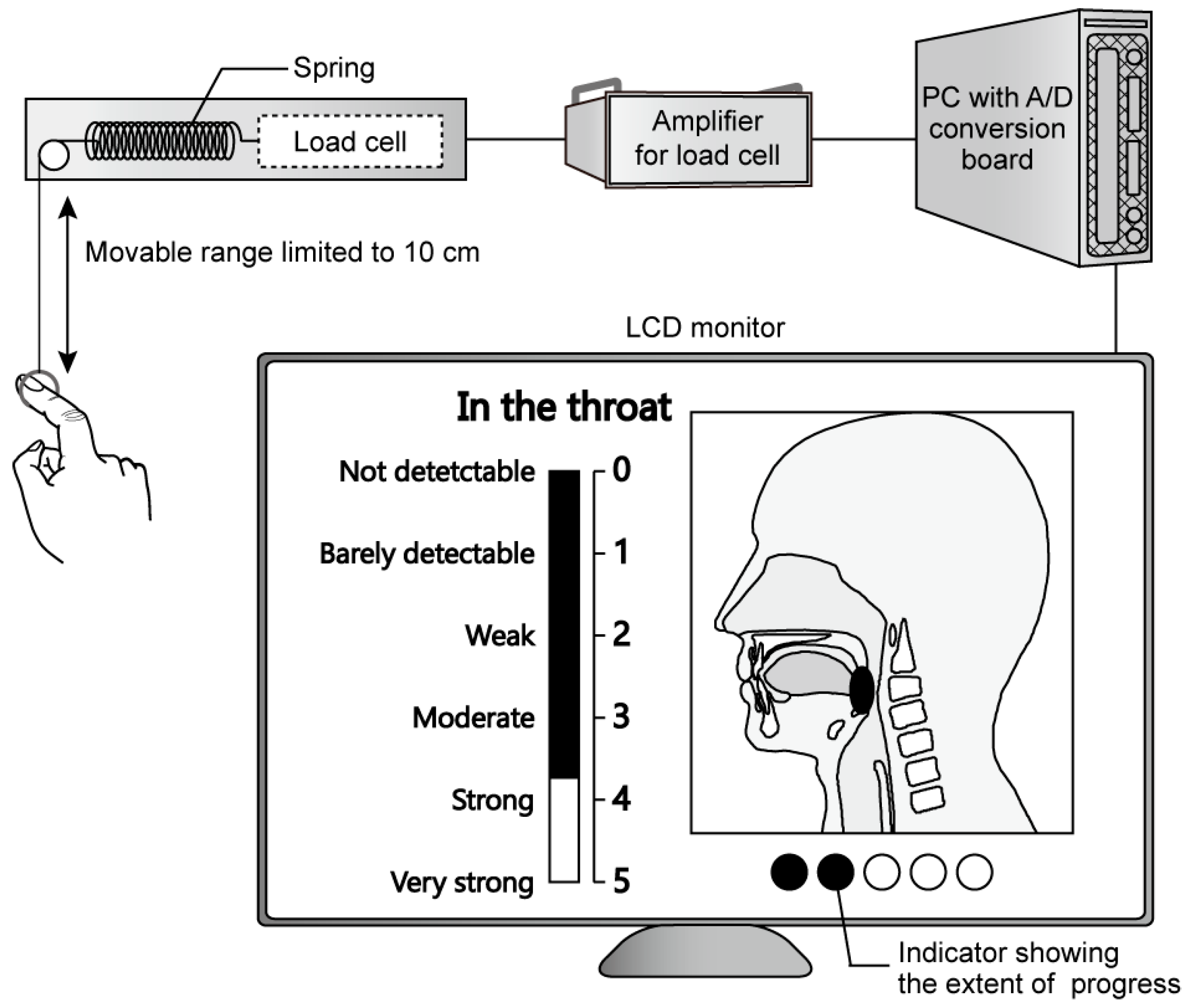
2.3. TI Evaluation System
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Analysis
2.5.1. Comparison of TI Parameters among Trials
2.5.2. Comparison of TI Curves among Trials
2.5.3. Approximation of the TI Curve
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of TI Parameters among Trials
3.2. Comparison of TI Curves among Trials
3.3. Approximation of the TI Curve
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal Change of Retronasal Aroma Intensity
4.2. Role as a Warm-Up Sample
4.3. Improvement of Olfactory Sensitivity by Short-Term Consumption Experience
4.4. Current Limitation and Future Issues
5. Implication
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sudre, J.; Pineau, N.; Loret, C.; Martin, N. Comparison of methods to monitor liking of food during consumption. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 24, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Mesz, B.; Spence, C. Assessing the impact of music on basic taste perception using time intensity analysis. In MHFI’17 Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGCHI International Workshop on Multisensory Approaches to Human-Food Interaction; Velasco, C., Nijholt, A., Obrist, M., Okajima, K., Schifferstein, R., Spence, C., Eds.; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lee III, W.E. Single-point versus time-intensity sensory measurements: An informational entropy analysis. J. Sens. Stud. 1989, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, R.S.; Bolini, H.M.A. Time–intensity analysis and acceptance test for traditional and light vanilla ice cream. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Marshall, R.; Heymann, H.; Fernando, L. Effect of milk fat content on flavor perception of vanilla ice cream. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 3133–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallemand, M.; Giboreau, A.; Rytz, A.; Colas, B. Extracting parameters from time-intensity curves using a trapezoid mode: The example of some sensory attributes of ice cream. J. Sens. Stud. 1999, 14, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvönen, L.; Linna, M.; Tuorila, H.; Dijksterhuis, G. Perception of melting and flavor release of ice cream containing different types and Contents of fat. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.M.; Linforth, R.S.T.; Hollowood, T.A.; Taylor, A.J. Effect of sucrose on the perceived flavor intensity of chewing gum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4336–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duizer, L.M.; Bloom, K.; Findlay, C.J. Dual-attribute time-intensity sensory evaluation: A new method for temporal measurement of sensory perceptions. Food Qual. Prefer. 1997, 8, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potineni, R.V.; Peterson, D.G. Influence of flavor solvent on flavor release and perception in sugar-free chewing gum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3254–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinbach, H.C.; Meinert, L.; Ballabio, D.; Aaslyng, M.D.; Bredie, W.L.P.; Olsena, K.; Møller, P. Interactions between oral burn, meat flavor and texture in chili spiced pork patties evaluated by time-intensity. Food Qual. Prefer. 2007, 18, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM E1909-13(2017), Standard Guide for Time–Intensity Evaluation of Sensory Attributes; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Duizer, L.M.; Bloom, K.; Findlay, C.J. Dual-attribute time–intensity measurement of sweetness and peppermint perception of chewing gum. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuesten, C.; Bi, J.; Feng, Y. Exploring taffy product consumption experiences using a multi-attribute time–intensity (MATI) method. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 30, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lavergne, M.D.; van Delft, M.; van de Velde, F.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Stieger, M. Dynamic texture perception and oral processing of semi-solid food gels: Part 1: Comparison between QDA, progressive profiling and TDS. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H. Temporal Dominance of Sensations (TDS): A new methodology of temporal dynamics measurements of sensations. J. Cookery Sci. Jpn. 2016, 49, 243–247. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Pineau, N.; Schlich, P.; Cordelle, S.; Mathonnière, C.; Issanchou, S.; Imbert, A.; Rogeaux, M.; Etiévant, P.; Köster, E. Temporal Dominance of Sensations: Construction of the TDS curves and comparison with time–intensity. Food Qual. Prefer. 2009, 20, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, D.; Pineau, N.; Matthey-Doret, W.; Ali, S.; Sudre, J.; Germain, J.C.; Kolodziejczyk, E.; Pollien, P.; Labbe, D.; Jarisch, C.; et al. Impact of crema on the aroma release and the in-mouth sensory perception of espresso coffee. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, M.; Romano, A.; Yener, S.; Barnabà, M.; Navarini, L.; Märk, T.D.; Biasoli, F.; Gasperi, F. Understanding flavour perception of espresso coffee by the combination of a dynamic sensory method and in-vivo nosespace analysis. Food Res. Int. 2015, 69, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnella, C.; Masi, C.; Naes, T.; Monteleone, E. A new approach in TDS data analysis: A case study on sweetened coffee. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 30, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Lawlor, J.B.; Chandra, S.; Chaya, C.; Hewson, L.; Hort, J. Using quantitative descriptive analysis and temporal dominance of sensations analysis as complementary methods for profiling commercial blackcurrant squashes. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 25, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meillon, S.; Urbano, C.; Schlich, P. Contribution of the Temporal Dominance of Sensations (TDS) method to the sensory description of subtle differences in partially dealcoholized red wines. Food Qual. Prefer. 2009, 20, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meillon, S.; Viala, D.; Medel, M.; Urbano, C.; Guillot, G.; Schlich, P. Impact of partial alcohol reduction in Syrah wine on perceived complexity and temporality of sensations and link with preference. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowsky, M.; Fischer, U. Evaluation of bitterness in white wine applying descriptive analysis, time-intensity analysis, and temporal dominance of sensations analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 732, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolowsky, M.; Rosenberger, A.; Fischer, U. Sensory impact of skin contact on white wines characterized by descriptive analysis, time–intensity analysis and temporal dominance of sensations analysis. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 39, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déléris, I.; Saint-Eve, A.; Guo, Y.; Lieben, P.; Cypriani, M.