Micro(nano)plastic and Related Chemicals: Emerging Contaminants in Environment, Food and Health Impacts
Abstract
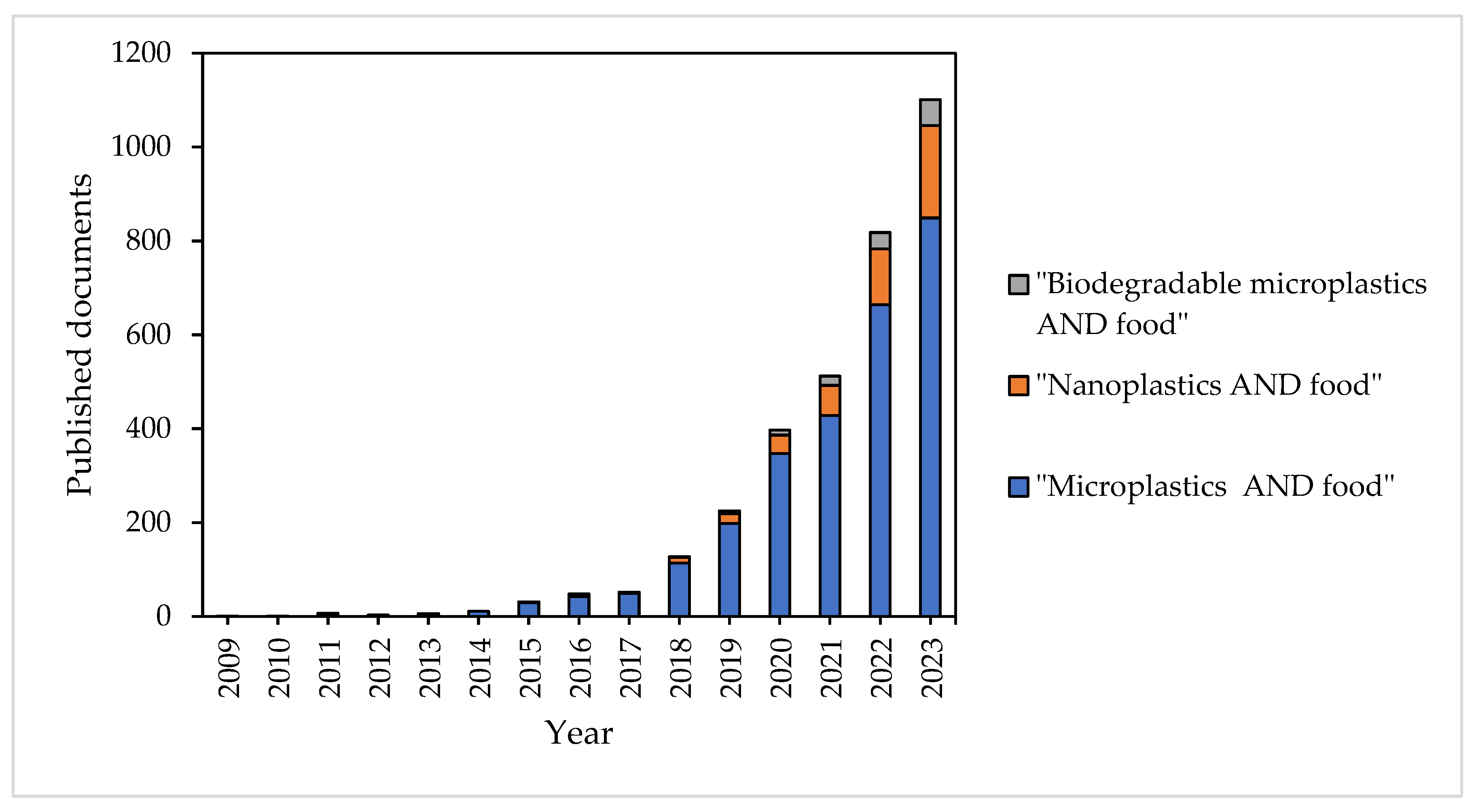
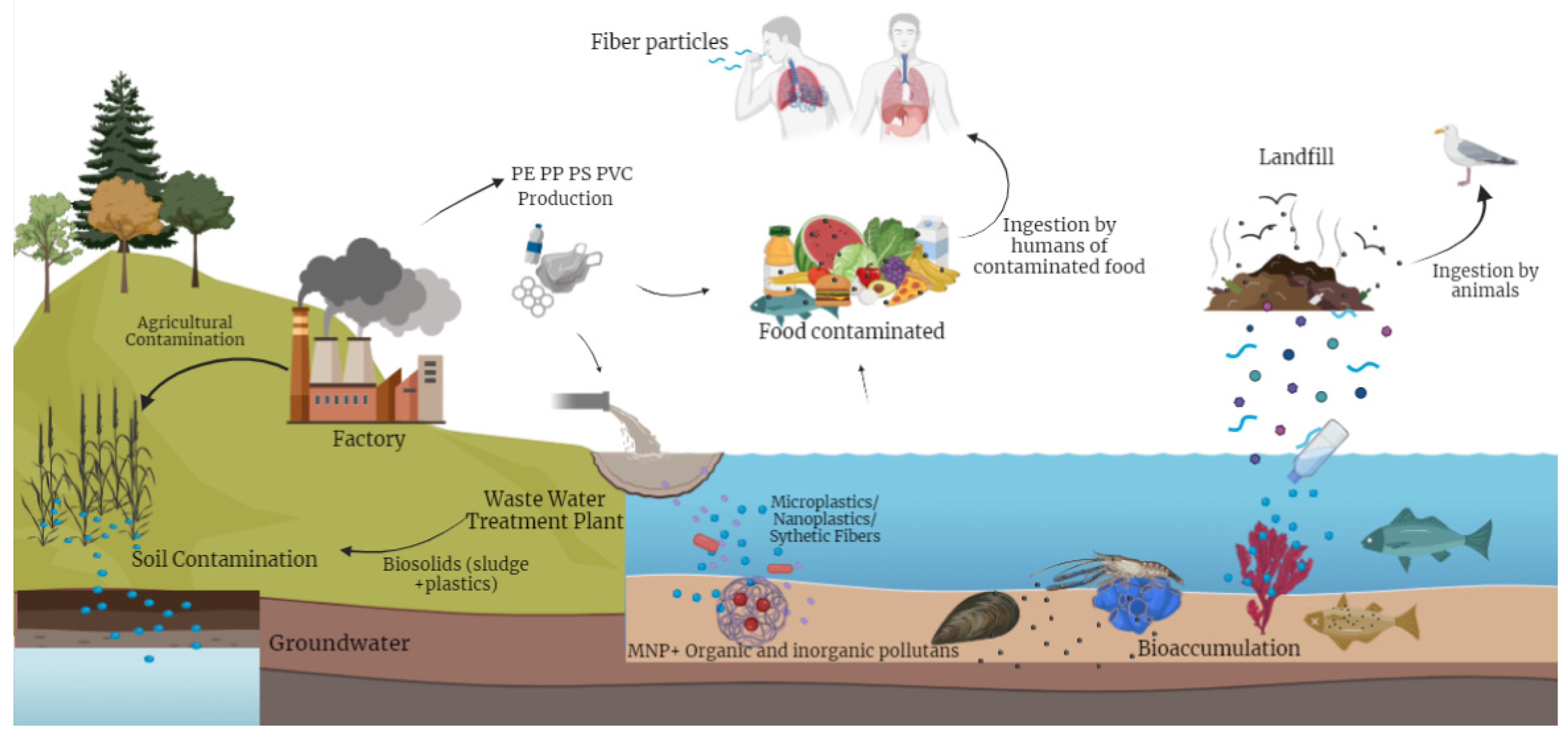
1. Introduction
2. Microplastics (MPs), Biodegradable Microplastics (BMPs), and Nanoplastics (NPs)
2.1. Additives in Microplastics
| Function | Substance Name | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Light stabilizers | Resorcinol | |
| Octabenzone | 0.2–5.0 | |
| 2-(2H-benzotriazol-2-yl)-4,6-bis(1-methyl-1-phenylethyl)phenol | 0.2–5.0 | |
| N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-N′-(2-ethylphenyl)oxamide | 0.7 | |
| Nucleating agents | Sodium benzoate | 0.2 |
| Fumes, silica (flame retardant) | n.a. | |
| 2,2′-Methylene bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl) sodium phosphate | 0.2 | |
| Antistatic | Sodium acetate | n.a. |
| Zinc oxide | 5 | |
| Disodium tetraborate, anhydrous | 5 | |
| Phosphoric acid, dodecyl ester, potassium salt | n.a | |
| Heat stabilizers | Dibutyltin dilaurate | 3 |
| Triphenyl phosphite | 3 | |
| Pentalead tetraoxide sulphate | 2 | |
| Diisodecyl phenyl phosphite | 3 | |
| Antioxidants | 6,6′-Di-tert-butyl-4,4′-butylidenedi-m-cresol | 0.5 |
| 6,6′-di-tert-butyl-4,4′-thiodi-m-cresol | n.a | |
| Dioctadecyl 3,3′-thiodipropionate | 0.25–3.0 | |
| 2,4-Bis(octylthiomethyl)-6-methylphenol | 0.015–0.2 | |
| Pigments agents | Perylene-3,4:9,10-tetracarboxydiimide | 2 |
| Chromium (III) oxide | 1 | |
| Zinc sulphide | 2.0–10.0 | |
| Carbon black | 2.5–40.0 | |
| 2,9-Dichloro-5,12-dihydroquino[2,3-b]acridine-7,14-dione | 2 | |
| Flame retardants | Triethyl phosphate | 10 |
| Melamine | 25 | |
| Cyanuric acid | n.a. | |
| Diantimony trioxide | 8 | |
| Aluminum sodium tetrahydroxide | n.a. | |
| Plasticizers | Tributyl-O-acetyl citrate | 10.0–35.0 |
| Triethyl citrate | 10.0–35.0 | |
| 2,2′-Ethylenedioxydiethyl bis(2-ethylhexanoate) | n.a. | |
| Triphenyl phosphate (flame retardant) | 2 | |
| Amides, C16-C18 (even), N,N′-ethylenebis | 1 |
2.2. Other Contaminants Adhered to Microplastics
2.3. Methods to Extract, Identify, and Quantify Microplastics
2.4. Presence and Toxicity of Biodegradable MPs and Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Environment
2.5. Occurrence of MPs in Food
| Sample | Source | Digestion | Qualitative/Quantitative Analysis | Qualitative Info | Quantity Info | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bivalves: Ostrea. Denselamellosa Sinonovacula. Constricta | Xiangshan Bay, China | 10% KOH + 30% H2O2, 24 h at 60 °C | Optical/Microscope + μ-FTIR | Fiber. | 0.31 ± 0.10 0.21 ± 0.05 0.36 ± 0.07 (items/g) | [107] |
| Shrimp | Xiangshan Bay, China | 10% KOH + 30% H2O2, 24 h at 60 °C | Optical/Microscope + μ-FTIR | Fiber. | 0.25 ± 0.08 items/g | [107] |
| Fish: Konosirus punctatus Larimichthys crocea | Xiangshan Bay, China | 10% KOH + 30% H2O2, 24 h at 60 °C | Optical/Microscope + μ-FTIR | Fiber. | 0.044 ± 0.025 0.008 ± 0.006 items/g | [107] |
| Fish | Bangladesh | 10% KOH, 72 h at 40 °C | Optical/Microscope | Mostly fiber (50%), fragment (15%), and line (12%). Mostly 300 to 1500 μm. Most colors were transparent (30%), gray (26%) and black (23%). | 7 to 51 particles/fish | [108] |
| Fish | Iran | 10% KOH, 48 h at 60 °C | Optical/Microscope + Staining and Fluorescence Microscope + SEM-EDX | Mainly fibers followed by fragments and synthetic microbeads. Mostly <500 μm in light colors. | 11.4 MP items per fish | [109] |
| Fish | Pakistan | 10% H2O2 overnight at 60 °C | Optical/Microscope | Microfibers and microfragments. | ~6.62 items/individual | [110] |
| Salted and dried fish | West coast of India | Mostly Nitric acid (69 %) or sodium hydroxide (10 %) or hydrogen peroxide (30 %) 72 h at 60 °C | Optical/Microscope + Staining + μ-FT-IR | Mostly <100 μm 47.21 %) and by 100–250 μm size group (23.98 %). Mostly fragments and fibers. Mostly translucent and black. | 35.57 ± 10.4 to 61.20 ± 21.8 items/g of dried fish | [111] |
| Seafood varieties | Sri Lanka | 30% H2O2 24–48 h at 65 °C | Optical/Microscope + Staining + m-FT-IR | Mostly LDPE, PP, HDPE, Nylon-66, and PS. Mostly fibers (52%) and fragments (19%). Mostly blue (69%) and black (17%). | 0.04 ± 0.02 MP/g to 1.8 ± 0.21 MPs/g | [112] |
| Eggs | 10% H2O2 12/24/48 h at 60 °C | Optical/Microscope + Fluorescence + ATR-FT-IR + FESEM-EDX | Spherical and 50–100 μm. | 11.67 ± 3.98 particles/egg | [113] | |
| Seaweed | Korea | 35% H2O2 72–120 h | Optical/Microscope + FT-IR | Mostly PP and PE, mostly 20–99 μm. | 0.20 to 14.30 particles/g | [114] |
| Honey | Korea | Ethanol and H2O2 | Optical/Microscope + FT-IR | Mostly PP and PE, mostly 20–99 μm. | n. d. to 46.0 particles/L | [114] |
| Infant milk powder: boxed and canned | China, the Netherlands, Ireland, China, Switzerland, France, and New Zealand | Artificial gastric juice for 3 h at 37 °C | FT-IR | Mostly fragment and fibers. Mostly PE and PET. Average of 139 ± 343 μm and 193 ± 415 μm for boxed and canned, respectively. | 1 ± 1 to 11 ± 1 items/100 g | [103] |
| Soft drinks: PET and Tetra Pak bottles | Turkey | - | Optical/Microscope + FT–IR | Mostly PA and PET. Mostly 50–100 μm. Mostly fiber (60%) and fragment (34%). Mostly transparent (57%) and blue (28%). | 5 to 18 polymers/sample | [115] |
| Beer | Korea | - | Optical/Microscope + FT-IT | Mostly PP and PE, mostly 20–99 μm. | 0.01 to 1.02 particles/g | [114] |
| Food ice cubes | Mexico City | 30% H2O2 1 h at 65 °C | Epifluorescence Optical/Microscope + SEM-EDX + ATR-FTIR | Fibers (87%), fragments (12.7%), and films (0.3%). Mostly PP and PE. | 19 ± 4 to 178 ± 78 items/L | [116] |
| Mineral water in PET bottles | Iran | - | Optical/Microscope + ATR-FTIR + Raman Microscopy | Mostly fragment (93%). Mostly PET, PS, and PE, 1280–4.200 μm. Mostly transparent, black. | 0 to 36 particles/L | [117] |
| Mineral water in PET bottles | China | - | Optical/Microscope + μ-FTIR + SEM | Mostly fiber and fragment. Mostly PET, PE, PS and PA. Mostly 0.050–0.300 mm. | 2 to 23 particles/bottle | [118] |
2.6. Trophic Transfer in the Food Chain
3. Presence in Humans and Health Impacts
4. Legislation and Initiatives
