A Comparable icELISA and Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Sensitive and Rapid Detection of 4,4′-Dinitrocarbanilide in Chicken
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Development and Optimization of icELISA for DNC in Buffer Solution
2.2.1. Experimental Steps of icELISA
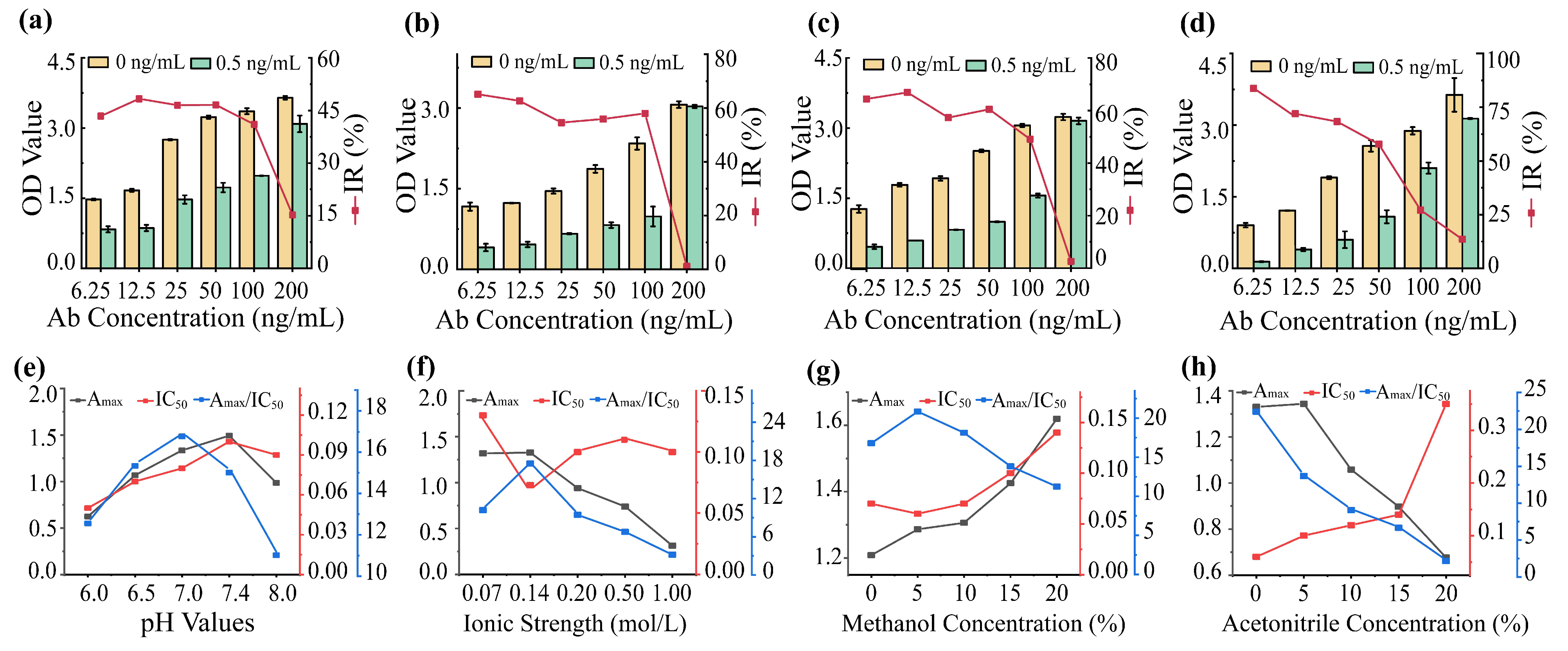
2.2.2. Optimization of icELISA
2.3. Development and Optimization of LFIA for DNC in Buffer Solution
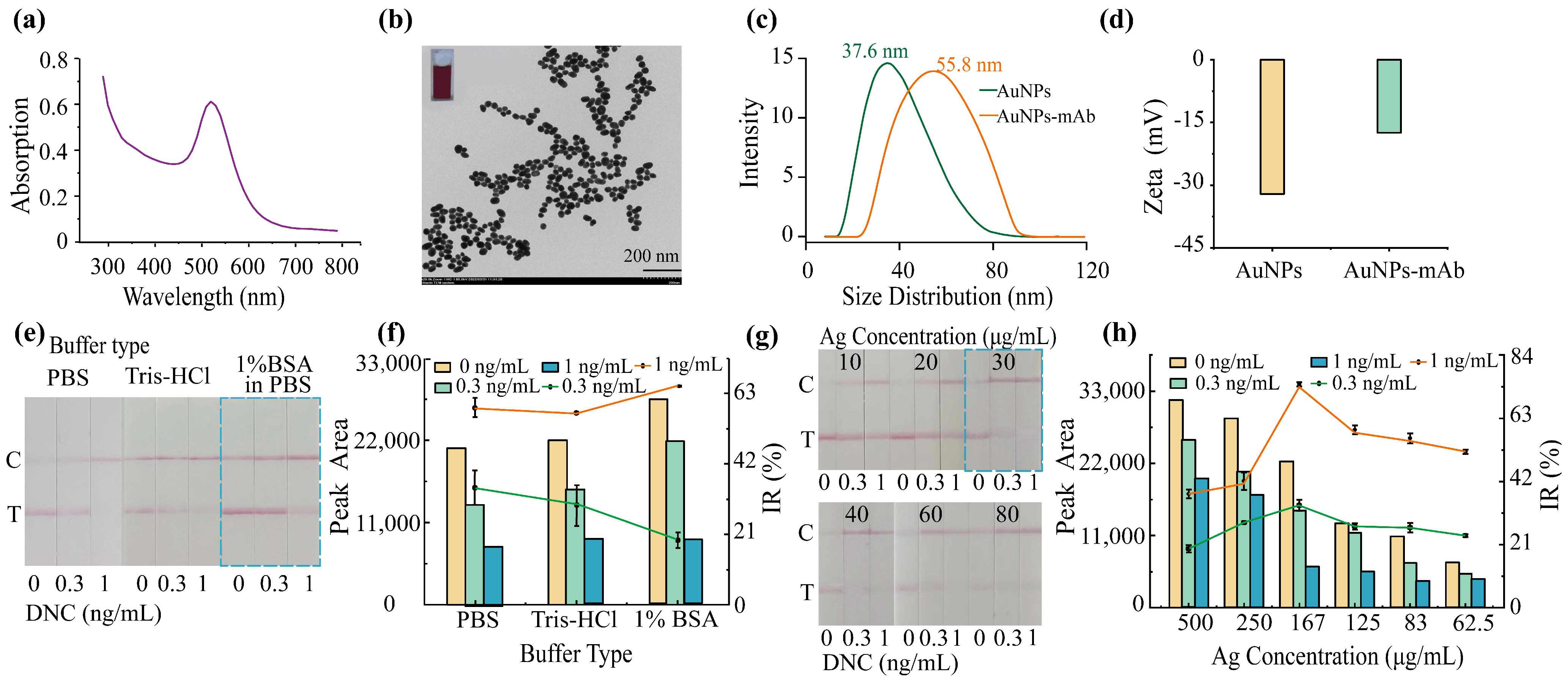
2.3.1. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles
2.3.2. Preparation of AuNPs–mAb Conjugate
2.3.3. Assembling of Lateral Flow Test Strips
2.3.4. Optimization of LFIA Parameters
