Lysosomal Membrane Stability of Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) as a Biomarker of Cellular Stress for Environmental Contamination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Procedure
2.2. Environmental Data
2.3. Chemical Analyses
2.3.1. Sample Processing
2.3.2. Organic Contaminants in Seawater and Tissue
2.3.3. Heavy Metals in Seawater and Tissue
2.4. Lysosomal Membrane Stability Assessment
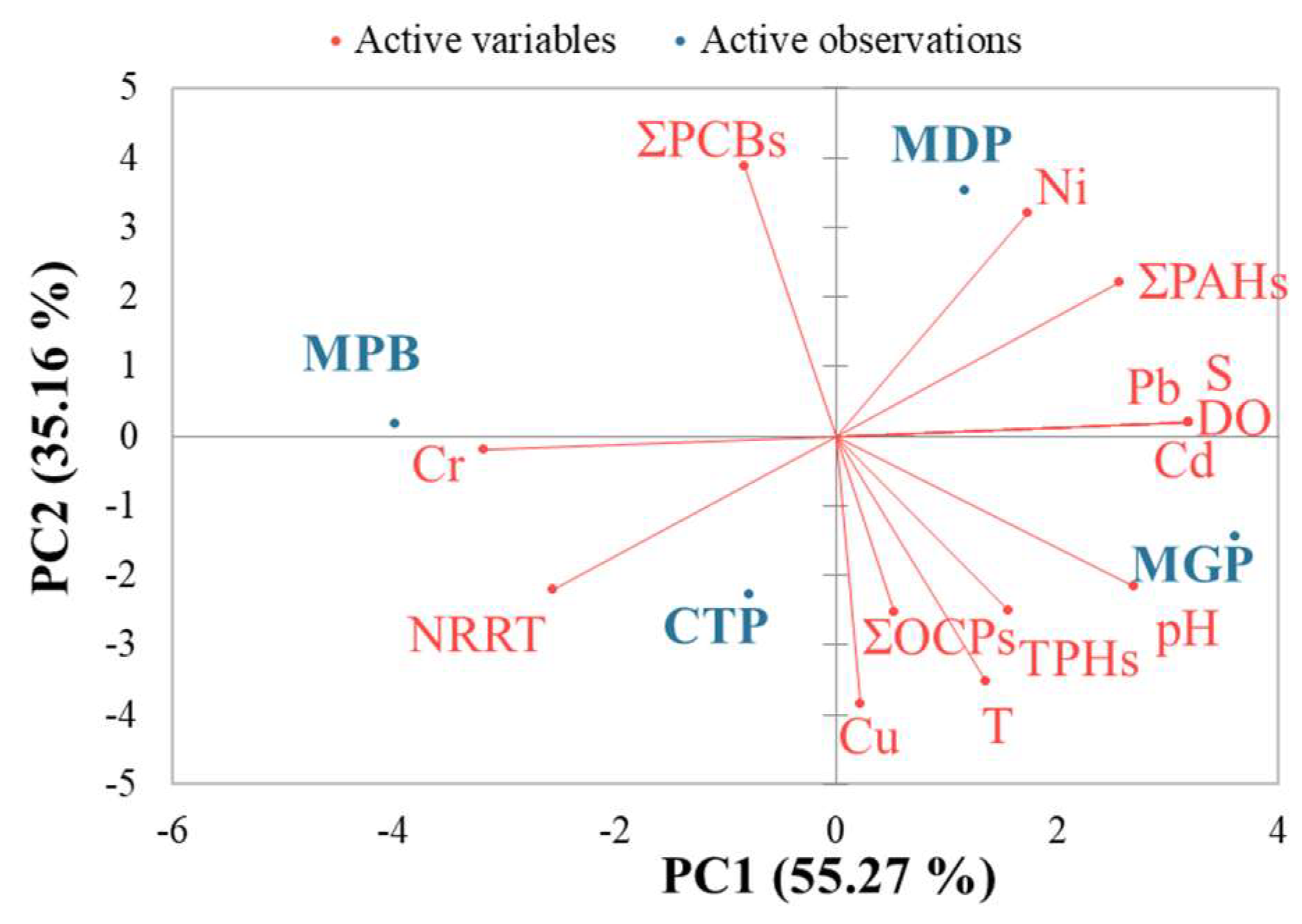
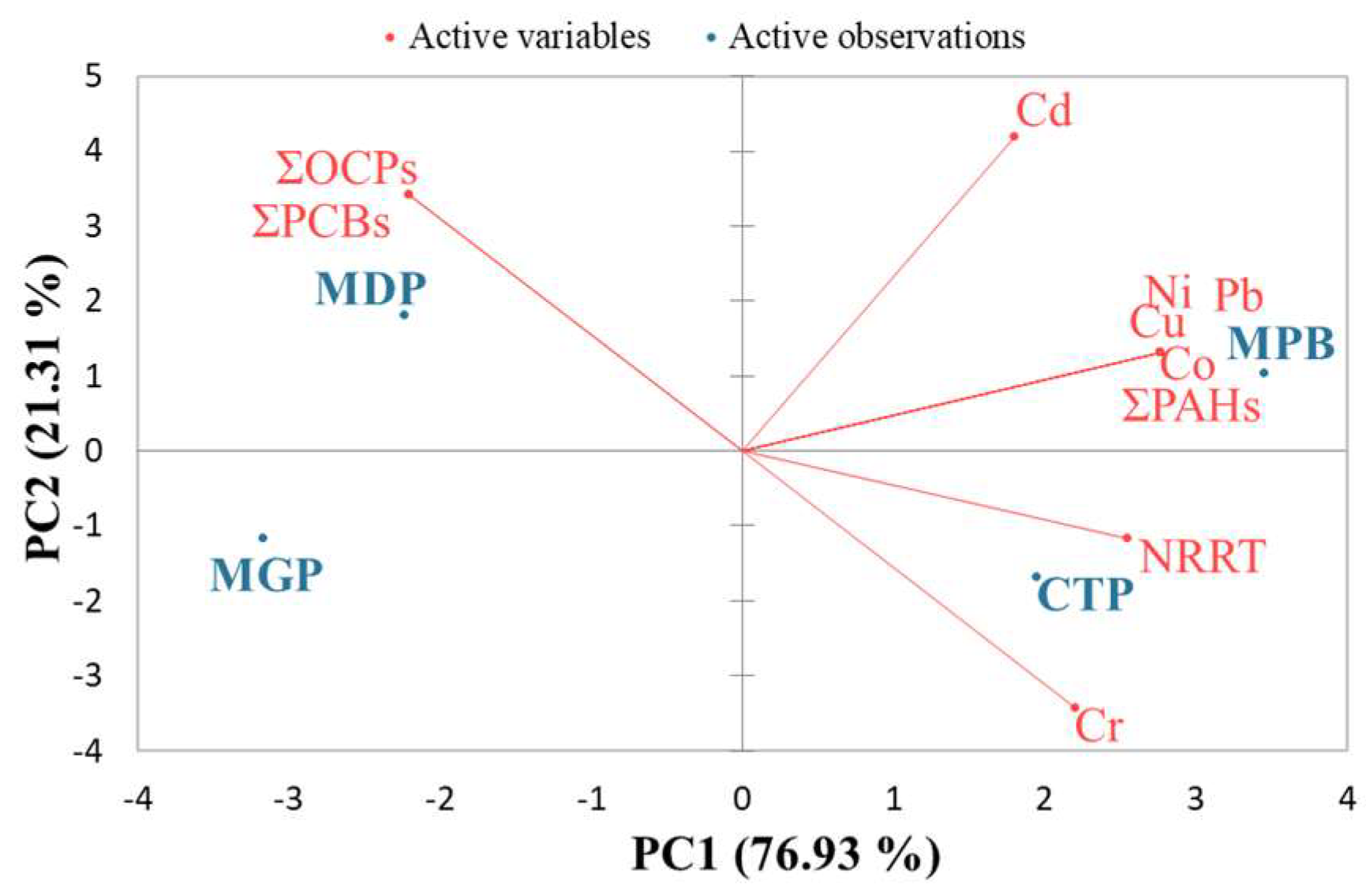
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Conditions in the Study Areas
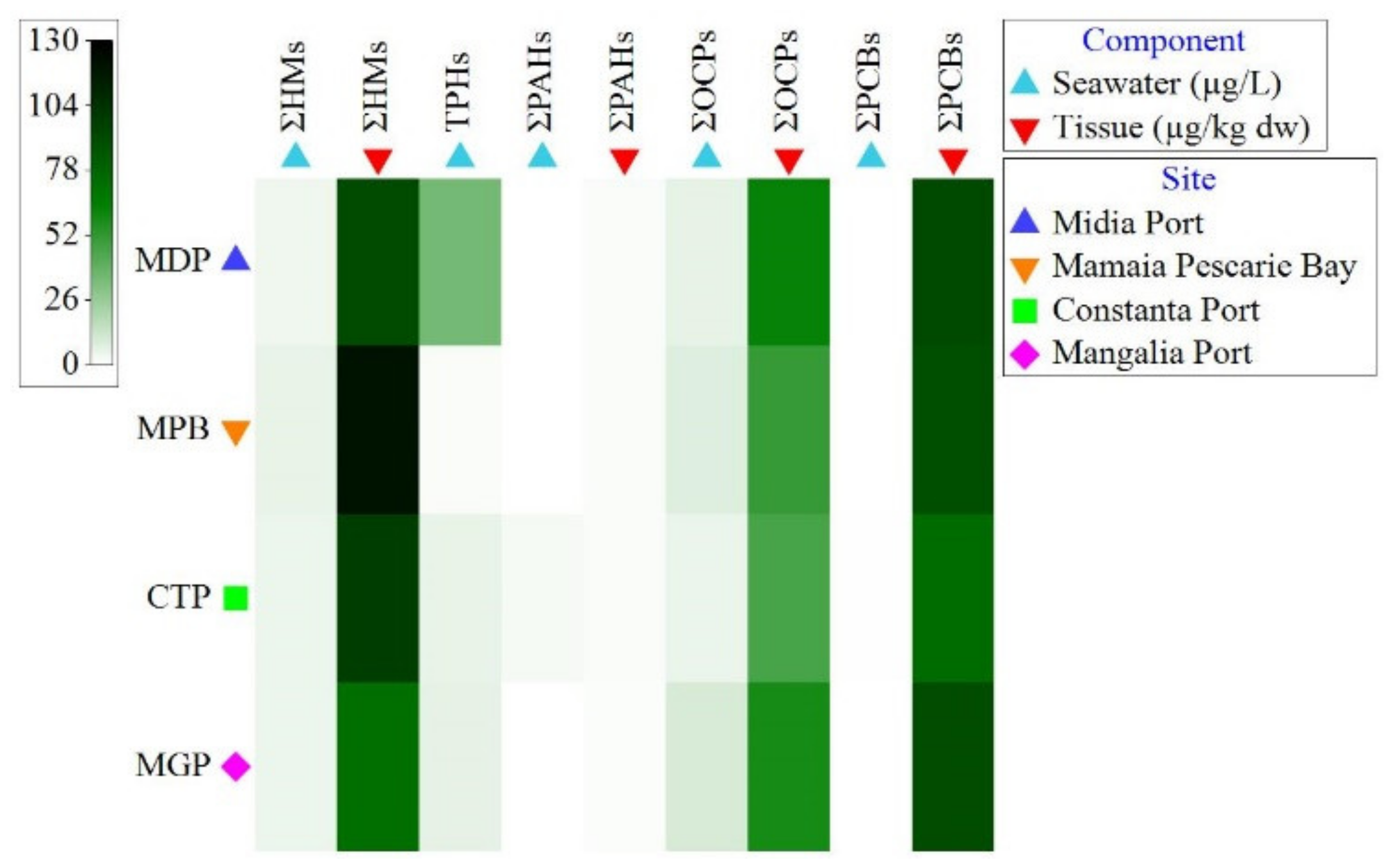
3.2. Organic Contaminant Concentration in Seawater and Tissue
3.3. Heavy Metal Concentration in Seawater and Tissue
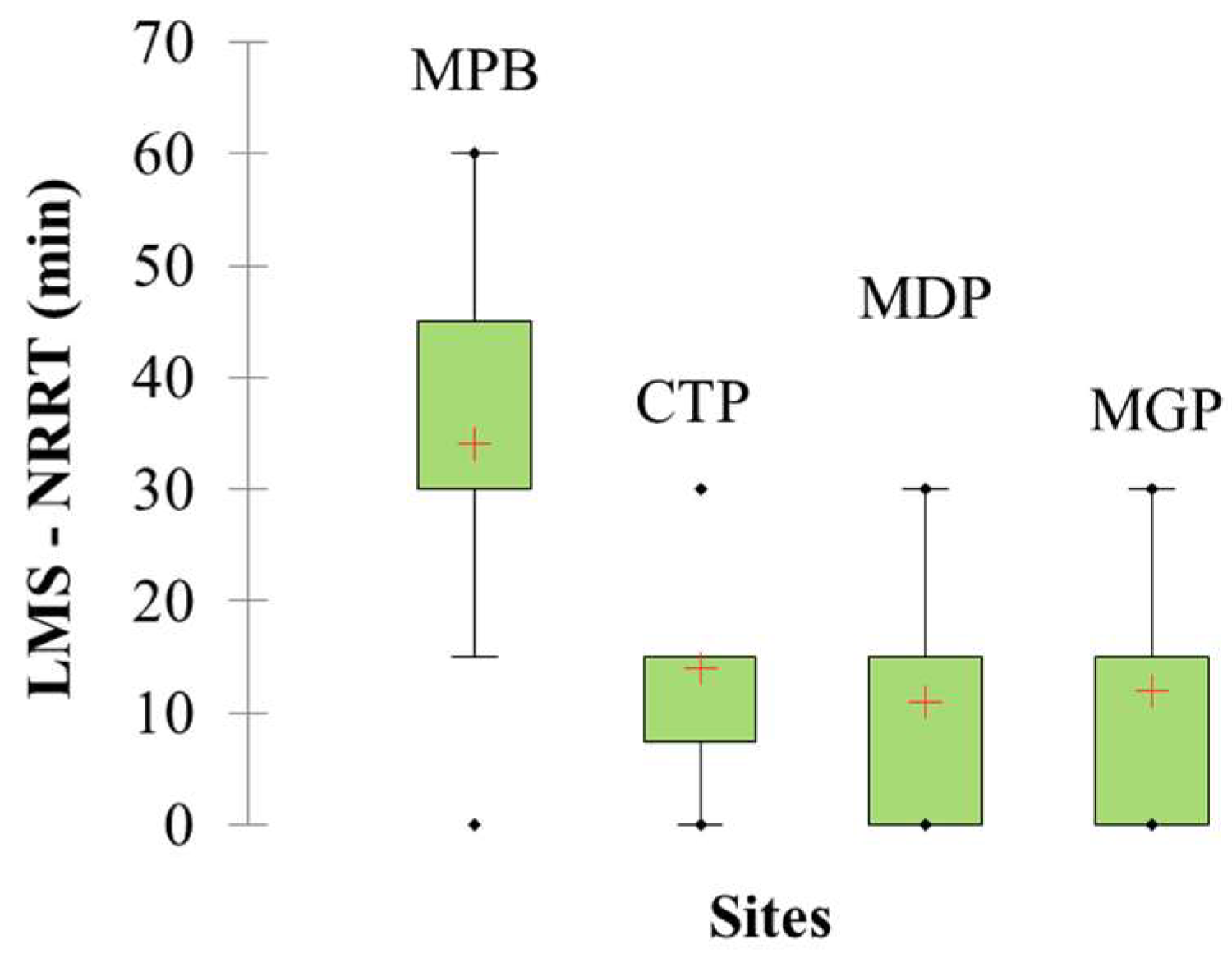
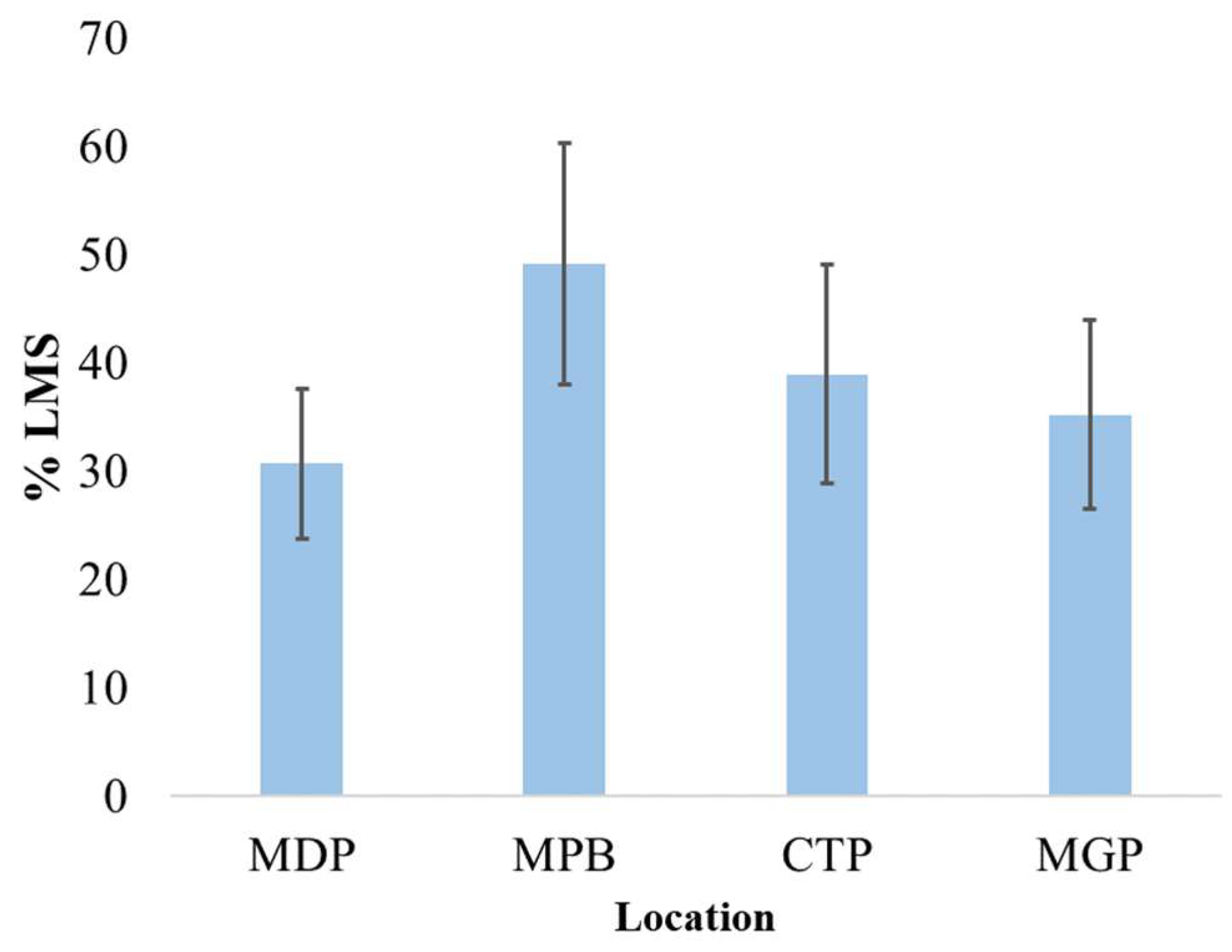
3.4. Lysosomal Membrane Stability
4. Discussion
4.1. Contaminant Concentrations in Seawater
4.2. Tissue Concentrations and Accumulation of Contaminants
4.3. Lysosomal Response to Contaminant Levels
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Ros, L.; Moschino, V.; Macic, V.; Schintu, M. An ecotoxicological approach for the Boka Kotorska Bay (South-Eastern Adriatic Sea): First evaluation of lysosomal responses and metallothionein induction in mussels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.N.; Wedderburn, R.J.; Clarke, K.R.; McFadzen, I.R.B.; Lowe, D.M.; Readman, J.W. Emergent synergistic lysosomal toxicity of chemical mixtures in molluscan blood cells (hemocytes). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchetti, R.; Regoli, F. Seasonal variability of oxidative biomarkers, lysosomal parameters, metallothioneins and peroxisomal enzymes in the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis from Adriatic Sea. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 913–921. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, M.; Buchholz, C.; Heemken, O.; Buck, B.H.; Köhler, A. Health and growth performance of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) from two hanging cultivation sites in the German Bight: A nearshore-offshore comparison. Aquacult. Int. 2012, 20, 751–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gómez, C.; Robinson, C.D.; Burgeot, T.; Gubbins, M.; Halldorsson, H.P.; Albentosa, M.; Bignell, J.P.; Hylland, K.; Vethaak, A.D. Biomarkers of general stress in mussels as common indicators for marine biomonitoring programmes in Europe: The ICON experience. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 124, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viarengo, A.; Lowe, D.; Bolognesi, C.; Fabbri, E.; Koehler, A. The use of biomarkers in biomonitoring: A 2-tier approach assessing the level of pollutant-induced stress syndrome in sentinel organisms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.P.; Dondero, F.; Moore, M.N.; Negri, A.; Dagnino, A.; Readman, J.W.; Lowe, D.R.; Frickers, P.E.; Beesley, A.; Thain, J.E.; et al. Integration of biochemical, histochemical and toxicogenomic indices for the assessment of health status of mussels from the Tamar Estuary, U.K. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 72, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turja, R.; Soirinsuo, A.; Budzinski, H.; Devier, M.H.; Lehtonen, K.K. Biomarker responses and accumulation of hazardous substances in mussels (Mytilus trossulus) transplanted along a pollution gradient close to an oil terminal in the Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 157, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turja, R.; Höher, N.; Snoeijs, P.; Baršienė, J.; Butrimavičienė, L.; Kuznetsova, T.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Devier, M.H.; Budzinski, H.; Lehtonen, K.K. A multibiomarker approach to the assessment of pollution impacts in two Baltic Sea coastal areas in Sweden using caged mussels (Mytilus trossulus). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbi, T.; Fabbri, R.; Montagna, M.; Camisassi, G.; Canesi, L. Seasonal variability of different biomarkers in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) farmed at different sites of the Gulf of La Spezia, Ligurian Sea, Italy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 348–356. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, M.N. Lysosomal cytochemistry in marine environmental monitoring. Histochem. J. 1990, 22, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.N. Cellular responses to pollutants. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1985, 16, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.N. Cytochemical responses of the lysosomal system and NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase in molluscs to environmental and experimental exposure to xenobiotics. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 46, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.M.; Pipe, R.K. Contaminant induced lysosomal membrane damage in marine mussel digestive cells: An in vitro study. Aquat. Toxicol. 1994, 30, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.M.; Fossato, V.U.; Depledge, M.H. Contaminant-induced lysosomal membrane damage in blood cells of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Venice Lagoon: An in vitro study. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 129, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Bebianno, M.J.; Blasco, J.; Porte, C.; Sarasquete, C.; Viarengo, A. The use of biomarkers to assess the impact of pollution in coastal environments of the Iberian Peninsula: A practical approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 247, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Gómez, C.; Bignell, J.; Lowe, D. (Eds.) Lysosomal Membrane Stability in Mussels; ICES Techniques in Marine Environmental Sciences; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015; Volume 56, p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, M.N.; Allen, J.I.; McVeigh, A. Environmental Prognostics: An integrated model supporting lysosomal stress responses as predictive biomarkers of animal health status. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 61, 278–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocan, C. Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. lysosomal membrane stability: A biomarker of marine pollution. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 1997, 29–30, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, M.N.; Lowe, D.M.; Wedderburn, R.J.; Wade, T.; Balashov, G.; Büyükgüngör, H.; Daurova, Y.; Denga, Y.; Kostylev, E.; Mihnea, P.; et al. International Mussel Watch (UNESCO/IOC) in the Black Sea: A Pilot Study for Biological Effects and Contaminant Residues. In Environmental Degradation of the Black Sea: Challenges and Remedies; NATO Science Series; Beşiktepe, S.T., Ünlüata, Ü., Bologa, A.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 56, pp. 273–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ciocan, C. Lysosomal membrane stability in blood cells of the soft-shelled clam (Mya arenaria L. ) Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2002, 34, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- ESRI. ArcGIS Desktop, version 10.7; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2019.
