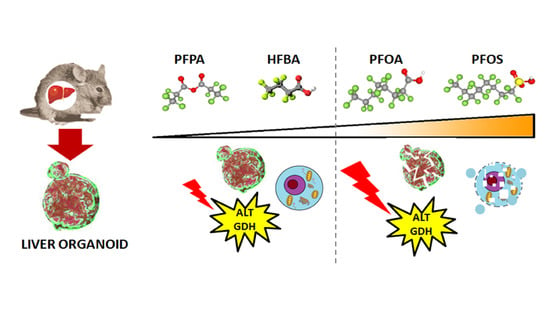
Early Warnings by Liver Organoids on Short- and Long-Chain PFAS Toxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Organoid Isolation
2.3. Cell Viability Assay (EC50, Effective Concentration 50)
2.4. Histological and Immunohistochemical Staining
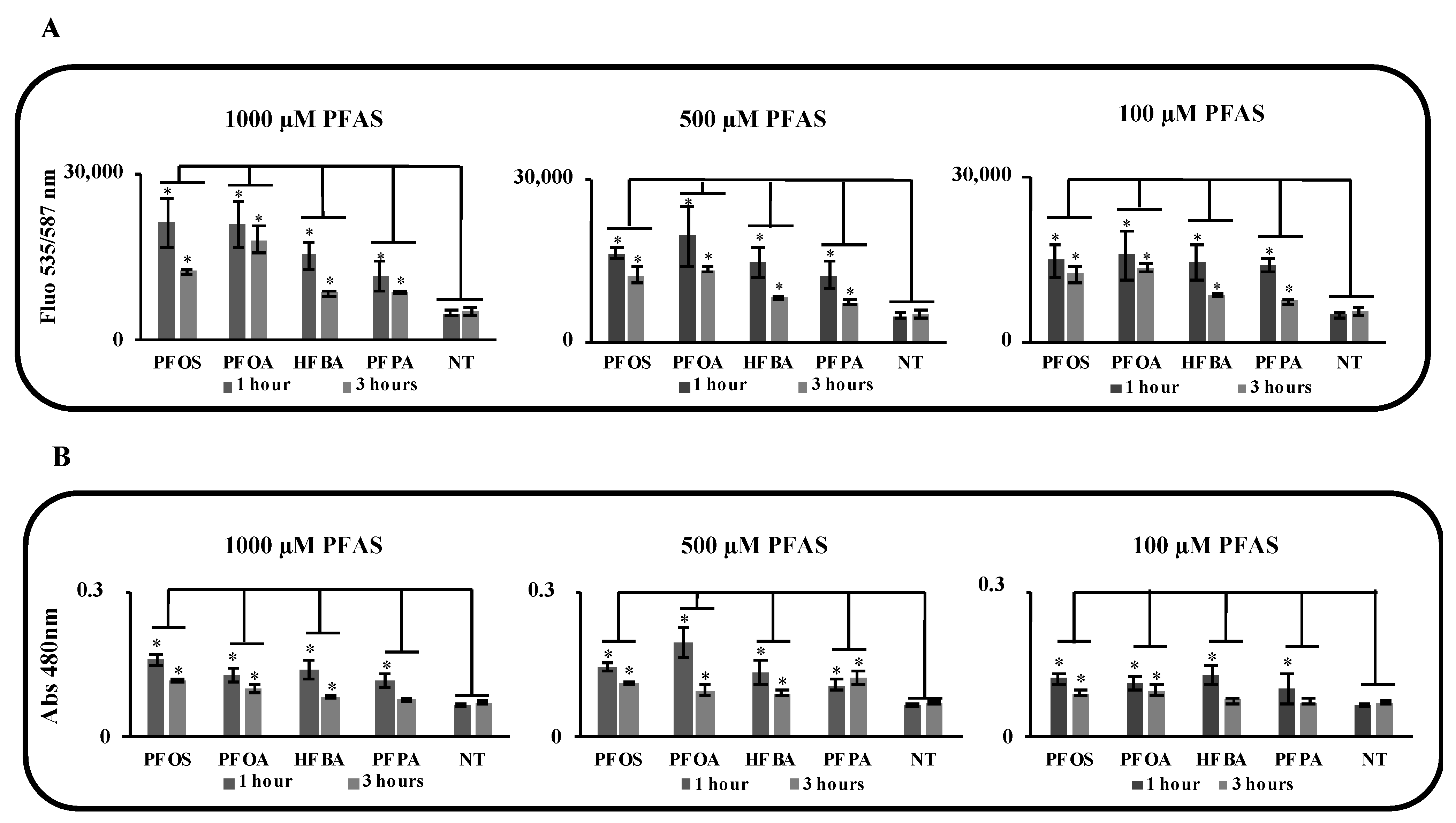
2.5. ALT and GDH Activity Assay
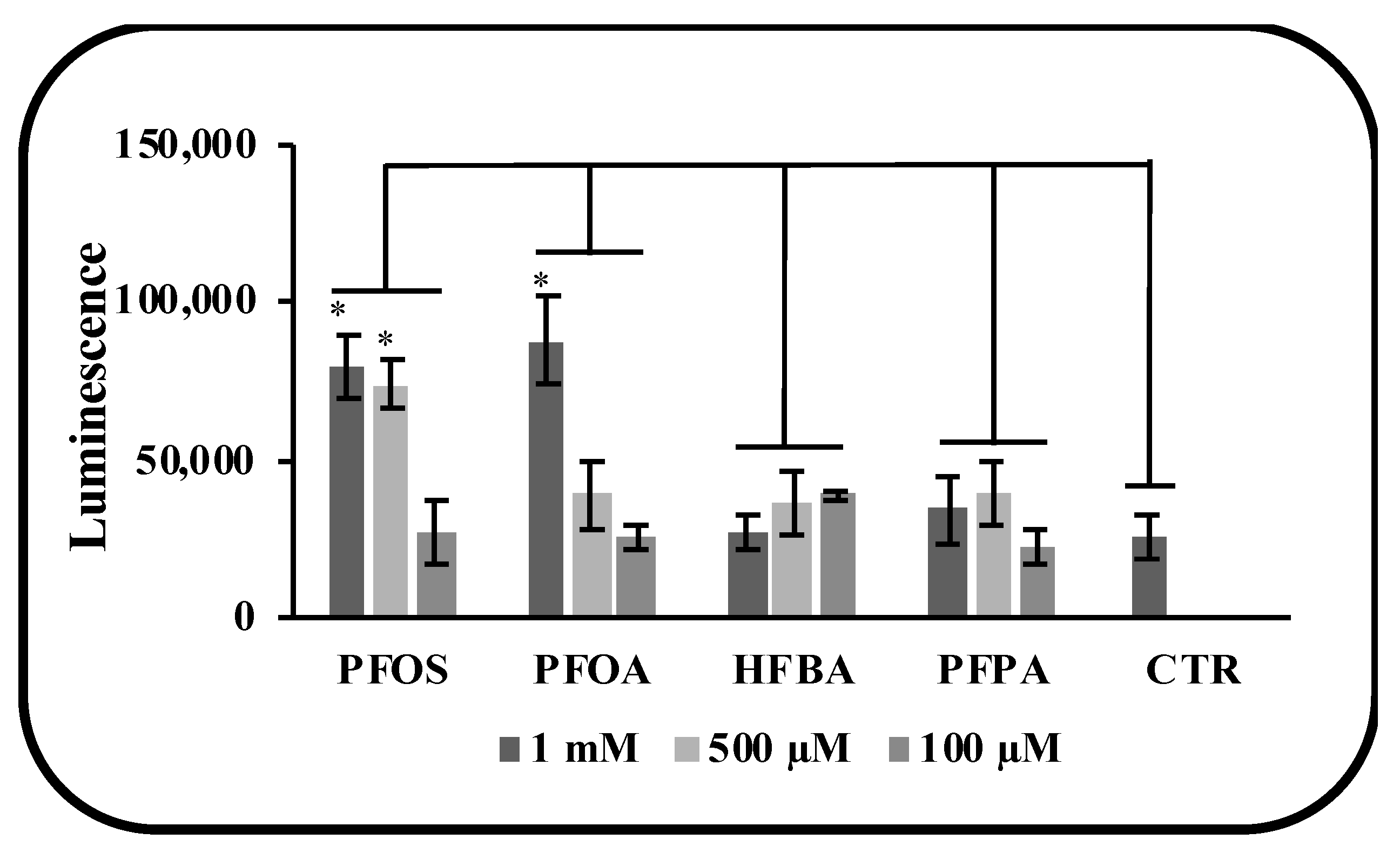
2.6. Caspases 3/7 Activity
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of PFAS on Mouse Liver Organoids Viability
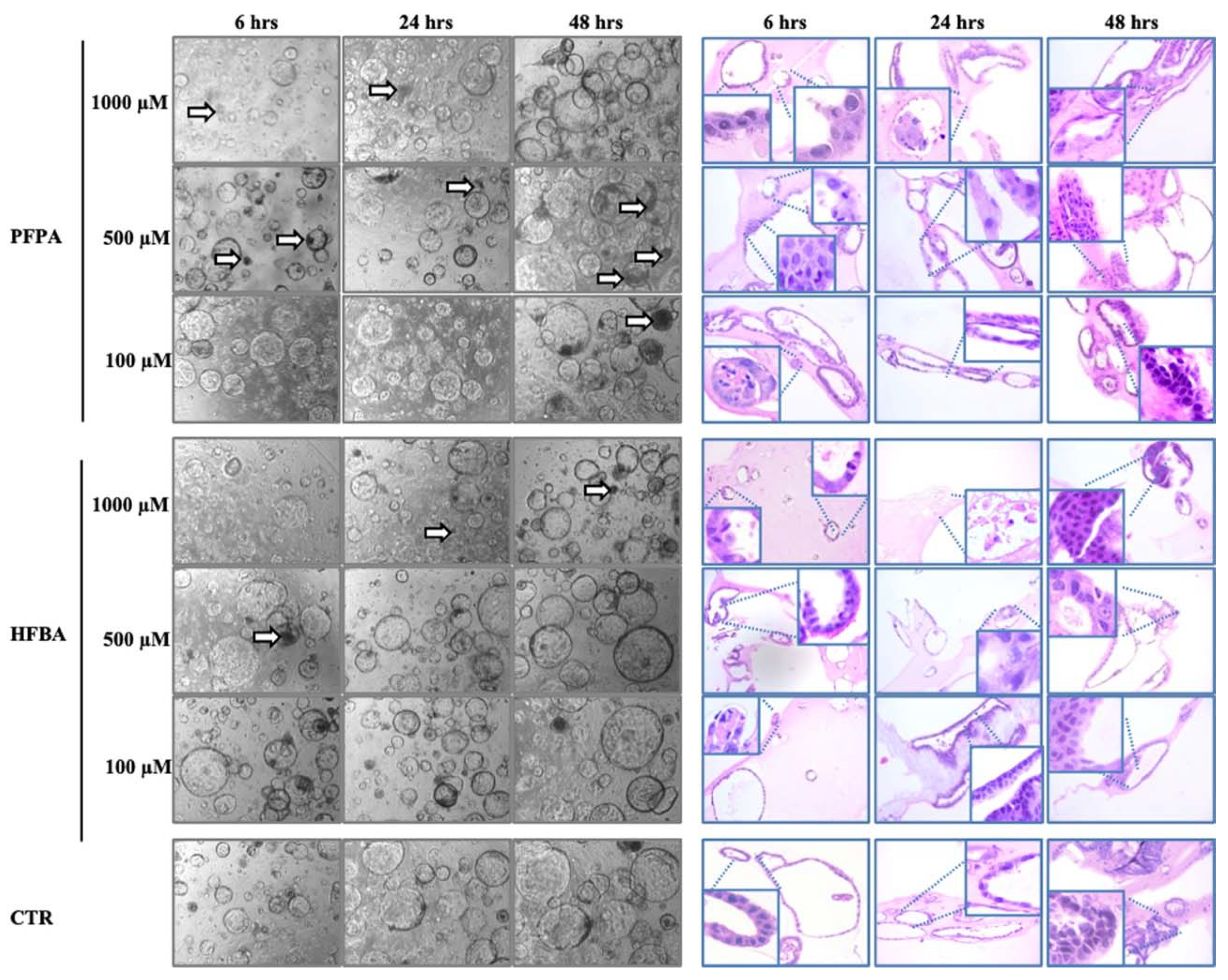
3.2. Structural Alterations in Liver Organoids
3.3. Long and Short PFASs Alter the Activity of Key Liver Enzymes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, A.G.; Jones, K.C.; Sweetman, A.J. A first global production, emission, and environmental inventory for perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, B.C.; Ikonomou, M.G.; Blair, J.D.; Surridge, B.; Hoover, D.; Grace, R.; Gobas, F.A.P.C. Perfluoroalkyl contaminants in an arctic marine food web: Trophic magnification and wildlife exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4037–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescord, G.L.; Kidd, K.A.; De Silva, A.O.; Williamson, M.; Spencer, C.; Wang, X.; Muir, D.C.G. Perfluorinated and polyfluorinated compounds in lake food webs from the Canadian High Arctic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2694–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Anderson, R.H.; Guo, B. PFAS concentrations in soils: Background levels versus contaminated sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, Q.; Song, X.; Chen, X.; Fan, R.; Ding, D.; Liu, Y. Distribution, source identification and health risk assessment of PFASs and two PFOS alternatives in groundwater from non-industrial areas. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 152, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Simcik, M.F.; Halbach, T.R.; Gulliver, J.S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in soils and groundwater of a U.S. metropolitan area: Migration and implications for human exposure. Water Res. 2015, 72, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lein, N.P.H.; Fujii, S.; Tanaka, S.; Nozoe, M.; Tanaka, H. Contamination of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in surface water of the Yodo River basin (Japan). Desalination 2008, 226, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. Human exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) through drinking water: A review of the recent scientific literature. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dassuncao, C.; Lohmann, R.; Sunderland, E.M. North Atlantic Deep Water formation inhibits high Arctic contamination by continental perfluorooctane sulfonate discharges. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.L.; Berger, U.; Chaemfa, C.; Huber, S.; Jahnke, A.; Temme, C.; Jones, K.C. Analysis of per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances in air samples from Northwest Europe. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubleski, J.; Salihovic, S.; Lind, L.; Lind, P.M.; van Bavel, B.; Kärrman, A. Changes in serum levels of perfluoroalkyl substances during a 10-year follow-up period in a large population-based cohort. Environ. Int. 2016, 95, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP. Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) as Amended in 2009. In The IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology; Annex B; 2009; p. 41. Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/chemi/pops/treaty/treaty_en2009.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Cordner, A.; De La Rosa, V.Y.; Schaider, L.A.; Rudel, R.A.; Richter, L.; Brown, P. Guideline levels for PFOA and PFOS in drinking water: The role of scientific uncertainty, risk assessment decisions, and social factors. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zushi, Y.; Hogarh, J.N.; Masunaga, S. Progress and perspective of perfluorinated compound risk assessment and management in various countries and institutes. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2012, 14, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability Towards a Toxic-Free Environment. In Commission Staff Working Document; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; pp. 1–22. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/pdf/chemicals/2020/10/SWD_PFAS.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.R.; Leblanc, J.-C.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the risk to human health related to the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in food. EFSA J. 2020, 16, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glüge, J.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; Dewitt, J.C.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Trier, X.; Wang, Z. An overview of the uses of per- And polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2345–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Field, J.A.; Luna-Velasco, A.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Microbial toxicity and biodegradability of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and shorter chain perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2016, 18, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, P. A review of sources, multimedia distribution and health risks of novel fluorinated alternatives. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, H.; Li, F.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Q. Sorption of short- and long-chain perfluoroalkyl surfactants on sewage sludges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xia, X.; Dong, J.; Xia, N.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y. Short- and long-chain perfluoroalkyl substances in the water, suspended particulate matter, and surface sediment of a turbid river. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; MacLeod, M.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Using COSMOtherm to predict physicochemical properties of poly- and perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs). Environ. Chem. 2011, 8, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felizeter, S.; McLachlan, M.S.; De Voogt, P. Uptake of perfluorinated alkyl acids by hydroponically grown lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11735–11743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisi, R.; Vamerali, T.; Manzetti, S. Accumulation of perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in agricultural plants: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischel, H.N.; Macmanus-Spencer, L.A.; Zhang, C.; Luthy, R.G. Strong associations of short-chain perfluoroalkyl acids with serum albumin and investigation of binding mechanisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendel, S.; Fetter, É.; Staude, C.; Vierke, L.; Biegel-Engler, A. Short-chain perfluoroalkyl acids: Environmental concerns and a regulatory strategy under REACH. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H. Modeling Development and Disease with Organoids. Cell 2016, 165, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, T.C. Development and Translation of Stem Cell-Derived Therapies Enabling Technologies for Cell-Based Clinical Translation Enabling Technologies for Cell-Based Clinical Translation. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scattolin, T.; Bortolamiol, E.; Visentin, F.; Palazzolo, S.; Caligiuri, I.; Perin, T.; Canzonieri, V.; Demitri, N.; Rizzolio, F.; Togni, A. Palladium(II)-η3-Allyl Complexes Bearing N-Trifluoromethyl N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: A New Generation of Anticancer Agents that Restrain the Growth of High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Tumoroids. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 11868–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granchi, C.; Bononi, G.; Ferrisi, R.; Gori, E.; Mantini, G.; Glasmacher, S.; Poli, G.; Palazzolo, S.; Caligiuri, I.; Rizzolio, F.