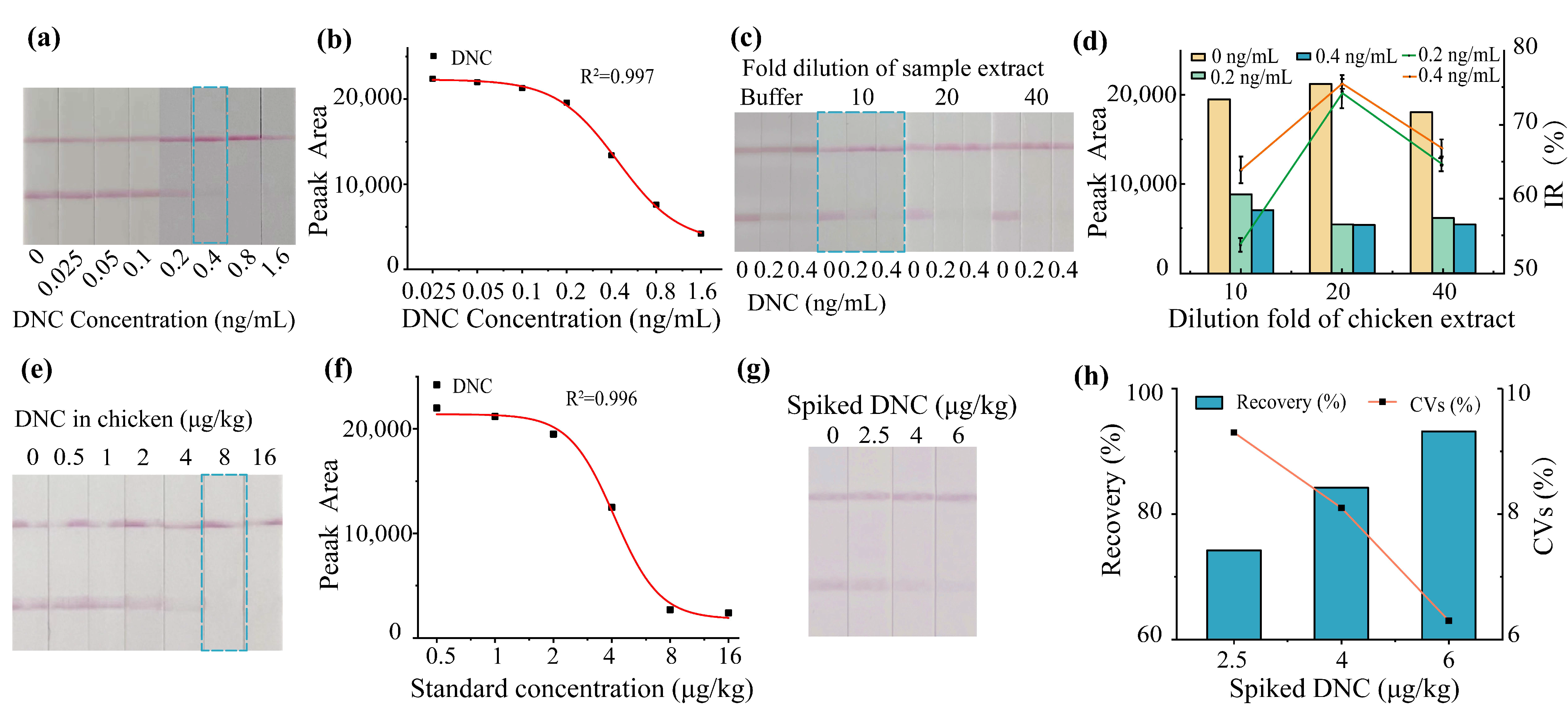
2.4. Sample Pretreatment of Chicken
2.5. Detection Properties of icELISA and LFIA
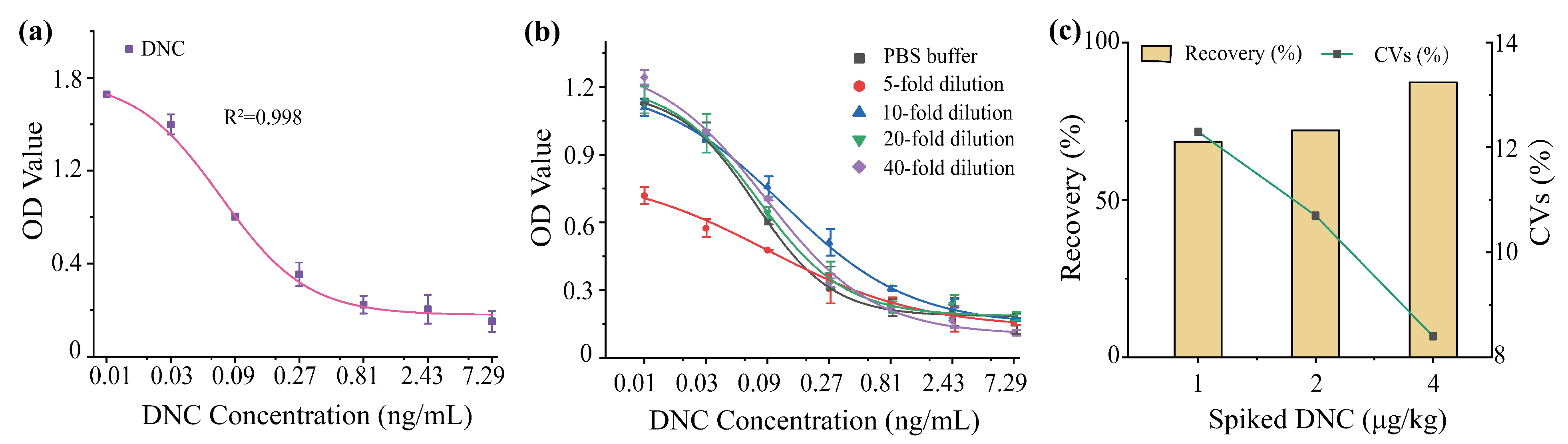
2.5.1. Limit of Detection
2.5.2. Specificity
2.5.3. Spiked and Recovery Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assay Principle of icELISA and LFIA
3.2. Development and Optimization of icELISA for DNC
3.3. Characterization of AuNPs and the AuNPs–mAb Conjugate
3.4. Development and Optimization of LFIA for DNC
3.5. Sensitivity, Specificity, and Accuracy of icELISA and LFIA in Chicken
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarke, L.; Fodey, T.L.; Crooks, S.R.; Moloney, M.; O’Mahony, J.; Delahaut, P.; O’Kennedy, R.; Danaher, M. A review of coccidiostats and the analysis of their residues in meat and other food. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 358–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bampidis, V.; Bastos, M.L.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Kouba, M.; Kos Durjava, M.; López-Alonso, M.; López Puente, S.; Marcon, F.; Mayo, B.; et al. Safety for the environment of Monimax® (monensin sodium and nicarbazin) for chickens for fattening, chickens reared for laying and for turkeys for fattening. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05888. [Google Scholar]
- Bacila, D.M.; Feddern, V.; Mafra, L.I.; Scheuermann, G.N.; Molognoni, L.; Daguer, H. Current research, regulation, risk, analytical methods and monitoring results for nicarbazin in chicken meat: A perspective review. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, R.C.; Stanker, L.H. An antigen based on molecular modeling resulted in the development of a monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay for the coccidiostat nicarbazin. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2001, 444, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 37/2010. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2010, 15, 1–72.
