A Comparison of Health Risks from PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Exposure in Industrial Complexes in Dangjin and Yeosu·Gwangyang
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurement Sites
2.2. Collection and Analysis of Data on Particle Composition and Concentration
2.3. Quality Assurance and Control
2.4. Health Risk Assessment
3. Results
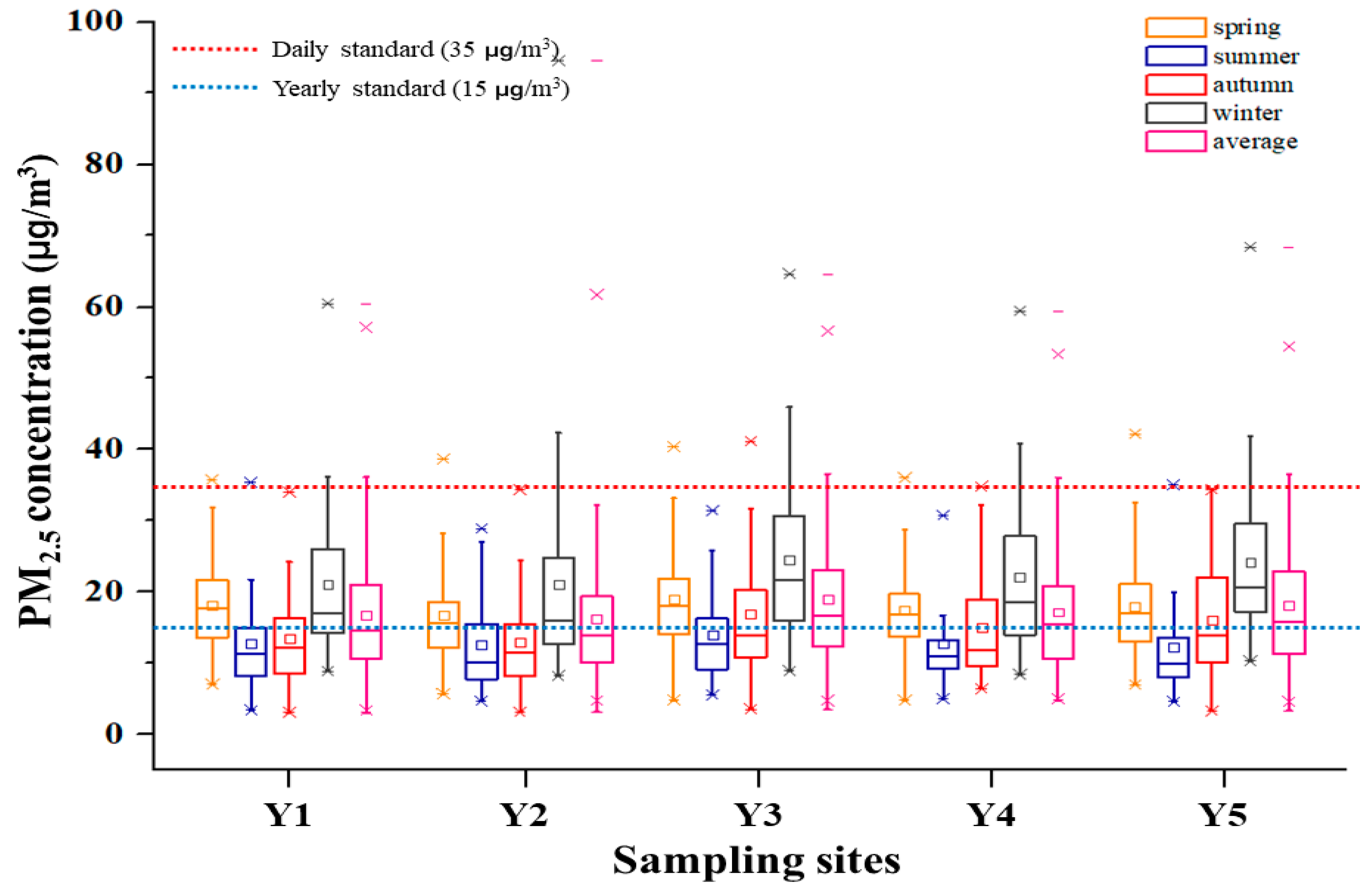
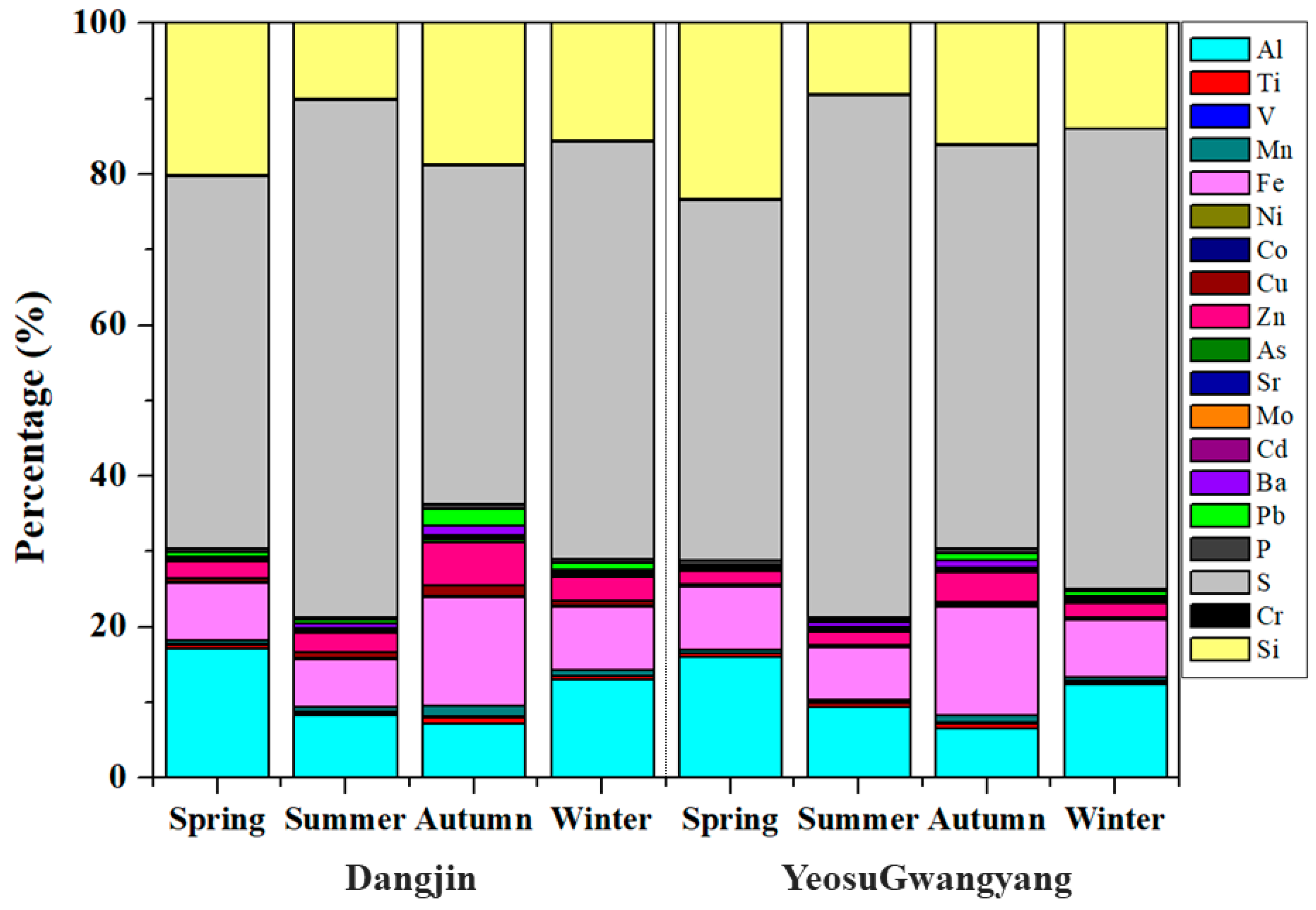
3.1. PM2.5 and Component Concentrations
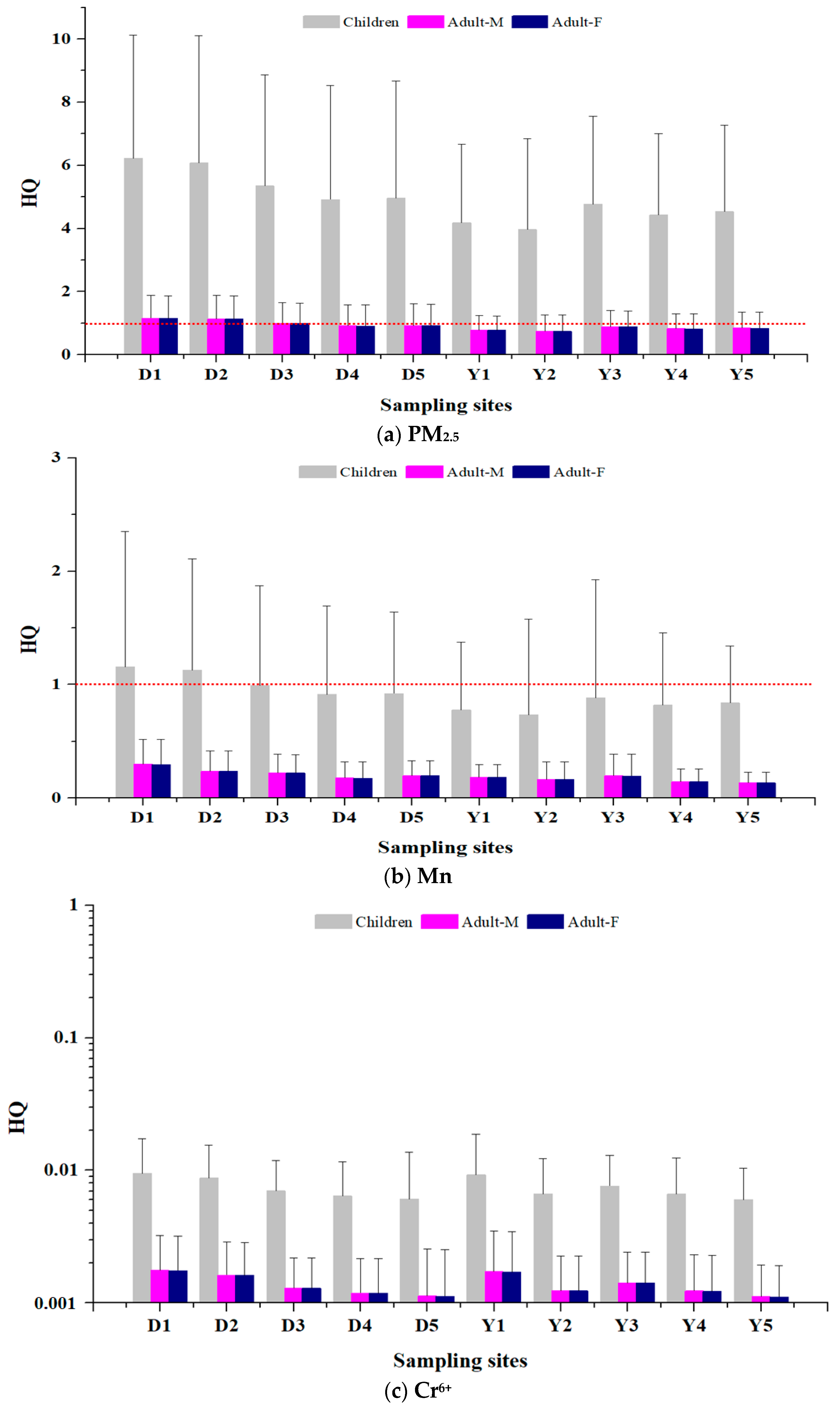
3.2. Health Risk Assessment for Non-Carcinogens
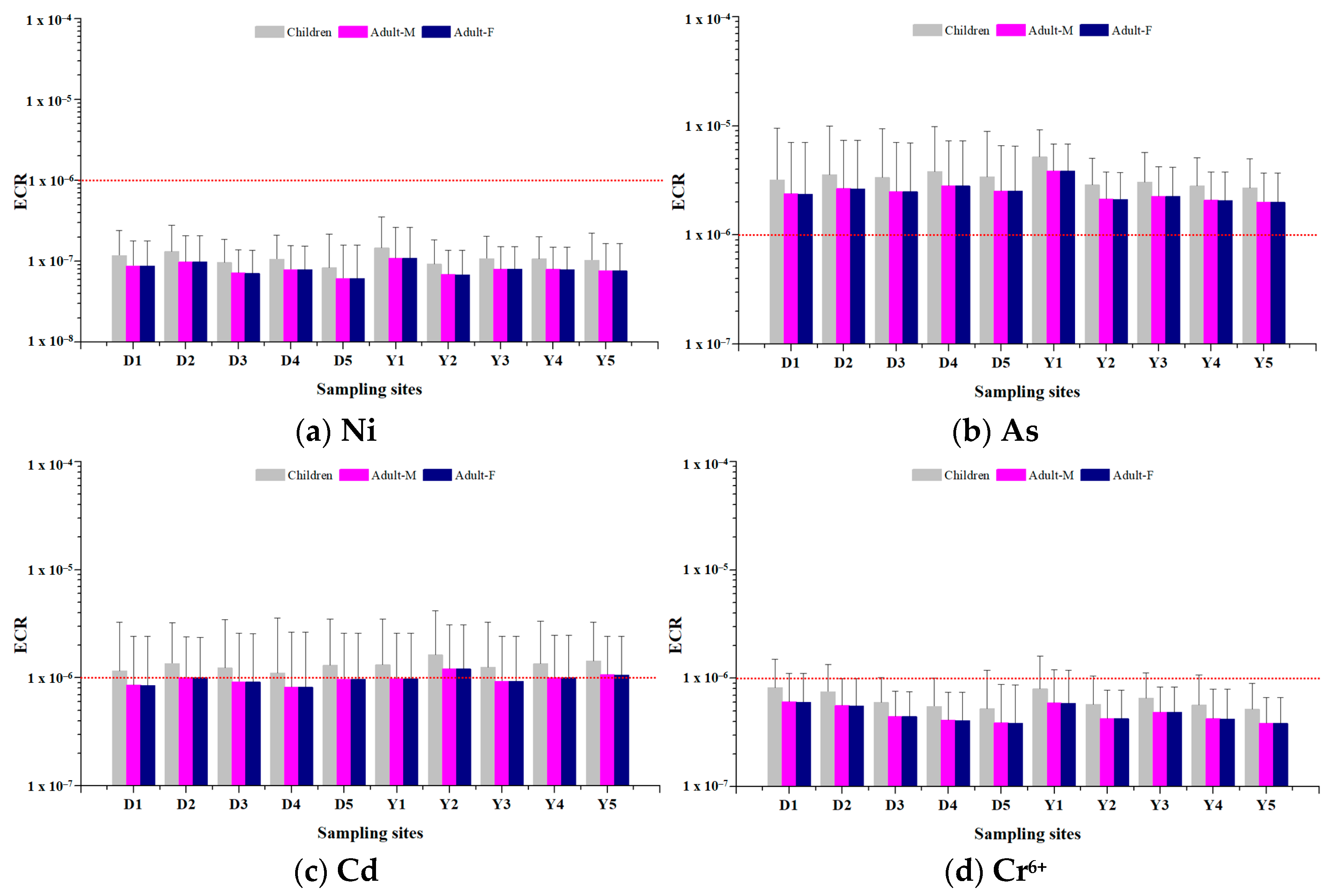
3.3. Health Risk Assessment for Carcinogens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gan, S.Y.; Bae, H.J. Assessing the health benefits of PM2.5 reduction using AirQ+ and BenMAP. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2023, 49, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, L.T.; Adebanjo, S.A.; Adeoye, B.K. Assessment of atmospheric particulate matter and heavy metals: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 15, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, M.K.; Cho, I.G.; Lee, H.Y.; Choi, S.D. Contamination characteristics of hazardous air pollutants in particulate matter in the atmospheric of Ulsan, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Anal. 2018, 21, 281–291. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.H.; Arafath, S.M.; Lee, K.T.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Han, Y.T. Chemical characteristics of filterable and condensable PM2.5 emissions from industrial boilers with five different fuels. Fuel 2018, 232, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B. Assessment and estimation of particulate matter formation potential and respiratory effects from air emission matters in industrial sectors and cities/regions. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2017, 39, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, R.B. The health impact of common inorganic components of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ambient air: A critical review. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 811–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chai, E. Research progress of different components of PM2.5 and ischemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Xu, X. Ambient PM2.5 human health effects-findings in China and research directions. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.K.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, J.S.; Oh, S.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Bae, M.S. Chemical characteristics and oxidation potential of PM1.0 at a suburban location in metropolitan areas. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 38, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expósito, A.; Markiv, B.; Ruiz-Azcona, L.; Santibáñez, M.; Fernández-Olmo, I. Understanding how methodological aspects affect the release of trace metal(loid)s from urban dust in inhalation bioaccessibility tests. Chemophere 2021, 267, 129181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Choi, J.H.; Park, M.K.; Son, B.S. Health risk assessment for heavy metal exposure in the living environment. J. Odor Indoor Environ. 2016, 15, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraufnagel, D.E.; Balmes, J.R.; Cowl, C.T.; De Matteis, S.; Jung, S.H.; Mortimer, K.; Wuebbles, D.J. Air pollution and noncommunicable diseases: A review by the forum of international respiratory societies’ environmental committee, Part 2: Air pollution and organ system. Chest 2019, 155, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.W.; Jeong, M.H.; Jeon, J.M.; Lee, H.S. The characteristics of PM.25 and acidic air pollutants in the vicinity of industrial complexes in Gwangyang. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 27, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- KOSIS, 2023 Korean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS). Available online: http://kosis.kr/index/index.do (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Korea Environment Corporation (KECO). Clean SYS. Available online: https://cleansys.or.kr/index.do#none (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Hwang, I.J.; Lee, T.J.; Kim, T.O.; Bae, G.N. Characteristics of air pollutant emissions and distribution for particulate matter concentration of air pollution networks in Gyeongsangbuk-do. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 37, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, J.B.; Cho, C.R.; Kim, S.H.; Song, M.J. An analysis of meteorological characteristics for fine particles on the Korean Peninsula during wintertime, 2015–2021. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 38, 394–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammuaylojaroen, T.; Parasin, N. Future health risk assessment of exposure to PM2. 5 in different age groups of children in Northern Thailand, Toxics 2023, 11, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Environmental Research. Korean Exposure Factors Handbook. Available online: https://ecolibrary.me.go.kr/nier/#/search/detail/5685463 (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- National Institute of Environmental Research. Korean Exposure Factors Handbook for Children. Available online: https://ecolibrary.me.go.kr/nier/#/search/detail/5685462 (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- KOSTAT, 2023 Korean Statistical Classification (KOSTAT). Available online: https://kostat.go.kr/ansk/ (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Jung, J.H.; Han, Y.J. Study on characteristics of PM2.5 and its ionic constituents in Chuncheon, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 24, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, H.W.; Han, Y.J.; Kim, W.J. Characteristics of fine particles measured in two different functional areas and identification of factors enhancing their concentrations. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 32, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.J.; Kim, T.O. Chemical characteristics of ambient PM2.5 at industrial complex in Gyeongbuk Area. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 35, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, K.C.; Kim, P.H.; Shin, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.B. Characteristics analysis of PM2.5 in industrial complex near area according to domestic and foreign influences in case of high concentration PM2.5 episode occurrence. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 39, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.Y.; Park, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, H.E.; Hong, Y.D.; Hong, J.H. The characteristics of element components in PM2.5 in Seoul and Daejeon. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Anal. 2015, 18, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.Y.; Oh, G.Y.; Park, H.S.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, B.R.; Park, C.O.; Bae, M.S. Assessment of regional source contribution of PM2.5 in the Gwangyang Bay Area. J. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2021, 24, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansha, M.; Ghauri, B.; Rahman, S.; Amman, A. Characterization and source apportionment of ambient air particulate matter (PM2.5) in Karachi. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Murari, V.; Kumar, M.; Barman, S.C.; Banergee, T. Fine particulates over South Asia: Review and meta-analysis of PM2.5 source apportionment through receptor model. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Meng, R.; Lei, Y.; Wu, S.; Jiang, Y. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals from PM2.5 in China’s 29 provincial capital cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 63028–63040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, G.G.; Kim, D.W.; Song, M.J. PM2.5 Concentrations and chemical compositions in Jeonju from 2017 to 2018. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 34, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.J.; Park, S.S. Temporal and spatial variabilities of concentrations of criteria air pollutants during early summer in 2018 in South Chungcheong Province. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 35, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.C.; Park, S.S.; Bae, M.A.; Kim, S.T. A study on characteristics of high PM2.5 pollution observed around large-scale stationary sources in Chungcheongnam-do Province. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 36, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Yoon, S.H.