- Grasshoff, K.; Kremling, K.; Ehrhardt, M. (Eds.) Methods of Seawater Analysis, 3rd ed.; Willey-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- IAEA-MEL. Training Manual on the Measurement of Organochlorine and Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Environmental Samples; International Atomic Energy Agency-Marine Environmental Laboratory: Monaco, Monaco, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- IAEA-MEL. Training Manual on the Measurement of Heavy Metals in Environmental Samples; International Atomic Energy Agency-Marine Environmental Laboratory: Monaco, Monaco, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Addinsoft. XLSTAT Software, Version 2021.2.1; Addinsoft: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v7: User Manual/Tutorial; Plymouth Routines in Multivariate Ecological Research (PRIMER-E): Plymouth, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Official Gazette of Romania. Order no. 161/2006 of the Ministry of the Environment and Water Management of 16 February 2006 for the Approval of Regulation on the Classification of Surface Water Quality in Order to Establish the Ecological Status of Water Bodies; Official Gazette of Romania: Bucharest, Romania, 2006; p. 511. [Google Scholar]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Maddela, N.R.; Megharaj, M.; Venkateswarlu, K. Ecological Impacts of Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons. In Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 95–138. [Google Scholar]
- Neațu, L. 2023. Poluare cu Păcură în Portul Midia Năvodari. O Tonă de Combustibil a Ajuns în Apă. Available online: https://www.lumeapresei.ro/poluare-cu-pacura-in-portul-midia-navodari-o-tona-de-combustibil-a-ajuns-in-apa (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Oros, A.; Lazăr, L.; Coatu, V.; Țigănuș, D. Recent Data from Pollution Monitoring And Assessment Of The Romanian Black Sea Ecosystem, Within Implementation Of The European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. In Marine and Ocean Ecosystem, Proceedings of the 16th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference (SGEM 2016), Albena, Bulgaria, 30 June−6 July 2016; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 821–828. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as regards priority substances in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, L226/1, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Oros, A. Monitoring and Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Romanian Black Sea Ecosystem during 2006-2018, in the Context of Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) 2008/56/EC Implementation. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2019, 49, 8–33. [Google Scholar]
- Coatu, V.; Oros, A.; Ţigănuş, D.; Shtereva, G.; Bat, L. Assessment of the Contaminants in Biota from the Western Black Sea Basin in respect with MSFD Requirements in the frame of the MISIS Project. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2016, 46, 82–97. [Google Scholar]
- Oros, A.; Coatu, V.; Tolun, L.-G.; Atabay, H.; Denga, Y.; Damir, N.; Danilov, D.; Aslan, E.; Litvinova, M.; Oleinik, Y.; et al. Hazardous Substances Assessment in Black Sea Biota. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2021, 51, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorita, I.; Apraiz, I.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M.; Orbea, A.; Cancio, I.; Soto, M.; Marigómez, I.; Cajaraville, M.P. Assessment of biological effects of environmental pollution along the NW Mediterranean Sea using mussels as sentinel organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekube, X.; Izagirre, U.; Soto, M.; Marigómez, I. Lysosomal and tissue-level biomarkers in mussels cross-transplanted among four estuaries with different pollution levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kožul, D.; Herceg Romanić, S.; Kljaković-Gašpić, Z.; Veža, J. Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in wild mussels from two different sites in central Croatian Adriatic coast. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 179, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSPAR. Background Document on CEMP Assessment Criteria for QSR 2010; Monitoring and Assessment Series; Commission for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic (OSPAR Commission): London, UK, 2009; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, L364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mititelu, M.; Neacșu, S.M.; Oprea, E.; Dumitrescu, D.-E.; Nedelescu, M.; Drăgănescu, D.; Nicolescu, T.O.; Roșca, A.C.; Ghica, M. Black Sea Mussels Qualitative and Quantitative Chemical Analysis: Nutritional Benefits and Possible Risks through Consumption. Nutrients 2022, 14, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, J.; Thomas, K.V. A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubiana, V.K.; Blust, R. Effects of temperature on scope for growth and accumulation of Cd, Co, Cu and Pb by the marine bivalve Mytilus edulis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 63, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milun, V.; Grgas, D.; Radman, S.; Štefanac, T.; Ibrahimpašić, J.; Landeka Dragičević, T. Organochlorines Accumulation in Caged Mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis—Possible Influence of Biological Parameters. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.W., Jr.; Anderson, R.D. The influence of salinity on the toxicity of various classes of chemicals to aquatic biota. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1995, 25, 281–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyden, C.R. Trace element content and body size in molluscs. Nature 1974, 251, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossa, D.; Bourget, E.; Pouliot, D.; Piuze, J.; Chanut, J.P. Geographical and seasonal variations in the relationship between trace metal content and body weight in Mytilus edulis. Mar. Biol. 1980, 58, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muncaster, B.W.; Hebert, P.D.; Lazar, R. Biological and physical factors affecting the body burden of organic contaminants in freshwater mussels. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1990, 19, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruner, K.A.; Fisher, S.W.; Landrum, P.F. The Role of the Zebra Mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, in Contaminant Cycling: I—The Effect of Body Size and Lipid Content on the Bioconcentration of PCBs and PAHs. J. Great Lakes Res. 1994, 20, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlas, O. Phytoplankton Structural and Functional Changes in Mamaia Bay over the Last Two Decades. Ph.D. Thesis, Ovidius University of Constanta, Doctoral School of Applied Sciences, Constanta, Romania, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lazăr, L.; Boicenco, L.; Denga, Y. Anthropogenic Pressures and Impacts on the Black Sea Coastal Ecosystem; CD Press: Bucharest, Romania, 2021; pp. 18–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hervé-Fernández, P.; Houlbrèque, F.; Boisson, F.; Mulsow, S.; Teyssié, J.L. Cadmium bioaccumulation and retention kinetics in the Chilean blue mussel Mytilus chilensis: Seawater and food exposure pathways. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 99, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baussant, T.; Sanni, S.; Jonsson, G.; Skadsheim, A.; Børseth, J.F. Bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic compounds: 1. Bioconcentration in two marine species and in semipermeable membrane devices during chronic exposure to dispersed crude oil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.N.; Viarengo, A.; Donkin, P.; Hawkins, A.J. Autophagic and lysosomal reactions to stress in the hepatopancreas of blue mussels. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 84, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giron-Perez, M. Relationships between innate immunity in bivalve molluscs and environmental pollution. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2010, 7, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Olabarrieta, I.; Marigomez, I. In vitro activities in mussel hemocytes as biomarkers of environmental quality: A case study in the Abra Estuary (Biscay Bay). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1996, 35, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, D.R. Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viarengo, A.; Marro, A.; Marchi, B.; Burlando, B. Single and combined effects of heavy metals and hormones on lysosomes of haemolymph cells from the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Biol. 2000, 137, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.N. Cellular responses to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phenobarbital in Mytilus edulis. Mar. Environ. Res. 1979, 2, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
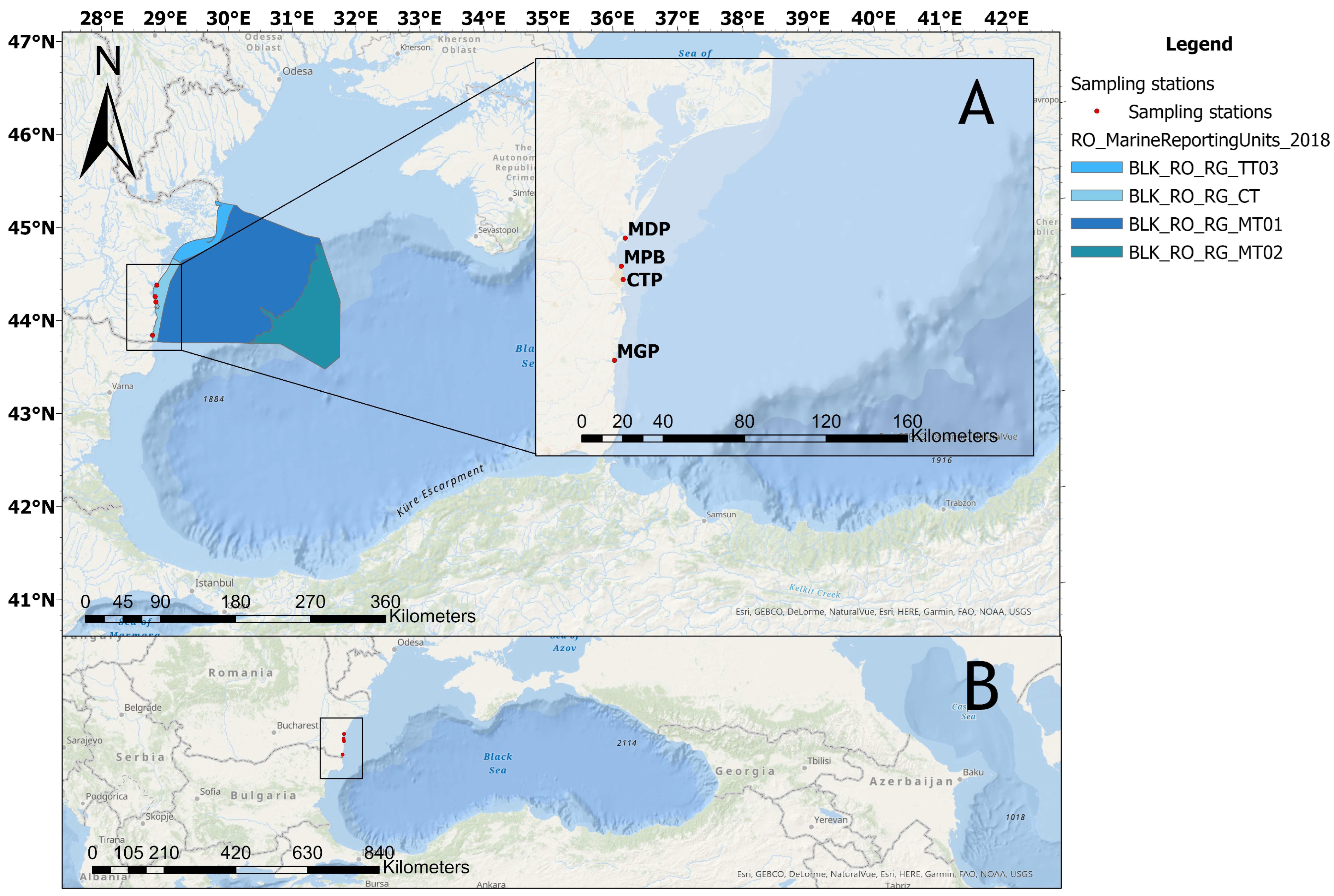

| Location | Sampling Site Code | Lat. (°N) | Long. (°E) | Anthropogenic Pressures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midia Port | MDP | 44.342436 | 28.681631 | Urban and industrial sewage discharge, oil refinery, petrochemical activities, and intense maritime traffic. |
| Mamaia Pescarie Bay | MPB | 44.219671 | 28.649602 | Urban sewage discharge, moderate maritime traffic, small fishing boat dock. |
| Constanta Port | CTP | 44.160792 | 28.657107 | Urban and industrial sewage discharge, intense maritime traffic, intense cargo operations (crude oil and derivative products, coal, ore, chemicals, fertilizers, etc.) |
| Mangalia Port | MGP | 43.807017 | 28.582175 | Urban sewage discharge, yacht and small boat docks, tourism in summer. |
| Site | T (°C) | S (psu) | DO (mg/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDP | 23.0 | 14.63 | 13.56 | 8.26 |
| MPB | 23.6 | 13.81 | 5.97 | 8.07 |
| CTP | 23.9 | 14.09 | 6.23 | 8.37 |
| MGP | 26.0 | 15.08 | 17.80 | 8.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantea, E.-D.; Coatu, V.; Damir, N.-A.; Oros, A.; Lazar, L.; Rosoiu, N. Lysosomal Membrane Stability of Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) as a Biomarker of Cellular Stress for Environmental Contamination. Toxics 2023, 11, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080649
Pantea E-D, Coatu V, Damir N-A, Oros A, Lazar L, Rosoiu N. Lysosomal Membrane Stability of Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) as a Biomarker of Cellular Stress for Environmental Contamination. Toxics. 2023; 11(8):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080649
Chicago/Turabian StylePantea, Elena-Daniela, Valentina Coatu, Nicoleta-Alexandra Damir, Andra Oros, Luminita Lazar, and Natalia Rosoiu. 2023. "Lysosomal Membrane Stability of Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) as a Biomarker of Cellular Stress for Environmental Contamination" Toxics 11, no. 8: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080649
APA StylePantea, E.-D., Coatu, V., Damir, N.-A., Oros, A., Lazar, L., & Rosoiu, N. (2023). Lysosomal Membrane Stability of Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) as a Biomarker of Cellular Stress for Environmental Contamination. Toxics, 11(8), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080649









