Assessment of the Anthropogenic Impact and Distribution of Potentially Toxic and Rare Earth Elements in Lake Sediments from North-Eastern Romania
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
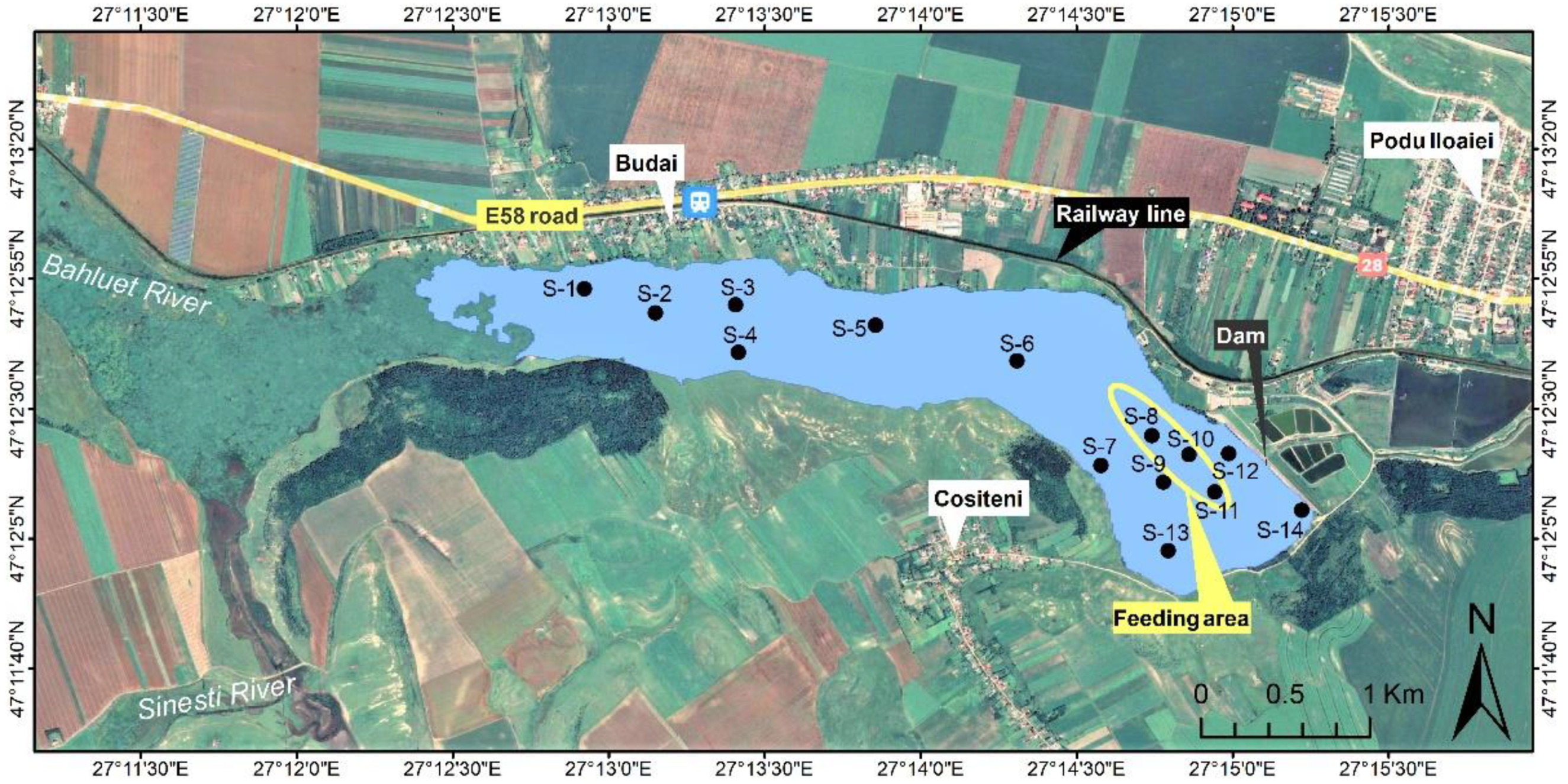
2.1. Site Description and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Preparation of the Sediment
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Statistical Approaches for Source Assessment
2.4.2. REEs Normalization and Anomalies
2.4.3. Sediment Contamination Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
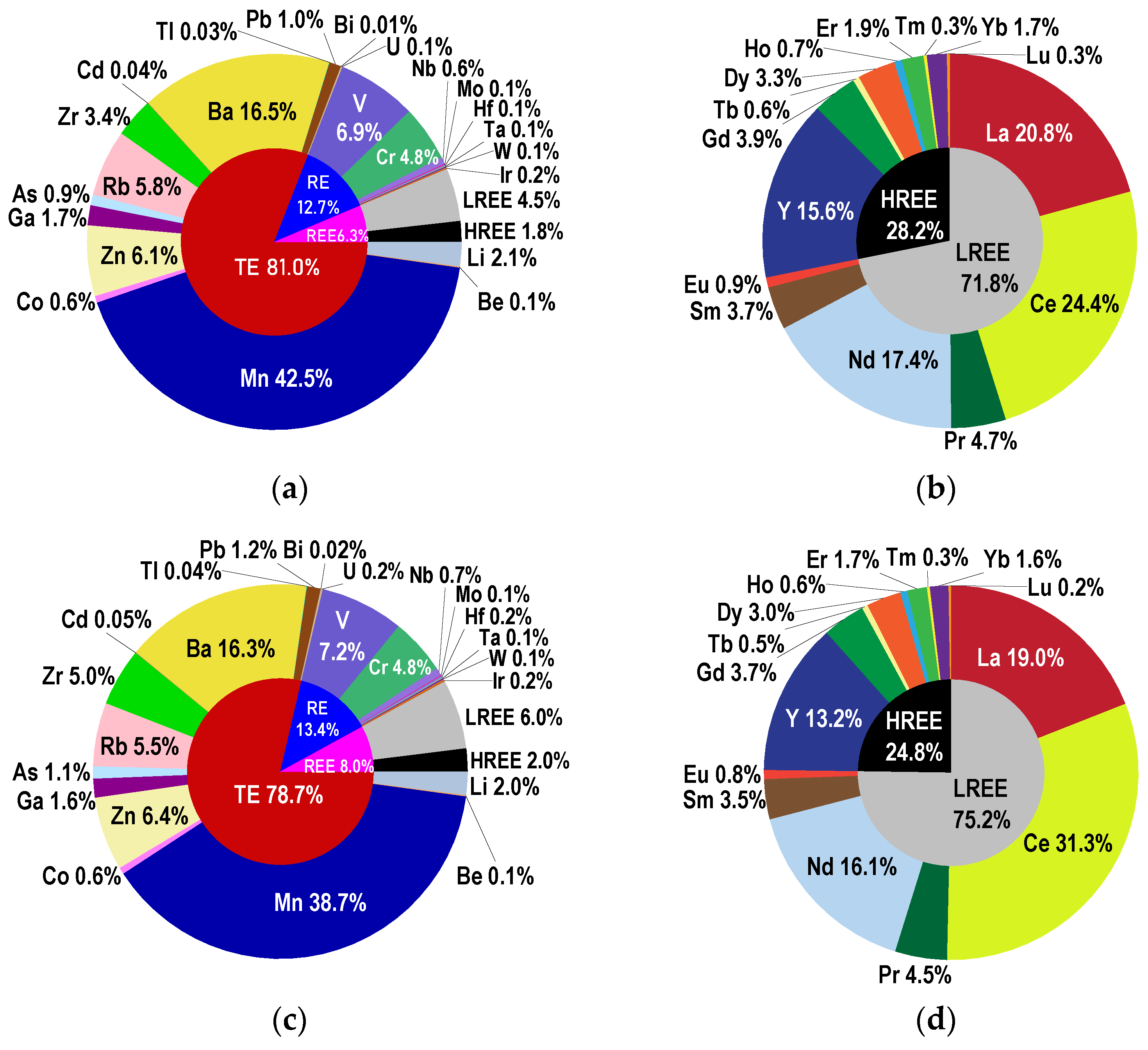
3.1. Elements Concentration in Sediment Samples
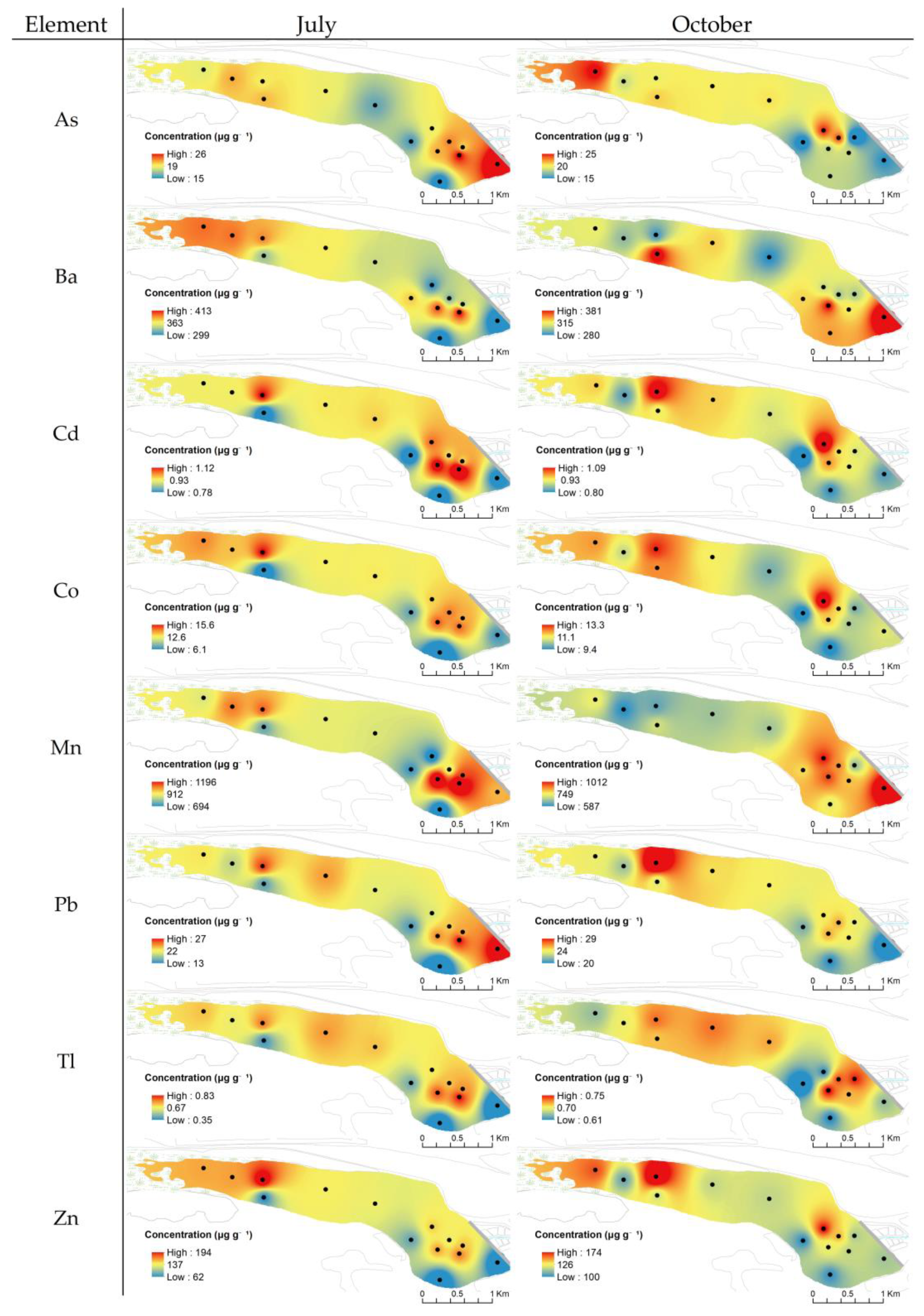
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Elements
3.3. REEs Normalization and Anomalies
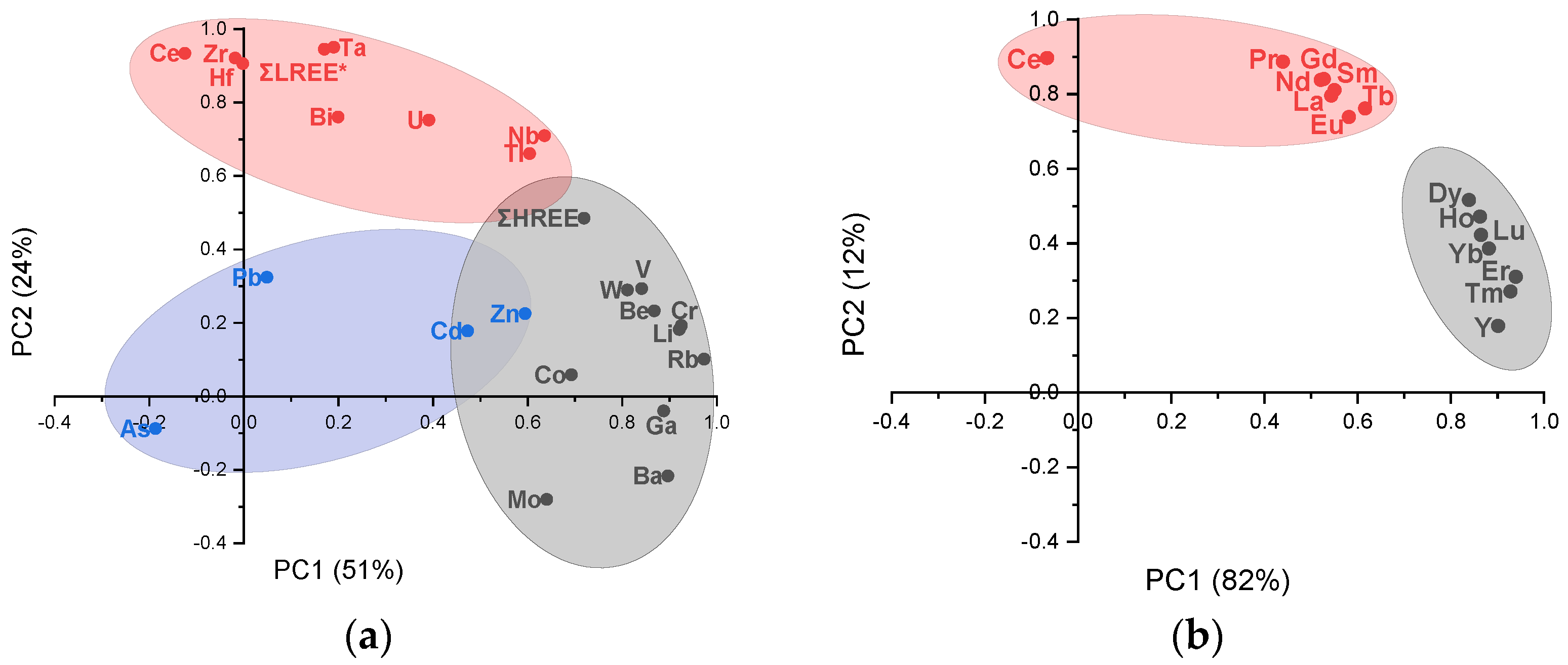
3.4. Correlation Analysis and Principal Component Analysis
3.5. Contamination Assessment and Potentially Harmful Elements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, V.; Sankar, M.S.; Vattikuti, S.; Dash, P.; Arslan, Z. Pollution assessment and land use land cover influence on trace metal distribution in sediments from five aquatic systems in southern USA. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, G.F.; Olmos, M.A. Sediment-bound heavy metals as indicators of human influence and biological risk in coastal water bodies. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algul, F.; Beyhan, M. Concentrations and sources of heavy metals in shallow sediments in Lake Bafa, Turkey. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Shan, J.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Yi, M.; Zhao, X. Distribution characteristics and sources of trace metals in sediment cores from a trans-boundary watercourse: An example from the Shima River, Pearl River Delta. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 134, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Peng, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Luo, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, S.; Yang, G.; Wan, H.; Wu, L. Levels and health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban soils in Dongguan, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 148, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strungaru, S.A.; Nicoara, M.; Teodosiu, C.; Baltag, E.; Ciobanu, C.; Plavan, G. Patterns of toxic metals bioaccumulation in a cross-border freshwater reservoir. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Choinski, A.; Ptak, M.; Siepak, M. The variability of lake water chemistry in the Bory Tucholskie National Park (Northern Poland). Water 2020, 12, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Pourret, O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M. Distribution of rare earth elements in sediments of the North China Plain: A probe of sedimentation process. