Behavioral Effects of Buspirone in Juvenile Zebrafish of Two Different Genetic Backgrounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
2.2. Experimental Design and Behavioral Testing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
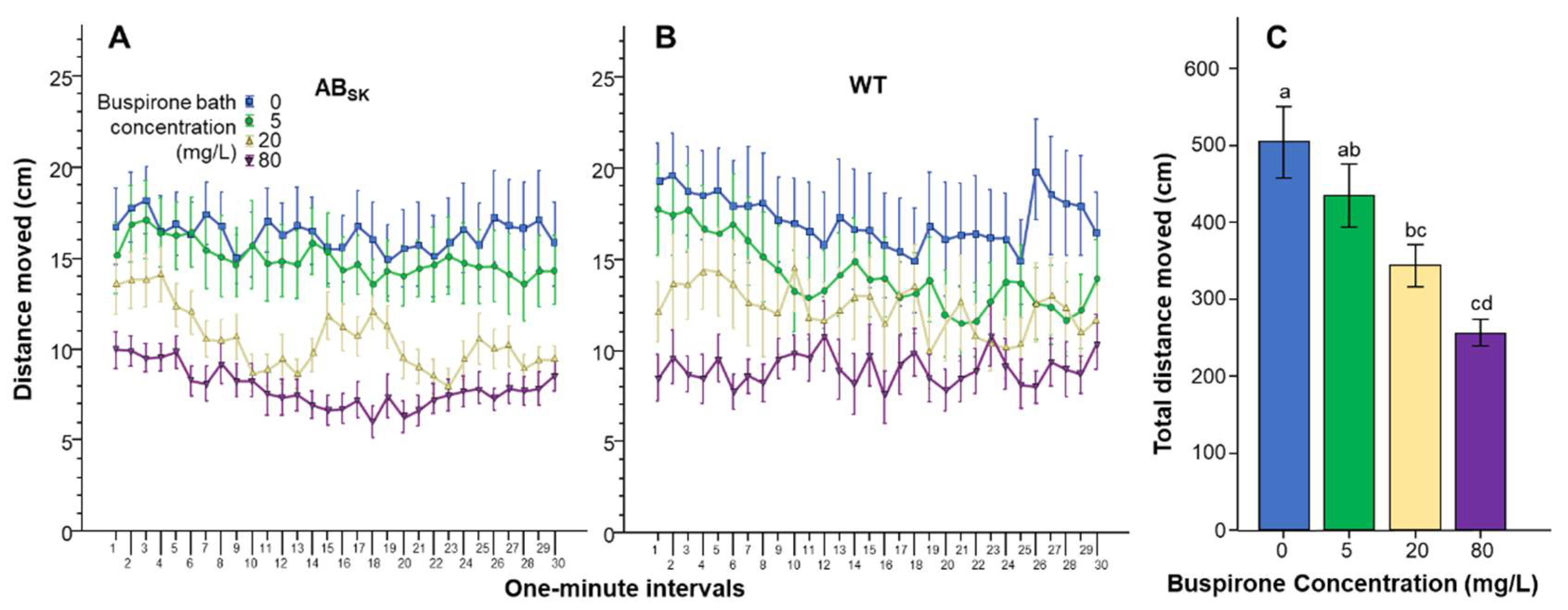
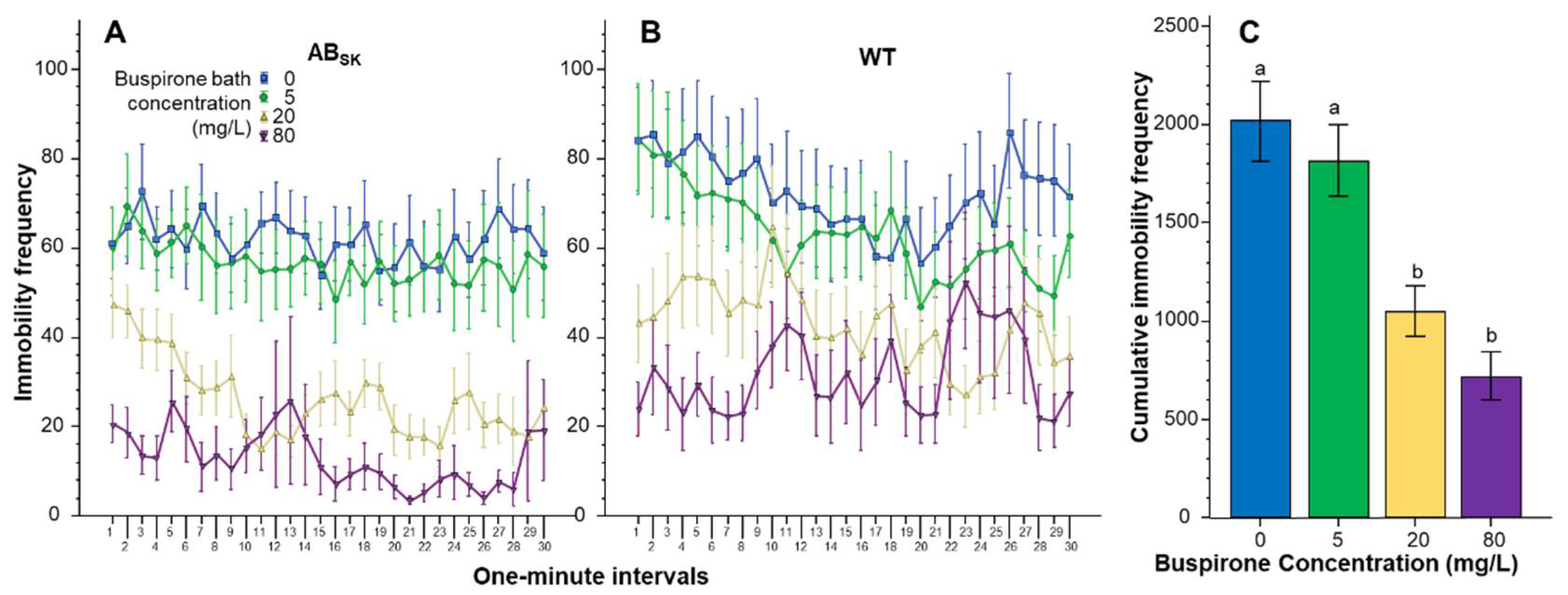
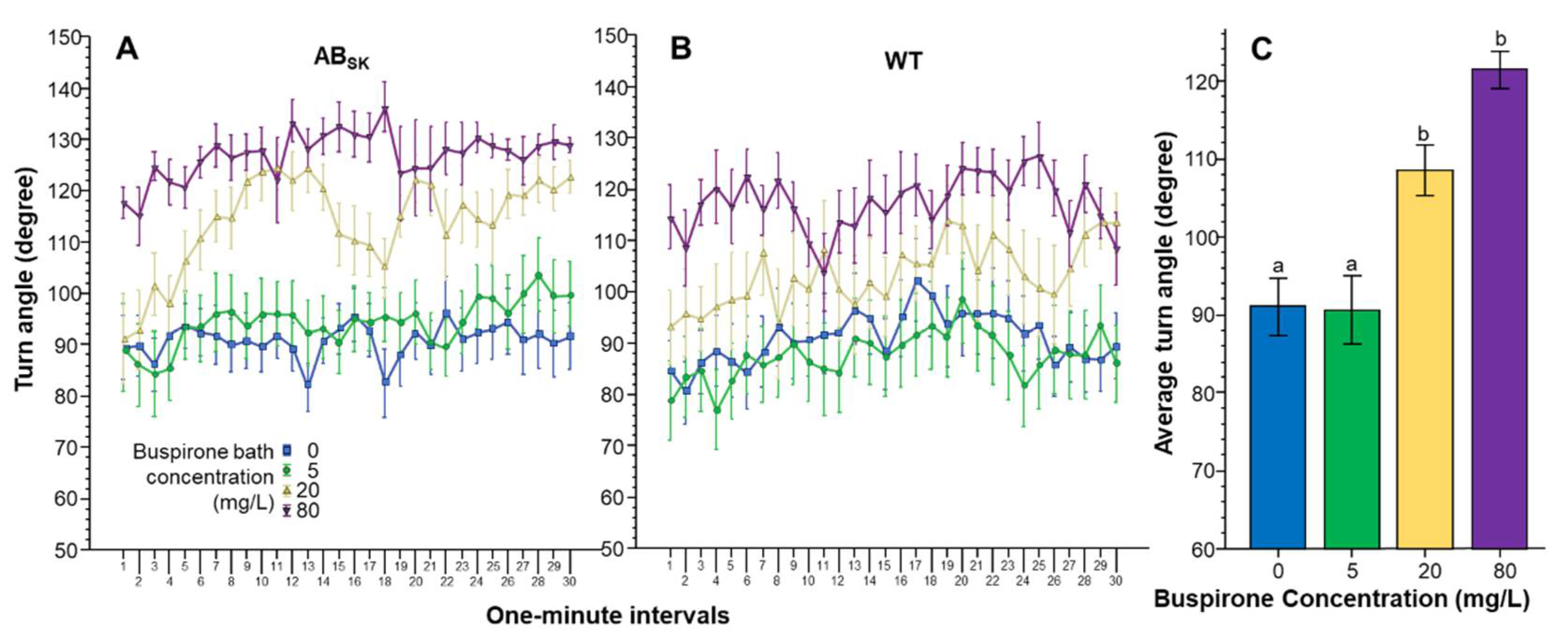
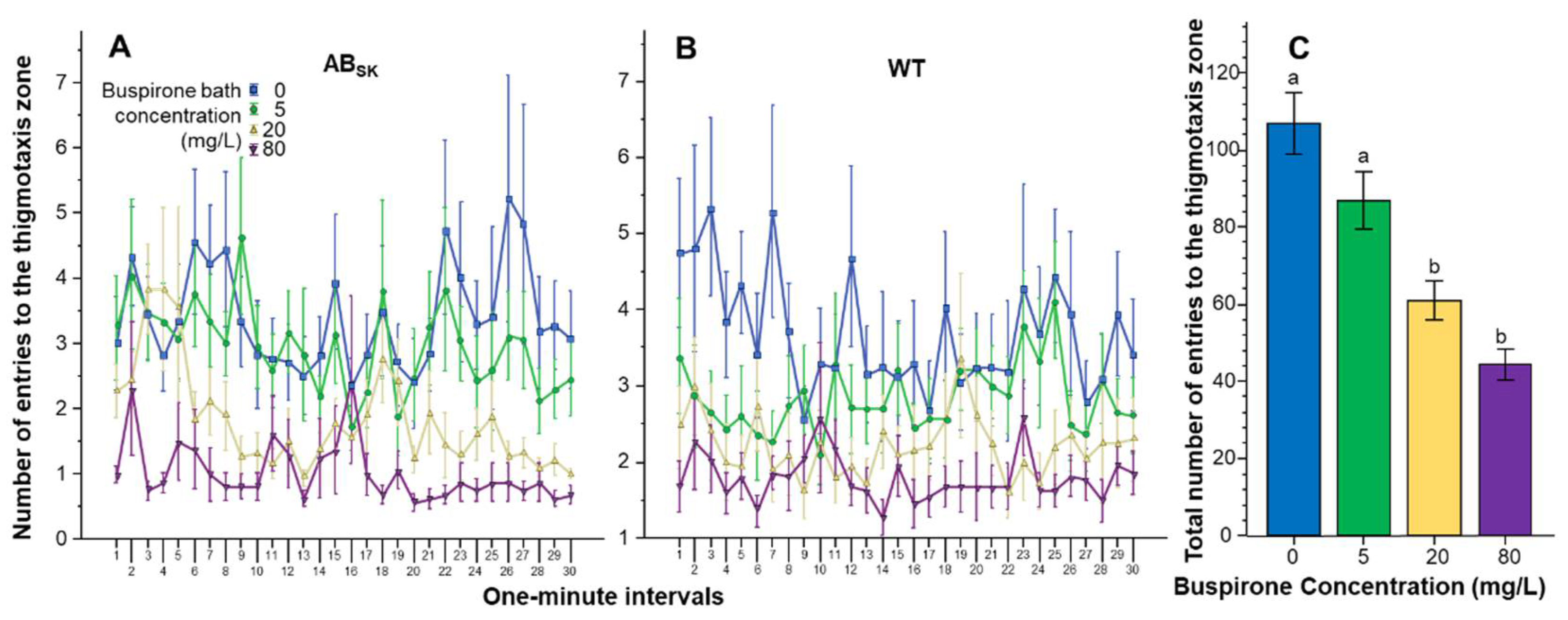
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koen, N.; Stein, D.J. Pharmacotherapy of anxiety disorders: A critical review. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 13, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bandelow, B.; Michaelis, S.; Wedekind, D. Treatment of anxiety disorders. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 19, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gelfuso, É.A.; Rosa, D.S.; Fachin, A.L.; Mortari, M.R.; Cunha, A.O.; Beleboni, R.O. Anxiety: A systematic review of neurobiology, traditional pharmaceuticals and novel alternatives from medicinal plants. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, S.J. Neurocognitive mechanisms of anxiety: An integrative account. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2007, 11, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, L.H.; Cryan, J.F. Genetic Approaches to Modeling Anxiety in Animals. Behav. Neurobiol. Anxiety Its Treat. 2010, 2, 161–201. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, S.J.; Coplan, J.D.; Gorman, J.M. Neurobiological mechanisms of social anxiety disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2001, 158, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourin, M.; Petit-Demoulière, B.; Nic Dhonnchadha, B.; Hascöet, M. Animal models of anxiety in mice. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 21, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganella, D.E.; Kim, J.H. Developmental rodent models of fear and anxiety: From neurobiology to pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4556–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, C.; Roseboom, P.H.; Nanda, S.A.; Lane, J.C.; Speers, J.M.; Kalin, N.H. Anxiety-related behavioral inhibition in rats: A model to examine mechanisms underlying the risk to develop stress-related psychopathology. Genes Brain Behav. 2010, 9, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, S.B.; Whittle, N.; Hetzenauer, A.; Singewald, N. Magnesium deficiency induces anxiety and HPA axis dysregulation: Modulation by therapeutic drug treatment. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahrens, S.; Wu, M.; Furlan, A.; Hwang, G.-R.; Paik, R.; Li, H.; Penzo, M.A.; Tollkuhn, J.; Li, B. A central extended amygdala circuit that modulates anxiety. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 5567–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brydges, N.M.; Jin, R.; Seckl, J.; Holmes, M.C.; Drake, A.J.; Hall, J. Juvenile stress enhances anxiety and alters corticosteroid receptor expression in adulthood. Brain Behav. 