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, K.H.; Noh, S.J.; Bae, G.N. Spatial and temporal distributions of PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations in Chungcheongnam-do. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 36, 464–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C. Measurement methods to determine compliance with ambient air quality standards for suspended particles. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1995, 45, 320–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.W.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, K.M.; Seo, Y.K.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Baek, S.O. A study on the concentrations distribution of airborne heavy metals in major industrial complexes in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 34, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.Y.; Oh, S.H.; Song, M.K.; Jeon, H.J.; Yu, G.H.; Bae, M.S. Primary source apportionment of PM2.5 in the national steel industrial complex—Implication of PMF model (PART I). J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 39, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhou, H.; Fan, Z.; Lin, M.; Wu, D.; Xia, B. Characteristics, sources and health risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in PM2.5 at a megacity of southwest China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.S. High influential factor of cadmium and lead exposure in outdoor workers. J. Korean Soc. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2020, 30, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morakinyo, O.M.; Mukhola, M.S.; Mokgobu, M.I. Health risk analysis of elemental components of an industrially emitted respirable particulate matter in an urban area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Specifications for Analysis | |
|---|---|
| Angle between the X-ray tube and detector | 80 °C |
| Distance between SDD detector and sample | ≤15 mm |
| Distance between X-ray tube target and sample | ≤40 mm |
| X-ray generator voltage range | 4~50 kV |
| X-ray generator current range | 0~3.0 mA |