-L.; Jacquet, N.; Brunerie, P.; Souchon, I. Impact of swallowing on the dynamics of aroma release and perception during the consumption of alcoholic beverages. Chem. Senses 2011, 6, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schlich, P. Temporal Dominance of Sensations (TDS): A new deal for temporal sensory analysis. Curr. Opin Food Sci. 2017, 15, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.F.; de Souza, V.R.; Lima, R.R.; de Deus Souza Carneiro, J.; Nunes, C.A.; Pinheiro, A.C.M. Temporal Dominance of Sensations (TDS) panel behavior: A preliminary study with chocolate. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 54, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, P.; Cicerale, S.; Pang, E.; Keast, R. A comparison of Temporal Dominance of Sensation (TDS) and Quantitative Descriptive Analysis (QDA™) to identify flavors in strawberries. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, A.; Salvador, A.; Schlich, P.; Fiszman, S. Comparison between temporal dominance of sensations (TDS) and key-attribute sensory profiling for evaluating solid food with contrasting textural layers: Fish sticks. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 24, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmarini, M.V.; Loiseau, A.L.; Visalli, M.; Schlich, P. Use of multi-intake Temporal Dominance of Sensations (TDS) to evaluate the influence of cheese on wine perception. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, S2566–S2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehlholm, C. Descriptive sensory evaluations: Comparison and applicability of novel rapid methodologies. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kunieda, S. A study of temporal dominance of sensations (TDS) for flavor development. Aroma Res. 2013, 14, 29–35. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Gotow, N.; Moritani, A.; Hayakawa, Y.; Akutagawa, A.; Hashimoto, H.; Kobayakawa, T. High consumption increases sensitivity to after-flavor of canned coffee beverages. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 44, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food: Principles and Practices; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Marks, L.E. Effect of endogenous attention on detection of weak gustatory and olfactory flavors. Percept. Psychophys. 2004, 6, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K.; Laing, D.G.; Jinks, A.L.; Hutchinson, I. The capacity of humans to identify components in complex odor-taste mixtures. Chem. Senses 2006, 31, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Johnson, M.B. Potential mechanisms of retronasal odor referral to the mouth. Chem. Senses 2011, 36, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Johnson, M.B. The role of congruency in retronasal odor referral to the mouth. Chem. Senses 2012, 37, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawless, H.T.; Skinner, E.Z. The duration and perceived intensity of sucrose taste. Percept. Psychophys. 1979, 25, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentová, H.; Skrovánková, S.; Panovská, Z.; Pokorný, J. Time-intensity studies of astringent taste. Food Chem. 2002, 78, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotow, N.; Moritani, A.; Hayakawa, Y.; Akutagawa, A.; Hashimoto, H.; Kobayakawa, T. Development of a time–intensity evaluation system for consumers: Measuring bitterness and retronasal aroma of coffee beverages in 106 untrained panelists. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, S1343–S1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotow, N.; Moritani, A.; Hayakawa, Y.; Akutagawa, A.; Hashimoto, H.; Kobayakawa, T. Effect of a warm-up sample on stabilizing the performance of untrained panelists in time–intensity evaluation. J. Sens. Stud. 2018, 33, e12309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotow, N.; Esumi, S.; Kubota, H.; Kobayakawa, T. Comparison of temporal profiles among sucrose, sucralose, and acesulfame potassium after swallowing sweetened coffee beverages and sweetened water solutions. Beverages 2018, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, S.C.; Ribeiro, M.N.; Pinto, J.P.; Vichi, T.M.; Souza, V.R.; Pinheiro, A.C.M. Multiple-sip TDS correlated with acceptance test: A study about special beers. In Proceedings of the 11th Pangborn Sensory Science Symposium, Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–27 August 2015; p. 1251. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha-Parra, D.; García-Burgos, D.; Munsch, S.; Chirife, J.; Zamora, M.C. Application of hedonic dynamics using multiple-sip temporal-liking and facial expression for evaluation of a new beverage. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 52, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Soft Drink Association. Changes in output of Soft Drinks by Item. Available online: http://www.j-sda.or.jp/about-jsda/english/sd-statistics/sd-statistics03.php (accessed on 27 June 2018).
- Japanese Association of Tea Production & Zenkoku Cha Shusan Fuken Nokyoren Renraku Kyogikai. Changes in Consumption of Tea in Japan. Available online: https://www.zennoh.or.jp/bu/nousan/tea/seisan01b.htm (accessed on 28 August 2018). (In Japanese).
- Japanese Association of Tea Production & Zenkoku Cha Shusan Fuken Nokyoren Renraku Kyogikai. Changes in Production of Tea Beverages in Japan. Available online: https://www.zennoh.or.jp/bu/nousan/tea/seisan01c.htm (accessed on 28 August 2018). (In Japanese).
- Wang, C.; Lv, S.; Wu, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Meng, Q. Oolong tea made from tea plants from different locations in Yunnan and Fujian, China showed similar aroma but different taste characteristics. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanishi, T.; Kobayashi, A. Progress of tea aroma chemistry: 30 years of progress. In Flavor Chemistry: Thirty Years of Progress; Teranishi, R., Wick, E.L., Hornstein, I., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.-H.; Yang, C.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Wu, C.-C.; Tzen, J.T.C. Catechin content and the degree of its galloylation in oolong tea are inversely correlated with cultivation altitude. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.P.; Yin, J.F.; Chen, G.S.; Wang, F.; Xu, Y.Q. Flavor characteristics and chemical compositions of oolong tea processed using different semi-fermentation times. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, N.J.N.; Huang, Y.J. The effect of membrane-processed water on sensory properties of oolong tea drinks. Food Qual. Prefer. 2000, 11, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-Q.; Zou, C.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.-X.; Wang, F.; Chen, G.-S.; Yin, J.-F. Effect of the type of brewing water on the chemical composition, sensory quality and antioxidant capacity of Chinese teas. Food Chem. 2017, 236, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmarini, M.V.; Loiseau, A.L.; Visalli, M.; Schlich, P. How about some cheese with that wine? Use of multi-intake Temporal Dominance of Sensations to evaluate the influence of cheese on wine perception and appreciation. In Proceedings of the 11th Pangborn Sensory Science Symposium, Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–27 August 2015; p. 1189. [Google Scholar]