2014, 4, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Song, N.; Mao, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Han, H.-L.; Ding, Y.-Q.; Xu, L. Abnormal anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in mice lacking both central serotonergic neurons and pancreatic islet cells. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Jin, X.; You, Z.; Wang, S.; Lim, G.; Yang, J.; McCabe, M.; Li, N.; Marota, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Persistent nociception induces anxiety-like behavior in rodents: Role of endogenous neuropeptide S. Pain 2014, 155, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapiz-Bluhm, M.D.S.; Bondi, C.O.; Doyen, J.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Bédard-Arana, T.; Morilak, D.A. Behavioural assays to model cognitive and affective dimensions of depression and anxiety in rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 1115–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leibrock, C.; Ackermann, T.F.; Hierlmeier, M.; Lang, F.; Borgwardt, S.; Lang, U.E. Akt2 deficiency is associated with anxiety and depressive behavior in mice. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Bok, P.; Tsai, C.Y.; Sun, C.P.; Liu, H.; Deussing, J.M.; Huang, G.J. NPTX2 is a key component in the regulation of anxiety. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cachat, J.; Canavello, P.; Elegante, M.; Bartels, B.; Hart, P.; Bergner, C.; Egan, R.; Duncan, A.; Tien, D.; Chung, A.; et al. Modeling withdrawal syndrome in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.; Gaikwad, S.; Kyzar, E.; Green, J.; Roth, A.; Kalueff, A.V. Modeling anxiety using adult zebrafish: A conceptual review. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bencan, Z.; Sledge, D.; Levin, E.D. Buspirone, chlordiazepoxide and diazepam effects in a zebrafish model of anxiety. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 94, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaser, R.; Chadwick, L.; McGinnis, G. Behavioral measures of anxiety in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, W.; Bally-Cuif, L. Adult zebrafish as a model organism for behavioural genetics. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collier, A.D.; Kalueff, A.V.; Echevarria, D.J. Zebrafish models of anxiety-like behaviors. In The Rights and Wrongs of Zebrafish: Behavioral Phenotyping of Zebrafish; Kalueff, A.V., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 45–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlai, R. High-throughput behavioral screens: The first step towards finding genes involved in vertebrate brain function using zebrafish. Molecules 2010, 15, 2609–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, H.A.; Granato, M. The neurogenetic frontier—Lessons from misbehaving zebrafish. Brief. Funct. Genom. Proteom. 