Improved Calculations of Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients for Evaluating Potential Ecological Risk in Sediments Based on Seven Major Chinese Water Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Influencing Factors of Potential Ecological Risk Index
- (1)
- Content condition: the concentration of metals in the surface sediment. The RI value should increase with the increase of surface metal contamination.
- (2)
- Quantitative conditions: the number of metal contaminants. The RI value of sediment contaminated with multiple metals should be higher than that of sediment contaminated with only a few metals.
- (3)
- Toxic conditions: the toxicity levels of metals. Different metals have different toxicity levels and metals with higher toxicity should contribute more to the RI value than those with lower toxicity.
- (4)
- Sensitivity conditions: the sensitivity of the water body to metal pollution. Water bodies with high sensitivity to metal pollution should have higher RI values than water bodies with low sensitivity.
2.2. Calculation of Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.3. Calculation of Metal Toxicity Coefficients
3. Results
3.1. Improved Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients
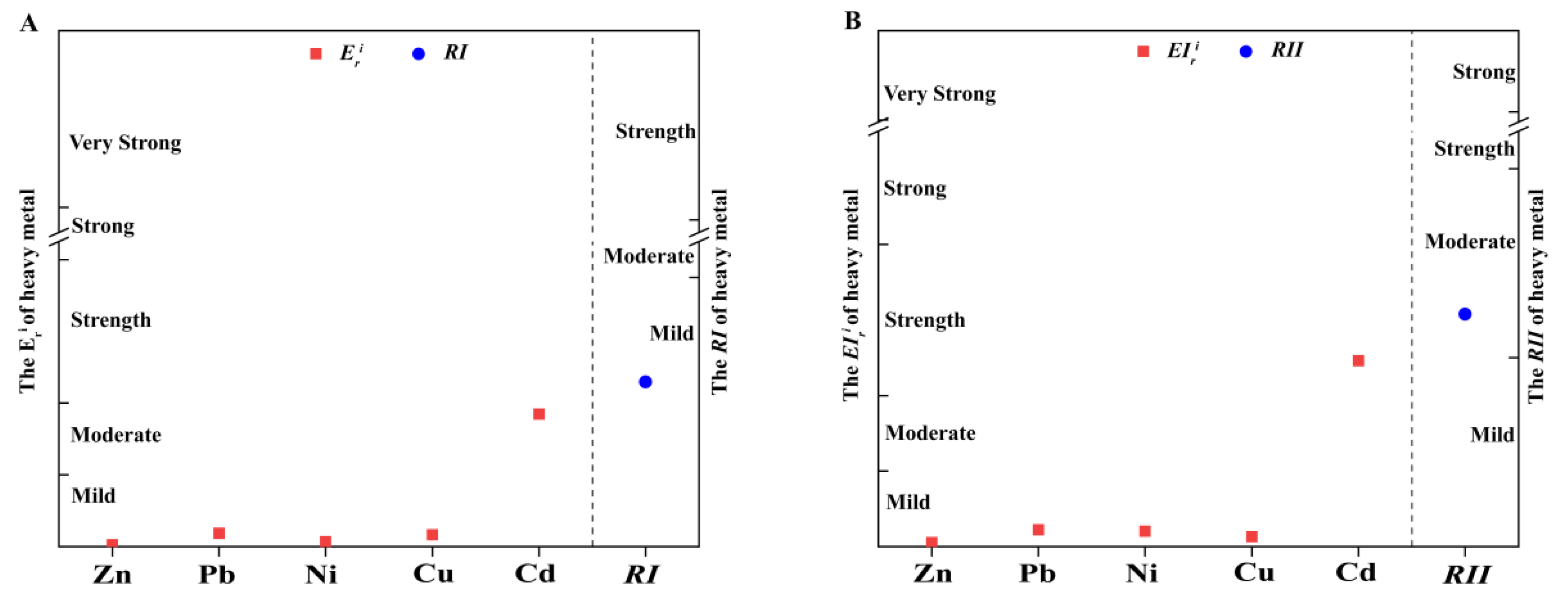
3.2. Pollution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in the Henan Section of the Yellow River
4. Discussion
4.1. Improved Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients
4.2. Pollution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in the Henan Section of the Yellow River
4.3. The Applicability of the Improved Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients
5. Conclusions
- The toxicity coefficients of the seven heavy metals examined in this paper rank as follows: Cd > As > Cr = Ni = Pb > Cu > Zn, with toxicity coefficients of 20, 10, 5, 5, 5, 2, 1, respectively. These updated values provide a basis for calculating the degree of heavy metal pollution in sediments.