- Galmarini, M.V.; Visallia, M.; Schlich, P. Advances in representation and analysis of mono and multi-intake Temporal Dominance of Sensations data. Food Qual. Prefer. 2017, 56, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goupil de Bouille, A.; Peleteiro, S. Dynamic perception of cocktails using a multi-sip approach with naïve consumers. In Proceedings of the 11th Pangborn Sensory Science Symposium, Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–27 August 2015; p. 1084. [Google Scholar]
- Zorn, S.; Alcaire, F.; Vidal, L.; Giménez, A.; Ares, G. Application of multiple-sip temporal dominance of sensations to the evaluation of sweeteners. Food Qual. Prefer. 2014, 36, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.P. Time as a factor in gustation: Temporal patterns of taste stimulation and response. In Taste Olfaction and the Central Nervous System: A Festschrift in Honor Carl Pfaffmann; Pfaff, D.W., Ed.; The Rockefeller University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 181–209. ISBN 0874700396. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman, S.S.; Sattely-Miller, E.A.; Graham, B.G.; Zervakis, J.; Butchko, H.H.; Stargel, W.W. Effect of repeated presentation on sweetness intensity of binary and ternary mixtures of sweeteners. Chem. Senses 2003, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, S.S.; Pecore, S.D.; Booth, B.J.; Losee, M.L.; Carr, B.T.; Sattely-Miller, E.; Graham, B.G.; Warwick, Z.S. Adaptation of sweeteners in water and in tannic acid solutions. Physiol. Behav. 1994, 55, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesurolle, J.; Saint-Eve, A.; Déléris, I.; Souchon, I. Impact of fruit piece structure in yogurts on the dynamics of aroma release and sensory perception. Molecules 2013, 18, 6035–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventanas, S.; Puolanne, E.; Tuorila, H. Temporal changes of flavour and texture in cooked bologna type sausages as affected by fat and salt content. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S. Measurement method for olfaction. In Sensory and Perceptual Psychology Handbook; Oyama, T., Imai, S., Wake, T., Eds.; Seishin Shobo: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; pp. 1371–1382. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Dransfield, R. Quantitative analysis for economists. In Business Economics; Routledge: Oxin, UK, 2014; pp. 19–48. ISBN 0415837651. [Google Scholar]
- Distel, H.; Ayabe-Kanamura, S.; Martínez-Gómez, M.; Schicker, I.; Kobayakawa, T.; Saito, S.; Hudson, R. Perception of everyday odors—Correlations between intensity, familiarity and strength of hedonic judgement. Chem. Senses 1999, 24, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki-Kawai, H.; Toda, H.; Gotow, N.; Kobayakawa, T. Proper times for odor detections: What is the critical element to determine the detection time of odorants? In Proceedings of the 21st Annual Meeting of the Japanese Association for the Study of Tate and Smell, Tokyo, Japan, 26–28 July 2007. (In Japanese). [Google Scholar]
