A Review: Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances—Biological Degradation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Chemical Stability of PFASs in the Environment
2.1. Production of the PFAS
2.2. Occurrence in the Environment
2.3. Toxicological and Ecological Effect of the PFAS
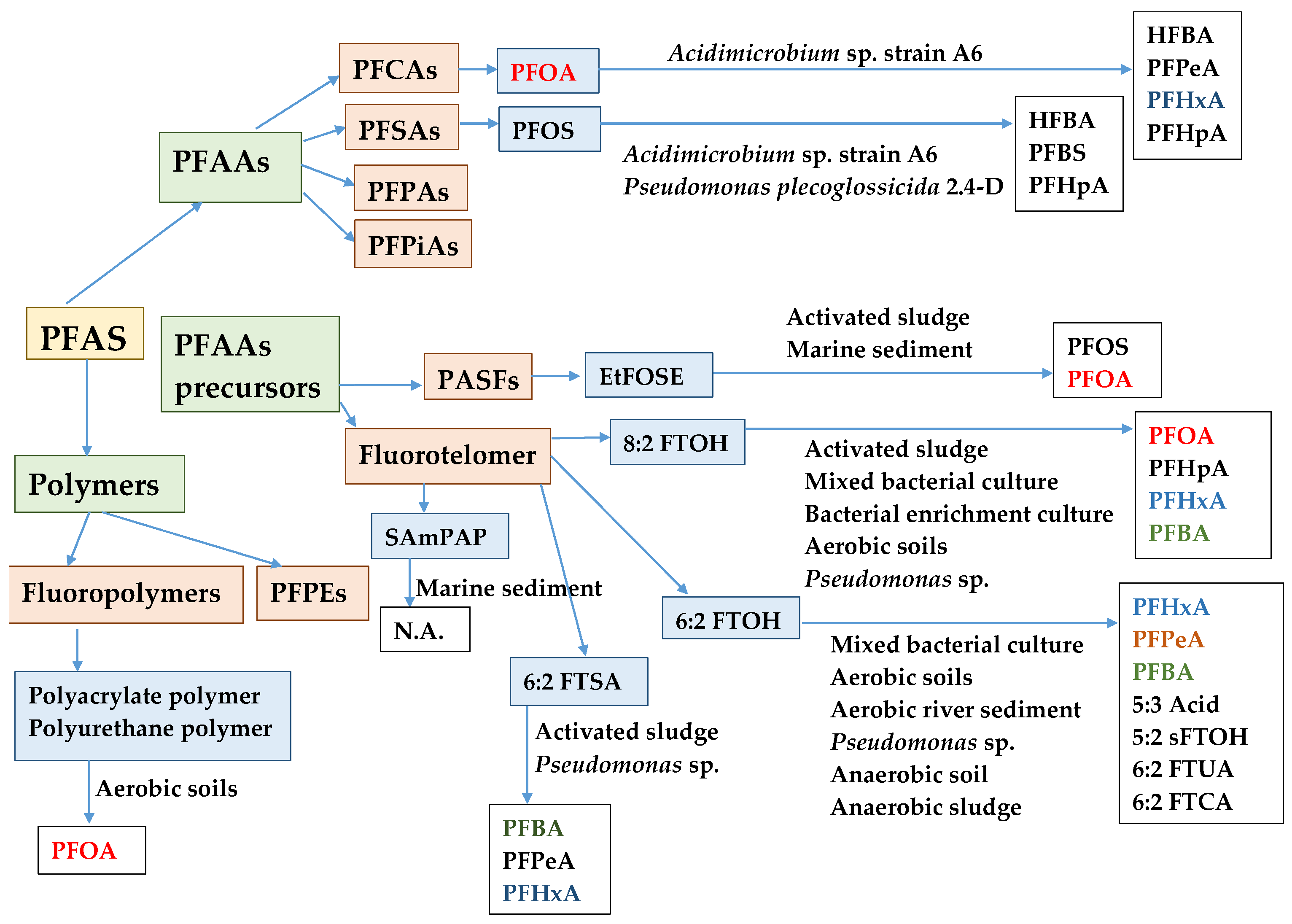
3. Bacteria in Biodegradation/Transformation of PFASs
4. Fungi in Biodegradation/Transformation of PFASs
5. Enzymes for the Transformation of PFASs
5.1. Laccases
5.2. Peroxidases
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 6:2 FTS fluorotelomer sulfonate |
| 6:2 FTSA 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonic acid |
| AFFFs aqueous film-forming foams |
| BOD biological oxygen demand |
| CPO chloroperoxidase |
| ECOC enzyme-catalyzed oxidative coupling |
| ECOHRs enzyme catalysed oxidative humification reactions |
| ESI-HRMS Electrospray ionization-High-resolution mass spectrometry |
| EtFOSE N-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamidoethanol |
| FTOH fluorotelomer alcohol |
| GC-MS gas chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| HBT 1-hydroxybenzotriazole |
| HPLC high-performance liquid chromatograph |
| HR-MS high resolution mass spectrometry |
| HRP horseradish peroxidase |
| IC ion chromatography |
| LaC laccase |
| LC-MS/MS liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| LiP lignin peroxidase |
| MBRs membrane bioreactors |
| MnP manganese peroxidase |
| MS Mass Spectrometry |
| MS/MS Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| OECD Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| PFAA perfluoroalkyl acids |
| PFASs perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| PFBS perfluorobutane sulfonate |
| PFCs perfluorocarbons |
| PFCA perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acid |
| PFHxA perfluorohexanoate |
| PFHxS perfluorohexane sulfonate |
| PFOA perfluorooctanoic acid |
| PFOS perfluorooctane sulfonic acid |
| PFPEs perfluoropolyethers |
| PFSA perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acid |
| PPOSA perfluoroalkyl sulfonamides |
| SBP soybean peroxidase |
| TCE trichloroethene |
| TFA trifluoroacetic acid |
| WWTP wastewater treatment plant |
References
- Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Glüge, J.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Scheringer, M.; Wangm, Z. The high persistence of PFAS is sufficient for their management as a chemical class. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Reconciling terminology of the universe of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). In Recommendations and Practical Guidance (PDF); OECD Environment, Health and Safety Publications Series on Risk Management No. 61; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and Origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Bundschus, M. Fate and effects of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in the aquatic environment: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Xu, T.; Zhao, D. Treatment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in landfill leachate: Status, chemistry and prospects. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1814–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Risk Management for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) under TSCA. 2023. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/assessing-and-managing-chemicals-under-tsca/risk-management-and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council (ITRC). PFAS Chemistry and Naming Conventions, History and Use of PFAS, and Sources of PFAS Releases to the Environment (PFAS). 2023. Available online: https://pfas-1.itrcweb.org/2-pfas-chemistry-and-naming-conventions-history-and-use-of-pfas-and-sources-of-pfas-releases-to-the-environment-overview/ (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Butt, C.M.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.A. Biotransformation pathways of fluorotelomer-based polyfluoroalkyl substances: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 243–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, D.C.G.; Howard, P.H. Are there other persistent organic pollutants? A challenge for environmental chemists. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7157–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.S.C.; Szostek, B.; DeRito, C.M.; Madsen, E.L. Investigating the biodegradability of perfluorooctanoic acid. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis, M.I.; Wang, Z.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T. A modeling assessment of the physicochemical properties and environmental fate of emerging and novel per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance toxicity and human health review: Current state of knowledge and staregies for informing future research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M. Physicochemical properties and aquatic toxicity of poly- and perfluorinated compounds. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 598–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Field, J.A.; Luna-Velsaco, A.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Microbial toxicity and biodegradability of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and shorter chain perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2016, 18, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, A.A.; Rooney, J.P.; Butt, C.M.; Meyer, J.N.; Mabury, S.A. Cellular toxicity associated with exposure to perfluorinated carboxylates (PFCAs) and their metabolic precursors. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.M.; Dinglasan-Panlilio, M.J.A.; Mabury, S.A.; Solomon, K.R.; Sibley, P.K. Fluorotelomer acids are more toxic than perfluorinated acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7159–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWitt, J.C.; Peden-Adams, M.M.; Keller, J.M.; Germolec, D.R. Immunotoxicity of perfluorinated compounds: Recent developments. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasty, R.C.; Wolf, D.C.; Grey, B.E.; Lau, C.S.; Rogers, J.M. Prenatal window of susceptibility to perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced neonatal mortality in the Sprague-Dawley rat. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2003, 68, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.; Thibodeaux, J.R.; Hanson, R.G.; Rogers, J.M.; Grey, B.E.; Stanton, M.E.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Stevenson, L.A. Exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate during pregnancy in rat and mouse. II: Postnatal evaluation. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 74, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luebker, D.J.; York, R.G.; Hansen, K.J.; Moore, J.A.; Butenhoff, J.L. Neonatal mortality from in utero exposure to perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) in Sprague-Dawley rats: Dose-response, and biochemical and pharamacokinetic parameters. Toxicology 2005, 215, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP United Nations Environment Programme. The New POPs under the Stockholm Convention. 2009. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/Convention/ThePOPs/TheNewPOPs/tabid/2511/Default.aspx (accessed on 16 October 2013).