- Cd, As, and Cr are more toxic, and their emissions should be strictly controlled during the production, manufacturing, and disposal of items containing these metals.
- Compared to the original RI formulation, the improved RII calculation is more sensitive to heavy metal pollution and thus provides a better indication of ecological risk. This is a necessary improvement to provide more accurate pollution assessments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, O.V.; Labana, S.; Pandey, G.; Budhiraja, R.; Jain, R.K. Phytoremediation: An overview of metallic ion decontamination from soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Ding, W.; Liu, B.; Liu, Q. Comprehensive evaluation of environmental availability, pollution level and leaching heavy metals behavior in non-ferrous metal tailings. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the rhine river. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Proshad, R.; Kormoker, T.; Abdullah Al, M.; Islam, M.S.; Khadka, S.; Idris, A.M. Receptor model-based source apportionment and ecological risk of metals in sediments of an urban river in Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control—A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of potential hazards of metal pollution in water bodies by applying sedimentological methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 9, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Ni, S.; Tuo, X.; Zhang, C. Calculation of Heavy Metals’Toxicity Coefficient in the Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risk Index. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 31, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liang, M.; Feng, B. Average Background Values of 39 Chemical Elements in Stream Sediments of China. Earth Sci. 2016, 41, 234–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, L. Chemical forms of soil heavy metals and their environmental significance. Chin. J. Ecol. 2005, 24, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, P.; Zhang, H.; Shan, B.; Lv, S.; Tang, W. Heavy metals in estuarine surface sediments of the Hai River Basin, variation characteristics, chemical speciation and ecological risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7869–7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Tian, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, M. Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient levels on heavy metal contents and fractions in river surface sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wan, C. Spatial distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediment of the Hai River and its tributaries in Tianjin, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S. Distribution characteristics and potential risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Huaihe River Basin in Henan Province. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2017, 45, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Pan, W.; Zhu, Z.; Geng, Q.; Li, P.; Xie, D.; Liu, Y. Concentrations and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Riverine Wetlands Located in the Huaihe River Watershed, China. Clean Soil Air Water 2015, 43, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; An, S.; Zhu, Z.; Pan, W. Speciation and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Sediments Taken from Wetland in the Huaihe River Basin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, C5015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, K.; Xin, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; He, S.; Zhao, Z.; Tong, M.; Cui, Y. Distribution pattern and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Henan section of the Yellow River. Water Supply 2022, 22, 6195–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, R.; Zhen, S.; Ling, T.; Jianxiu, H. Speciation and contamination assessment of metals in the sediments from the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2017, 43, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. Variations in concentrations and bioavailability of heavy metals in rivers caused by water conservancy projects: Insights from water regulation of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir in the Yellow River. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 74, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Gui, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, W. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Zhu, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, N.; Yang, L.; Du, Y. Sediment Quality Criteria and Ecological Risk Assessment for Heavy Metals in Taihu Lake and Liao River. Res. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; He, M.; Lin, C. Environmental impacts of heavy metals (Co, Cu, Pb, Zn) in surficial sediments of estuary in Daliao River and Yingkou Bay (northeast China): Concentration level and chemical fraction. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, H.; Xu, M.; Xu, L. Concentrations, speciation, and ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediment of the Songhua River in an urban area with petrochemical industries. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Zhan, W.; Zhang, J. Heavy metal contamination status and source apportionment in sediments of Songhua River Harbin region, Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3214–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y. Distribution and Fractionation of Heavy Metals in Long-Term and Short-Term Contaminated Sediments. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2012, 29, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Q.; Shao, S.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.; Liu, C. Heavy Metal Pollution, Fractionation, and Potential Ecological Risks in Sediments from Lake Chaohu (Eastern China) and the Surrounding Rivers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 14115–14131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Li, F.; Dominech, S.; Wen, X.; Yang, S. Heavy metals of surface sediments in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary: Distribution, speciation and environmental risks. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 198, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Niu, J.; Tang, Z. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, Z.; Chu, B.; Zhang, N.; Cai, S.; Fang, J. Heavy metals in coastal wetland sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 149, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Tian, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Leung, J.Y.S. Contamination, toxicity and speciation of heavy metals in an industrialized urban river: Implications for the dispersal of heavy metals. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Kang, M. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediment of the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent shelf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1947–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.A.A.; Sathishkumar, P.; Ameen, F.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Gu, F.L. Heavy metal pollution in immobile and mobile components of lentic ecosystems—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4134–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Li, Y. Distributions and sources of heavy metals in sediments of the Bohai Sea, China: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24753–24764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Guo, L.; Men, C.; Wang, Q.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z. Spatial-temporal variation of heavy metals’ sources in the surface sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Z.; Peng, S.; Chen, T.; Zhang, L. Occurrence, source identification and ecological risk evaluation of metal elements in surface sediment: Toward a comprehensive understanding of heavy metal pollution in Chaohu Lake, Eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 23, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Gu, J.; Qian, X.; Yin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X. Effects of adding different surfactants on antibiotic resistance genes and intI1 during chicken manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Cheng, H.; Zeng, E.Y.; Hu, Y. Heavy metal pollution in sediments of a typical mariculture zone in South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G. Extraction procedures for the determination of heavy metals in contaminated soil and sediment. Talanta 1998, 46, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Ater, M.; Sunahara, G.I.; Robidoux, P.Y. Phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation of copper and chromium using barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) in spiked artificial and natural forest soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.F.; Gagneten, A.M.; Paggi, J.C. Copper and Chromium Alter Life Cycle Variables and the Equiproportional Development of the Freshwater Copepod Notodiaptomus conifer (SARS). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 213, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brdarić, E.; Popović, D.; Soković Bajić, S.; Tucović, D.; Mutić, J.; Čakić-Milošević, M.; Đurđić, S.; Tolinački, M.; Aleksandrov, A.P.; Golić, N.; et al. Orally Administrated Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BGAN8-Derived EPS-AN8 Ameliorates Cd Hazards in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Bi, C.; Jia, J.; Deng, L.; Chen, Z. Impact of intensive land use on heavy metal concentrations and ecological risks in an urbanized river network of Shanghai. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Element | Igneous Rocks | Fresh Water | Land Plants | Land Animals | Sediments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 1.8 | 0.0004 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 9 |