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 134, 105089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Richter, H.; Sparovek, G.; Schnug, E. Physiological and biochemical effects of rare earth elements on plants and their agricultural significance: A Review. J. Plant Nutr. 2004, 27, 183–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatje, V.; Bruland, K.W.; Flegal, A.R. Increases in anthropogenic Gadolinium anomalies and rare earth element concentrations in San Francisco Bay over a 20 Year record. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4159–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodin, S.; Godet, A.; Westermann, S.; Föllmi, K.B. Secular change in northwestern Tethyan water-mass oxygenation during the late Hauterivian-early Aptian. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 374, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y. Rare earth elements and their isotopes in the Ocean. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences, 1st ed.; Steele, J.H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Greaves, M.J. The rare earth elements in seawater. Nature 1982, 296, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laveuf, C.; Cornu, S. A Review on the potentiality of rare earth elements to trace pedogenetic processes. Geoderma 2009, 154, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Deng, H. REEs fractionation and sedimentary implication in surface sediments from eastern South China Sea. J. Rare Earths 2012, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclennan, S.M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. In Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements; Lipin, B.R., McKay, G.A., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1989; pp. 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1997; pp. 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Whitfield, M.; Burton, J.D.; Bacon, M.P.; Liss, P.S. The oceanic chemistry of the rare-earth elements. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1988, 325, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Holliday, B.P.; Elderfield, H. Redox cycling of rare earth elements in the suboxic zone of the Black Sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 3553–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostevin, R.; Shields, G.A.; Tarbuck, G.M.; He, T.; Clarkson, M.O.; Wood, R.A. Effective use of Cerium anomalies as a redox proxy in carbonate-dominated marine settings. Chem. Geol. 2016, 438, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi, P.; Barbieri, M. Gadolinium as an emerging microcontaminant in water resources: Threats and opportunities. Geosciences 2019, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Han, X.; Ding, S.; Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, H. Combining multiple methods for provenance discrimination based on rare earth element geochemistry in lake sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Lin, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, W. A comprehensive assessment of anthropogenic impacts, contamination, and ecological risks of toxic elements in sediments of urban rivers: A case study in Qingdao, East China. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Hu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, W.; Chen, S.; Xu, D.; Shi, Z. Improved mapping of potentially toxic elements in soil via integration of multiple data sources and various geostatistical methods. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman, P.C.; Ahado, S.K.; Boruvka, L.; Biney, J.K.M.; Sarkodie, V.Y.O.; Kebonye, N.M.; Kingsley, J. Trend analysis of global usage of digital soil mapping models in the prediction of potentially toxic elements in soil/sediments: A bibliometric review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 1715–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexakis, D.; Kokmotos, I.; Gamvroula, D.; Varelidis, G. Wildfire effects on soil quality: Application on a suburban area of West Attica (Greece). Geosci. J. 2021, 25, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doufexi, M.; Gamvroula, D.E.; Alexakis, D.E. Elements’ content in stream sediment and wildfire ash of suburban areas in West Attica (Greece). Water 2022, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzola, E.L.; Rosa, L.M.T.; Toppa, R.H.; Martines, M.R.; Pitombo, L.M.; Cavagis, A.D.M.; do Carmo, J.B.; Botero, W.G.; de Oliveira, L.C. Spatial modeling applied to environmental monitoring: Identifying sources of potentially toxic metals in aquatic system. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleiwi, A.S.; Al-Dabbas, M. Assessment of contamination along the Tigris River from Tharthar-Tigris canal to Azizziyah, middle of Iraq. Water 2022, 14, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah -Al- Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Meeresun. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angulo, E. The Tomlinson Pollution Load Index applied to heavy metal, “Mussel-Watch” data: A useful index to assess coastal pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 187, 19–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Cebula, J.; Pelczar, J.; Wiechula, D.; Kwapulinski, J. Use of enrichment, and contamination factors together with geoaccumulation indexes to evaluate the content of Cd, Cu, and Ni in the Rybnik water reservoir in Poland. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 1997, 93, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gasiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination—A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buat-Menard, P.; Chesselet, R. variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 42, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M. The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. J. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 5, 1000237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; MacDonald, D.D. Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 1998, 4, 1019–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, A.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Malik, R.N.; Ahmed, Z. Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah-Feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake Reservoir, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, M.C.; Soroaga, L.V.; Balaban, S.I.; Chelariu, C.; Chiscan, O.; Iancu, G.O.; Arsene, C.; Olariu, R.I. Trace elements distribution in stream sediments of an abandoned U mining site in the Eastern Carpathians, Romania, with particular focus on REEs. Geochemistry 2021, 81, 125761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarandei, C.; Negru, A.G.; Soroaga, L.V.; Cucu-Man, S.M.; Olariu, R.I.; Arsene, C. Assessment of surface water quality in the Podu Iloaiei Dam Lake (North-Eastern Romania): Potential implications for aquaculture activities in the area. Water 2021, 13, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WATER PIN Limited Liability Company. Securing the Podu Iloaiei Reservoir, on the Bahluet River, Iasi County, Synthesis Memoir. 2011. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/375298910/Memoriu-de-Sinteza-Ac-Podu-Iloaiei (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Climate Change—Department for Waters Forests and Fisheries National Administration “Romanian Waters” Management-Bucharest, National Institute of Hydrology and Water, Prut-Barlad River Basin Management Plan, 2016–2021, in Accordance with Article No. 2015. Available online: https://vdocuments.mx/plan-management-prut-barlad-31032015.html (accessed on 14 March 2022).
- Lu, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, D. The application of microwave digestion in decomposing some refractory ore samples with solid fusion agent. Talanta 2018, 186, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, P.J. Inductively coupled plasma—mass spectrometry. In A Handbook of Silicate Rock Analysis; Potts, P.J., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The geochemical the continental evolution crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreira, R.M.A.; Pahnke, K.; Böning, P.; Hatje, V. tracking hospital effluent-derived gadolinium in Atlantic coastal waters off Brazil. Water Res. 2018, 145, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojka, M.; Choinski, A.; Ptak, M.; Siepak, M. Causes of variations of trace and rare earth elements concentration in lakes bottom sediments in the Bory Tucholskie National Park, Poland. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Shin, W.-J.; Ryu, J.-S.; Shin, H.S.; Chung, H.; Lee, K.-S. Anthropogenic rare earth elements and their spatial distributions in the Han River, South Korea. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, H. Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth’s Crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, N.; Ravisankar, R.; Gandhi, M.S.; Kanagasabapathy, K.; Prasad, M.V.R.; Satapathy, K. Heavy metal assessment in sediments of east coast of Tamil Nadu using energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. Radiat. Prot. Environ. 2017, 40, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abata, E.O.; Aiyesanmi, F.; Adebayo, A.O.; Ajayi, O.O.; Kazuhiko, T.; Hiroshi, S. Contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in the sediment of Ala River, South—West Nigeria: An index—Analysis approach. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2016, 7, 1392–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Saygı, Y.; Yigit, S.A. Heavy metals in Yeniçaǧa Lake and its potential sources: Soil, water, sediment, and plankton. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Leermakers, M.; Osan, J.; Torok, S.; Baeyens, W. Heavy metals in Lake Balaton: Water column, suspended matter, sediment and biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 340, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Multielement contamination of land in the margin of highways. Land 2021, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.; Guan, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhong, J.; Zhu, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Hou, D.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Guan, Y.; Liu, A. Quantitative source tracking of heavy metals contained in urban road deposited sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, A.R.; Zeh, A.; Vianna, N.C.; Ackerman, L.; Pašava, J.; Lehmann, B.; Chrastný, V. Molybdenum-isotope signals and cerium anomalies in Palaeoproterozoic manganese ore survive high-grade metamorphism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kechiched, R.; Laouar, R.; Bruguier, O.; Kocsis, L.; Salmi-Laouar, S.; Bosch, D.; Ameur-Zaimeche, O.; Foufou, A.; Larit, H. Comprehensive REE + Y and sensitive redox trace elements of Algerian Phosphorites (Tébessa, eastern Algeria): A geochemical study and depositional environments tracking. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 208, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.J.; Jacobsen, S.B. Rare Earth Elements in River Waters. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1988, 89, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuwa, Y.; Matsumoto, R. Cerium negative anomaly just before the Permian and Triassic boundary event—The upward expansion of anoxia in the water column. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 229, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, A.D.; Caravan, P.; Lenkinski, R.E. Primer on gadolinium chemistry. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darnall, D.W.; Birnbaum, E.R. Lanthanide ions activate α-amylase. Biochemistry 1973, 12, 3489–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, R.E.; Sholkovitz, E.R. The development of middle rare earth element enrichments in freshwaters: Weathering of phosphate minerals. Chem. Geol. 2001, 175, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecuyer, C.; Reynard, B.; Grandjean, P. Rare earth element evolution of Phanerozoic seawater recorded in biogenic apatites. Chem. Geol. 2004, 204, 63–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R. The aquatic chemistry of rare earth elements in rivers and estuaries. Aquat. Geochem. 1995, 1, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orians, K.J.; Merrin, C.L. Refractory Metals. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences, 1st ed.; Steele, H., Thorpe, S., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; Volume 4, pp. 2387–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, Y.; Rosen, M.A.; Al-Rawabdeh, A.M. Assessment of metal pollution in urban road dusts from selected highways of the Greater Toronto Area in Canada. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 1847–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasimov, N.S.; Vlasov, D.V.; Kosheleva, N.E. Urban climate enrichment of road dust particles and adjacent environments with metals and metalloids in Eastern Moscow. Urban Clim. 2020, 32, 100638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, P.; Raso, M.; Yechieli, Y.; Ginat, H.; Saiano, F.; Zuddas, P.; Brusca, L.; D’Alessandro, W.; Inguaggiato, C. Geochemistry of Zr, Hf, and REE in a wide spectrum of Eh and water composition: The case of Dead Sea Fault system (Israel). Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2017, 18, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, Nordic Council of Ministers. Cadmium Review. Report No. 1, Issue No. 4, Geneva, 2003. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/chemical-safety/cadmium/nmr-cadmium.pdf?sfvrsn=36032d8_2&download=true (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Robson, T.C.; Braungardt, C.B.; Rieuwerts, J.; Worsfold, P. Cadmium contamination of agricultural soils and crops resulting from sphalerite weathering. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Defarge, N.; Spiroux de Vendomois, J.; Seralini, G.E. Toxicity of formulants and heavy metals in glyphosate-based herbicides and other pesticides. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, B.K. A dynamic model for the global cycling of anthropogenic vanadium. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiedler, S.; Siebe, C.; Herre, A.; Roth, B.; Cram, S.; Stahr, K. Contribution of oil industry activities to environmental loads of heavy metals in the Tabasco Lowlands, Mexico. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 197, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu-Olayan, A.H.; Thomas, B.V. Bourgeoning impact of the technology critical elements in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon-Negru, A.G.; Olariu, R.I.; Arsene, C. Size-resolved measurements of PM 2.5 water-soluble elements in Iasi, North-Eastern Romania: Seasonality, source apportionment and potential implications for human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M.; Rodushkin, I. A concise guide for the determination of less-studied technology-critical elements (Nb, Ta, Ga, In, Ge, Te) by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in environmental samples. Spectrochim. Acta-Part B At. Spectrosc. 2018, 141, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



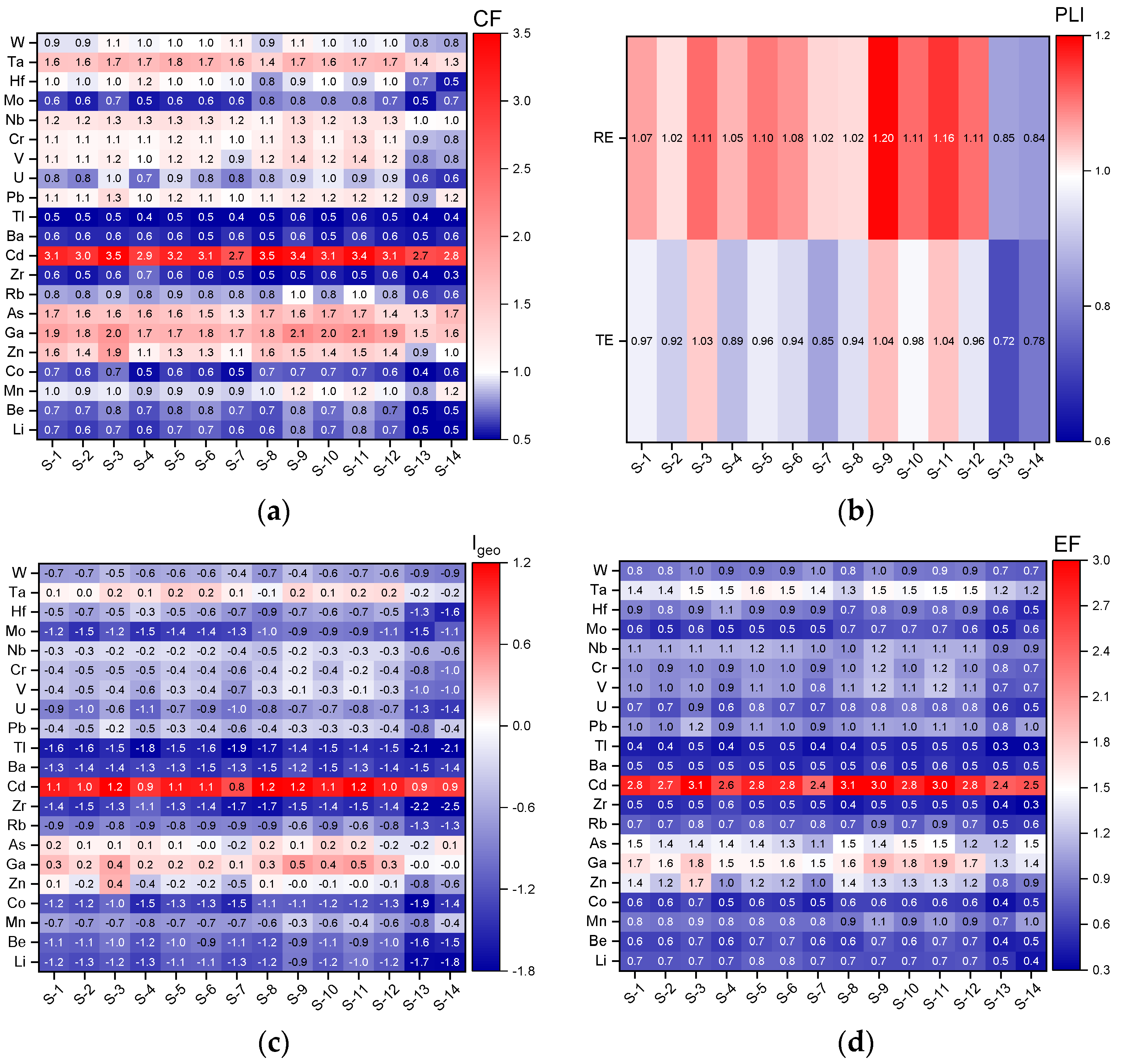

| Pollution Index | Equation | Evaluation Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Contamination factor (CF) [34,52,53] | <1, low degree of contamination 1 ÷ 3, moderate degree of contamination 3 ÷ 6, considerable degree of contamination >6, very high degree of contamination | |
| Pollution load index (PLI) [32,33] | 0, no pollution 0 ÷ 1, only baseline pollutants >1, progressive deterioration | |
| Geoaccumulation index (Igeo) [1,37,54] | ≤0, no contamination 0 ÷ 1, none to moderate contamination 1 ÷ 2, moderate contamination 2 ÷ 3, moderate to heavy contamination 3 ÷ 4, heavy contamination 4 ÷ 5, heavy to extreme contamination >5, extreme contamination | |
| Enrichmentfactor (EF) [1,2,31,34,36] | 0 ÷ 1.5, natural processes 1.5 ÷ 3, minor anthropogenic modification 3 ÷ 5, moderate anthropogenic modification 5 ÷ 10, severe anthropogenic modification >10, very severe anthropogenic modification |
| Element | July | October |
|---|---|---|
| As | 19.8 (15.0–25.5) | 20.7 (15.2–25.0) |
| Ba | 358 (299–413) | 319 (280–381) |
| Be | 2.25 (1.23–2.97) | 1.96 (1.60–2.25) |
| Bi | 0.27 (0.12–0.35) | 0.33 (0.25–0.43) |
| Cd | 1.62 (0.73–1.98) | 1.81 (1.35–2.06) |
| Co | 12.4 (6.11–15.6) | 11.1 (9.40–13.3) |
| Ga | 37.1 (19.8–47.3) | 32.0 (25.6–39.6) |
| Li | 45.6 (20.4–62.9) | 39.9 (31.2–47.8) |
| Mn | 922 (694–1196) | 757 (587–1012) |
| Pb | 22.1 (13.3–27.3) | 23.2 (19.9–28.5) |
| Rb | 125 (59.2–171) | 107 (94.4–130) |
| Tl | 0.65 (0.35–0.83) | 0.70 (0.61–0.75) |
| U | 2.87 (1.58–3.49) | 3.20 (2.75–3.68) |
| Zn | 132 (62.3–194) | 125 (100–174) |
| Zr | 74.0 (25.5–115) | 97.8 (65.3–127) |
| ΣTE | 1755 (1241–2205) | 1540 (1311–1830) |
| Cr | 103 (45.3–143) | 94.6 (80.2–111) |
| Hf | 2.27 (0.90–3.33) | 3.02 (2.05–3.84) |
