Effect of Foliar Spraying of Gibberellins and Brassinolide on Cadmium Accumulation in Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.1.1. Hydroponic Experiment
2.1.2. Pot Experiment
2.2. Measurement Equipment and Methods
2.2.1. Root Index Determination
2.2.2. Determination of Maximum Fluorescence Value of Leaves
2.2.3. Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes Activities
2.2.4. Determination of Cd Content
2.2.5. Photosynthesis Determination in Mature Rice
2.2.6. Determination of Chemical Morphology of Cd in Rice Plants
2.2.7. Determination of Subcellular Cd Content in Rice
2.2.8. Calculation of Cd Transfer Coefficient
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Foliage Spray Application of GA and BR on Growth and Cd Uptake of Rice Seedlings under Cd Stress
3.1.1. Effects of Foliage Spray Application of GA and BR on Growth of Rice Seedlings under Cd Stress
3.1.2. Effects of Foliage Spray Application of GA and BR on Root Morphology of Rice Seedings under Cd Stress
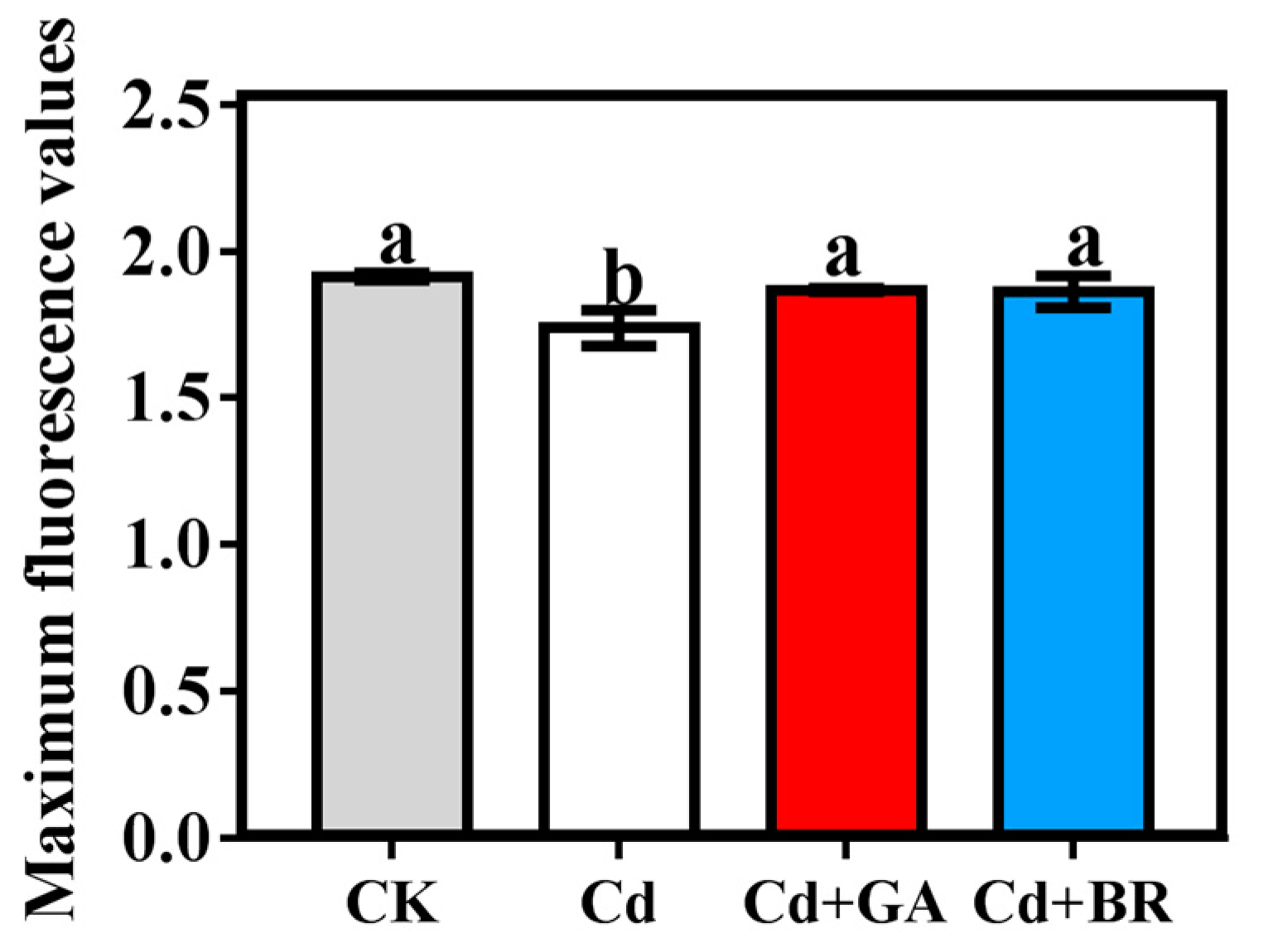
3.1.3. Effects of Foliar Application of GA and BR on Maximum Fluorescence Value of Rice Leaves under Cd Stress
3.1.4. Effects of Foliar Application of GA and BR on SOD, POD, CAT and MDA Content in Rice Seedlings under Cd Stress
3.1.5. Effects of Foliage Spray Application of GA and BR on Cd Content and Translocation Coefficient of Rice Seedlings under Cd Stress
3.2. Effects of Foliage Spray Application of GA and BR on Migration and Accumulation of Cd in Rice under Cd Stress
3.2.1. Effects of Foliar Application of GA and BR on Biomass and Yield of Rice under Cd Stress
3.2.2. Effects of Foliar Application of GA and BR on Cd Chemical Morphology in Rice Plants under Cd Stress
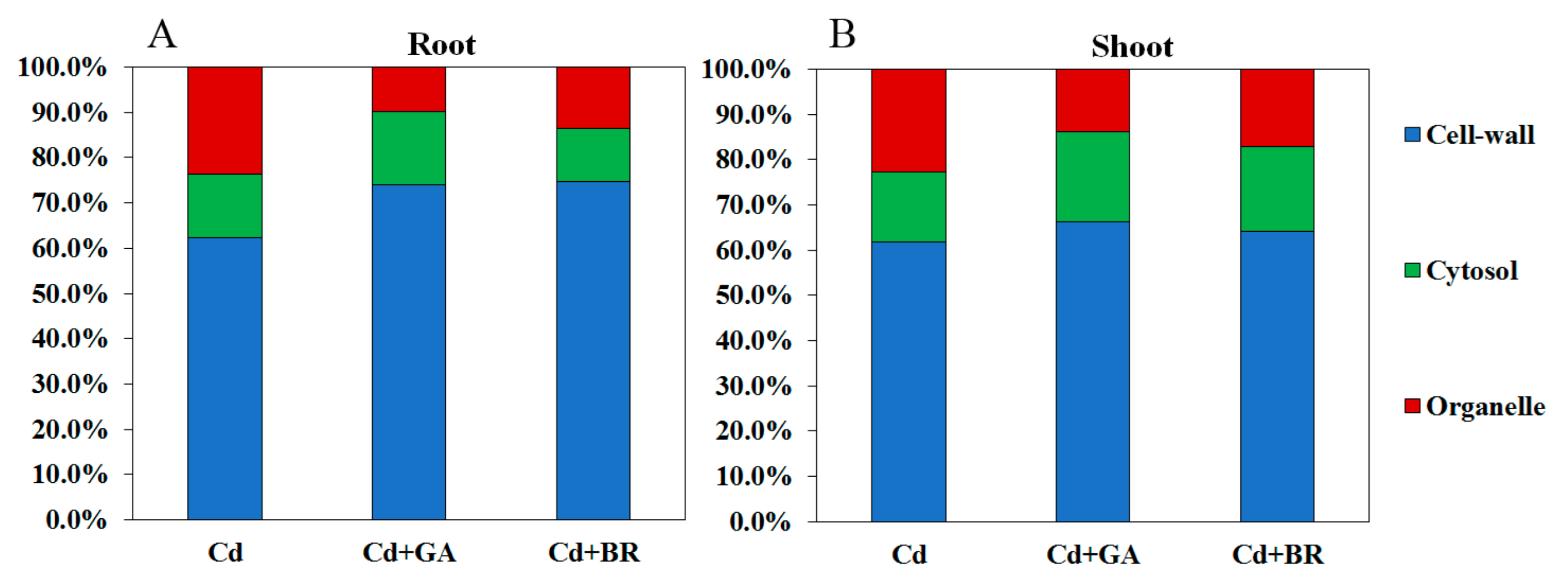
3.2.3. Effects of Foliar Application of GA and BR on Subcellular Distribution of Cd in Rice Cells under Cd Stress
3.2.4. Effects of Foliar Application of GA and BR on Cd Content of the Different Parts of Rice under Cd Stress
3.2.5. Effects of Foliar Application of GA and BR on Cd Transfer Coefficient of Rice under Cd Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahimzadeh, M.R.; Rahimzadeh, M.R.; Kazemi, S.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, S.; Cheng, X.Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, H.G.; Yan, Q.; Hou, L.L.; Sun, X.; Chen, Z.N. Cadmium contamination of rice from various polluted areas of China and its potential risks to human health. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Qian, J.; Xie, E.; Shi, X.Z.; Zhao, Y.C. Spatio-temporal change and pollution risk of agricultural soil cadmium in a rapidly industrializing area in the yangtze delta region of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 15, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabella, E.; Luvisi, A.; Genga, A.; De Bellis, L.; Aprile, A. Molecular responses to cadmium exposure in two contrasting durum wheat genotypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanovic, V.; Smutka, L. Asian