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, China. Maximum Residue Limits for Veterinary Drugs in Foods, in National Food Safety Standard. 2019. Available online: http://down.foodmate.net/standard/yulan.php?itemid=126484 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Buiarelli, F.; Di Filippo, P.; Riccardi, C.; Pomata, D.; Giannetti, L.; Neri, B.; Rago, D. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry analysis of synthetic coccidiostats in eggs. Separations 2017, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, C.; Sun, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, B.; Yi, Y.; Mei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, G. Generation and characterization of an anti-diclazuril monoclonal antibody and development of adiagnostic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for poultry. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 910876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagren, V.; Crooks, S.R.H.; Elliott, C.T.; Lövgren, T.; Tuomola, M. An all-in-one dry chemistry immunoassay for the screening of coccidiostat nicarbazin in poultry eggs and liver. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2429–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; You, M.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Liu, C.; Gong, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, F. Paper-based point-of-care immunoassays: Recent advances and emerging trends. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 39, 107442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wei, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Song, H.; Pan, C.; Xu, N. Immunoassay based on Au-Ag bimetallic nanoclusters for colorimetric/fluorescent double biosensing of dicofol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 194, 113611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, D.; Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, B.Z.; Li, P. AIEgens enabled ultrasensitive point-of-care test for multiple targets of food safety: Aflatoxin B1 and cyclopiazonic acid as an example. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Xu, L.; Kuang, H. Preparation of an anti-4,4′-dinitrocarbanilide monoclonal antibody and its application in an immunochromatographic assay for anticoccidial drugs. Food Agr. Immunol. 2018, 29, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, B.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Yi, Y.; Mei, J.; et al. Preparation and identification of an anti-nicarbazin monoclonal antibody and its application in the agriculture and food industries. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Kong, L.; Huang, B.; Xu, Y.; Hou, R. AuNPs-based lateral flow immunoassay for point-of-needs analysis of four neonicotinoids in tea samples: Effects of grinding degrees, solvent types and contents on extraction efficiency. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Kuang, H.; Cui, G.; Xu, C. Gold immunochromatography assay for the rapid detection of spiramycin in milk and beef samples based on a monoclonal antibody. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, e1900224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, G.; Hu, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Kwee, S.; Tang, L.; Xing, G.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, G. A rapid colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic strip assay for monitoring nitroxynil in milk. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1860–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Eremin, S.A.; Yakup, O.; Yao, G.; Zhang, X. Detection of kanamycin and gentamicin residues in animal-derived food using IgY antibody based ic-ELISA and FPIA. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, H.; Wen, K.; Ke, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Current advances in immunoassays for quinolones in food and environmental samples. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Dong, B.; Mujtaba, M.; Wei, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, X.; Wen, K. Generic hapten synthesis, broad-specificity monoclonal antibodies preparation, and ultrasensitive ELISA for five antibacterial synergists in chicken and milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11170–11179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, L.; Huet, A.; Daeseleire, E.; Huyghebaert, G.; Fodey, T.; Elliott, C.; Delahaut, P.; Van Peteghem, C. Deposition and depletion of five anticoccidials in eggs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7142–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnacombe-Willson, G.; Conti, Y.; Stefancu, A.; Weiss, P.; Cortés, E.; Scarabelli, L. Direct bottom-up in situ growth: A paradigm shift for studies in wet-chemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2023, 13, 8613–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Baker, W.; Ye, H.; Li, Y. pH-Dependent aggregation and pH-independent cell membrane adhesion of monolayer-protected mixed charged gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7371–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Ma, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Y. Overview-gold nanoparticles-based sensitive nanosensors in mycotoxins detection. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zou, M.