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Wang, B.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sui, Q.; Xu, D.; Qu, H.; Yu, G. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in domestic, industrial, agricultural and aquacultural wastewater sources: A case study in Changzhou, China. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, R.; Landrigan, P.J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Bathan, G.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Brauer, M.; Caravanos, J.; Chiles, T.; Cohen, A.; Corra, L.; et al. Pollution and health: A progress update. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e535–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurier, H.S.; Goddard, J.M. Biodegradation of microplastics in food and agriculture. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimoh, J.O.; Rahmah, S.; Mazelan, S.; Jalilah, M.; Olasunkanmi, J.B.; Lim, L.-S.; Ghaffar, M.A.; Chang, Y.M.; Bhubalan, K.; Liew, H.J. Impact of face mask microplastics pollution on the aquatic environment and aquaculture organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statista. Annual Production of Plastics Worldwide from 1950 to 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950/ (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- Plastics Europe. Plastics—The Facts 2021 An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data; Plastics Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Plastics Europe. Plastics—The Facts 2020. An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data; Plastics Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; 64p. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, I.; Simioni, C.; Varano, G.; Brenna, C.; Costanzi, E.; Neri, L.M. Legislation to limit the environmental plastic and microplastic pollution and their influence on human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, H.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Peters, R.J.B. Potential Health Impact of Environmentally Released Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Human Food Production Chain: Experiences from Nanotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8932–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif Lahimer, M.; Ayed, N.; Horriche, J.; Belgaied, S. Characterization of plastic packaging additives: Food contact, stability and toxicity. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1938–S1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Lambert, S. Freshwater Microplastics; The handbook of environmental chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- Mateos-Cárdenas, A.; van Pelt, F.N.A.M.; O’Halloran, J.; Jansen, M.A.K. Adsorption, uptake and toxicity of micro- and nanoplastics: Effects on terrestrial plants and aquatic macrophytes. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, S.; Yu, Y.; Xu, M. Effects of Microplastics on Higher Plants: A Review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Li, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ouyang, Z.; Guo, X. Review of the toxic effect of microplastics on terrestrial and aquatic plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Weert, S.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Diepens, N.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on the growth of sediment-rooted macrophytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zantis, L.J.; Carroll, E.L.; Nelms, S.E.; Bosker, T. Marine mammals and microplastics: A systematic review and call for standardisation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Liu, X.; Hou, Q.; Wang, Z. From natural environment to animal tissues: A review of microplastics(nanoplastics) translocation and hazards studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Pham, T.D.; Tarafdar, A.; Hong, S.; Chun, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, D.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.B.; et al. Microplastics in Food: A Review on Analytical Methods and Challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udovicki, B.; Andjelkovic, M.; Cirkovic-Velickovic, T.; Rajkovic, A. Microplastics in food: Scoping review on health effects, occurrence, and human exposure. Int. J. Food Contam. 2022, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Kannan, D.; Kapoor, A.; Prabhakar, S. Extraction and detection methods of microplastics in food and marine systems: A critical review. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercogliano, R.; Avio, C.G.; Regoli, F.; Anastasio, A.; Colavita, G.; Santonicola, S. Occurrence of Microplastics in Commercial Seafood under the Perspective of the Human Food Chain. A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5296–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-L.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.J.; Gowen, A.A. A review of potential human health impacts of micro- and nanoplastics exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Scherer, C.; Alvarez-Muñoz, D.; Brennholt, N.; Bourrain, X.; Buchinger, S.; Fries, E.; Grosbois, C.; Klasmeier, J.; Marti, T.; et al. Microplastics in freshwater ecosystems: What we know and what we need to know. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivleva, N.P.; Wiesheu, A.C.; Niessner, R. Microplastic in Aquatic Ecosystems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1720–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Liu, X.; Junaid, M.; Liao, H.; Chen, G.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J. Toxicological impacts of micro(nano)plastics in the benthic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigault, J.; Halle, A.T.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.-Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.-L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current opinion: What is a nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.; Pagter, E.; Nash, R.; O’Connor, I.; Carretero, O.; Filgueiras, A.; Viñas, L.; Gago, J.; Antunes, J.; Bessa, F. Standardised Protocol for Monitoring Microplastics in Sediments; Deliverable 4.2; JPI-Oceans BASEMAN Project: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.-F.; Li, J.-X.; Sun, C.-J.; He, C.-F.; Jiang, F.-H.; Gao, F.-L.; Zheng, L. Separation and Identification of Microplastics in Digestive System of Bivalves. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 46, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, E.H.; Pires, L.d.N.; Costa, L.C.; Passador, F.R.; Pessan, L.A. Analysis of the Degradation During Melt Processing of PLA/Biosilicate® Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, S.H.; Abdullah, L.C.; Aung, M.M.; Ratnam, C.T. Thermal and Structural Analysis of Epoxidized Jatropha Oil and Alkaline Treated Kenaf Fiber Reinforced Poly(Lactic Acid) Biocomposites. Polymers 2020, 12, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordanskii, A.L.; Bychkova, A.V.; Gumargalieva, K.Z.; Berlin, A.A. Chapter 6—Magnetoanisotropic biodegradable nanocomposites for controlled drug release. In Nanobiomaterials in Drug Delivery; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 171–196. [Google Scholar]