| Resolution | 140 eV@Mn Ka 100 kcps |
| Maximum | 1.5 Mcps |
| Window | 8 μm (0.315 mil) Beryllium |
| Pollutants | Non-Carcinogenic | Carcinogenic |
|---|---|---|
| RfC 1 (mg/m3) | Inhalation Unit Risk ((μg/m3)−1) | |
| PM2.5 | 0.015 | - |
| Mn | 5.00 × 10−5 | - |
| Ni | - | 2.40 × 10−4 |
| As | - | 4.30 × 10−3 |
| Cd | - | 1.80 × 10−3 |
| Cr6+ | 1.00 × 10−4 | 1.20 × 10−2 |
| Unit | Value for Age Categories | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Adult Men | Adult Women | |||
| IR 1 | m3/day | 12.73 | 16.21 | 13.03 | [19,20] |
| EF 2 | day/year | 365 | This study | ||
| ED 3 | year | 6 | 24 | 24 | This study |
| BW 4 | kg | 10.42 | 71.5 | 57.7 | [19,20] |
| AT 5 | day | 2190 | 8760 | 8760 | This study |
| LT 6 | day | 30,514 | 30,514 | 30,514 | [21] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, J.-I.; Jung, J.-Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-W.; Lee, J.-I.; Lee, C.-M. A Comparison of Health Risks from PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Exposure in Industrial Complexes in Dangjin and Yeosu·Gwangyang. Toxics 2024, 12, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020158
Jeon J-I, Jung J-Y, Park S-Y, Lee H-W, Lee J-I, Lee C-M. A Comparison of Health Risks from PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Exposure in Industrial Complexes in Dangjin and Yeosu·Gwangyang. Toxics. 2024; 12(2):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020158
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Jeong-In, Ji-Yun Jung, Shin-Young Park, Hye-Won Lee, Jeong-Il Lee, and Cheol-Min Lee. 2024. "A Comparison of Health Risks from PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Exposure in Industrial Complexes in Dangjin and Yeosu·Gwangyang" Toxics 12, no. 2: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020158
APA StyleJeon, J.-I., Jung, J.-Y., Park, S.-Y., Lee, H.-W., Lee, J.-I., & Lee, C.-M. (2024). A Comparison of Health Risks from PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Exposure in Industrial Complexes in Dangjin and Yeosu·Gwangyang. Toxics, 12(2), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020158