2008, 7, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish as an emerging model for studying complex brain disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reimers, M.J.; Hahn, M.; Tanguay, R.L. Two Zebrafish Alcohol Dehydrogenases Share Common Ancestry with Mammalian Class I, II, IV, and V Alcohol Dehydrogenase Genes but Have Distinct Functional Characteristics. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 38303–38312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levin, E.D.; Bencan, Z.; Cerutti, D.T. Anxiolytic effects of nicotine in zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 90, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.; Seguin, D.; Gerlai, R. An automated predator avoidance task in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 216, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Echevarria, D.J.; Hammack, C.M.; Pratt, D.W.; Hosemann, J.D. A novel behavioral test battery to assess global drug effects using the zebrafish. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2008, 21, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L. Zebrafish mutants: Behavioral genetic studies of visual system defects. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2001, 221, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandiwad, A.A.; Zeddies, D.; Raible, D.W.; Rubel, E.W.; Sisneros, J. Auditory sensitivity of larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) measured using a behavioral prepulse inhibition assay. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 3504–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maximino, C.; da Silva, A.W.B.; Gouveia, A., Jr.; Herculano, A.M. Pharmacological analysis of zebrafish (Danio rerio) scototaxis. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeDoux, J.E.; Pine, D.S. Using neuroscience to help understand fear and anxiety: A two-system framework. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, M.; Walker, D.L.; Miles, L.; Grillon, C. Phasic vs. sustained fear in rats and humans: Role of the extended amygdala in fear vs anxiety. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 105–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerlai, R.; Fernandes, Y.; Pereira, T. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) responds to the animated image of a predator: Towards the development of an automated aversive task. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 201, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luca, R.M.; Gerlai, R. In search of optimal fear inducing stimuli: Differential behavioral responses to computer animated images in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 226, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerlai, R.; Lee, V.; Blaser, R. Effects of acute and chronic ethanol exposure on the behavior of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 85, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Speedie, N.; Gerlai, R. Alarm substance induced behavioral responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 188, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnörr, S.; Steenbergen, P.; Richardson, M.; Champagne, D. Measuring thigmotaxis in larval zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 228, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, H.; Tsang, B.; Ahmed, H.; Lee, R.C.Y.; Tran, S.; Gerlai, R. Diazepam fails to alter anxiety-like responses but affects motor function in a white-black test paradigm in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozaid, A.; Hung, J.; Tsang, B.; Motlana, K.; Al-Ani, R.; Gerlai, R. Behavioral effects of acute ethanol in larval zebrafish (D. rerio) depend on genotype and volume of experimental well. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 112, 110411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, X.; Feng, X. Cardiovascular toxicity and anxiety-like behavior induced by deltamethrin in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richendrfer, H.; Pelkowski, S.; Colwill, R.; Creton, R. On the edge: Pharmacological evidence for anxiety-related behavior in zebrafish larvae. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 228, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; da Silva Batista, A.W.; Herculano, A.M.; Morato, S.; Gouveia, A., Jr. Measuring anxiety in zebrafish: A critical review. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loane, C.; Politis, M. Buspirone: What is it all about? Brain Res. 2012, 1461, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; Puty, B.; Benzecry, R.; Araújo, J.; Lima, M.G.; Batista, E.D.J.O.; Oliveira, K.R.D.M.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E.; Herculano, A.M. Role of serotonin in zebrafish (Danio rerio) anxiety: Relationship with serotonin levels and effect of buspirone, WAY 100635, SB 224289, fluoxetine and para-chlorophenylalanine (pCPA) in two behavioral models. Neuropharmacology 2013, 71, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaswinkel, H.; Zhu, L.; Weng, W. The immediate and the delayed effects of buspirone on zebrafish (Danio rerio) in an open field test: A 3-D approach. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 234, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, M.S.; Giacomini, A.C.V.; Gusso, D.; Rosa, J.G.; Koakoski, G.; Kalichak, F.; Idalêncio, R.; Oliveira, T.A.; Barcellos, H.H.; Bonan, C.D.; et al. Acute exposure to waterborne psychoactive drugs attract zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 179, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Escobedo, P.A.; Gould, G.G. Visual social preferences of lone zebrafish in a novel environment: Strain and anxiolytic effects. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebauer, D.L.; Pagnussat, N.; Piato, Â.L.; Schaefer, I.C.; Bonan, C.D.; Lara, D.R. Effects of anxiolytics in zebrafish: Similarities and differences between benzodiazepines, buspirone and ethanol. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 99, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steenbergen, P.; Richardson, M.K.; Champagne, D.L. Patterns of avoidance behaviours in the light/dark preference test in young juvenile zebrafish: A pharmacological study. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 222, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, B.W.; Moeskops, M.; Veenvliet, A.R. Color Preference in Danio rerio: Effects of age and anxiolytic treatments. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winslow, J.T.; Noble, P.L.; Davis, M. Modulation of fear-potentiated startle and vocalizations in juvenile rhesus monkeys by morphine, diazepam, and buspirone. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Hendrie, C.; Eilam, D.; Weiss, S.M. Effects of diazepam and buspirone on the behaviour of wild voles (Microtus socialis) in two models of anxiety. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 58, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, J.; Horvath, Z.; Bakos, N. The effect of buspirone on normal and hypoarousal-driven abnormal aggression in rats. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.W.; Temel, Y.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Steinbusch, H.; Schruers, K.; Hameleers, R.; Esquivel, G.; Griez, E.; Blokland, A. Effect of buspirone on the behavioral regulation of rats in low versus high anxiety conditions. Arzneimittelforschung 2008, 58, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, D.J.; Nawaz, S.; Salman, T. Dose related effects of buspirone on pain, learning/memory and food intake. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 99, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkevich, I.P.; Mikhailenko, V.A.; Vershinina, E.A.; Barr, G.A. Differences between the prenatal effects of fluoxetine or buspirone alone or in combination on pain and affective behaviors in prenatally stressed male and female rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, M.J.; Cullen, W.K.; Moulton, B. Buspirone impairment of performance of passive avoidance and spatial learning tasks in the rat. Psychopharmacology 1990, 100, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, J.T.; Ichikawa, K.M. iPhone® applications as versatile video tracking tools to analyze behavior in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 106, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, C.; Paul, S.M.; Crawley, J.N. Characterization of benzodiazepine-sensitive behaviors in the A/J and C57BL/6J inbred strains of mice. Behav. Genet. 