Enhanced Solubility of Rapeseed Meal Protein Isolates Prepared by Sequential Isoelectric Precipitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Protein Isolates
2.2. Chemical Analyses
2.3. Amino Acid Analyses and Amino Acid Score Calculation
2.4. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.5. Protein Solubility
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biochemical Characterization of PI10.5–2.5 and PI2.5–8.5
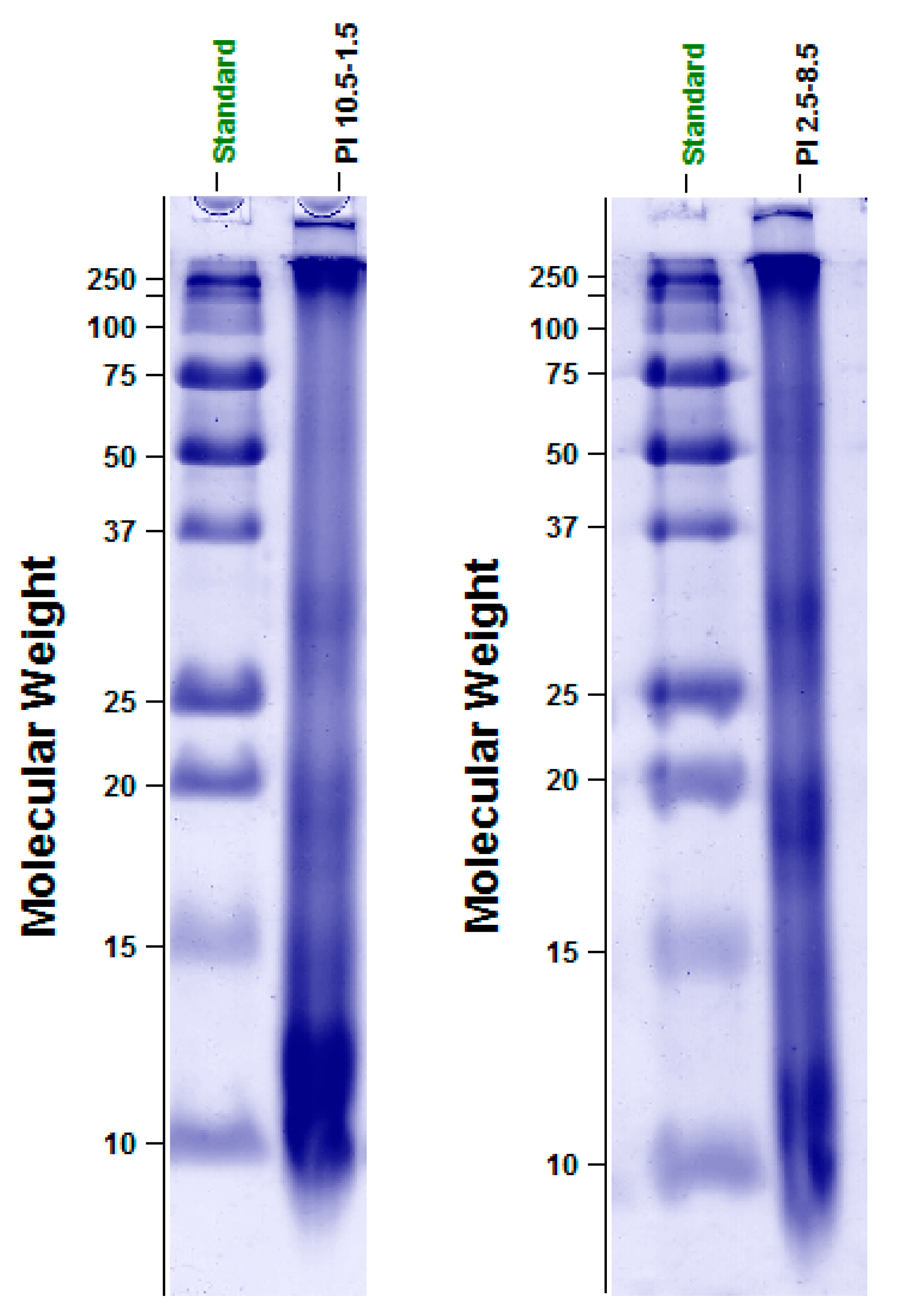
3.2. Electrophoretic Protein Profile of PI10.5–2.5 and PI2.5–8.5
3.3. Amino Acid and Microelemental Composition of PI10.5–2.5 and PI2.5–8.5 Protein Isolates
3.4. Solubility of PI10.5–2.5 and PI2.5–8.5 Protein
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Revision of World Population Prospects, United Nations. Available online: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/publications/files/keyfindingswpp2015.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Henchion, M.; Hayes, M.; Mullen, A.M.; Fenelon, M.; Tiwari, B. Future protein supply and demand: Strategies and factors influencing a sustainable equilibrium. Foods 2017, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chove, B.E.; Grandison, A.S.; Lewis, M.J. Emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate fractions obtained by isoelectric precipitation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasundara, J.P.; McIntosh, T.C.; Perera, S.P.; Withana-Gamage, T.S.; Mitra, P. Canola/rapeseed protein-functionality and nutrition. OCL 2016, 23, D407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Guo, Z. Complete utilization of rapeseed meal to produce lipophilic antioxidants, protein, and monosugars in a concordant manner. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6218–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroche, J.; Yust, M.M.; Lqari, H.; Girón-Calle, J.; Alaiz, M.; Vioque, J.; Millán, F. Brassica carinata protein isolates: Chemical composition, protein characterization and improvement of functional properties by protein hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshie-Stark, Y.; Wada, Y.; Wäsche, A. Chemical composition, functional properties, and bioactivities of rapeseed protein isolates. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Purkayastha, M.; Gogoi, J.; Kalita, D.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Nakhuru, K.S.; Goyary, D.; Mahanta, C.L. Physicochemical and functional properties of rapeseed protein isolate: Influence of antinutrient removal with acidified organic solvents from rapeseed meal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7903–7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaydzhiev, H.; Ivanova, P.; Silva, C.L.; Chalova, V.I. Functional properties of protein isolate and acid soluble protein-rich ingredient co-produced from ethanol-treated industrial rapeseed meal. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2019, 69, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vioque, J.; Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Clemente, A.; Pedroche, J.; Millán, F. Partially hydrolyzed rapeseed protein isolates with improved functional properties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabanon, G.; Chevalot, I.; Framboisier, X.; Chenu, S.; Marc, I. Hydrolysis of rapeseed protein isolates: Kinetics, characterization and functional properties of hydrolysates. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nockrashy, A.S.; Mukherjee, K.D.; Mangold, H.K. Rapeseed protein isolates by countercurrent extraction and isoelectric precipitation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1977, 25, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsvali, A.; Khodaparast, M.H.; Vosoughi, M.; Diosady, L.L. Preparation of canola protein materials using membrane technology and evaluation of meals functional properties. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Janson, J.C. Studies on Brassica seed proteins: I. The low molecular weight proteins in rapeseed. Isolation and characterization. BBA-Protein Struct. 1972, 278, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Method 979.09: Protein in Grains; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1994.
- ICC Standard №104/1. Approved 1960, Revised 1990. Determination of Ash in Cereals and Cereal Products; International Association for Cereal Science and Technology: Vienna, Austria, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, N.; Ivanov, I.; Denev, P.; Pavlov, A. Bioactive substance and free radical scavenging activities of flour from Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) tubers–a comparative study. Türk Tarımve Doğa Bilimleri Dergisi 2014, 1, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth, E.A.; Gillespie, K.M. Estimation of total phenolic content and other oxidation substrates in plant tissues using Folin–Ciocalteu reagent. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezek, J.; Haggett, B.G.; Atkinson, A.; Rawson, D.M. Determination of glucosinolates using their alkaline degradation and reaction with ferricyanide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4669–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11885:2007. Water Quality-Determination of Selected Elementsby Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES). Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=36250 (accessed on 6 January 2019).
- BDS 11374. Available online: http://www.bdsbg.org/bg/standard/?natstandard_document_id=5976 (accessed on 16 February 2019).