- USEPA US Environmental Protection Agency, 2010/2015 PFOA Stewardship Program. 2006. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/opptintr/pfoa/pubs/stewardship/ (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- ECHA European Chemical Agency. Candidate List of Substances of Very High Concern for Authorization. 2013. Available online: http://echa.europa.eu/web/guest/candidate-list-table (accessed on 14 September 2013).
- Liu, J.; Avendaño, S.M. Microbial degradation of polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the environment: A review. Environ. Int. 2013, 61, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, D.M.; Jeffries, T.C.; Lee, M.J.; Le, S.T.; Yeung, A.; Wallace, S.; Battye, N.; Patch, D.J.; Manefield, M.J.; Weber, K.P. Developing a roadmap to determine per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances-microbial population interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 135994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, N.; Wang, M.; Ambrocio, R.; Mak, K.; O’Connor, E.; Gao, A.; Hawley, E.L.; Deeb, R.A.; Tseng, L.Y.; Mahendra, S. Fungal biotransformation of 6:2 fluorotelomer alcohol. Remediation 2018, 28, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, N. Feasibility of Biodegradation of Polyfluoroalkyl and Perfluoroalkyl Substances. Master’s Thesis, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, J.R.; Sáez, M.; Dolfing, J.; de Voogt, P. Biodegradation of perfluorinated compounds. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 196, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Liang, S.; Huang, Q. Laccase induced degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid in a soil slurry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Feng, M.; Chiang, S.Y.D.; Woodward, D.; Huang, Q. Laccase-catalyzed degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 2, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, K.R.; Janssen, E.M.L.; Luthy, R.G.; Criddle, C.S. Aerobic biotransformation and fate of N-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamidoethanol (N-EtFOSE) in activated sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2873–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Buck, R.C.; Korzeniowski, S.H.; Wolstenholme, B.W.; Folsom, P.W.; Sulecki, L.M. 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate aerobic biotransformation in activated sludge of waste water treatment plants. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECHA European Chemicals Agency. Five European States Call for Evidence on Broad PFAS Restriction. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/sv/-/five-european-states-call-for-evidence-on-broad-pfas-restriction#:~:text=The%20national%20authorities%20of%20Germany,PFAS)%20by%2031%20July%202020 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Ignatyev, M.; Seidel, M.; Hierse, W.; Montenegro, E.; Kirsch, P.; Bathe, A. Fluorten-Side. Patent No. DE102006031143. 24 January 2008. Available online: https://www.freepatentsonline.com/DE102006031143.html (accessed on 19 April 2023).