countries in the global rice market. ACTA Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2017, 65, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallin, M.; Barregard, L.; Sallsten, G.; Lundh, T.; Karlsson, M.K.; Lorentzon, M.; Ohlsson, C.; Mellström, D. Low-level cadmium exposure is associated with decreased bone mineral density and increased risk of incident fractures in elderly men: The MrOS Sweden Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aoshima, K. Itai-itai disease: Renal tubular osteomalacia induced by environmental exposure to cadmium—Historical review and perspectives. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 62, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bashir, S.; Adeel, M.; Gulshan, A.B.; Iqbal, J.; Khan, S.; Rehman, M.; Azeem, M. Effects of organic and inorganic passivators on the immobilization of cadmium in contaminated soils: A review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, Z.; Huang, Q. Study on principles and mechanisms of new biochar passivation of cadmium in soil. BioChar 2021, 3, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.U.; Li, Y.; Hussain, S.; Hussain, B.; Riaz, L.; Ashraf, M.N.; Khaliq, M.A.; Du, Z.; Cheng, H. Role of phytohormones in heavy metal tolerance in plants: A review. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Sui, C.; Luo, K.; Chen, Z.; Feng, C.; Dong, X.; Zeng, B.; Dong, X.; Liu, X. Effects of α-naphthylacetic acid on cadmium stress and related factors of tomato by regulation of gene expression. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, S.; Cuypers, A.; Vangronsveld, J.; Remans, T. Gene networks involved in hormonal control of root development in arabidopsis thaliana: A framework for studying its disturbance by metal stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19195–19224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chmur, M.; Bajguz, A. Melatonin involved in protective effects against cadmium stress in wolffia arrhizal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betti, C.; Della Rovere, F.; Piacentini, D.; Fattorini, L.; Falasca, G.; Altamura, M.M. Jasmonates, ethylene and brassinosteroids control adventitious and lateral rooting as stress avoidance responses to heavy metals and metalloids. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, S.; Kaur, N.; Pati, P.K. Phytohormones: Key players in the modulation of heavy metal stress tolerance in plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.B.; Qurat-Ul-Ain, R.; Hafiz, M.A.R.; Muhammad, U.S.; Abdur, R.; Kashif, A.K.; Muhammad, I.; Muhammad, W. Key Aspects of Plant Hormones in Agricultural Sustainability under Climate Change. In Plant Hormones: Recent Advances, New Perspectives and Applications, 5th ed.; Christophe, H., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Della Rovere, F.; Piacentini, D.; Fattorini, L.; Girardi, N.; Bellanima, D.; Falasca, G.; Altamura, M.M.; Betti, C. Brassinosteroids mitigate cadmium effects in arabidopsis root system without any cooperation with nitric oxide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Xie, C.; Hu, D.; Pu, S.; Xiong, X.; Ma, J.; Sun, L.