- Omnexus. BIOCYCLE® 1000 Technical Datasheet. Available online: https://omnexus.specialchem.com/product/t-phb-industrial-biocycle-1000 (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Crossman, J.; Hurley, R.R.; Futter, M.; Nizzetto, L. Transfer and transport of microplastics from biosolids to agricultural soils and the wider environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, X.; Su, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Kolandhasamy, P.; Li, D.; Shi, H. Microplastics in mussels along the coastal waters of China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Microplastics in commercial bivalves from China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbetts, J.; Krause, S.; Lynch, I.; Sambrook Smith, G.H. Abundance, Distribution, and Drivers of Microplastic Contamination in Urban River Environments. Water 2018, 10, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, M.; Rathod, T.D.; Ajmal, P.Y.; Bhangare, R.C.; Sahu, S.K. Distribution and characterization of microplastics in beach sand from three different Indian coastal environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-González, V.; Andrade-Garda, J.M.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. Impact of weathering on the chemical identification of microplastics from usual packaging polymers in the marine environment. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1142, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyt, A.S.; Malik, S.S. 16—Can Biodegradable Plastics Solve Plastic Solid Waste Accumulation? In Plastics to Energy, Al-Salem, S.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 403–423. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, P.; Yu, H.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. A review on the occurrence and influence of biodegradable microplastics in soil ecosystems: Are biodegradable plastics substitute or threat? Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wen, X.; Tang, W. Are biodegradable plastics a promising solution to solve the global plastic pollution? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashter, S.A. Overview of biodegradable polymers. In Introduction to Bioplastics Engineering; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, P.; Mehrotra, S.; Priya, S.; Gnansounou, E.; Sharma, S.K. Recent advances in the sustainable design and applications of biodegradable polymers. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Chen, C.; Song, B.; Shen, M.; Cao, W.; Yang, H.; Zeng, G.; Gong, J. A review of biodegradable plastics to biodegradable microplastics: Another ecological threat to soil environments? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Yaqoob, M.; Aggarwal, P. An overview of biodegradable packaging in food industry. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Sanahuja, A.; Benito-Kaesbach, A.; Sánchez-García, N.; Sanz-Lázaro, C. Degradation of conventional and biobased plastics in soil under contrasting environmental conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Chen, Q. Biodegradable plastics in the air and soil environment: Low degradation rate and high microplastics formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Sze-Yin Leung, K.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging contaminants: A One Health perspective. The Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Santos-Echeandía, J.; Rocha-Santos, T. Significance of interactions between microplastics and POPs in the marine environment: A critical overview. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Ji, H.; Wu, X.; Li, N.; Yang, Y.; Bu, J.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, L.; Yu, H.; Xu, N.; et al. Detection and quantification analysis of chemical migrants in plastic food contact products. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoueson, F.; Chbib, C.; Brémard, A.; Monchy, S.; Paul-Pont, I.; Doyen, P.; Dehaut, A.; Duflos, G. Identification of plastic additives: Py/TD-GC-HRMS method development and application on food containers. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 168, 105745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, Q.; Yuan, M.; Lu, S. Discovery of 18 Organophosphate Esters and 3 Organophosphite Antioxidants in Food Contact Materials Using Suspect and Nontarget Screening: Implications for Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 17870–17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambolino, A.; Iniguez, E.; Herrera, I.; Kaufmann, M.; Dinis, A.; Cordeiro, N. Microplastic ingestion and plastic additive detection in pelagic squid and fish: Implications for bioindicators and plastic tracers in open oceanic food webs. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Yang, L.; Huang, D.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, D. Contamination of Baby Foods by Plastic Additives: A Pilot Screening Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.A.; André, L.C.; Cardeal, Z.d.L. Analysis of plasticiser migration to meat roasted in plastic bags by SPME–GC/MS. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Holderbeke, M.; Geerts, L.; Vanermen, G.; Servaes, K.; Sioen, I.; De Henauw, S.; Fierens, T. Determination of contamination pathways of phthalates in food products sold on the Belgian market. Environ. Res. 2014, 134, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, E.; Cirillo, T.; Esposito, F.; Lacorte, S. Migration of monomers and plasticizers from packed foods and heated microwave foods using QuEChERS sample preparation and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O. Commercial beers: A source of phthalates and di-ethylhexyl adipate. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnol, L.; Schummer, C.; Moris, G. Quantification of Six Phthalates and One Adipate in Luxembourgish Beer Using HS-SPME-GC/MS. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Hernández, C.; Ortega-Zamora, C.; González-Sálamo, J.; Hernández-Borges, J. Determination of phthalic acid esters and di(2-ethylhexyl) adipate in coffee obtained from capsules. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Toni, L.; Tisato, F.; Seraglia, R.; Roverso, M.; Gandin, V.; Marzano, C.; Padrini, R.; Foresta, C. Phthalates and heavy metals as endocrine disruptors in food: A study on pre-packed coffee products. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.L.G.; Ferreira, G.O.; Suquila, F.A.C.; de Almeida, F.G.; Bertoldo, L.A.; Segatelli, M.G.; Ribeiro, E.S.; Tarley, C.R.T. Development of new analytical method for preconcentration/speciation of inorganic antimony in bottled mineral water using FIA-HG AAS system and SiO2/Al2O3/SnO2 ternary oxide. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneado, S.; Hernández-Nataren, E.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A. Migration of antimony from polyethylene terephthalate used in mineral water bottles. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Chemicals Agency. Mapping Exercise—Plastic Additives Initiative. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/mapping-exercise-plastic-additives-initiative (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Gallo, F.; Fossi, C.; Weber, R.; Santillo, D.; Sousa, J.; Ingram, I.; Nadal, A.; Romano, D. Marine litter plastics and microplastics and their toxic chemicals components: The need for urgent preventive measures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.H.; Alvarez, G.; Pozo, K.; Pribylova, P.; Klanova, J.; Rodríguez Pirani, L.S.; Picone, A.L.; Alvarez, M.; Tombesi, N. Beached microplastics at the Bahia Blanca Estuary (Argentina): Plastic pellets as potential vectors of environmental pollution by POPs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkanorachaki, K.; Kiparissis, S.; Kalogerakis, G.C.; Yiantzi, E.; Psillakis, E.; Kalogerakis, N. Plastic pellets, meso- and microplastics on the coastline of Northern Crete: Distribution and organic pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Tenebe, I.T.; Ayejuyo, O.O.; Benson, N.U. Microplastics and associated organic pollutants in beach sediments from the Gulf of Guinea (SE Atlantic) coastal ecosystems. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Bhagwat, G.; Oluyoye, I.; Benson, N.U.; Ayejuyo, O.O.; Palanisami, T. Interaction of chemical contaminants with microplastics: Principles and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gateuille, D.; Naffrechoux, E. Transport of persistent organic pollutants: Another effect of microplastic pollution? WIREs Water 2022, 9, e1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabianca, S.; Capellacci, S.; Giacobbe, M.G.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Tartaglione, L.; Varriale, F.; Narizzano, R.; Risso, F.; Moretto, P.; Dagnino, A.; et al. Plastic-associated harmful microalgal assemblages in marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinho, S.D.; Fernandes, V.C.; Figueiredo, S.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Study of the Potential Accumulation of the Pesticide Alpha-Endosulfan by Microplastics in Water Systems. Polymers 2022, 14, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.K.; Naik, M.M.; D’Costa, P.M.; Shaikh, F. Microplastics in ballast water as an emerging source and vector for harmful chemicals, antibiotics, metals, bacterial pathogens and HAB species: A potential risk to the marine environment and human health. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Luan, Y.; Dai, W. Adsorption behavior of organic pollutants on microplastics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 217, 112207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Chen, G.; Bao, J.; Song, M.; Li, Y.; Luo, C. Interactions between microplastics and organic compounds in aquatic environments: A mini review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lo, H.-S.; Wong, H.-M.; Zhou, M.; Wong, C.-Y.; Tam, N.F.-Y.; Cheung, S.-G. Heavy metals contamination of sedimentary microplastics in Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Martínez, I.E.; Shruti, V.C. Overview of microplastics pollution with heavy metals: Analytical methods, occurrence, transfer risks and call for standardization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Dueñas-Moreno, J.; Mahlknecht, J. Microplastics as a vector of arsenic contamination. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 33, 100461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Ayejuyo, O.O.; Tenebe, I.T.; Benson, N.U. Occurrence and distribution of micro(meso)plastic-sorbed heavy metals and metalloids in sediments, Gulf of Guinea coast (SE Atlantic). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, N.; Aqeel, M.; Noman, A.; Khan, S.M.; Akhter, N. Interactions and effects of microplastics with heavy metals in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Guo, M.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X. Adsorption of antibiotics on different microplastics (MPs): Behavior and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 161022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavelli, R.; Callens, M.; Grootaert, C.; Abdallah, M.F.; Rajkovic, A. Foodborne pathogens in the plastisphere: Can microplastics in the food chain threaten microbial food safety? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.-L.; Liu, L.-Y.; Hu, Y.