- Blackburn, S. Amino Acid Determination: Methods and Techniques; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in Human Nutrition: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation; WHO technical report series, no. 935; United Nations University: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Method 46–15: Crude Protein–5-min Biuret Method for Wheat and Other Grains. Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, P.; Kalaydzhiev, H.; Rustad, T.; Silva, C.L.; Chalova, V.I. Comparative biochemical profile of protein-rich products obtained from industrial rapeseed meal. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2017, 29, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aluko, R.E.; McIntosh, T. Polypeptide profile and functional properties of defatted meals and protein isolates of canola seeds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sęczyk, Ł.; Świeca, M.; Kapusta, I.; Gawlik-Dziki, U. Protein–phenolic interactions as a factor affecting the physicochemical properties of white bean proteins. Molecules 2019, 24, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szydłowska-Czerniak, A. Rapeseed and its products—sources of bioactive compounds: A review of their characteristics and analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aider, M.; Barbana, C. Canola proteins: Composition, extraction, functional properties, bioactivity, applications as a food ingredient and allergenicity—A practical and critical review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaydzhiev, H.; Ivanova, P.; Stoyanova, M.; Pavlov, A.; Rustad, T.; Silva, C.L.; Chalova, V.I. Valorization of rapeseed meal: Influence of ethanol antinutrients removal on protein extractability, amino acid composition and fractional profile. Waste Biomass Valor. 2020, 11, 2709–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Der Haar, D.; Müller, K.; Bader-Mittermaier, S.; Eisner, P. Rapeseed proteins–Production methods and possible application ranges. OCL 2014, 21, D104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monsalve, R.I.; Rodriguez, R. Purification and characterization of proteins from the 2S fraction from seeds of the Brassicaceae family. J. Exp. Bot. 1990, 41, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglund, A.S.; Rödin, J.; Larsson, E.; Rask, L. Distribution of napin and cruciferin in developing rape seed embryos. Plant Physiol. 1992, 98, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Muir, A.D. Comparative structural, emulsifying, and biological properties of 2 major canola proteins, cruciferin and napin. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, C210–C216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, H.N.; Tressel, R.P.; Pudel, F.; Slawski, H.; Schulz, C. Rapeseed use in aquaculture. OCL 2014, 21, D105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wanasundara, J.P. Proteins of Brassicaceae oilseeds and their potential as a plant protein source. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 635–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesundera, C.; Boiteau, T.; Xu, X.; Shen, Z.; Watkins, P.; Logan, A. Stabilization of fish oil-in-water emulsions with oleosin extracted from canola meal. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C1340–C1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.P.; McIntosh, T.C.; Wanasundara, J.P. Structural properties of cruciferin and napin of Brassica napus (canola) show distinct responses to changes in pH and temperature. Plants 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barber-Zucker, S.; Shaanan, B.; Zarivach, R. Transition metal binding selectivity in proteins and its correlation with the phylogenomic classification of the cation diffusion facilitator protein family. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehri, A.; Marjan, R.F. Trace elements in human nutrition: A review. Int. J. Med. Investig. 2013, 2, 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; Zuo, L. Nutritional and Anti-Nutritional Composition of Rapeseed Meal and Its Utilization as a Feed Ingredient for Animal; International Consultative Group for Research on Rapeseed: Wuhan, China, 2007; pp. 