Severe and Fatal Fentanyl Poisonings from Transdermal Systems after On-Skin and Ingestion Application
Abstract
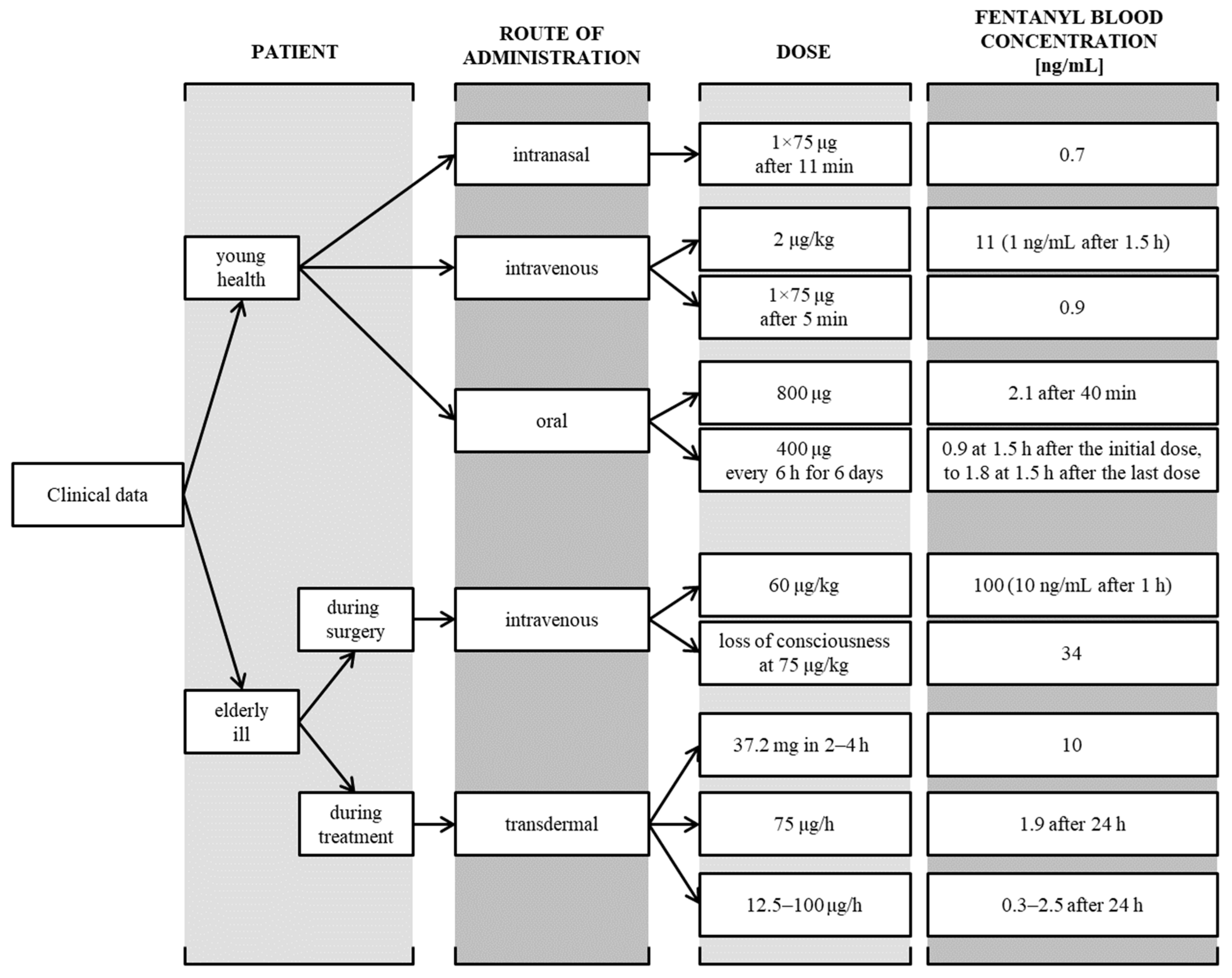
:1. Introduction
2. Case Reports
2.1. Case 1
2.2. Case 2
2.3. Case 3
2.4. Fentanyl and Norfentanyl Analysis
2.5. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanley, T.H. The Fentanyl Story. J. Pain. 2014, 15, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardwell, G.; Wood, E.; Brar, R. Fentanyl Assisted Treatment: A Possible Role in the Opioid Overdose Epidemic? Subst. Abus. Treat Prev. Policy 2019, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latkin, C.A.; Dayton, L.; Davey-Rothwell, M.A.; Tobin, K.E. Fentanyl and Drug Overdose: Perceptions of Fentanyl Risk, Overdose Risk Behaviors, and Opportunities for Intervention among People Who Use Opioids in Baltimore, USA. Subst. Use Misuse 2019, 54, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weesie, Y.M.; van Dijk, L.; Bouvy, M.L.; Hek, K. Immediate Release Fentanyl in General Practices: Mostly off-Label Prescribing. Eur. J. Gen. Pract. 2023, 29, 2165644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, H.E.; Huhn, A.S.; Dunn, K.E. Fentanyl Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion: Narrative Review and Clinical Significance Related to Illicitly Manufactured Fentanyl. J. Addict. Med. 2023, 17, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comer, S.D.; Cahill, C.M. Fentanyl: Receptor Pharmacology, Abuse Potential, and Implications for Treatment. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 106, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassinari, D.; Drudi, F.; Rosati, M.; Maltoni, M. Transdermal Opioids as Front-Line Treatment of Moderate to Severe Cancer Pain: A Systemic Review. Palliat Med. 2011, 25, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häuser, W.; Buchser, E.; Finn, D.P.; Dom, G.; Fors, E.; Heiskanen, T.; Jarlbaek, L.; Knaggs, R.D.; Kosek, E.; Krcevski-Škvarč, N.; et al. Is Europe Also Facing an Opioid Crisis?-A Survey of European Pain Federation Chapters. Eur. J. Pain. 2021, 25, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.-D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. A Classification of Chronic Pain for ICD-11. Pain 2015, 156, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, H.G.; Boss, H.; Delvin, T.; Lahu, G.; Lophaven, S.; Marx, M.; Skorjanec, S.; Wagner, T. Transdermal Fentanyl Matrix Patches Matrifen and Durogesic DTrans Are Bioequivalent. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 75, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, M.N.; Kalia, Y.N.; Horstmann, M.; Roberts, M.S. Transdermal Patches: History, Development and Pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 2179–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, M.E. The Transdermal Delivery of Fentanyl. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, A.; Mattern, D.; Cooperman, N.; Williams, J.M.; Dooley-Budsock, P.; Foglia, R.; Borys, S. Opioid Overdose in the Age of Fentanyl: Risk Factor Differences among Subpopulations of Overdose Survivors. Int. J. Drug. Policy 2021, 90, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christrup, L.L.; Foster, D.; Popper, L.D.; Troen, T.; Upton, R. Pharmacokinetics, Efficacy, and Tolerability of Fentanyl Following Intranasal versus Intravenous Administration in Adults Undergoing Third-Molar Extraction: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Two-Way, Crossover Study. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, M.; Nowak, K. Fentanyl and its derivatives as a group of new psychoactive substances (designer drugs). Postępy. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2018, 72, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, S.A.; Ting, S. Fentanyl Formulations in the Management of Pain: An Update. Drugs 2017, 77, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, D.L.; Eisele, J.H. Fentanyl Pharmacokinetics in Awake Volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1980, 20, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, T.D.; Sharma, A.; Ashburn, M.A.; Kievit, J.; Pace, N.L.; Streisand, J.B. Multiple Dose Pharmacokinetics of Oral Transmucosal Fentanyl Citrate in Healthy Volunteers. Anesthesiology 2000, 92, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yan, W.; Zheng, Y.; Khan, M.Z.; Yuan, K.; Lu, L. The Rising Crisis of Illicit Fentanyl Use, Overdose, and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.; Kirby, M.; Robertson, P.; Hellriegel, E.; Jiang, J.G. Single-Dose and Steady-State Pharmacokinetics of Fentanyl Buccal Tablet in Healthy Volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovill, J.G.; Sebel, P.S. Pharmacokinetics of High-Dose Fentanyl. A Study in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 1980, 52, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunn, J.K.; Stanley, T.H.; Eisele, J.; Webster, L.; Woodward, A. High Dose Fentanyl Anesthesia for Coronary Artery Surgery: Plasma Fentanyl Concentrations and Influence of Nitrous Oxide on Cardiovascular Responses. Anesth. Analg. 1979, 58, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, L.J.; DeSio, J.M.; Radvany, T.; Bikhazi, G.B. Transdermal Fentanyl in Postoperative Pain. Reg. Anesth. 1997, 22, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson Healthcare Staff, Physicians’ Desk Reference 2008, 62nd ed.; Thomson PDR: Montvale, NJ, USA, 2007.