- Peschka, M.; Fichtner, N.; Hierse, W.; Kirsch, P.; Montenegro, E.; Seidel, M.; Wilken, R.D.; Knepper, T.P. Synthesis and analytical follow-up of the mineralization of a new fluorosurfactant prototype. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Schmidt, J.; Talmon, Y.; Hori, H.; Asai, T.; Ameduri, B. A degradable fluorinated surfactant for emulsion polymerization of vinylidene fluoride. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11399–11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joudan, S.; Liu, R.; D’eon, J.C.; Mabury, S.A. Unique analytical considerations for laboratory studies identifying metabolic products of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Trends Analyt. Chem. 2020, 124, 115431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissa, E. Fluorinated Surfactants and Repellents, 2nd ed.; Revised and Expanded; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, T.L. The Strengths of Chemical Bonds, 2nd ed.; Butterworths Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Steinle-Darling, E.; Reinhard, M. Nanofiltration for trace organic contaminant removal: Structure, solution, and membrane fouling effects on the rejection of perfluorochemicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5292–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Estimation Programs Interface Suite for Microsoft Windows, v 4.11; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Du, Z.; Deng, S.; Bei, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of perfluorinated compounds on various adsorbents–a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.W.; Mabury, S.A.; Solomon, K.R.; Muir, D.C.G. Bioconcentration and tissue distribution of perfluorinated acids in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, H.; Li, L.Y.; Grace, J.R. Review of the fate and transformation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in landfills. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.G.; Jones, K.C.; Sweetman, A.J. A first global production, emission, and environmental inventory for perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’eon, J.C.; Mabury, S.A. Production of perfluorinated carboxylic acids (PFCAs) from the biotransformation of polyfluoroalkyl phosphate surfictants (PAPS): Exploring routes of human contamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4799–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hollander, W.; de Voogt, P.; De Coen, W.; Bervoets, L. Perfluorinated substances in human food and other sources of human exposure. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 208, 179–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, N.; Kannan, K.; Taniyasu, S.; Horii, Y.; Petrick, G.; Gamo, T. A global survey of perfluorinated acids in oceans. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeib, M.; Harner, T.; Vlahos, P. Perfluorinated chemicals in the Arctic atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7577–7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L. Polyfluoroalkyl compounds in the aquatic environment: A review of their occurrence and fate. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Felizeter, S.; Sturm, R.; Xie, Z.; Ebinghaus, R. Polyfluorinated compounds in waste water treatment plant effluents and surface waters along the River Elbe, Germany. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollender, J.; Zimmermann, S.G.; Koepke, S.; Krauss, M.; McArdell, C.S.; Ort, C.; Singer, H.; von Gunten, U.; Siegrist, H. Elimination of organic micropollutants in a municipal wastewater treatment plant upgraded with a full-scale post-ozonation followed by sand filtration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7862–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Removal of perfluorinated surfactants by sorption onto granular activated carbon, zeolite and sludge. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.R.; Allred, B.M.; Field, J.A.; Levis, J.W.; Barlaz, M.A. National estimate of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) release to US municipal landfill leachate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.F.; Peldszus, S.; Anderson, W.B. Behaviour and fate of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2014, 50, 318–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.G.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, C.P.; Luthy, R.G. Sorption of perfluorinated surfactants on sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7251–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shih, K. Adsorption of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on alumina: Influence of solution pH and cations. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2925–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Deng, S.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Sorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate on activated carbons and resin: Kinetic and isotherm study. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Cousins, I.T.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhou, Q. Perfluoroalkyl acids in municipal landfill leachates from China: Occurrence, fate during leachate treatment and potential impact on groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benskin, J.P.; Li, B.; Ikonomou, M.G.; Grace, J.R.; Li, L.Y. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in landfill leachate: Patterns, time trends, and sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11532–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Li, L.Y.; Grace, J.R.; Benskin, J.P.; Ikonomou, M.G. Compositional effects on leaching of stain-guarded (perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substance-treated) carpet in landfill leachate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6564–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, T.G.; Powell, J.; Jain, P.; Xu, Q.; Tolaymat, T.; Reinhart, D. Sustainable Practices for Landfill Design and Operation (Part of Book Series Waste Management Principles and Practice); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Benskin, J.P.; Ikonomou, M.G.; Woudneh, M.B.; Cosgrove, J.R. Rapid characterization of perfluoralkyl carboxylate, sulfonate, and sulfonamide isomers by highperformance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1247, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F. Emerging poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances in the aquatic environment: A review of current literature. Water Res. 2017, 124, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.J.; Mabury, S.A. Atmospheric perfluorinated acid precursors: Chemistry, occurrence, and impacts. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 208, 1–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.W.; Ellis, D.A.; Mabury, S.A.; Hurley, M.D.; Wallington, T.J. Atmospheric chemistry of perfluoroalkanesulfonamides: Kinetic and product studies of the OH radical and Cl atom initiated oxidation of n-ethyl perfluorobutanesulfonamide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guelfo, J.L.; Korzeniowski, S.; Mills, M.A.; Anderson, J.; Anderson, R.H.; Arblaster, J.A.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; Dasu, K.; Henry, B.J.; et al. Environmental Sources, Chemistry, Fate, and Transport of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: State of the Science, Key Knowledge Gaps, and Recommendations Presented at the August 2019 SETAC Focus Topic Meeting. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 3234–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Barber, J.L.; Xie, Z.; Ebinghaus, R. Longitudinal and latitudinal distribution of perfluoroalkyl compounds in the surface water of the Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3122–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdo, C.J.; Ellis, D.A.; Webster, E.; Butler, J.; Christensen, R.D.; Reid, L.K. Aerosol enrichment of the surfactant PFO and mediation of the water-air transport of gaseous PFOA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3969–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Hashizume, N.; Yakata, N.; Murakami, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kikushima, E.; Otsuka, M. Unique physicochemical properties of perfluorinated compounds and their bioconcentration in common carp Cyprinus carpio L. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 62, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Yamashita, N.; Lam, P.K.S.; Ebinghaus, R. Distribution of polyfluoroalkyl compounds in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Petrick, G.; Wei, S.; Gamo, T.; Lam, P.K.S.; Kannan, K. Perfluorinated acids as novel chemical tracers of global circulation of ocean waters. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Xiao, F.; Shen, C.; Chen, J.; Park, C.M.; Sun, Y.; Flury, M.; Wang, D. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in subsurface environments: Occurrence, fate, transport, and research prospect. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2021RG000765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Emerging Contaminants–Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA); Emerginge Contaminants Fact Sheet–PFOS and PFOA; EPA 505-F-14-001; Solid Waste and Emergency Responses; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Steenland, K.; Fletcher, T.; Savitz, D.A. Epidemiologic evidence on the health effects of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. Framework for Human Health Risk Assessment to Inform Decision Making (EPA/100/R-14/001); EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/framework-human-health-risk-assessment-inform-decision-making (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- EPA. Health Effects Support Document for Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) EPA 822-R-16-003; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-05/documents/pfoa_hesd_final-plain.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- EPA. Health Effects Support Document for Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) EPA 822-R-16-002; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-05/documents/pfos_hesd_final_508.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Yu, J.; Hu, J.; Tanaka, S.; Fujii, S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in sewage treatment plants. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2399–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allred, B.M.; Lang, J.R.; Barlaz, M.A.; Field, J.A. Physical and biological release of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from municipal solid waste in anaerobic model landfill reactors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7648–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.M.; Higgins, C.P.; Huset, C.A.; Luthy, R.G.; Barofsky, D.F.; Field, J.A. Fluorochemical mass flows in a municipal wastewater treatment facility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7350–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuertes, I.; Gómez-Lavín, S.; Elizalde, M.P.; Urtiaga, A. Perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs) in northern Spain municipal solid waste landfill leachates. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Szostek, B.; Buck, R.C.; Folsom, P.W.; Sulecki, L.M.; Gannon, J.T. 8-2 Fluorotelomer alcohol aerobic soil biodegradation: Pathways, metabolites and metabolite yields. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Szostek, B.; Buck, R.C.; Panciroli, P.K.; Folsom, P.W.; Sulecki, L.M.; Bellin, C.A. 6-2 Fluorotelomer alcohol aerobic biodegradation in soil and mixed bacterial culture. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinglasan, M.J.A.; Ye, Y.; Edwards, E.A.; Mabury, S.A. Fluorotelomer alcohol biodegradation yields poly- and perfluorinated acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2857–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, B.D.; Howell, R.D.; Criddle, C.S. Defluorination of organofluorine sulfur compounds by Pseudomonas Sp. strain D2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2283–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Jaffé, P.R. Defluorination of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) by Acidimicrobium sp. Strain A6. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11410–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, B.G.; Lim, H.J.; Na, S.H.; Choi, B.I.; Shin, D.S.; Chung, S.Y. Biodegradation of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) as an emerging contaminant. Chemosphere 2014, 109, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Somogyi, A.; Jacobsen, N.E.; Wysocki, V.H.; Field, J.A. Reductive defluorination of perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3260–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.H.; Berti, W.R.; Szostek, B.; Buck, R.C. Investigation of the biodegradation potential of a fluoroacrylate polymer product in aerobic soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackett, L.P. Strategies for the Biodegradation of Polyfluorinated Compounds. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosi, L.M.; Pinto, R.A.; Huang, Q.; Weber, W.J. Peroxidase-mediated degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Huang, Q. Inclusion of persistent organic pollutants in humification processes: Direct chemical incorporation of phenanthrene via oxidative coupling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4221–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidja, A.; Huang, P.M.; Bollag, J.M. Comparison of reaction products from the transformation of catechol catalyzed by birnessite or tyrosinase. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, N.; Qu, Y.; Deeb, R.A.; Hawley, E.L.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Mahendra, S. Degradation and removal methods for perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 615–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, N.; Wang, N.; Szostek, B.; Mahendra, S. Biotransformation of 6:2 fluorotelomer alcohol (6:2 FTOH) by a wood-rotting fungus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4012–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Yan, X.; Lu, J.; Huang, Q. Perfluorooctanesulfonate Degrades in a Laccase-Mediator System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10617–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.R.; Chang, Y.S. Laccase-mediated oxidation of small organics: Bifunctional roles for versatile applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, A.I.; Camarero, S. Laccases and their natural mediators: Biotechnological tools for sustainable eco-friendly processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Wang, N.; Buck, R.C. Biotransformation potential of 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate (6:2 FTSA) in aerobic and anaerobic sediment. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Dada, T.K.; Whelan, A.; Cannon, P.; Sheehan, M.; Reeves, L.; Antunes, E. Microbial and thermal treatment techniques for degradation of PFAS in biosolids: A focus on degradation mechanisms and pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetverikov, S.P.; Sharipov, D.A.; Korshunova, T.Y.; Loginov, O.N. Degradation of perfluorooctanyl sulfonate by strain Pseudomonas plecoglossicida 2.4-D. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2017, 53, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.C. The Aerobic Biodegradation of N-EtFOSE Alcohol by the Microbial Activity Present in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Sludge; 3M Company: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger, B.; Vargo, J.D.; Schnoor, J.L.; Hornbuckle, K.C. Evaluation of perfluorooctane surfactants in a wastewater treatment systemand in a commercial surface protection product. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5524–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benskin, J.P.; Ikonomou, M.G.; Gobas, F.A.P.C.; Begley, T.H.; Woudneh, M.B.; Cosgrove, J.R. Biodegradation of N-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamido ethanol (EtFOSE) and EtFOSE-based phosphate diester (SAmPAP diester) in marine sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Szostek, B.; Buck, R.C.; Folsom, P.W.; Sulecki, L.M.; Capka, V.; Berti, W.R.; Gannon, J.T. Fluorotelomer alcohol biodegradation-direct evidence that perfluorinated carbon chains breakdown. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7516–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lee, L.S.; Nies, L.F.; Nakatsu, C.H.; Turco, R.F. Biotransformation of 8:2 fluorotelomer alcohol in soil and by soil bacteria isolates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8024–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Wang, N.; McDonald, T.; Chu, K.-H. Biodefluorination and biotransformation of fluorotelomer alcohols by two alkane-degrading Pseudomonas strains. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 3041–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Buck, R.C.; Wolstenholme, B.W.; Folsom, P.W.; Sulecki, L.M.; Bellin, C.A. Aerobic biodegradation of [14C] 6:2 fluorotelomer alcohol in a flow-through soil incubation system. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Folsom, P.W.; Wolstenholme, B.W.; Sun, H.; Wang, N.; Buck, R.C. 6:2 Fluorotelomer alcohol biotransformation in an aerobic river sediment system. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, B.D. Biotransformation of Non-Volatile Organofluorine Compounds. Ph.D. Thesis, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, M.H.; Berti, W.R.; Szostek, B.; Wang, N.; Buck, R.C. Evaluation of PFO formation from the biodegradation of a fluorotelomer-based urethane polymer product in aerobic soils. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alneyadi, A.H.; Rauf, M.A.; Ashraf, S.S. Oxidoreductases for the remediation of organic pollutants in water—A critical review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuofin, J.O.; Okoh, A.I.; Nwodo, U.U. Aptitude of oxidative enzymes for treatment of wastewater pollutants: A laccase perspective. Molecules 2019, 24, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Ashraf, S.S.; Barceló, D.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Biocatalytic degradation/redefining “removal” fate of pharmaceutically active compounds and antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 1190–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, C.A.; Ammann, E.M.; Shahgaldian, P.; Corvini, P.F.X. Laccases to take on the challenge of emerging organic contaminants in wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9931–9952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsi, R.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Ashraf, S.S. Laccases and peroxidases: The smart, greener and futuristic biocatalytic tools to mitigate recalcitrant emerging pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, A.O.; Mabinya, L.V.; Okoh, A.I.; Nwodo, U.U. Ligninolytic enzymes: Versatile biocatalysts for the elimination of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wastewater. Microbiologyopen 2018, 7, e00722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiocco, P.; Barreca, A.M.; Fabbrini, M.; Galli, C.; Gentili, P. Promoting laccase activity towards non-phenolic substrates: A mechanistic investigation with some laccase-mediator systems. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañas, A.I.; Alcalde, M.; Plou, F.; Martínez, M.J.; Martínez, Á.T.; Camarero, S. Transformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by laccase is strongly enhanced by phenolic compounds present in soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2964–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman, J.; Ceja, A.; Godoy, T.; Rodriguez Rivera, D.; Dionne, P.; Schipper, J.; Henkemeyer, S.; Cegielski, S.; Wong, G.; Kaur, A. Destruction of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) via Lacasse Enzymatic Degradation and Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation. In Proceedings of the Waste-Management Education Research Conference (WERC), Las Cruces, NM, USA, 11–14 April 2021; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingguo, J.H. Remediation of Perfluoroalkyl Contaminated Aquifers Using an In Situ Two-Layer Barrier: Laboratory Batch and Column Study; SERDP Project 2013, ER-2127; University of Georgia: Athens, AL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Battistuzzi, G.; Bellei, M.; Bortolotti, C.A.; Sola, M. Redox properties of heme peroxidases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 500, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grgas, D.; Petrina, A.; Štefanac, T.; Bešlo, D.; Landeka Dragičević, T. A Review: Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances—Biological Degradation. Toxics 2023, 11, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050446
Grgas D, Petrina A, Štefanac T, Bešlo D, Landeka Dragičević T. A Review: Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances—Biological Degradation. Toxics. 2023; 11(5):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050446
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrgas, Dijana, Ana Petrina, Tea Štefanac, Drago Bešlo, and Tibela Landeka Dragičević. 2023. "A Review: Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances—Biological Degradation" Toxics 11, no. 5: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050446
APA StyleGrgas, D., Petrina, A., Štefanac, T., Bešlo, D., & Landeka Dragičević, T. (2023). A Review: Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances—Biological Degradation. Toxics, 11(5), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050446