| Ir | 3.30 (1.68–4.78) | 4.38(3.40–6.03) |
| Mo | 1.83 (1.26–2.41) | 1.62 (1.12–2.30) |
| Nb | 13.2 (9.15–15.1) | 13.5 (11.1–14.7) |
| Ta | 1.19 (0.81–1.38) | 1.38 (1.11–1.49) |
| V | 149 (57.3–213) | 142 (117–168) |
| W | 1.79 (1.12–2.35) | 1.72 (1.39–1.95) |
| ΣRE | 276 (118–383) | 262 (231–306) |
| Ce | 33.5 (15.5–52.0) | 48.8 (23.5–63.5) |
| Eu | 1.20 (0.80–1.38) | 1.23 (1.09–1.33) |
| La | 28.5 (16.2–32.9) | 29.6 (24.1–32.7) |
| Nd | 23.8 (16.0–26.7) | 25.1 (22.3–27.6) |
| Pr | 6.48 (4.10–7.33) | 7.00 (6.03–7.65) |
| Sm | 5.10 (3.34–5.76) | 5.41 (4.83–5.78) |
| ΣLREE | 98.5 (57.5–124) | 117 (85.3–138) |
| Dy | 4.49 (3.32–5.05) | 4.66 (4.08–4.99) |
| Er | 2.59 (1.99–2.90) | 2.66 (2.29–2.99) |
| Gd | 5.33 (3.64–5.90) | 5.75 (4.91–6.34) |
| Ho | 0.89 (0.66–0.99) | 0.93 (0.80–1.04) |
| Lu | 0.36 (0.27–0.41) | 0.38 (0.33–0.45) |
| Tb | 0.76 (0.54–0.83) | 0.81 (0.68–0.84) |
| Tm | 0.37 (0.29–0.43) | 0.39 (0.36–0.45) |
| Y | 21.4 (16.5–24.5) | 20.5 (17.8–22.5) |
| Yb | 2.36 (1.73–2.74) | 2.50 (2.18–2.90) |
| ΣHREE | 38.6 (28.9–43.0) | 38.6 (33.5–42.2) |
| ΣREE | 137 (88.9–163) | 155 (118–178) |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | Elements | Factor | Elements |
| Factor 1 (50.9%) | Rb, Cr, Li, Ba, Ga, Be, V, W; ΣHREEs, Co, Mn, Mo, Nb, Tl, Zn. | Factor 1 (81.9%) | Er, Tm, Y, Yb, Lu, Ho, Dy; Tb, Eu, Sm, La, Gd, Nd. |
| Factor 2 (23.7%) | Ta, ΣLREEs *, Ce, Hf, Zr, Bi, U; Nb, Tl. | Factor 2 (11.6%) | Ce, Pr, Gd, Nd, Sm, La, Tb; Eu, Dy. |
| Factor 3 (21.4%) | Pb, As, Cd; Zn, Co, Mo. | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soroaga, L.V.; Amarandei, C.; Negru, A.G.; Olariu, R.I.; Arsene, C. Assessment of the Anthropogenic Impact and Distribution of Potentially Toxic and Rare Earth Elements in Lake Sediments from North-Eastern Romania. Toxics 2022, 10, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050242
Soroaga LV, Amarandei C, Negru AG, Olariu RI, Arsene C. Assessment of the Anthropogenic Impact and Distribution of Potentially Toxic and Rare Earth Elements in Lake Sediments from North-Eastern Romania. Toxics. 2022; 10(5):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050242
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoroaga, Laurentiu Valentin, Cornelia Amarandei, Alina Giorgiana Negru, Romeo Iulian Olariu, and Cecilia Arsene. 2022. "Assessment of the Anthropogenic Impact and Distribution of Potentially Toxic and Rare Earth Elements in Lake Sediments from North-Eastern Romania" Toxics 10, no. 5: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050242
APA StyleSoroaga, L. V., Amarandei, C., Negru, A. G., Olariu, R. I., & Arsene, C. (2022). Assessment of the Anthropogenic Impact and Distribution of Potentially Toxic and Rare Earth Elements in Lake Sediments from North-Eastern Romania. Toxics, 10(5), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050242