1994, 24, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiasen, L.; Mirza, N.; Rodgers, R. Strain- and model-dependent effects of chlordiazepoxide, L-838,417 and zolpidem on anxiety-like behaviours in laboratory mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.N.; Davis, L.G. Baseline exploratory activity predicts anxiolytic responsiveness to diazepam in five mouse strains. Brain Res. Bull. 1982, 8, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Laan, J.W.; De Boer, S.F.; Van der Gugten, J.; De Groot, G. Differences in the duration of sedative and anxiolytic effects of desmethyldiazepam in two outbred Wistar strains. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 39, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Lu, M.S.; Motegi, H.; Yoshii, T.; Misawa, M. Genetic differences in the development of physical dependence upon diazepam in Lewis and Fischer 344 inbred rat strains. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1992, 43, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, M.; Dostal, J.; Kimura, H.; Strohl, K.P. Effects of buspirone on posthypoxic ventilatory behavior in the C57BL/6J and A/J mouse strains. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 105, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingebretson, J.J.; Masino, M.A. Quantification of locomotor activity in larval zebrafish: Considerations for the design of high-throughput behavioral studies. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abozaid, A.; Trzuskot, L.; Najmi, Z.; Paul, I.; Tsang, B.; Gerlai, R. Developmental stage and genotype dependent behavioral effects of embryonic alcohol exposure in zebrafish larvae. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 97, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R. Zebrafish antipredatory responses: A future for translational research? Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 207, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miklósi, Á.; Andrew, R.J. The zebrafish as a model for behavioral studies. Zebrafish 2006, 3, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, R.; Gerlai, R. Behavioral phenotyping in zebrafish: Comparison of three behavioral quantification methods. Behav. Res. Methods 2006, 38, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abozaid, A.; Tsang, B.; Gerlai, R. The effects of small but abrupt change in temperature on the behavior of larval zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 227, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R. Zebrafish, a potential novel research tool for the analysis and modeling of anxiety. In Anxiety Disorder; Selek, S., Ed.; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2011; Chapter 7; pp. 137–158. [Google Scholar]