- La Buissonnière-Ariza, V.; Lepore, F.; Kojok, K.M.; Frasnelli, J. Increased odor detection speed in highly anxious healthy adults. Chem. Senses 2013, 38, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croy, I.; Krone, F.; Walker, S.; Hummel, T. Olfactory processing: Detection of rapid changes. Chem. Senses 2015, 40, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moskowitz, H.R.; Beckley, J.H.; Resurreccion, A.V.A. What types of tests do sensory researchers do? And … why do they do them? In Sensory and Consumer Research in Food Product Design and Development; Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2006; pp. 219–294. ISBN 0813816327. [Google Scholar]
- Plemmons, L.E.; Resurreccion, A.V.A. A warm-up sample improves reliability of responses in descriptive analysis. J. Sens. Stud. 1998, 13, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.W.; Resurreccion, A.V.A.; Paguio, L.P. Age appropriate hedonic scales to measure food preferences of young children. J. Sens. Stud. 1996, 11, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, I.B.; Resurreccion, A.V.A.; McWaiters, K.H. Descriptive sensory analysis of irradiated frozen or refrigerated chicken. J. Food Sci. 1995, 60, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malundo, T.M.M.; Resurreccion, A.V.A. Peanut extract and emulsifier concentrations affect sensory and physical properties of liquid whitener. J. Food Sci. 1994, 59, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bett, K.L.; Vercellotti, J.R.; Lovegren, N.V.; Sanders, T.H.; Hinsch, R.T.; Rasmussen, G.K. A comparison of the flavor and compositional quality of peanuts from several origins. Food Chem. 1994, 51, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, S.J.; MacDaniel, M.R. Carbonated water lexicon: Temperature and CO2 level influence on descriptive ratings. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Jeon, S.Y.; Kim, K.-O.; O’Mahony, M. Thurstonian models and variance I: Experimental confirmation of cognitive strategies for difference tests and effects of perceptual variance. J. Sens. Stud. 2006, 21, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, M.; Thieme, U.; Goldstein, L.R. The warm-up effect as a means of increasing the discriminability of sensory difference tests. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 1848–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, B.; O’Mahony, M. Sensory difference tests: Thurstonian and SSA predictions for vanilla flavored yogurts. J. Sens. Stud. 1997, 12, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, W.S. Odor intensity: Differences in the exponent of the psychophysical function. Percept. Psychophys. 1969, 6, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, R.L. An examination of relationships between the pleasantness, intensity, and concentration of 10 odorous stimuli. Percept. Psychophys. 1975, 17, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, T. Olfactory psychophysics. In Handbook of Sensory Physiology; Beidler, L.M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1971; pp. 216–244. ISBN 3642651281. [Google Scholar]