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of second-generation benzoylpiperidine derivatives as reversible monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scattolin, T.; Bortolamiol, E.; Palazzolo, S.; Caligiuri, I.; Perin, T.; Canzonieri, V.; Demitri, N.; Rizzolio, F.; Cavallo, L.; Dereli, B.; et al. The anticancer activity of an air-stable Pd(i)-NHC (NHC = N-heterocyclic carbene) dimer. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 12238–12241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, H.; Stappenbeck, T.S. In vitro expansion and genetic modification of gastrointestinal stem cells in spheroid culture. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzolo, S.; Hadla, M.; Spena, C.R.C.R.; Bayda, S.; Kumar, V.; Lo Re, F.; Adeel, M.; Caligiuri, I.; Romano, F.; Corona, G.; et al. Proof-of-Concept Multistage Biomimetic Liposomal DNA Origami Nanosystem for the Remote Loading of Doxorubicin. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzolo, S.; Hadla, M.; Spena, C.R.; Caligiuri, I.; Rotondo, R.; Adeel, M.; Kumar, V.; Corona, G.; Canzonieri, V.; Toffoli, G.; et al. An effective multi-stage liposomal DNA origami nanosystem for in vivo cancer therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Limdi, J.K.; Hyde, G.M. Evaluation of abnormal liver function tests. Postgrad. Med. J. 2003, 79, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macon, M.B.; Villanueva, L.T.R.; Tatum-Gibbs, K.; Zehr, R.D.; Strynar, M.J.; Stanko, J.P.; White, S.S.; Helfant, L.; Fenton, S.E. Prenatal perfluorooctanoic acid exposure in CD-1 mice: Low-dose developmental effects and internal dosimetry. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 122, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- NTP National Toxicology Program (NTP). NTP Monograph Immunotoxicity Associated with Exposure to Perfluorooctanoic Acid or Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services: Washington, DC, USA. Available online: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/ohat/pfoa_pfos/pfoa_pfosmonograph_508.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, C.; Xue, C.; Xue, L.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Q. Changes in the levels of L-carnitine, acetyl-L-carnitine and propionyl-L-carnitine are involved in perfluorooctanoic acid induced developmental cardiotoxicity in chicken embryo. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamendulis, L.M.; Wu, Q.; Sandusky, G.E.; Hocevar, B.A. Perfluorooctanoic acid exposure triggers oxidative stress in the mouse pancreas. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, K.S.; Choi, E.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Hong, S.M.; Park, S.Y.; Rhee, S.Y.