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Li, X. Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on reactive oxygen species and antioxidative defense systems in tall fescue plants under lead stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.A.H.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Ahmed, I.M.; Zheng, W.; Cao, F. Genotype-dependent effect of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide on chromium-induced changes in ultrastructure and physicochemical traits in tobacco seedlings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18229–18238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakla, H.R.; Sharma, S.; Urfan, M.; Yadav, N.S.; Rajput, P.; Kotwal, D.; Pal, S. Gibberellins target shoot-root growth, morpho-physiological and molecular pathways to induce cadmium tolerance in Vigna radiata L. Agronomy 2021, 11, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Asghar, H.N.; Khan, M.Y.; Zahir, Z.A. Gibberellic acid in combination with pressmud enhances the growth of sunflower and stabilizes chromium(VI)-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10610–10617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogugua, U.V.; Kanu, S.A.; Ntushelo, K. Gibberellic acid improves growth and reduces heavy metal accumulation: A case study in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) seedlings exposed to acid mine water. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulanningtyas, H.S.; Gong, Y.; Li, P.; Sakagami, N.; Nishiwaki, J.; Komatsuzaki, M. A cover crop and no-tillage system for enhancing soil health by increasing soil organic matter in soybean cultivation. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, N.; Huang, G.; Zhou, Q. Soil microbial community driven by soil moisture and nitrogen in milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.)–rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) intercropping. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Wang, P. Arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice and mitigation strategies. Plant Soil 2020, 446, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demim, S.; Drouiche, N.; Aouabed, A.; Benayad, T.; Dendene-Badache, O.; Semsari, S. Cadmium and nickel: Assessment of the physiological effects and heavy metal removal using a response surface approach by L. gibba. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, F.; Bano, A.; Fuller, M.P. The improved phytoextraction of lead (Pb) and the growth of maize (Zea mays L.): The role of plant growth regulators (GA3 and IAA) and EDTA alone and in combinations. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanstraelen, M.; Benková, E. Hormonal interactions in the regulation of plant development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Seilaniantz, A.; Grant, M.; Jones, J.D. Hormone crosstalk in plant disease and defense: More than just jasmonate-salicylate antagonism. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 317–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Hormonal impact on photosynthesis and photoprotection in plants. Plant Physiol. 2021, 185, 1500–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadioglu, A. The effects of gibberellic acid on photosynthetic pigments and oxygen evolution in Chlamydomonas and Anacystis. Biol. Plant. 1992, 34, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Nazar, R.; Khan MI, R.; Masood, A.; Khan, N.A. Role of gibberellins in regulation of source-sink relations under optimal and limiting environmental conditions. Curr. Sci. 2011, 100, 998–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Biemelt, S.; Tschiersch, H.; Sonnewald, U. Impact of altered gibberellin metabolism on biomass accumulation, lignin biosynthesis, and photosynthesis in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Bian, Z. Effects of brassinosteroids on photosynthetic performance and nitrogen metabolism in pepper seedlings under chilling stress. Agronomy 2019, 9, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, P.; Azher Nawaz, M.; Li, F.; Bai, L.; Li, J. Brassinosteroids regulate antioxidant system and protect chloroplast ultrastructure of autotoxicity-stressed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seedlings. Agronomy 2019, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alharby, H.F.; Rizwan, M.; Iftikhar, A.; Hussaini, K.M.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Alharbi, B.M.; Asrar, M.; Yasmeen, T.; Ali, S. Effect of gibberellic acid and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on growth, antioxidant defense system and mineral nutrient uptake in wheat. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, S.; Singh, V.P.; Srivastava, P.K.; Maurya, J.N. Modification of chromium (VI) phytotoxicity by exogenous gibberellic acid application in Pisum sativum (L.) seedlings. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, T.F.S.N.; dos Santos Dias, D.C.F.; Oliveira, A.M.S.; Ribeiro, D.M.; dos Santos Dias, L.A. Exogenous brassinosteroids increase lead stress tolerance in seed germination and seedling growth of Brassica juncea L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, S.; Fujiwara, T. Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: Perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation. Rice 2012, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Wu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhan, J.; Wang, K.; Li, T. The predominant role of pectin in binding Cd in the root cell wall of a high Cd accumulating rice line (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loix, C.; Huybrechts, M.; Vangronsveld, J.; Gielen, M.; Keunen, E.; Cuypers, A. Reciprocal interactions between Cadmium-Induced Cell Wall Responses and Oxidative Stress in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krzesłowska, M. The cell wall in plant cell response to trace metals: Polysaccharide remodeling and its role in defense strategy. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stant, M.Y. The Effect of gibberellic acid on cell width and the cell-wall of some phloem fibres. Ann. Bot. 1963, 27, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Dixon, R.A. Brassinosteroid mediated cell wall remodeling in grasses under abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Krishnan, S.; Merewitz, E.; Xu, J.; Huang, B. Gibberellin-regulation and genetic variations in leaf elongation for tall fescue in association with differential gene expression controlling cell expansion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; van der Does, D.; Ladwig, F.; Sticht, C.; Kolbeck, A.; Schürholz, A.K.; Augustin, S.; Keinath, N.; Rausch, T.; Greiner, S.; et al. A receptor-like protein mediates the response to pectin modification by activating brassinosteroid signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15261–15266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Treatments | Shoots DW (mg/Plant) | Roots DW (mg/Plant) |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 566.67 ± 5.77c | 214.00 ± 3.61c |
| Cd | 463.33 ± 5.77d | 157.67 ± 2.52d |
| Cd + GA | 686.67 ± 5.77a | 290.67 ± 4.04a |
| Cd + BR | 606.67 ± 5.77b | 229.67 ± 3.06b |
| Treatments | Root Biomass (DW, g/Pot) | Shoot Biomass (DW, g/Pot) | Yield (DW, g/Pot) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 6.303 ± 0.48c | 34.48 ± 1.30c | 73.93 ± 4.13b |
| Cd + GA | 8.853 ± 0.51a | 47.76 ± 1.75a | 91.48 ± 2.82a |
| Cd + BR | 7.660 ± 0.55b | 38.29 ± 1.85b | 78.29 ± 2.90b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Wang, S.; You, X.; Wen, Z.; Huang, G.; Huang, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, K.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, M.; et al. Effect of Foliar Spraying of Gibberellins and Brassinolide on Cadmium Accumulation in Rice. Toxics 2023, 11, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040364
Li B, Wang S, You X, Wen Z, Huang G, Huang C, Li Q, Chen K, Zhao Y, Gu M, et al. Effect of Foliar Spraying of Gibberellins and Brassinolide on Cadmium Accumulation in Rice. Toxics. 2023; 11(4):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040364
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bei, Song Wang, Xiaoshuang You, Zhenzhou Wen, Guirong Huang, Caicheng Huang, Qiaoxian Li, Kuiyuan Chen, Yihan Zhao, Minghua Gu, and et al. 2023. "Effect of Foliar Spraying of Gibberellins and Brassinolide on Cadmium Accumulation in Rice" Toxics 11, no. 4: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040364
APA StyleLi, B., Wang, S., You, X., Wen, Z., Huang, G., Huang, C., Li, Q., Chen, K., Zhao, Y., Gu, M., Li, X., Wei, Y., & Qin, Y. (2023). Effect of Foliar Spraying of Gibberellins and Brassinolide on Cadmium Accumulation in Rice. Toxics, 11(4), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040364