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Mourato, M.P.; Moreira, I.N.; Leitão, I.; Pinto, F.R.; Sales, J.R.; Martins, L.L. Effect of heavy metals in plants of the genus Brassica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17975–17998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, V.; Sharma, G. Effects of industrial effluent on soil characteristics: A review. IJAET 2014, 3, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; Sui, X.; Qi, B.; Zhou, L. Relationship between surface hydrophobicity and structure of soy protein isolate subjected to different ionic strength. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Timasheff, S.N. Theory of protein solubility. Methods Enzymol. 1985, 114, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, M.; Tavares, F.W.; Finet, S.; Skouri-Panet, F.; Tardieu, A.; Ninham, B.W. Why forces between proteins follow different Hofmeister series for pH above and below pI. Biophys. Chem. 2005, 117, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, Y.R.; Schmit, J.D. Ion specificity and nonmonotonic protein solubility from salt entropy. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Component | Content * (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| PI10.5–2.5 | PI2.5–8.5 | |
| Crude protein | 68.67 ± 0.16 b | 72.84 ± 0.45 a |
| Ash | 13.18 ± 0.73 a | 10.45 ± 0.11 b |
| Total lipids | 2.85 ± 0.14 a | 2.83 ± 0.03 а |
| Total carbohydrates | 4.02 ± 0.10 а | 3.76 ± 0.30 а |
| Total phenols | 0.42 ± 0.01 b | 0.71 ± 0.05 a |
| Glucosinolates | ND | ND |
| Proteins | Protein Distribution (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| PI2.5–8.5 | PI10.5–2.5 | |
| LMW | 81.8 | 77.8 |
| MMW | 9.1 | 11.1 |
| HMW | 9.1 | 11.1 |
| Amino Acid | Reference Protein * (g/100 g Protein) | PI2.5–8.5 | PI10.5–2.5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (g/100 g Protein) | Amino Acid Score (%) | Content (g/100 g Protein) | Amino Acid Score (%) | ||
| Valine | 3.9 | 3.99 ± 0.14 | 102.30 | 5.95 ± 0.20 | 152.56 |
| Leucine | 5.9 | 5.26 ± 0.90 | 89.15 | 6.74 ± 0.16 | 114.23 |
| Isoleucine | 3.0 | 1.96 ± 0.30 | 65.36 | 2.25 ± 0.18 | 75.00 |
| Threonine | 2.3 | 2.66 ± 0.15 | 115.65 | 2.99 ± 0.13 | 130.00 |
| Lysine | 4.5 | 4.51 ± 0.22 | 100.22 | 7.55 ± 0.11 | 167.77 |
| Phenylalanine+ tyrosine | 3.8 | 4.72 ± 0.27 | ND | 4.82 ± 0.94 | ND |
| Methionine+ cysteine | 2.2 | 3.95 ± 0.25 | ND | 3.99 ± 0.13 | ND |
| Amino Acid | PI2.5–8.5 | PI10.5–2.5 |
|---|---|---|
| Content (g/100 g Protein) | Content (g/100 g Protein) | |
| Alanine | 5.64 ± 0.11 | 7.38 ± 0.15 |
| Glycine | 2.05 ± 0.27 | 2.54 ± 0.19 |
| Arginine | 3.92 ± 0.15 | 4.93 ± 0.24 |
| Serine | 3.07 ± 0.10 | 1.52 ± 0.27 |
| Aspartate | 18.03 ± 0.17 | 4.36 ± 0.18 |
| Glutamate | 10.55 ± 0.16 | 11.79 ± 0.12 |
| Histidine | 1.75 ± 0.09 | 1.39 ± 0.17 |
| Proline | 3.77 ± 0.10 | 5.22 ± 0.24 |
| Component | Content * (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|
| PI2.5–8.5 | PI10.5–2.5 | |
| Copper (Cu) | 28.85 ± 0.02 a | 18.63 ± 0.06 b |
| Iron (Fe) | 178.81 ± 0.37 b | 301.53 ± 16.28 a |
| Manganese (Mn) | 129.15 ± 4.03 b | 143.17 ± 1.43 a |
| Selenium (Se) | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 137.25 ± 8.83 a | 119.90 ± 1.36 b |
| Lead (Pb) | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | <0.01 | <0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalaydzhiev, H.; Georgiev, R.; Ivanova, P.; Stoyanova, M.; Silva, C.L.M.; Chalova, V.I. Enhanced Solubility of Rapeseed Meal Protein Isolates Prepared by Sequential Isoelectric Precipitation. Foods 2020, 9, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060703
Kalaydzhiev H, Georgiev R, Ivanova P, Stoyanova M, Silva CLM, Chalova VI. Enhanced Solubility of Rapeseed Meal Protein Isolates Prepared by Sequential Isoelectric Precipitation. Foods. 2020; 9(6):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060703
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalaydzhiev, Hristo, Radoslav Georgiev, Petya Ivanova, Magdalena Stoyanova, Cristina L. M. Silva, and Vesela I. Chalova. 2020. "Enhanced Solubility of Rapeseed Meal Protein Isolates Prepared by Sequential Isoelectric Precipitation" Foods 9, no. 6: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060703
APA StyleKalaydzhiev, H., Georgiev, R., Ivanova, P., Stoyanova, M., Silva, C. L. M., & Chalova, V. I. (2020). Enhanced Solubility of Rapeseed Meal Protein Isolates Prepared by Sequential Isoelectric Precipitation. Foods, 9(6), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060703