- Champagne, D.L.; Hoefnagels, C.C.; de Kloet, R.; Richardson, M.K. Translating rodent behavioral repertoire to zebrafish (Danio rerio): Relevance for stress research. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, J.A.; Kaitin, K.I.; Dement, W.C.; Peroutka, S.J. The effects of buspirone on sleep in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1986, 72, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokk, P.; Zharkovsky, A. The effects of buspirone on the behaviour of control and stressed mice. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 1998, 49, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, W.F.; Cohen, S.A.; Bliwise, N.G.; Dement, W.C. Buspirone: An anxiolytic without sedative effect. Psychopharmacology 1985, 87, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.E.; Wahlstrom-Helgren, S.; Wiggin, T.D.; Corwin, B.M.; Lillesaar, C.; Masino, M.A. Intraspinal serotonergic signaling suppresses locomotor activity in larval zebrafish. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 807–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Mussulini, B.H.M.; Moro, L.; de Assis, A.M.; Rosemberg, D.B.; de Oliveira, D.L.; Rocha, J.B.; Schwab, R.S.; Schneider, P.H.; Souza, D.O.; et al. Anxiolytic effects of diphenyl diselenide on adult zebrafish in a novelty paradigm. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 54, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, S.; Fulcher, N.; Nowicki, M.; Desai, P.; Tsang, B.; Facciol, A.; Chow, H.; Gerlai, R. Time-dependent interacting effects of caffeine, diazepam, and ethanol on zebrafish behaviour. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 75, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.H. Developmental exposures to ethanol or dimethylsulfoxide at low concentrations alter locomotor activity in larval zebrafish: Implications for behavioral toxicity bioassays. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 102, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosemberg, D.B.; Braga, M.M.; Rico, E.P.; Loss, C.M.; Córdova, S.D.; Mussulini, B.H.M.; Blaser, R.E.; Leite, C.E.; Campos, M.M.; Dias, R.D.; et al. Behavioral effects of taurine pretreatment in zebrafish acutely exposed to ethanol. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.P.; D’Eath, R.B.; Healy, S.D. Environmental enrichment enhances spatial cognition in rats by reducing thigmotaxis (wall hugging) during testing. Anim. Behav. 2009, 77, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y. Bright lighting conditions during testing increase thigmotaxis and impair water maze performance in BALB/c mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 226, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, P.; Dupuis, R.; Costentin, J. Thigmotaxis as an index of anxiety in mice. Influence of dopaminergic transmissions. Behav. Brain Res. 1994, 61, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treit, D.; Fundytus, M. Thigmotaxis