The Food Systems in the Era of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic Crisis
Abstract
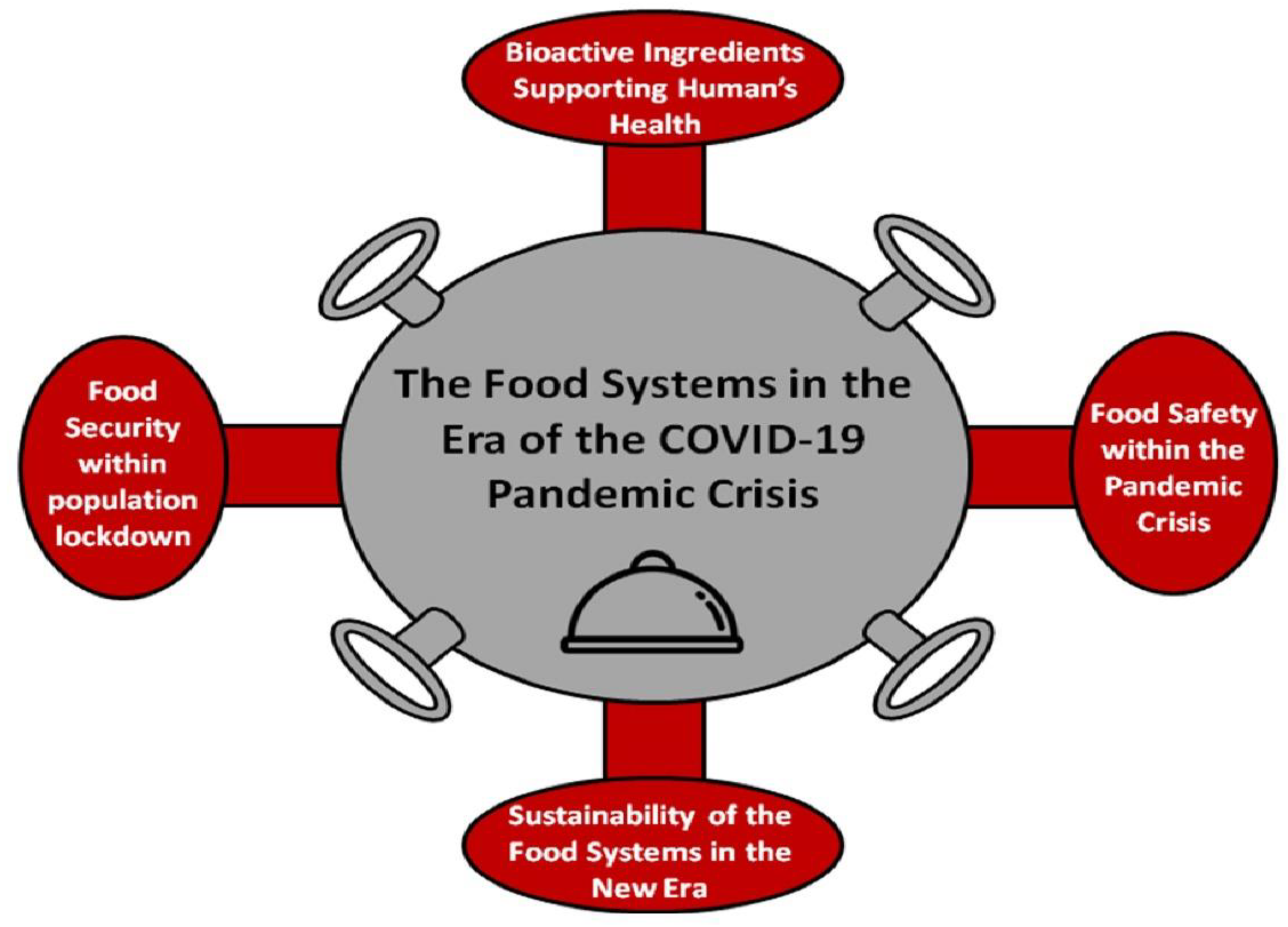
:1. Introduction
2. The Role of Bioactive Ingredients in Supporting the Human Immune System
3. Food Safety within the Pandemic Crisis
4. Food Security with the Globe’s Population Lockdown
5. Sustainability of Food Systems in the New Era of Pandemic Crises
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.M.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coronavirus COVID-19 (2019-nCoV). Available online: https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594740fd40299423467b48e9ecf6 (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Countries where Coronavirus has Spread—Worldometer. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/countries-where-coronavirus-has-spread/ (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- How Coronavirus Spreads | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/how-covid-spreads.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fcoronavirus%2F2019-ncov%2Fprepare%2Ftransmission.html (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Coronavirus: Loss of Smell and Taste may Be Hidden Symptom of COVID-19—Business Insider. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.com/coronavirus-symptoms-loss-of-smell-taste-covid-19-anosmia-hyposmia-2020-3 (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Huff, A.G.; Beyeler, W.E.; Kelley, N.S.; McNitt, J.A. How resilient is the United States’ food system to pandemics? J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 2015, 5, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, U.N. Can Bioactive Lipids Inactivate Coronavirus (COVID-19)? Arch. Med. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, A.; Edgar, J.D.; Neville, C.E.; Gilchrist, S.E.C.M.; McKinley, M.C.; Patterson, C.C.; Young, I.S.; Woodside, J.V. Effect of fruit and vegetable consumption on immune function in older people: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naik, S.R.; Thakare, V.N.; Joshi, F.P. Functional foods and herbs as potential immunoadjuvants and medicines in maintaining healthy immune system: A commentary. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2010, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Maggini, S. Vitamin C and immune function. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemilä, H. Vitamin C intake and susceptibility to pneumonia. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1997, 16, 836–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qi, G.; Brand, D.; Zheng, S. Role of Vitamin A in the Immune System. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, S.; Cheng, K.; Aldape, K.; Schiff, E.; Ruppin, E. Systematic Cell Line-Based Identification of Drugs Modifying ACE2 Expression. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, D.; Liu, Q. A review of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) based on current evidence. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 105948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnecke, B.J.; McGill, J.L.; Ridpath, J.F.; Sacco, R.E.; Lippolis, J.D.; Reinhardt, T.A. Acute phase response elicited by experimental bovine diarrhea virus (BVDV) infection is associated with decreased vitamin D and E status of vitamin-replete preruminant calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 5566–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adem, S.; Eyupoglu, V.; Sarfraz, I.; Rasul, A.; Ali, M. Identification of Potent COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) Inhibitors from Natural Polyphenols: An in Silico Strategy Unveils a Hope against CORONA. Preprints 2020, 2020030333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Im, K.; Kim, J.; Min, H. Ginseng, the natural effectual antiviral: Protective effects of Korean red ginseng against viral infection. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolodziej, H. Antimicrobial, antiviral and immunomodulatory activity studies of pelargonium sidoides (EPs® 7630) in the context of health promotion. Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 1295–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Tang, Q.L.; Shang, Y.X.; Liang, S.B.; Yang, M.; Robinson, N.; Liu, J. Can Chinese Medicine Be Used for Prevention of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)? A Review of Historical Classics, Research Evidence and Current Prevention Programs. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 26, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Patients Infected with 2019-New Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A Review and Perspective. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, L.; Lee, H.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Lee, M.S. Herbal medicine and pattern identification for treating COVID-19: A rapid review of guidelines. Integr. Med. Res. 2020, 9, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consumer Research Supports Global Demand for Immunity Products. Available online: https://www.naturalproductsinsider.com/business-resources/consumer-research-supports-global-demand-immunity-products-white-paper (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Q & A on COVID-19. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/questions-answers (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Coronavirus: No Evidence that Food is a Source or Transmission Route. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/coronavirus-no-evidence-food-source-or-transmission-route (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Food Safety and the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) | FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-safety-during-emergencies/food-safety-and-coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19 (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Can the New Type of Coronavirus be Transmitted via Food and Objects?—BfR. Available online: https://www.bfr.bund.de/en/can_the_new_type_of_coronavirus_be_transmitted_via_food_and_objects_-244090.html (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- FSHN20-21/FS349: COVID-19 and Food Safety FAQ: Is Coronavirus a Concern with Takeout? Available online: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs349 (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- No Evidence of COVID-19 Transmission through Food, Says EFSA – EURACTIV.com. Available online: https://www.euractiv.com/section/coronavirus/news/no-evidence-of-covid-19-transmission-through-food-says-efsa/ (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Countries that are on Lockdown Because of Coronavirus—Business Insider. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.com/countries-on-lockdown-coronavirus-italy-2020-3 (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- EC FOOD 2030 Independent Expert Group. Recipe for Change: An Agenda for Sustainable Food System; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; ISBN 9789279803567. [Google Scholar]
- Coronavirus could double number of people going hungry | World news | The Guardian. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/apr/09/coronavirus-could-double-number-of-people-going-hungry (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- COVID-19 and the risk to food supply chains: How to respond? |Policy Support and Governance| Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/policy-support/resources/resources-details/en/c/1269383/ (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Coronavirus: Italy’s food Industry Warns of “Brake” on Sector Growth. Available online: https://www.foodnavigator.com/Article/2020/02/25/Coronavirus-Italy-s-food-industry-warns-of-brake-on-sector-growth?utm_source=copyright&utm_medium=OnSite&utm_campaign=copyright (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- How China Kept Its Supermarkets Stocked as Coronavirus Raged—WSJ. Available online: https://www.wsj.com/articles/how-china-fed-its-people-while-under-lockdown-11584009757 (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Flanagan, K.; Robertson, K.; Hanson, C. Reducing Food Loss and Waste: Setting a Global Action Agenda; World Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: https://wriorg.s3.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/reducing-food-loss-waste-global-action-agenda_1.pdf (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Wesana, J.; Gellynck, X.; Dora, M.K.; Pearce, D.; de Steur, H. Measuring food losses in the supply chain through value stream mapping: A case study in the dairy sector. In Saving Food: Production, Supply Chain, Food Waste and Food Consumption; Galanakis, C., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Madhav, N.; Oppenheim, B.; Gallivan, M.; Mulembakani, P.; Rubin, E.; Wolfe, N. Pandemics: Risks, Impacts, and Mitigation. In Disease Control Priorities, Third Edition (Volume 9): Improving Health and Reducing Poverty; International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 315–345. ISBN 9781464805271. [Google Scholar]
- Home: Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/ (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Scherhaufer, S.; Moates, G.; Hartikainen, H.; Waldron, K.; Obersteiner, G. Environmental impacts of food waste in Europe. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. Lipids and Edible Oils: Properties, Processing and Applications; Academis Press: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 9780128173725. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.; Zinoviadou, K.G.; Galanakis, C.M.; Orlien, V.; Grimi, N.; Vorobiev, E.; Lebovka, N.; Barba, F.J. The Effects of Conventional and Non-conventional Processing on Glucosinolates and Its Derived Forms, Isothiocyanates: Extraction, Degradation, and Applications. Food Eng. Rev. 2015, 7, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselló-Soto, E.; Barba, F.J.; Parniakov, O.; Galanakis, C.M.; Lebovka, N.; Grimi, N.; Vorobiev, E. High Voltage Electrical Discharges, Pulsed Electric Field, and Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Protein and Phenolic Compounds from Olive Kernel. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselló-Soto, E.; Galanakis, C.M.; Brnčić, M.; Orlien, V.; Trujillo, F.J.; Mawson, R.; Knoerzer, K.; Tiwari, B.K.; Barba, F.J. Clean recovery of antioxidant compounds from plant foods, by-products and algae assisted by ultrasounds processing. Modeling approaches to optimize processing conditions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 42, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfarazi, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Rajabzadeh, G.; Galanakis, C.M. Evaluation of microwave-assisted extraction technology for separation of bioactive components of saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 111978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. Emerging technologies for the production of nutraceuticals from agricultural by-products: A viewpoint of opportunities and challenges. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. Recovery of high added-value components from food wastes: Conventional, emerging technologies and commercialized applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M.; Tsatalas, P.; Galanakis, I.M. Implementation of phenols recovered from olive mill wastewater as UV booster in cosmetics. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M.; Tsatalas, P.; Charalambous, Z.; Galanakis, I.M. Polyphenols recovered from olive mill wastewater as natural preservatives in extra virgin olive oils and refined olive kernel oils. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 10, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursać Kovačević, D.; Barba, F.J.; Granato, D.; Galanakis, C.M.; Herceg, Z.; Dragović-Uzelac, V.; Putnik, P. Pressurized hot water extraction (PHWE) for the green recovery of bioactive compounds and steviol glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Food Losses and Food Waste. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/mb060e/mb060e00.htm (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- State of Food and Agriculture 2019. Moving forward on food loss and waste reduction | Policy Support and Governance| Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/policy-support/resources/resources-details/en/c/1242090/ (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Cheng, V.C.C.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Kwok, Y.Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus as an agent of emerging and reemerging infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 660–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jalava, K. First respiratory transmitted food borne outbreak? Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 226, 113490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, S.S. Factors in the emergence of infectious diseases. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1995, 1, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensuring Food Security in the Era of COVID-19—United Nations Sustainable Development. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/blog/2020/04/ensuring-food-security-covid-19/ (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Vieux, F.; Perignon, M.; Gazan, R.; Darmon, N. Dietary changes needed to improve diet sustainability: Are they similar across Europe? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springmann, M.; Wiebe, K.; Mason-D’Croz, D.; Sulser, T.B.; Rayner, M.; Scarborough, P. Health and nutritional aspects of sustainable diet strategies and their association with environmental impacts: A global modelling analysis with country-level detail. Lancet Planet. Heal. 2018, 2, e451–e461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galanakis, C. Preface. In Proteins: Sustainable Source, Processing and Applications; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, L.M.; da Silva Lucas, A.J.; Cadaval, C.L.; Mellado, M.S. Bread enriched with flour from cinereous cockroach (Nauphoeta cinerea). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 44, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, K.; Zaplatic, E.; Spoor, J. Highlight report: Diploptera Functata (cockroach) milk as next superfood. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 721–723. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrowicz, L.; Green, R.; Joy, E.J.M.; Smith, P.; Haines, A. The impacts of dietary change on greenhouse gas emissions, land use, water use, and health: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chriki, S.; Hocquette, J.-F. The Myth of Cultured Meat: A Review. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galanakis, C.M. Separation of functional macromolecules and micromolecules: From ultrafiltration to the border of nanofiltration. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 42, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. Food Quality and Shelf Life; Academis Press: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 9780128171912. [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis, C.M. Food Security and Nutrition; Galanakis, C., Ed.; Elsevier-Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 9780128209325. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galanakis, C.M. The Food Systems in the Era of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic Crisis. Foods 2020, 9, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040523
Galanakis CM. The Food Systems in the Era of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic Crisis. Foods. 2020; 9(4):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040523
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalanakis, Charis M. 2020. "The Food Systems in the Era of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic Crisis" Foods 9, no. 4: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040523
APA StyleGalanakis, C. M. (2020). The Food Systems in the Era of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic Crisis. Foods, 9(4), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040523