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.W.; Pak, Y.K.; Choe, W.; et al. Perfluorooctanoic acid induces oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in pancreatic β-cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 3871–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Yin, N.; Faiola, F. PFOA and PFOS Disrupt the Generation of Human Pancreatic Progenitor Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.P.; Li, J.W.; Cheung, A.; Li, R.; Billah, M.B.; Chan, T.F.; Wong, C.K.C. Transcriptome sequencing reveals prenatal PFOS exposure on liver disorders. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, H.I.; Bae, H.I.; Yang, J.H. Perfluorooctanoic acid-induced hepatic toxicity following 21-day oral exposure in mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, A.; Berger, U.; Bignert, A.; Ullah, S.; Aune, M.; Lignell, S.; Darnerud, P.O. Perfluorinated alkyl acids in blood serum from primiparous women in Sweden: Serial sampling during pregnancy and nursing, and temporal trends 1996–2010. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9071–9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zhou, Q.F.; Liao, C.Y.; Fu, J.J.; Jiang, G. Bin Studies on the toxicological effects of PFOA and PFOS on rats using histological observation and chemical analysis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 56, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butenhoff, J.L.; Chang, S.C.; Olsen, G.W.; Thomford, P.J. Chronic dietary toxicity and carcinogenicity study with potassium perfluorooctanesulfonate in Sprague Dawley rats. Toxicology 2012, 293, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butenhoff, J.L.; Kennedy, G.L.; Chang, S.C.; Olsen, G.W. Chronic dietary toxicity and carcinogenicity study with ammonium perfluorooctanoate in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicology 2012, 298, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaunig, J.E.; Shinohara, M.; Iwai, H.; Chengelis, C.P.; Kirkpatrick, J.B.; Wang, Z.; Bruner, R.H. Evaluation of the chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity of perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA) in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatif, A.G.; Préat, V.; Taper, H.S.; Roberfroid, M. The modulation of rat liver carcinogenesis by perfluorooctanoic acid, a peroxisome proliferator. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1991, 111, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgo, A.J.; Quist, E.M.; Hoenerhoff, M.J.; Brix, A.E.; Kissling, G.E.; Fenton, S.E. Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA)–induced Liver Lesions in Two Strains of Mice Following Developmental Exposures:PPARα Is Not Required. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Yang, R.; Yin, N.; Faiola, F. The short-chain perfluorinated compounds PFBS, PFHxS, PFBA and PFHxA, disrupt human mesenchymal stem cell self-renewal and adipogenic differentiation. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 88, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, L.; Coperchini, F.; Tonacchera, M.; Imbriani, M.; Rotondi, M.; Chiovato, L. Effect of long- and short-chain perfluorinated compounds on cultured thyroid cells viability and response to TSH. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, N.; Cui, R.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Dai, J. Cytotoxicity of novel fluorinated alternatives to long-chain perfluoroalkyl substances to human liver cell line and their binding capacity to human liver fatty acid binding protein. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, F.; Rusconi, M.; Valsecchi, S.; Marziali, L. Evolutionary ecotoxicology of perfluoralkyl substances (PFASs) inferred from multigenerational exposure: A case study with Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae). Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 156, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulhaq, M.; Örn, S.; Carlsson, G.; Morrison, D.A.; Norrgren, L. Locomotor behavior in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae exposed to perfluoroalkyl acids. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 144–145, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, C.T.; Damayanti, N.P.; Guffey, S.C.; Serafin, J.S.; Irudayaraj, J.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Comparative in vitro toxicity assessment of perfluorinated carboxylic acids. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Fletcher, T.; Pineda, D.; Lindh, C.H.; Nilsson, C.; Glynn, A.; Vogs, C.; Norström, K.; Lilja, K.; Jakobsson, K.; et al. Serum half-lives for short-and long-chain perfluoroalkyl acids after ceasing exposure from drinking water contaminated by firefighting foam. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.H.; Nilsson, H.; Buck, R.C. Elimination kinetics of perfluorohexanoic acid in humans and comparison with mouse, rat and monkey. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Ehresman, D.J.; Froelich, J.W.; Seacat, A.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartell, S.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Lyu, C.; Kato, K.; Ryan, P.B.; Steenland, K. Rate of decline in serum PFOA concentrations after granular activated carbon filtration at two public water systems in Ohio and West Virginia. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Mo, M.S.; Chen, H.G.