| Cd | 0.2 | 0.00031 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.126 |
| Cr | 100 | 0.00018 | 0.23 | 0.075 | 54 |
| Cu | 55 | 0.01 | 14 | 2.4 | 20 |
| Ni | 75 | 0.01 | 3 | 0.8 | 23 |
| Pb | 12.5 | 0.005 | 2.7 | 2 | 23 |
| Zn | 70 | 0.01 | 100 | 160 | 67 |
| Element | Igneous Rocks | Fresh Water | Land Plants | Land Animals | Sediments | Abundance Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 55.6 | 25.0 | 500.0 | 800.0 | 7.4 | 588.0 | 147.0 |
| Cd | 500.0 | 32.3 | 166.7 | 320.0 | 531.7 | 1018.9 | 254.7 |
| Cr | 1.0 | 55.6 | 434.8 | 2133.3 | 1.2 | 492.6 | 123.1 |
| Cu | 1.8 | 1.0 | 7.1 | 66.7 | 3.4 | 13.3 | 3.3 |
| Ni | 1.3 | 1.0 | 33.3 | 200.0 | 2.9 | 38.6 | 9.6 |
| Pb | 8.0 | 2.0 | 37.0 | 80.0 | 2.9 | 50.0 | 12.5 |
| Zn | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 1.0 |
| Region | Proportion of Bioavailable Heavy Metals | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
| Haihe river | — | 21.30% | 3.10% | 3.80% | 3.20% | 5.40% | 11.17% |
| — | — | — | 27.10% | 5.10% | 8.70% | 10.80% | |
| — | 30% | 9% | 7% | 11.50% | 11.50% | 23% | |
| Huaihe river | — | 90% | 42% | 75% | 48% | 95% | 15% |
| — | 53.10% | 0.50% | 4.70% | — | 2.80% | 16.50% | |
| — | 27.55% | 1.80% | 6.40% | — | 0.30% | 55.60% | |
| Yellow River | — | 32.00% | — | 31.00% | 14.50% | 48.00% | 13.00% |
| — | 11.80% | 10.10% | 17.80% | 15.70% | 10.10% | — | |
| — | — | 3.00% | 7.50% | 7.50% | 21.50% | 7.50% | |
| Liao river | 10.16% | 27.42% | 0.32% | 5.48% | 12.64% | 4.93% | 8.84% |
| — | 23.00% | — | 17.00% | — | 0.30% | 11.00% | |
| — | — | — | 7.29% | — | 22.19% | 16.86% | |
| Songhua | — | — | 4.20% | 2.37% | 59.36% | 83.24% | 46.33% |
| 40.00% | 60.00% | — | 40.00% | 40.00% | 85.10% | 40.00% | |
| — | 98.20% | — | 53.00% | — | 83.70% | 76.30% | |
| Changjiang river | — | — | 21.60% | 41.15% | 34.05% | 58.40% | — |
| 5.00% | 42.00% | 2.00% | 10.20% | 6.00% | 14.00% | 5.00% | |
| 1.00% | 29.00% | 5.00% | 11.00% | 14.00% | 13.00% | 14.00% | |
| Zhujiang water | — | 56.60% | 13.70% | 4.50% | 16.70% | 49.00% | 59.90% |
| — | 94.50% | 49.50% | 63.00% | 68.00% | 26.00% | 81.00% | |
| — | — | 24.00% | 45.50% | 35.00% | 61.00% | 42.00% | |
| Median | 7.58% | 32.00% | 5.00% | 11.00% | 15.10% | 21.50% | 16.50% |
| Element | Release Factor | Abundance Index | Toxicity Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| As | 0.0758 | 147.00 | 11.1426 |
| Cd | 0.32 | 254.73 | 81.5136 |
| Cr | 0.05 | 123.14 | 6.157 |
| Cu | 0.11 | 3.33 | 0.3663 |
| Ni | 0.151 | 9.64 | 1.45564 |
| Pb | 0.215 | 12.49 | 2.68535 |
| Zn | 0.165 | 1.00 | 0.165 |
| Pollution Degree | RII | Pollution Degree | |
|---|---|---|---|
| <20 | Mild | <50 | Mild |
| 20–40 | Moderate | 50–100 | Moderate |
| 41–80 | Strength | 101–200 | Strength |
| 81–160 | Strong | >200 | Strong |
| 161–320 | Very Strong |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Yang, Q.; Zeng, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; et al. Improved Calculations of Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients for Evaluating Potential Ecological Risk in Sediments Based on Seven Major Chinese Water Systems. Toxics 2023, 11, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080650
Cao Y, Wang R, Liu Y, Li Y, Jia L, Yang Q, Zeng X, Li X, Wang Q, Wang R, et al. Improved Calculations of Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients for Evaluating Potential Ecological Risk in Sediments Based on Seven Major Chinese Water Systems. Toxics. 2023; 11(8):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080650
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yu, Ruimin Wang, Yanyan Liu, Yongjie Li, Lifen Jia, Qingxiang Yang, Xiangpeng Zeng, Xinlei Li, Qiang Wang, Ruifei Wang, and et al. 2023. "Improved Calculations of Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients for Evaluating Potential Ecological Risk in Sediments Based on Seven Major Chinese Water Systems" Toxics 11, no. 8: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080650
APA StyleCao, Y., Wang, R., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Jia, L., Yang, Q., Zeng, X., Li, X., Wang, Q., Wang, R., & Riaz, L. (2023). Improved Calculations of Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients for Evaluating Potential Ecological Risk in Sediments Based on Seven Major Chinese Water Systems. Toxics, 11(8), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080650