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Liang, X. Design, synthesis, and characterization of tracers and development of a fluorescence polarization immunoassay for rapid screening of 4,4′-dinitrocarbanilide in chicken muscle. Foods 2021, 10, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Peng, D.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wan, D.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z. A novel hapten and monoclonal-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for sulfonamides in edible animal tissues. Food chem. 2014, 154, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Ultrasensitive immunochromatographic strips for fast screening of the nicarbazin marker in chicken breast and liver samples based on monoclonal antibodies. Anal. Method 2020, 12, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, A.C.; Mortier, L.; Daeseleire, E.; Fodey, T.; Elliott, C.; Delahaut, P. Screening for the coccidiostats halofuginone and nicarbazin in egg and chicken muscle: Development of an ELISA. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilandzic, N.; Dolenc, J.; Gacnik, K.S.; Varenina, I.; Kolanovic, B.S. Feed additives diclazuril and nicarbazin in egg and liver samples from Croatian farms. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2013, 6, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, Y.; Tang, Q.; Liu, M.; Nan, L.; Wen, K.; Yu, X.; Yu, W.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Development of epitopephore-based rational hapten design strategy: A combination of theoretical evidence and experimental validation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, C.; Wen, K.; Yu, X.; Wang, Z. Broad-specificity antibody profiled by hapten prediction and its application in immunoassay for fipronil and major metabolites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strategy | Samples | LOD a (µg/kg or µg/L) | Dilution Factor | Recovery (%) | Extraction Procedure | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | Egg and chicken | 0.3 | 10 | 71–113.6 | Extract solvent: acetonitrile; extract supernatant diluted with PBS. | Zhang et al., 2023 [30] |
| ELISA | Chicken/duck | - b | 150 | 74.4–111.7 | Extract solvent: methanol; extract supernatant was diluted. | Shen et al., 2022 [14] |
| ELISA | Egg | 2.2 | 2 | 80.8 | Extract solvent: acetonitrile; extract supernatant was evaporated to dryness; hexane and methanol/water was added to remove fat; evaporated to dryness again; residues were reconstituted with methanol/water. | Bilandzic et al., 2013 [29] |
| ELISA | Chicken | 10 | - | 67 | Extract solvent: acetonitrile; extract supernatant was evaporated to dryness; hexane and methanol/water was added; evaporated to dryness again; residues were reconstituted with 5% methanol. | Huet et al., 2005 [28] |
| Egg | 3 | 85 | ||||
| ELISA | Chicken/pork/beef | 50 | 40 | 75–95 | Extract solvent: acetonitrile; extract supernatant was evaporated to dryness; the extraction was dissolved in sample diluent. | EAGEN™ |
| LFIA | Chicken | 2.5 | - | 93.5–115.6 | Extract solvent: methanol containing 1% acetic acid; extract supernatant was evaporated to dryness and then dissolved in PBST solution. | Xu et al., 2020 [27] |
| Liver | 5 | 99.6–108.0 | ||||
| LFIA | Milk | 100 | - | 99–100 | No sample pretreatment. | Wu et al., 2018 [13] |
| FPIA c | Chicken | 24.21 | 5 | 74.2–80.8 | Extract solvent: methanol; the supernatant was diluted with an assay buffer. | Zhang et al., 2021 [25] |
| Time-resolved fluorometry | Egg | 3.2 | 50 | 97.3–115.6 | Extract solvent: acetonitrile; extract supernatant was evaporated to dryness; methanol/deionized water reconstituted dried samples. | Hagren et al., 2004 [9] |
| Liver | 11.3 | 100 | 98.4–103.6 | Extract solvent: acetonitrile; extract supernatant was evaporated to dryness and continued with a hexane wash; methanol/deionized water reconstituted dried samples; mixture solution was evaporated to dryness, methanol/deionized water reconstituted dried samples. | ||
| ELISA | Chicken | 0.8 | 20 | 68.5–87.4 | Methanol was the extract solvent; the supernatant was diluted with an assay buffer. | This study |
| LFIA | 8–2.5 d | 10 | 74.2–93.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, W.; Zhang, N.; Yang, J.; Song, W.; Cai, H.; Hou, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, X. A Comparable icELISA and Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Sensitive and Rapid Detection of 4,4′-Dinitrocarbanilide in Chicken. Toxics 2023, 11, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070628
Liang Q, Chen C, Xu W, Zhang N, Yang J, Song W, Cai H, Hou R, Li H, Zhang X. A Comparable icELISA and Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Sensitive and Rapid Detection of 4,4′-Dinitrocarbanilide in Chicken. Toxics. 2023; 11(7):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070628
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Qianxin, Chen Chen, Wenqing Xu, Ning Zhang, Jielin Yang, Wei Song, Huimei Cai, Ruyan Hou, Hongfang Li, and Xiya Zhang. 2023. "A Comparable icELISA and Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Sensitive and Rapid Detection of 4,4′-Dinitrocarbanilide in Chicken" Toxics 11, no. 7: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070628
APA StyleLiang, Q., Chen, C., Xu, W., Zhang, N., Yang, J., Song, W., Cai, H., Hou, R., Li, H., & Zhang, X. (2023). A Comparable icELISA and Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Sensitive and Rapid Detection of 4,4′-Dinitrocarbanilide in Chicken. Toxics, 11(7), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070628