- Patte, F.; Etcheto, M.; Laffort, P. Selected and standardized values of suprathreshold odor intensities for 110 substances. Chem. Senses 1975, 1, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distel, H.; Hudson, R. Judgement of odor intensity is influenced by subjects’ knowledge of the odor source. Chem. Senses 2001, 26, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldermann, S.; Yang, Z.; Katsuno, T.; Tu, V.A.; Mase, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Watanabe, N. Discrimination of green, oolong, and black teas by GC-MS analysis of characteristic volatile flavor compounds. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 5, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuizen, M.G.; Small, D.M. Modality-specific neural effects of selective attention to taste and odor. Chem. Senses 2011, 36, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Luxenberg, E.; Parrish, T.; Gottfried, J.A. Learning to smell the roses: Experience-dependent neural plasticity in human piriform and orbitofrontal cortices. Neuron 2006, 52, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.C.; Lawless, H.T. Limiting response alternatives in time-intensity scaling: An examination of the halo-dumping effect. Chem. Senses 1994, 19, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescott, J. Flavour as a psychological construct: implications for perceiving and measuring the sensory qualities of foods. Food Qual. Prefer. 1999, 10, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.; Johnstone, V.; Francis, J. Odor-taste interactions: Effects of attentional strategies during exposure. Chem. Senses 2004, 29, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, H.; Chen, L.; Zhu, B.; He, Z.; Shibata, H.; Kiso, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Yao, X. Anti-stress effect of oolong tea in women loaded with vigil. J. Health Sci. 2003, 49, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singham, P.; Birwal, P.; Yadav, B.K. Importance of objective and subjective measurement of food quality and their inter-relationship. J. Food Process. Technol. 2015, 6, 488. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Trial | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9th | 10th | |
| Imax | 3.71 a | 4.13 b | 4.29 b | 4.21 b | 4.25 b | 4.22 b | 4.26 b | 4.29 b | 4.32 b | 4.20 b |
| (1.00) | (0.68) | (0.64) | (0.62) | (0.66) | (0.68) | (0.67) | (0.62) | (0.52) | (0.74) | |
| Tmax | 14.88 a | 7.92 b | 5.98 b | 5.97 b | 5.22 b | 7.10 b | 4.60 b | 8.36 b | 3.83 b | 5.95 b |
| (12.83) | (9.40) | (6.74) | (5.76) | (3.65) | (9.42) | (1.82) | (12.44) | (1.97) | (5.15) | |
| AUC | 110.16 a | 133.08 b | 143.25 b | 142.57 b | 145.59 b | 147.26 b | 149.78 b | 147.80 b | 151.45 b | 147.02 b |
| (43.20) | (42.82) | (41.31) | (46.43) | (50.76) | (42.87) | (44.59) | (50.85) | (50.38) | (52.72) | |
| Dplateau | 8.79 a | 8.83 a | 9.61 a | 12.66 a | 12.25 a | 11.73 a | 8.74 a | 9.67 a | 7.87 a | 7.52 a |
| (8.03) | (6.91) | (6.94) | (14.42) | (12.93) | (12.57) | (8.68) | (8.52) | (7.44) | (5.19) | |
| Rinc | 1.13 a | 2.28 b | 2.33 b | 2.28 b | 2.19 b | 2.59 b | 2.10 b | 2.34 b | 2.90 b | 2.87 b |
| (1.13) | (1.64) | (1.39) | (1.22) | (1.31) | (1.92) | (1.50) | (1.65) | (1.91) | (2.42) | |
| Rdec | −0.09 a | −0.07 a | −0.07 a | −0.11 a | −0.15 a | −0.12 a | −0.06 a | −0.06 a | −0.06 a | −0.06 a |
| (0.06) | (0.04) | (0.03) | (0.22) | (0.40) | (0.30) | (0.02) | (0.03) | (0.03) | (0.04) | |
| Time Window | Trial | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (in seconds) | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9th | 10th |
| 1 | 0.01 a | 0.43 ab | 0.75 bc | 0.84 bc | 0.90 bc | 0.97 c | 0.94 c | 0.95 c | 1.14 c | 0.98 c |
| (0.22) | (1.02) | (1.18) | (1.12) | (0.19) | (1.28) | (1.30) | (1.22) | (1.35) | (1.34) | |