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.L.; Zhao, D.H. Distribution and Exposure Risk Assessment of Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances in Aquatic Products along the Coastal Region of the South China Sea. Expo. Health 2021, 13, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Xia, X.; Hu, D.; Zhou, D.; Wang, H.; Zhai, Y.; Lin, H. Long-Chain Perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) Affect the Bioconcentration and Tissue Distribution of Short-Chain PFAAs in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12358–12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, K.; El-Khatib, A.H.; Schwerdtle, T.; Monien, B.H. Perfluorobutanoic acid (PFBA): No high-level accumulation in human lung and kidney tissue. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 237, 113830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbink, W.A.; Berger, U.; Cousins, I.T. Estimating human exposure to PFOS isomers and PFCA homologues: The relative importance of direct and indirect (precursor) exposure. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- IARC. IARC Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017; Volume 101, pp. 37–110. [Google Scholar]
- Corton, J.C.; Cunningham, M.L.; Hummer, B.T.; Lau, C.; Meek, B.; Peters, J.M.; Popp, J.A.; Rhomberg, L.; Seed, J.; Klaunig, J.E. Mode of action framework analysis for receptor-mediated toxicity: The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) as a case study. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compound | EC50 (µM) |
|---|---|
| PFOS (C8HF17O3S) | 670 ± 30 |
| PFOA (C8HF15O2) | 895 ± 7 |
| PFPA (CF3CF2CO)2O | NC |
| HFBA (C4HF7O2) | NC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palazzolo, S.; Caligiuri, I.; Sfriso, A.A.; Mauceri, M.; Rotondo, R.; Campagnol, D.; Canzonieri, V.; Rizzolio, F. Early Warnings by Liver Organoids on Short- and Long-Chain PFAS Toxicity. Toxics 2022, 10, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10020091
Palazzolo S, Caligiuri I, Sfriso AA, Mauceri M, Rotondo R, Campagnol D, Canzonieri V, Rizzolio F. Early Warnings by Liver Organoids on Short- and Long-Chain PFAS Toxicity. Toxics. 2022; 10(2):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10020091
Chicago/Turabian StylePalazzolo, Stefano, Isabella Caligiuri, Andrea Augusto Sfriso, Matteo Mauceri, Rossella Rotondo, Davide Campagnol, Vincenzo Canzonieri, and Flavio Rizzolio. 2022. "Early Warnings by Liver Organoids on Short- and Long-Chain PFAS Toxicity" Toxics 10, no. 2: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10020091
APA StylePalazzolo, S., Caligiuri, I., Sfriso, A. A., Mauceri, M., Rotondo, R., Campagnol, D., Canzonieri, V., & Rizzolio, F. (2022). Early Warnings by Liver Organoids on Short- and Long-Chain PFAS Toxicity. Toxics, 10(2), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10020091