as a test for anxiolytic activity in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1988, 31, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, V.C.; Segerdahl, A.R.; Blackbeard, J.; Pheby, T.; Rice, A.S. Anxiety-like behaviour is attenuated by gabapentin, morphine and diazepam in a rodent model of HIV anti-retroviral-associated neuropathic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 448, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; Colmanetti, R.; Pontes, A.A.A.; de Castro, H.M.; de Lacerda, R.I.T.; Morato, S.; Gouveia, A., Jr. Parametric analyses of anxiety in zebrafish scototaxis. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 210, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiamonte, M.; Parker, M.O.; Vinson, G.P.; Brennan, C.H. Sustained effects of developmental exposure to ethanol on zebrafish anxiety-like behaviour. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Lin, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, N.; Li, Q. Anxiety-related behavioral responses of pentylenetetrazole-treated zebrafish larvae to light-dark transitions. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2016, 145, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Raamsdonk, W.; Bosch, T.J.; Smit-Onel, M.J.; Maslam, S. Organisation of the zebrafish spinal cord: Distribution of motoneuron denfrites and 5-HT containing cells. Eur. J. Morphol. 1996, 34, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, J.P.; Mahmood, R.; Kyriakatos, A.; Söll, I.; Hauptmann, G.; Calabrese, R.L.; El Manira, A. Serotonergic modulation of locomotion in zebrafish: Endogenous release and synaptic mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 10387–10395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Airhart, M.J.; Lee, D.H.; Wilson, T.D.; Miller, B.E.; Miller, M.N.; Skalko, R.G. Movement disorders and neurochemical changes in zebrafish larvae after bath exposure to fluoxetine (PROZAC). Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2007, 29, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abozaid, A.; Gerlai, R. Behavioral Effects of Buspirone in Juvenile Zebrafish of Two Different Genetic Backgrounds. Toxics 2022, 10, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010022
Abozaid A, Gerlai R. Behavioral Effects of Buspirone in Juvenile Zebrafish of Two Different Genetic Backgrounds. Toxics. 2022; 10(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbozaid, Amira, and Robert Gerlai. 2022. "Behavioral Effects of Buspirone in Juvenile Zebrafish of Two Different Genetic Backgrounds" Toxics 10, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010022
APA StyleAbozaid, A., & Gerlai, R. (2022). Behavioral Effects of Buspirone in Juvenile Zebrafish of Two Different Genetic Backgrounds. Toxics, 10(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010022