| 3 | 0.65 a | 2.16 b | 2.76 c | 2.82 cd | 2.82 cd | 2.87 cd | 2.85 cd | 3.16 cd | 3.29 d | 2.83 cd |
| (1.06) | (1.69) | (1.63) | (1.65) | (1.47) | (1.38) | (1.50) | (1.24) | (1.18) | (1.48) | |
| 5 | 1.39 a | 3.17 b | 3.62 bc | 3.43 bc | 3.55 bc | 3.60 bc | 3.64 bc | 3.65 bc | 3.77 c | 3.61 bc |
| (1.56) | (1.50) | (1.24) | (1.34) | (1.20) | (1.03) | (1.03) | (1.17) | (0.89) | (1.12) | |
| 7 | 2.06 a | 3.45 b | 3.69 b | 3.51 b | 3.62 b | 3.63 b | 3.62 b | 3.54 b | 3.68 b | 3.59 b |
| (1.58) | (1.30) | (1.02) | (1.27) | (1.11) | (0.97) | (1.06) | (1.23) | (0.97) | (1.11) | |
| 9 | 2.49 a | 3.41 b | 3.71 b | 3.53 b | 3.64 b | 3.67 b | 3.62 b | 3.58 b | 3.69 b | 3.61 b |
| (1.54) | (1.15) | (0.82) | (1.06) | (0.82) | (0.76) | (0.86) | (0.91) | (0.70) | (0.80) | |
| 11 | 2.69 a | 3.31 b | 3.51 b | 3.39 b | 3.38 b | 3.36 b | 3.40 b | 3.37 b | 3.47 b | 3.41 b |
| (1.55) | (1.05) | (1.05) | (1.11) | (1.08) | (1.09) | (1.08) | (1.07) | (1.07) | (1.16) | |
| 13 | 2.58 a | 3.19 b | 3.49 b | 3.39 b | 3.36 b | 3.43 b | 3.43 b | 3.36 b | 3.49 b | 3.46 b |
| (1.57) | (1.04) | (0.77) | (0.84) | (0.80) | (0.75) | (0.83) | (0.86) | (0.81) | (0.84) | |
| 15 | 2.56 a | 3.12 b | 3.32 b | 3.24 b | 3.17 b | 3.28 b | 3.23 b | 3.29 b | 3.27 b | 3.26 b |
| (1.37) | (1.05) | (0.85) | (0.94) | (0.85) | (0.88) | (0.91) | (0.87) | (0.92) | (0.93) | |
| 39 | 1.74 a | 1.97 ab | 2.18 ab | 2.03 ab | 2.17 ab | 2.20 ab | 2.33 b | 2.16 ab | 2.26 ab | 2.25 ab |
| (0.01) | (1.00) | (0.88) | (0.96) | (1.02) | (0.84) | (0.82) | (1.07) | (1.00) | (1.05) | |
| Parameter | Trial | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9th | 10th | |
| Coefficient | 4.250 a | 5.145 a | 5.048 a | 4.816 a | 4.602 a | 4.561 a | 4.405 a | 4.712 a | 4.587 a | 4.708 a |
| (1.892) | (1.948) | (1.635) | (1.623) | (1.491) | (1.278) | (1.209) | (1.579) | (1.405) | (1.661) | |
| Time constant | 0.022 a | 0.028 a | 0.024 a | 0.024 a | 0.022 a | 0.021 a | 0.019 a | 0.023 a | 0.020 a | 0.022 a |
| (0.019) | (0.023) | (0.014) | (0.016) | (0.017) | (0.012) | (0.012) | (0.021) | (0.015) | (0.020) | |
| Goodness of fit | 0.662 a | 0.867 b | 0.908 b | 0.900 b | 0.848 b | 0.894 b | 0.894 b | 0.839 b | 0.906 b | 0.895 b |
| (0.395) | (0.234) | (0.122) | (0.191) | (0.255) | (0.208) | (0.171) | (0.290) | (0.178) | (0.200) | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gotow, N.; Omata, T.; Uchida, M.; Matsuzaki, N.; Takata, S.; Hagiwara, I.; Kobayakawa, T. Multi-Sip Time–Intensity Evaluation of Retronasal Aroma after Swallowing Oolong Tea Beverage. Foods 2018, 7, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7110177
Gotow N, Omata T, Uchida M, Matsuzaki N, Takata S, Hagiwara I, Kobayakawa T. Multi-Sip Time–Intensity Evaluation of Retronasal Aroma after Swallowing Oolong Tea Beverage. Foods. 2018; 7(11):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7110177
Chicago/Turabian StyleGotow, Naomi, Takanobu Omata, Masaaki Uchida, Naoyuki Matsuzaki, Sadaki Takata, Ippei Hagiwara, and Tatsu Kobayakawa. 2018. "Multi-Sip Time–Intensity Evaluation of Retronasal Aroma after Swallowing Oolong Tea Beverage" Foods 7, no. 11: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7110177
APA StyleGotow, N., Omata, T., Uchida, M., Matsuzaki, N., Takata, S., Hagiwara, I., & Kobayakawa, T. (2018). Multi-Sip Time–Intensity Evaluation of Retronasal Aroma after Swallowing Oolong Tea Beverage. Foods, 7(11), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7110177