- Biedrzycki, O.J.; Bevan, D.; Lucas, S. Fatal Overdose Due to Prescription Fentanyl Patches in a Patient with Sickle Cell/β-Thalassemia and Acute Chest Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2009, 30, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoVecchio, F.; Ramos, L. Suicide by Duragesic Transdermal Fentanyl Patch Toxicity. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 29, 131.e1-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coopman, V.; Cordonnier, J.; Pien, K.; Van Varenbergh, D. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Fentanyl and Norfentanyl in a Fatality Due to Application of Multiple Durogesic Transdermal Therapeutic Systems. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 169, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.; Goodin, J.C.; Caplan, Y.H. A Fentanyl Fatality Involving Midazolam. Forensic Sci. Int. 1990, 45, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharp, A.M.; Winecker, R.E.; Winston, D.C. Fatal Intravenous Fentanyl Abuse: Four Cases Involving Extraction of Fentanyl from Transdermal Patches. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2004, 25, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, H.J.; Knight, L.D.; Dudley, M.H.; Garg, U. A Fatality Involving an Unusual Route of Fentanyl Delivery: Chewing and Aspirating the Transdermal Patch. Leg. Med. 2010, 12, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, K.L.; Martin, T.L.; McLellan, B.A. Oral Abuse of Fentanyl Patches (Duragesic): Seven Case Reports. J. Forensic Sci. 2008, 53, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppliger, M.; Mauermann, E.; Ruppen, W. Are Transdermal Opioids Contraindicated in Patients at Risk of Suicide? An Underappreciated. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. EJA 2016, 33, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakovic, M.; Nestic, M.; Mayer, D. Death by Band-Aid: Fatal Misuse of Transdermal Fentanyl Patch. Int. J. Legal. Med. 2015, 129, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doris, M.K.; Sandilands, E.A. Life-Threatening Opioid Toxicity from a Fentanyl Patch Applied to Eczematous Skin. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2014208945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, P.W.; Palmer, R.B.; Donovan, J.W. Fatal Fentanyl Patch Misuse in a Hospitalized Patient with a Postmortem Increase in Fentanyl Blood Concentration. J. Forensic Sci. 2015, 60, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrvos, R.; Feuchter, A.C.; Katz, K.D.; Duback-Morris, L.F.; Brooks, D.E.; Krenzelok, E.P. Whole Fentanyl Patch Ingestion: A Multi-Center Case Series. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 42, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.T.; Muto, J.J. Duragesic Transdermal Patch: Postmortem Tissue Distribution of Fentanyl in 25 Cases. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2000, 24, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Intravenous (i.v.) | TDDS | per os (p.o.) |
|---|---|---|
| After intravenous administration, fast effects (a few minutes), duration after administration of 100 µg up to 60 min | After transdermal administration directly into the circulation, bypassing the first pass effect, reduction of side effects | After oral administration (chewing and swallowing) of fentanyl patches, relatively low bioavailability (30–50%), toxicity may result from a relatively large dose of the drug in the patch |
| Quick redistribution to muscles, adipose tissue and then slowly to the bloodstream | Possible administration of the drug in a constant continuous dose for 3 days | There are known cases of acute/fatal poisoning after: ingestion or exposure through the respiratory tract (drinking the obtained extract or inhaling vapors when cooking fentanyl patches) or after ingesting an intact patch |
| Only a constant infusion ensures tissue saturation, drug accumulation and longer effects | The release rate depends on the size of the patch | |
| Therapeutic concentration within 12 h, constant after 36–48 h |
| Source of Ionisation | Electrospray (Agilent 6410B, Wildnington, DE, USA) |
|---|---|
| MS mode of operation | MRM, recording two reactions for each compound |
| Column | Poroshell 120 EC-18 3.0 × 75 mm, 2.7 μm (Agilent, USA) |
| Mobile phases | 0.1% formic acid in water [A] and 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile [B] |
| Flow rate | 0.5 mL/min |
| Case No | Patient’s Sex | Age [Years] | Marking | Specimen Type | CFNTL [ng/mL] | CNOR [ng/mL] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Female | 66 | living, after 2, 6 and 12 h | blood | 2 h: 10.0 6 h: 1.2 12 h: <1 | 2 h: 49.7 6 h: 31.2 12 h: 16.1 |
| 2 | Female | 31 | posthumous | blood | 38.7 | 149.0 |
| 3 | Male | 25 | posthumous | blood and urine | 29.1 in blood 4.5 in urine | 12.9 in blood 112.0 in urine |
| Case No | Dose of Drug per Patch [µg/h] | Method of Application | Duration of Use | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 75 | on skin | 4 days | own drug |
| 2 | 50 | on skin | probably several or several dozen hours | family member’s drug |
| 3 | 75 | swallowed, in the stomach | probably a few hours | no data |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sommerfeld-Klatta, K.; Jiers, W.; Łukasik-Głębocka, M.; Tezyk, A.; Dolińska-Kaczmarek, K.; Walter, K.; Świderski, P.; Rzepczyk, S.; Zielińska-Psuja, B.; Żaba, C. Severe and Fatal Fentanyl Poisonings from Transdermal Systems after On-Skin and Ingestion Application. Toxics 2023, 11, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100872
Sommerfeld-Klatta K, Jiers W, Łukasik-Głębocka M, Tezyk A, Dolińska-Kaczmarek K, Walter K, Świderski P, Rzepczyk S, Zielińska-Psuja B, Żaba C. Severe and Fatal Fentanyl Poisonings from Transdermal Systems after On-Skin and Ingestion Application. Toxics. 2023; 11(10):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100872
Chicago/Turabian StyleSommerfeld-Klatta, Karina, Wiktoria Jiers, Magdalena Łukasik-Głębocka, Artur Tezyk, Klaudia Dolińska-Kaczmarek, Kamil Walter, Paweł Świderski, Szymon Rzepczyk, Barbara Zielińska-Psuja, and Czesław Żaba. 2023. "Severe and Fatal Fentanyl Poisonings from Transdermal Systems after On-Skin and Ingestion Application" Toxics 11, no. 10: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100872