-B.; Zeng, E.Y.; Guo, Y. Microplastics: A review of analytical methods, occurrence and characteristics in food, and potential toxicities to biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivleva, N.P. Chemical Analysis of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: Challenges, Advanced Methods, and Perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11886–11936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. Simultaneous Trace Identification and Quantification of Common Types of Microplastics in Environmental Samples by Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5052–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbumani, S.; Kakkar, P. Ecotoxicological effects of microplastics on biota: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14373–14396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbery, M.; O’Connor, W.; Palanisami, T. Trophic transfer of microplastics and mixed contaminants in the marine food web and implications for human health. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, S.D.; Fernandes, V.C.; Figueiredo, S.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Microplastic Pollution Focused on Sources, Distribution, Contaminant Interactions, Analytical Methods, and Wastewater Removal Strategies: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Leng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Microplastic pollution in vegetable farmlands of suburb Wuhan, central China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C. Microplastics in soil: A review on methods, occurrence, sources, and potential risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Kumar, A.; Neale, P.A.; Leusch, F.D.L. Environmentally relevant concentrations of polyethylene microplastics negatively impact the survival, growth and emergence of sediment-dwelling invertebrates. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Vimalkumar, K. A Review of Human Exposure to Microplastics and Insights Into Microplastics as Obesogens. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 724989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senathirajah, K.; Attwood, S.; Bhagwat, G.; Carbery, M.; Wilson, S.; Palanisami, T. Estimation of the mass of microplastics ingested—A pivotal first step towards human health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-N.; Wen, B.; Zhu, J.-G.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Gao, J.-Z.; Chen, Z.-Z. Exposure to microplastics impairs digestive performance, stimulates immune response and induces microbiota dysbiosis in the gut of juvenile guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 138929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bao, Z.; Wan, Z.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastic exposure disturbs hepatic glycolipid metabolism at the physiological, biochemical, and transcriptomic levels in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde-Velázquez, G.A.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M. Microplastics in aquatic environments: A review on occurrence, distribution, toxic effects, and implications for human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, X.; Pelaez, A.M.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Beriot, N.; Gertsen, H.; Garbeva, P.; Geissen, V. Macro- and micro- plastics in soil-plant system: Effects of plastic mulch film residues on wheat (Triticum aestivum) growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, C.; Peters, R.J.B.; Janssen, H.-G.; Nielen, M.W.F. Microplastics and nanoplastics in food, water, and beverages; part I. occurrence. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 159, 116670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cverenkárová, K.; Valachovičová, M.; Mackuľak, T.; Žemlička, L.; Bírošová, L. Microplastics in the Food Chain. Life 2021, 11, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Rao, W.; Qian, X. Microplastics in infant milk powder. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, L.M.; Xu, E.G.; Larsson, H.C.E.; Tahara, R.; Maisuria, V.B.; Tufenkji, N. Plastic Teabags Release Billions of Microparticles and Nanoparticles into Tea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12300–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Shi, H. Microplastics in take-out food containers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 122969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, Y.Y.; Weston, K.; Suratman, S. The effect of storage conditions and washing on microplastic release from food and drink containers. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 32, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Leung, J.Y.S.; Huang, W.; Zeng, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, A.; Yu, X.; Xu, X.; et al. Accumulation of microplastics in typical commercial aquatic species: A case study at a productive aquaculture site in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.A.M.; Uddin, A.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Rahman, M.; Islam, M.S.; Kibria, G. Microplastics in an anadromous national fish, Hilsa shad Tenualosa ilisha from the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh Rahmat Abadi, Z.; Abtahi, B.; Grossart, H.P.; Khodabandeh, S. Microplastic content of Kutum fish, Rutilus frisii kutum in the southern Caspian Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaiser, N.; Sidra, S.; Javid, A.; Iqbal, A.; Amjad, M.; Azmat, H.; Arooj, F.; Farooq, K.; Nimra, A.; Ali, Z. Microplastics abundance in abiotic and biotic components along aquatic food chain in two freshwater ecosystems of Pakistan. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukmangada, R.; Naidu, B.C.; Nayak, B.B.; Balange, A.; Chouksey, M.K.; Xavier, K.A.M. Microplastic contamination in salted and sun dried fish and implications for food security—A study on the effect of location, style and constituents of dried fish on microplastics load. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeyaya, K.B.K.D.K.; Ranatunga, S.; Ranatunga, R.R.M.K.P. Occurrence of microplastics in some commercially important seafood varieties from Negombo, Sri Lanka. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 62, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Yao, W.; Xie, Y. Microplastics contamination in eggs: Detection, occurrence and status. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, D.T.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Hong, S.; Jung, J.; Kwon, J.-H. Analysis of microplastics in various foods and assessment of aggregate human exposure via food consumption in korea. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunışık, A. Prevalence of microplastics in commercially sold soft drinks and human risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.C.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Roy, P.D.; Elizalde-Martínez, I. First evidence of microplastic contamination in ready-to-use packaged food ice cubes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhdoumi, P.; Amin, A.A.; Karimi, H.; Pirsaheb, M.; Kim, H.; Hossini, H. Occurrence of microplastic particles in the most popular Iranian bottled mineral water brands and an assessment of human exposure. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-J.; Wang, J.; Li, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-M.; Hua, J.; Zhang, D.L. Microplastic pollution of bottled water in China. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, S.N.; Albotra, S.D.; Gordon, C.A.; Monteleone, B.; Seaton, P.; Andrady, A.L.; Taylor, A.R.; Brander, S.M. Trophic transfer of microplastics in an estuarine food chain and the effects of a sorbed legacy pollutant. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2020, 5, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.W.; An, Y.-J. Trophic transfer and individual impact of nano-sized polystyrene in a four-species freshwater food chain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton-Howard, H.S.; Bond, A.L.; Rivers-Auty, J.; Lavers, J.L. ‘Plasticosis’: Characterising macro- and microplastic-associated fibrosis in seabird tissues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 131090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauly, J.L.; Stegmeier, S.J.; Allaart, H.A.; Cheney, R.T.; Zhang, P.J.; Mayer, A.G.; Streck, R.J. Inhaled cellulosic and plastic fibers found in human lung tissue. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1998, 7, 419–428. [Google Scholar]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Notarstefano, V.; Svelato, A.; Belloni, A.; Gioacchini, G.; Blondeel, C.; Zucchelli, E.; De Luca, C.; D’Avino, S.; Gulotta, A.; et al. Raman Microspectroscopy Detection and Characterisation of Microplastics in Human Breastmilk. Polymers 2022, 14, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Weng, J.; Jin, Z.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z. Detection and characterization of microplastics in the human testis and semen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotchell, J.M.; Jenner, L.C.; Chapman, E.; Bennett, R.T.; Bolanle, I.O.; Loubani, M.; Sadofsky, L.; Palmer, T.M. Detection of microplastics in human saphenous vein tissue using μFTIR: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, E.; Du, Z.; Peng, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, R.; Qin, Y.; Xue, M.; Li, F.; et al. Detection of Various Microplastics in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10911–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageel, H.K.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E. Occurrence, human exposure, and risk of microplastics in the indoor environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, T.; Cui, W.; Qi, X.; Xu, S. Combined negative effects of microplastics and plasticizer DEHP: The increased release of Nets delays wound healing in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengchen, W.; Jing, L.; Yujie, Y.; Yue, W.; Shiwen, X. Polystyrene microplastics-induced ROS overproduction disrupts the skeletal muscle regeneration by converting myoblasts into adipocytes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 125962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene microplastics cause cardiac fibrosis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.; Jeong, J.; Song, K.S.; Sung, J.H.; Oh, S.M.; Choi, J. Inhalation toxicity of polystyrene micro(nano)plastics using modified OECD TG 412. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lemos, B.; Ren, H. Tissue accumulation of microplastics in mice and biomarker responses suggest widespread health risks of exposure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, L.; Tu, W.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z. Impacts of polystyrene microplastic on the gut barrier, microbiota and metabolism of mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, D.; Xiao, F. Keap1-Nrf2 pathway up-regulation via hydrogen sulfide mitigates polystyrene microplastics induced-hepatotoxic effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Yuan, G.-H.; Jiang, B.-R.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Lv, H.-J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.-L.; Wu, Q.; Li, L. Effects of microplastics (MPs) and tributyltin (TBT) alone and in combination on bile acids and gut microbiota crosstalk in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Tian, Y.; Li, M.H.; Feng, Y.Q.; Kong, L.; Zhang, F.L.; Shen, W. Single-cell transcriptome dissection of the toxic impact of Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on primordial follicle assembly. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4992–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.; Latendresse, J.R.; Muskhelishvili, L.; Law, C.D.; Delclos, K.B. Effects of intravenous and oral di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) and 20% Intralipid vehicle on neonatal rat testis, lung, liver, and kidney. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 144, 111497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, T.; Li, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Qin, L.; Chen, R.; Gu, W.; et al. Lipidomics and transcriptomics insight into impacts of microplastics exposure on hepatic lipid metabolism in mice. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Yan, M.; Pan, C.; Liu, Z.; Sha, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, L.; Pan, M.; Li, D.; Han, X.; et al. Chronic exposure to polystyrene microplastics induced male reproductive toxicity and decreased testosterone levels via the LH-mediated LHR/cAMP/PKA/StAR pathway. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Reproductive toxicity of polystyrene microplastics: In vivo experimental study on testicular toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Gonzalez-Gil, G.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Li, Z. Effects of nano- and microplastics on kidney: Physicochemical properties, bioaccumulation, oxidative stress and immunoreaction. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Shen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Maternal exposure to different sizes of polystyrene microplastics during gestation causes metabolic disorders in their offspring. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Shen, L.; Ye, X.; Bai, G.; Liao, C.; Chen, Z.; Peng, T.; Li, X.; Kang, X.; An, G. Prenatal and postnatal exposure to polystyrene microplastics induces testis developmental disorder and affects male fertility in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, R.; Bonilla, M.M.; Yang, X.; Ren, H.; Lemos, B. Evidence that microplastics aggravate the toxicity of organophosphorus flame retardants in mice (Mus musculus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Araújo, A.P.; Malafaia, G. Microplastic ingestion induces behavioral disorders in mice: A preliminary study on the trophic transfer effects via tadpoles and fish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce hepatotoxicity and disrupt lipid metabolism in the liver organoids. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Size-dependent effects of polystyrene microplastics on cytotoxicity and efflux pump inhibition in human Caco-2 cells. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Halimu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Fu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Internalization and toxicity: A preliminary study of effects of nanoplastic particles on human lung epithelial cell. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.-D.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Lin, C.-H. Polystyrene microplastic particles: In vitro pulmonary toxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lu, T.-H.; Liao, C.-M. Toxicity-based toxicokinetic/toxicodynamic assessment for bioaccumulation of polystyrene microplastics in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, V.; Laurisch, C.; Franke, J.; Dönmez, M.H.; Voss, L.; Böhmert, L.; Braeuning, A.; Sieg, H. Uptake and cellular effects of PE, PP, PET and PVC microplastic particles. Toxicol. Vitr. 2021, 70, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Weng, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y. Microplastic: A potential threat to human and animal health by interfering with the intestinal barrier function and changing the intestinal microenvironment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Resolution Adopted by the General Assembly on 25 September 2015, 42809, 1–13. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/generalassembly/docs/globalcompact/A_RES_70_1_E.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- UNEP. ommitting to end plastic pollution, U.S. and European Commission join Clean Seas Campaign. 2022, United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi/Lisbon. Available online: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/press-release/committing-end-plastic-pollution-us-and-european-commission-join (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Halfar, J.; Brožová, K.; Čabanová, K.; Heviánková, S.; Kašpárková, A.; Olšovská, E. Disparities in Methods Used to Determine Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment: A Review of Legislation, Sampling Process and Instrumental Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, R.J. Using legislation to reduce one-time plastic bag usage. Econ. Aff. 2018, 38, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union Commission. Plastics Strategy. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/strategy/plastics-strategy_en (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- European Union Commission. Circular Economy: Commission Takes Action to Reduce Waste from Single-Use Plastics; European Union Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2022.
- Union, E. Commission Delegated Decision (EU) 2024/1441 of 11 March 2024 supplementing Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the Euripean Parliament and of the Council by laying down a methodology to measure microplastics in water intended for human consumption. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dec_del/2024/1441/oj (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Zhou, Y.; Ashokkumar, V.; Amobonye, A.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Sirohi, R.; Singh, V.; Flora, G.; Kumar, V.; Pillai, S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Current research trends on cosmetic microplastic pollution and its impacts on the ecosystem: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, A.A.; Prasetya, T.A.E.; Dewi, I.R.; Ahmad, M. Microplastics in human food chains: Food becoming a threat to health safety. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Microplastic Polymer | Density (g/cm3) | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Applications | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | 0.90–0.99 | 30,000–50,000 | Plastic bags, straws | [20] | |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 0.85–0.95 | ~67,000 | Bottle caps, netting | [20] | |
| Polystyrene (PS) | 0.95–1.1 | 1,00,000–4,00,000 | Food containers, foam cups | [20] | |
| Polyamide (PA) | 1.02–1.15 | 224.3 | Trap netting | [20] | |
| Polyester (PES) | 1.38 | 4000 | Clothes, fibers | [20] | |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | 1.1–1.58 | ~99,000 | Plastic films, cups | [20] | |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | 1.38–1.45 | 222.24 | Bottles | [20] | |
| Polylactic acid (PLA) | Biopolymers | 1.24 | 120,000 | Biomedicine | [31,32] |
| Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (P3HB) | 1.248 | 206,000 | Biotechnology, biomedicine | [33] | |
| Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) | 1.20 | 600,000 | Veterinary, flasks, pens | [34] |
| Model | Material Evaluated | Concentration | Size | Exposure | Health Impact | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mice | MPs and di (2-ethyl) hexyl phthalate (DEHP) | 0.1 g/L (MP/MP + DEHP); 200 µm/Kg DEHP | 1–10 µm | 1 week | Delayed skin healing. | [130] |
| Mice | Polystyrene MPs | 10 mg/L | 1–10 µm and 50–100 µm | 30 days | Delayed skeletal muscle regeneration. | [131] |
| Rats | Polystyrene MPs | 0.5 mg/L; 5 mg/L and 50 mg/L | 0.5 µm | 90 days | Damage on the muscle cardiac structure, apoptosis of myocardium and cardiac fibrosis. | [132] |
| Rats | Polystyrene MPs | 0.1% | 0.10 µm | 14 days | Alterations observed on endpoints in physiological, serum biochemical, hematological, and respiratory function markers. | [133] |
| Mice | Polystyrene MPs | 100 and 1000 µg/L | 0.5 and 50 µm | 5 weeks | Decrease of the secretion of mucin in gut, induced gut microbiota dysbiosis, induced hepatic lipid metabolism disorder. | [134] |
| Mice | Polystyrene MPs | 0.1 mg/day | 5 µm and 20 µm | 28 days | Disturbance of energy and lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, alteration of blood biomarkers of neurotoxicity. | [135] |
| Mice | Polystyrene MPs | 100 and 1000 µg/L | 5 µm | 6 weeks | Intestinal barrier dysfunction, gut microbiota dysbiosis, bile acid metabolism disorder. | [136] |
| Mice | Polystyrene MPs | 0.1 mg/day | 5 µm | 30 days | Inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress, hepatic injury. | [137] |
| Mice | Tributyltin + microplastics | 0.1 mg/day | 5 µm | 33 days | Inflammation and apoptosis in epidermis. | [138] |
| Mice | Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) | 40 µ/Kg | - | 17.5 DPC (days post coitum) | Obstruction of follicle assembly progress and interference with their developmental status, increase in DNA damage, and apoptosis in germ cells and/or somatic cells. | [139] |
| Neonatal rats | Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) | 60, 300, or 600 mg/day | - | 21 days | Reductions in testis weight, germ cell and Sertoli cell toxicity, lung granulomas, inhibition of lung alveolar development | [140] |
| Mice | Polystyrene MPs | 100–1000 µg/L | 1 µm | 8 weeks | Impaired glucose tolerance and hepatic lipid deposition; alteration in hepatic lipid species. | [141] |
| Mice | Polystyrene MPs | 100 µg/L and 1000 µg/L | 0.5 µm, 4 µm, and 10 µm | 180 days | Alterations in testicular morphology and reductions in testosterone, LH, and FSH contents in serum, decline in sperm viability and increase in rate of sperm abnormality. | [142] |
| Mice | Polystyrene MPs | 100 µg/L, 1000 µg/L, and 10 mg/L | 5 µm | 35 days | Sperm quality decline, abnormal testicular spermatogenesis. | [143] |
| Mice | Polystyrene NP-MPs | 100 mg/mL | NPs: 50 nm; MPs: 300 nm, 600 nm and 4 µm | 4 weeks | Kidney inflammation, histological damage of kidney, mice weight loss, increase in death rate. | [144] |
| Pregnant mice | Polystyrene MPs | 100 µg/L and 1000 µg/L | 0.5 µm and 5 µm | Gestation period | Potential risk of fatty acid metabolism disorder in offspring. | [145] |
| Pregnant and postnatal mice | Polystyrene MPs | 0.5 mg/L, 5 mg/L, and 50 mg/L | 0.5 µm | 35 and 70 PND (post-natal days) | Testis development disorder and male subfertility, likely regulated by the Hippo signaling pathway and involving an immune reaction. | [146] |
| Mice | Polyethylene and polystyrene MPs and organophosphorus flame retardants (OPFRs) | 10 µg/L and 100 µg/L | 0.5–1.0 µm | 90 days | Coexposure to MPs and OPFRs increased oxidative stress, induced greater neurotoxicity, and enhanced disruption of amino acid metabolism and energy metabolism. | [147] |
| Mice | Polyethylene MPs | 500 mg/L | Different sizes and shapes (35.46 µm ± 18.17 µm) | 7 days | Impacted animal behavior: higher anxiety index, slower locomotion speed, lack of defensive social aggregation, and reduction in risk assessment behavior. | [148] |
| Human organoids | Polystyrene MPs | 0.25 µg/L, 2.5 µg/L, and 25 µg/L | 1 µm | 48 h | Hepatotoxicity and disruption of lipid metabolism in human pluripotent stem cell-derived liver organoids. | [149] |
| Human cells | Polystyrene MPs | 1 µg/L, 10 µg/L, 20 µg/L, 50 µg/L, 80 µg/L, and 200 µg/L | 0.1 µm and 5 µm | 12 h | Induction of higher mitochondrial depolarization in human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells. | [150] |
| Human cells | Polystyrene MPs | NP25: 30, 25,20, 15, 10, 5, and 2.5 µg/mL; NP70: 300, 220, 160, 100, 60, 30, and 10 µg/mL | NP: 25 nm and 70 nm | 2 h, 4 h, and 8 h | Affected the viability, apoptosis, and cell cycles of A549 human lung epithelial cells. | [151] |
| Human cells | Polystyrene MPs | 10 and 1000 µg/cm2 | 1.72 ± 0.26 µm | 24 and 48 h | Pulmonary cytotoxicity, pulmonary barrier impairment, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. | [152] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, J.G.R.d.; Augusto, H.C.; Ferraz, R.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Fernandes, V.C. Micro(nano)plastic and Related Chemicals: Emerging Contaminants in Environment, Food and Health Impacts. Toxics 2024, 12, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12100762
Carvalho JGRd, Augusto HC, Ferraz R, Delerue-Matos C, Fernandes VC. Micro(nano)plastic and Related Chemicals: Emerging Contaminants in Environment, Food and Health Impacts. Toxics. 2024; 12(10):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12100762
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Juliana G. R. de, Helga Coelho Augusto, Ricardo Ferraz, Cristina Delerue-Matos, and Virgínia Cruz Fernandes. 2024. "Micro(nano)plastic and Related Chemicals: Emerging Contaminants in Environment, Food and Health Impacts" Toxics 12, no. 10: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12100762
APA StyleCarvalho, J. G. R. d., Augusto, H. C., Ferraz, R., Delerue-Matos, C., & Fernandes, V. C. (2024). Micro(nano)plastic and Related Chemicals: Emerging Contaminants in Environment, Food and Health Impacts. Toxics, 12(10), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12100762










