The Cocktail Effects on the Acute Cytotoxicity of Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals Frequently Detected in the Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Stock Solutions
2.2. Aliivibrio fischeri Acute Bioluminescence Assay (Microtox®)
2.3. Combination Index (CI) Method to Determine Joint Toxicities
- n(CI)x—the combination index (CI) for n chemicals at an inhibition rate of x%.
- (Dx)1−n—the sum of the concentrations of n chemicals, causing an inhibition rate of x% in the mixture.
- {[D]j/}—the proportionality of the individual concentration of n chemical causing an inhibition rate of x% in the mixture.
- (Dm)j{(fax)j/[1 − (fax)j]}1/mj—the concentration of each individual chemical causing an inhibition rate of x%, where Dm is the median-effect concentration (antilog of the x-intercept of the median-effect plot), fax is the fractional inhibition at x% inhibition, and m is the slope of the median-effect plot.
2.4. Statistical Analysis—Methods
- ECxA—the effective concentration divided by the number of compounds in the mixture containing the non-toxic component resulting in x% bioluminescence inhibition.
- n—the number of the chemicals in the mixture not containing the non-toxic component.
- ECxB—the effective concentration divided by the number of compounds in the mixture not containing the non-toxic component resulting in x% bioluminescence inhibition.
3. Results
3.1. Cytotoxicity on Aliivibrio fischeri
3.2. Combination Index Values and Enhancement by Terbuthylazine
3.3. Statistical Analysis of Synergism or Antagonism between Carbamazepine, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, S-metolachlor, and Tebuconazole
3.3.1. Pairwise Description
3.3.2. PERMANOVA
3.4. Enhancement by Terbuthylazine
3.4.1. Pairwise Description
3.4.2. PERMANOVA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naidu, R.; Biswas, B.; Willett, I.R.; Cribb, J.; Kumar Singh, B.; Paul Nathanail, C.; Coulon, F.; Semple, K.T.; Jones, K.C.; Barclay, A.; et al. Chemical Pollution: A Growing Peril and Potential Catastrophic Risk to Humanity. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUROSTAT Chemicals Production and Consumption Statistics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Chemicals_production_and_consumption_statistics#Total_production_of_chemicals (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Schwarzenbach, R.; Escher, B.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.; Johnson, A.; Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The Challenge of Micropollutants in Aquatic Systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, K.; Schirmer, M. Who Is Chasing Whom? A Call for a More Integrated Approach to Reduce the Load of Micro-Pollutants in the Environment. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W. Global Pesticide Use: Profile, Trend, Cost/Benefit and More. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2018, 8, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- IQVIA-Institute for Human Data Science. The Global Use of Medicines 2023. Outlook to 2027. Available online: https://www.iqvia.com/insights/the-iqvia-institute/reports-and-publications/reports/the-global-use-of-medicines-2023 (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Bottoni, P.; Grenni, P.; Lucentini, L.; Caracciolo, A.B. Terbuthylazine and Other Triazines in Italian Water Resources. Microchem. J. 2013, 107, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, P.M.; Quiñones, D.H.; Terrones, I.; Rey, A.; Beltrán, F.J. Insights into the Removal of Terbuthylazine from Aqueous Solution by Several Treatment Methods. Water Res. 2016, 98, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbrilli, G.; Bimbi, B.; Cioni, F.; Pagliai, L.; Luchi, F.; Lanciotti, E. Surface and Ground Waters Characterization in Tuscany (Italy) by Using Algal Bioassay and Pesticide Determinations: Comparative Evaluation of the Results and Hazard Assessment of the Pesticides Impact on Primary Productivity. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Guardo, A.; Volpi, E.; Finizio, A. Analysis of Large-Scale Monitoring Data to Identify Spatial and Temporal Trend of Risk for Terbuthylazine and Desethyl-Terbuthylazine in Surface Water Bodies of Po Plain (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrin, A.; Langone, L.; Miserocchi, S.; Turchetto, M.; Acri, F. Po River Plume on the Adriatic Continental Shelf: Dispersion and Sedimentation of Dissolved and Suspended Matter during Different River Discharge Rates. Mar. Geol. 2005, 222–223, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touloupakis, E.; Giannoudi, L.; Piletsky, S.A.; Guzzella, L.; Pozzoni, F.; Giardi, M.T. A Multi-Biosensor Based on Immobilized Photosystem II on Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Detection of Herbicides in River Water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carafa, R.; Wollgast, J.; Canuti, E.; Ligthart, J.; Dueri, S.; Hanke, G.; Eisenreich, S.J.; Viaroli, P.; Zaldívar, J.M. Seasonal Variations of Selected Herbicides and Related Metabolites in Water, Sediment, Seaweed and Clams in the Sacca Di Goro Coastal Lagoon (Northern Adriatic). Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.; Locoro, G.; Comero, S.; Contini, S.; Schwesig, D.; Werres, F.; Balsaa, P.; Gans, O.; Weiss, S.; Blaha, L.; et al. Pan-European Survey on the Occurrence of Selected Polar Organic Persistent Pollutants in Ground Water. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4115–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubeix, V.; Fauvelle, V.; Tison-Rosebery, J.; Mazzella, N.; Coste, M.; Delmas, F. Assessing the Impact of Chloroacetanilide Herbicides and Their Metabolites on Periphyton in the Leyre River (SW France) via Short Term Growth Inhibition Tests on Autochthonous Diatoms. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velisek, J.; Stara, A.; Zuskova, E.; Kubec, J.; Buric, M.; Kouba, A. Chronic Toxicity of Metolachlor OA on Growth, Ontogenetic Development, Antioxidant Biomarkers and Histopathology of Early Life Stages of Marbled Crayfish. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NFCSO—National Food Security Office. Hungary. Available online: https://portal.nebih.gov.hu/documents/10182/367102/2022_Szerforg_publikus.pdf/4212dc94-24c8-c38f-43d9-288b84a9fe5d?t=1699541239342 (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Ackerman, F. The Economics of Atrazine. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2007, 13, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrancq, M.; Jadas-Hécart, A.; La Jeunesse, I.; Landry, D.; Payraudeau, S. High Frequency Monitoring of Pesticides in Runoff Water to Improve Understanding of Their Transport and Environmental Impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Hernández, E.; Andrades, M.S.; Álvarez-Martín, A.; Pose-Juan, E.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J. Occurrence of Pesticides and Some of Their Degradation Products in Waters in a Spanish Wine Region. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Hernández, E.; Pose-Juan, E.; Sánchez-martín, M.J. Intra-Annual Trends of Fungicide Residues in Waters from Vineyard Areas in La Rioja Region of Northern Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22924–22936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiá, A.; Campo, J.; Navarro-Ortega, A.; Barceló, D.; Picó, Y. Pesticide Monitoring in the Basin of Llobregat River (Catalonia, Spain) and Comparison with Historical Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 503–504, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulava, V.M.; Cory, W.C.; Murphey, V.L.; Ulmer, C.Z. Sorption, Photodegradation, and Chemical Transformation of Naproxen and Ibuprofen in Soils and Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, I.K.; Hela, D.G.; Albanis, T.A. The Status of Pesticide Pollution in Surface Waters (Rivers and Lakes) of Greece. Part I. Review on Occurrence and Levels. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čelić, M.; Jaén-Gil, A.; Briceño-Guevara, S.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Gros, M.; Petrović, M. Extended Suspect Screening to Identify Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Riverine and Coastal Ecosystems and Assessment of Environmental Risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Huang, H.; Li, N.; Li, F.; Wang, D.; Luo, Q. Occurrence and Ecological Risk of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) and Pesticides in Typical Surface Watersheds, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 175, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, M.; Dallegrave, A.; Suchecki Barnet, L.; Zanchetti Meneghini, L.; de Araújo Gomes, A.; Pizzolato, T.M. Pharmaceuticals, Pesticides and Metals/Metalloids in Lake Guaíba in Southern Brazil: Spatial and Temporal Evaluation and a Chemometrics Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, G.; Háhn, J.; Szoboszlay, S.; Harkai, P.; Farkas, M.; Radó, J.; Göbölös, B.; Kaszab, E.; Szabó, I.; Urbányi, B.; et al. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Multi-Pesticide Residues in the Largest Central European Shallow Lake, Lake Balaton, and Its Sub-Catchment Area. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment–A Brief Summary. In Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: Sources, Fate, Effects and Risks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aus der Beek, T.; Weber, F.A.; Bergmann, A.; Hickmann, S.; Ebert, I.; Hein, A.; Küster, A. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment-Global Occurrences and Perspectives. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusi, E.; Rybicki, M.; Jungmann, D. The Database “Pharmaceuticals in the Environment”—Update and New Analysis; Final Report; Umweltbundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Loos, R.; Gawlik, B.M.; Locoro, G.; Rimaviciute, E.; Contini, S.; Bidoglio, G. EU-Wide Survey of Polar Organic Persistent Pollutants in European River Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C. Occurrence, Sources, and Fate of Pharmaceuticals in Aquatic Environment and Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belden, J.B.; Gilliom, R.J.; Lydy, M.J. How Well Can We Predict the Toxicity of Pesticide Mixtures to Aquatic Life? Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2007, 3, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedergreen, N. Quantifying Synergy: A Systematic Review of Mixture Toxicity Studies within Environmental Toxicology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, O.V. Synergistic Effects of Chemical Mixtures: How Frequent Is Rare? Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2023, 36, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe, S.; Muischenk, H. Kombinationswirkungen. 1. Mitteilung: Hilfsmittel Der Fragestellung. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Exp. Path. Pharmakol. 1926, 24, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, C.I. The Toxicity of Poisons Applied Jointly. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1939, 26, 585–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedergreen, N.; Christensen, A.M.; Kamper, A.; Kudsk, P.; Mathiassen, S.K.; Streibig, J.C.; Sørensen, H. A Review of Independent Action Compared to Concentration Addition as Reference Models for Mixtures of Compounds with Different Molecular Target Sites. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roell, K.R.; Reif, D.M.; Motsinger-Reif, A.A. An Introduction to Terminology and Methodology of Chemical Synergy-Perspectives from across Disciplines. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahatagahawatte, Y.B.P.; Hara-Yamamura, H. Review on Mixture Toxicity of Pharmaceuticals in Environmental Waters and Wastewater Effluents. In Resilience, Response, and Risk in Water Systems; Springer Transactions in Civil and Environmental Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 105–126. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, I.H.; Kim, Y.; Baik, S.; Kim, J. Investigation of the Synergistic Toxicity of Binary Mixtures of Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals on Aliivibrio fischeri in Major River Basins in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białk-Bielińska, A.; Grabarczyk, Ł.; Mulkiewicz, E.; Puckowski, A.; Stolte, S.; Stepnowski, P. Mixture Toxicity of Six Pharmaceuticals towards Aliivibrio fischeri, Daphnia magna, and Lemna minor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 26977–26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenburger, R.; Nendza, M.; Schüürmann, G. Mixture Toxicity and Its Modeling by Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 1900–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmani, S.; Rogers, S.C.; Barley, M.H.; Livingstone, D.J. Application of QSPR to Mixtures. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2006, 46, 2043–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wang, C.; Tang, Z.; Guo, X. Joint Toxicity of Aromatic Compounds to Algae and QSAR Study. Ecotoxicology 2007, 16, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A.; Benfenati, E.; Gini, G.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. CORAL: Models of Toxicity of Binary Mixtures. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2012, 119, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Wang, T.; Tian, D.; Zou, X.; Gao, Y.; Yin, D. Using Molecular Docking-Based Binding Energy to Predict Toxicity of Binary Mixture with Different Binding Sites. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tang, L.; Luan, F.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Prediction of the Toxicity of Binary Mixtures by Qsar Approach Using the Hypothetical Descriptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmar, S.S.; Grulke, C.M. The Effect of Noise on the Predictive Limit of QSAR Models. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfield, S.J.; Firman, J.W.; Enoch, S.J.; Madden, J.C.; Erik Tollefsen, K.; Cronin, M.T.D. A Review of Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Modelling Approaches to Predict the Toxicity of Mixtures. Comput. Toxicol. 2023, 25, 100251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienzler, A.; Berggren, E.; Bessems, J.; Bopp, S.; Van Der Linden, S.; Worth, A. Assessment of Mixtures-Review of Regulatory Requirements and Guidance; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; ISBN 9789279384790. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, G.; Háhn, J.; Kriszt, B.; Szoboszlay, S. Acute and Chronic Toxicity of Herbicides and Their Mixtures Measured by Aliivibrio fischeri Ecotoxicological Assay. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Theoretical Basis, Experimental Design, and Computerized Simulation of Synergism and Antagonism in Drug Combination Studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, H.; Guo, D.; Wang, Q.; Qian, Y. Mixture Toxicity of Four Commonly Used Pesticides at Different Effect Levels to the Epigeic Earthworm, Eisenia Fetida. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative Analysis of Dose-Effect Relationships: The Combined Effects of Multiple Drugs or Enzyme Inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C.; Martin, T. CompuSyn for Drug Combinations: PC Software and User’s Guide: A Computer Program for Quantification of Synergism and Antagonism in Drug Combinations and the Determination of IC50 and ED50 and LD50 Values; ComboSyn, Inc.: Paramus, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. Distance-Based Tests for Homogeneity of Multivariate Dispersions. Biometrics 2006, 62, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.J.; Ellingsen, K.E.; McArdle, B.H. Multivariate Dispersion as a Measure of Beta Diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.E.; Mathews, K. A Weighted Least Squares Approach to Levene’s Test of Homogeneity of Variance. Aust. New Zeal. J. Stat. 2000, 42, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stier, A.C.; Geange, S.W.; Hanson, K.M.; Bolker, B.M. Predator Density and Timing of Arrival Affect Reef Fish Community Assembly. Ecology 2013, 94, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Preclinical versus Clinical Drug Combination Studies. Leuk. Lymphoma 2008, 49, 2059–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, T.M. 300-Fold Higher Neuro- and Immunotoxicity from Low-Redox Transformation of Carbamazepine. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 11, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, R.N.; Stephen, A.D.; Justin, P.; Saravanan, K.; Macchi, P.; Jelsch, C. Topological and Electrostatic Properties of Diclofenac Molecule as a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1196, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nica, V.; Villa, S.; Finizio, A. Toxicity of Individual Pharmaceuticals and Their Mixtures to Aliivibrio fischeri: Evidence of Toxicological Interactions in Binary Combinations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukić; Sigurnjak, M.; Cvetnić, M.; Markić, M.; Stankov, M.N.; Rogošić, M.; Rasulev, B.; Lončarić Božić, A.; Kušić, H.; Bolanča, T. Toxicity of Pharmaceuticals in Binary Mixtures: Assessment by Additive and Non-Additive Toxicity Models. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuriaga, E.; Lomba, L.; German, B.; Lanuza, P.M.; Aldea, L.; Ribate, M.P.; García, C.B.; Giner, B. Ecotoxicity in Aliivibrio fischeri of Ibuprofen, Omeprazole and Their Mixtures. Chem. Ecol. 2019, 35, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymała, J.; Kalka, J. Ecotoxic Interactions between Pharmaceuticals in Mixtures: Diclofenac and Sulfamethoxazole. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Zhou, M.; Lv, D.; Wang, M.; Xie, D.; Yang, X.; Dong, C.; Li, S.; Lin, P. Novel Segmented Concentration Addition Method to Predict Mixture Hormesis of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride and Oxytetracycline Hydrochloride to Aliivibrio fischeri. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedergreen, N.; Kamper, A.; Streibig, J.C. Is Prochloraz a Potent Synergist across Aquatic Species? A Study on Bacteria, Daphnia, Algae and Higher Plants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigurnjak, M.; Ukić; Cvetnić, M.; Markić, M.; Novak Stankov, M.; Rasulev, B.; Kušić, H.; Lončarić Božić, A.; Rogošić, M.; Bolanča, T. Combined Toxicities of Binary Mixtures of Alachlor, Chlorfenvinphos, Diuron and Isoproturon. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, V.A.; Weber, A.G.; Gueretz, J.S.; Walz, G.C.; Tagliari-Corrêa, C.V.; Toumi, H.; Férard, J.F.; Radetski, C.M.; Somensi, C.A.; Cotelle, S. An Alternative Approach to Assess Ecotoxicological Effects of Agrochemical Combinations Used in Brazilian Aquaculture Farms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 70713–70721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, S.; Migliorati, S.; Monti, G.S.; Vighi, M. Toxicity on the Luminescent Bacterium Vibrio fischeri (Beijerinck) II: Response to Complex Mixtures of Heterogeneous Chemicals at Low Levels of Individual Components. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 86, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, R.S.; de Souza Santos, L.V.; d’Auriol, M.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; Moreira, V.R.; Lange, L.C. Diazepam, Metformin, Omeprazole and Simvastatin: A Full Discussion of Individual and Mixture Acute Toxicity. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Nawaz Khan, K.; Saif Ur Rehman, M.; Mustafa, G.; Faizan Nazar, M.; Sun, Q.; Iqbal, J.; Mulla, S.I.; Yu, C.P. Ecological Risk Assessment of Pharmaceuticals in the Receiving Environment of Pharmaceutical Wastewater in Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 136, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, M.; Rashid, J.; Malik, M.; Iqbal, A.; Xu, M. Physicochemical Analysis and Detection of Exceptionally High Diclofenac Concentration in the Pharmaceutical Wastewaters Collected from the Production Units of National Industrial Zone, Rawat, Pakistan. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Kumar, D. Ibuprofen as an Emerging Organic Contaminant in Environment, Distribution and Remediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, A.; Otto, S.; Zanin, G. Herbicides Runoff in Vegetative Filter Strips: Evaluation and Validation of a Recent Rainfall Return Period Model. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2013, 93, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.; Pappalardo, S.E.; Cardinali, A.; Masin, R.; Zanin, G.; Borin, M. Vegetated Ditches for the Mitigation of Pesticides Runoff in the Po Valley. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, D.; Diel, P.; Epe, B.; Hellwig, M.; Lampen, A.; Mally, A.; Marko, D.; Villar Fernández, M.A.; Guth, S.; Roth, A.; et al. Basic Concepts of Mixture Toxicity and Relevance for Risk Evaluation and Regulation. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 3005–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, J.; Domingues, I.; Monteiro, M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S. Synergistic Effects Caused by Atrazine and Terbuthylazine on Chlorpyrifos Toxicity to Early-Life Stages of the Zebrafish Danio Rerio. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4671–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
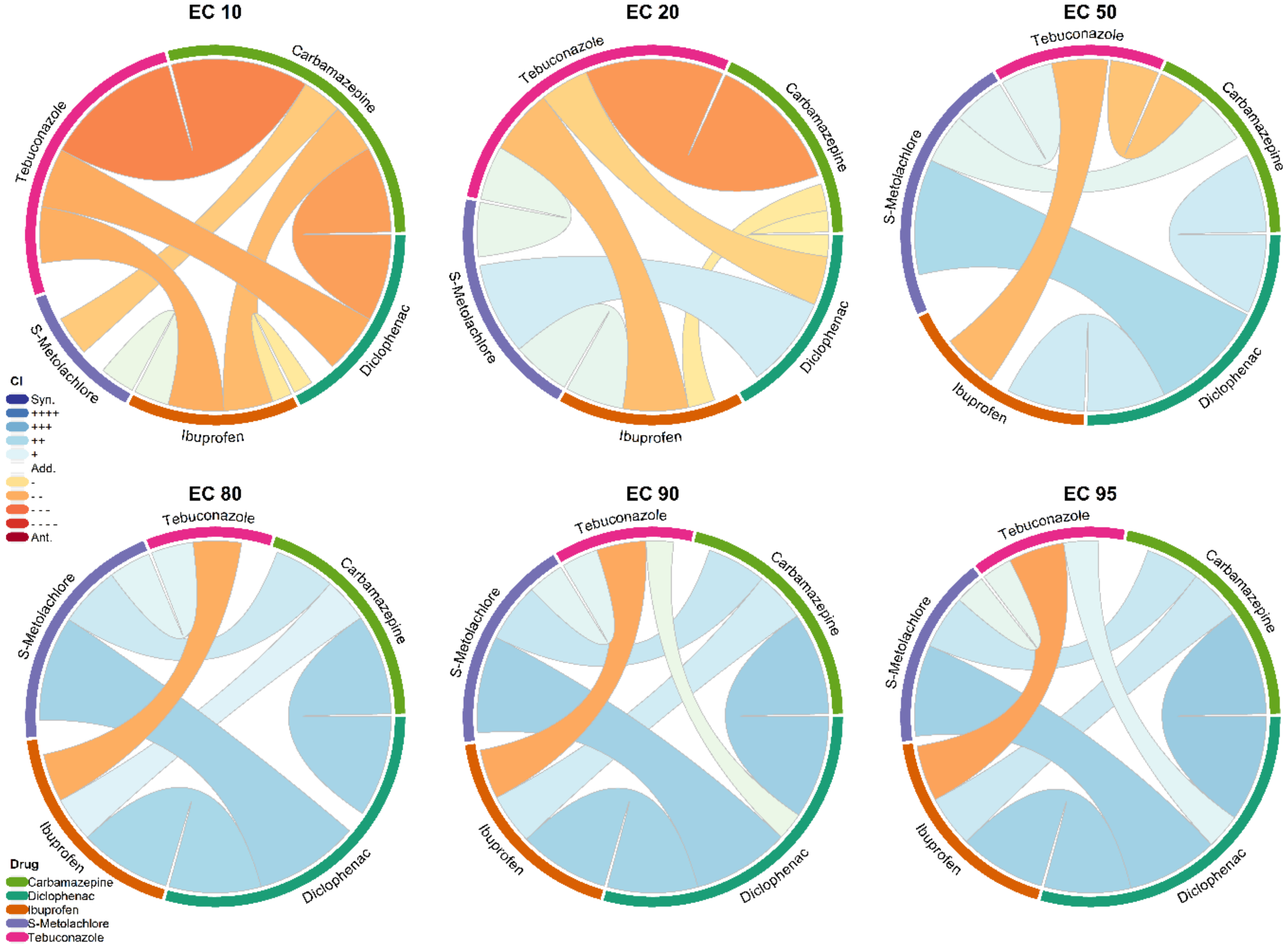




| Effective Concentration Values at Different Effective Sizes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC10 | EC20 | EC50 | EC80 | EC90 | EC95 | EC10 | EC20 | EC50 | EC80 | EC90 | EC95 | ||
| mg/L | mg/L | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 4 | 14 | 86 | 520 | 1478 | 3866 | 2 + 3 + 4 | 4 | 8 | 22 | 64 | 118 | 208 |
| 2 | 7 | 13 | 27 | 50 | 77 | 107 | 2 + 3 + 5 | 10 | 20 | 54 | 144 | 258 | 442 |
| 3 | 2 | 5 | 23 | 96 | 222 | 471 | 2 + 3 + 6 | 2 | 4 | 14 | 38 | 68 | 114 |
| 4 | 55 | 100 | 265 | 715 | n.t. | n.t. | 2 + 4 + 5 | 6 | 8 | 20 | 42 | 66 | 98 |
| 5 | 8 | 14 | 32 | 74 | 120 | 188 | 2 + 4 + 6 | 3 | 6 | 22 | 82 | 177 | 360 |
| 6 | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | 2 + 5 + 6 | 20 | 28 | 51 | 93 | 132 | 182 |
| 1 + 2 | 12 | 16 | 28 | 50 | 70 | 94 | 3 + 4 + 5 | 2 | 4 | 30 | 178 | 488 | 1240 |
| 1 + 3 | 6 | 12 | 40 | 120 | 230 | 418 | 3 + 4 + 6 | 2 | 5 | 33 | 226 | 694 | 1953 |
| 1 + 4 | 16 | 32 | 88 | 232 | 408 | 688 | 3 + 5 + 6 | 7 | 15 | 50 | 169 | 345 | 665 |
| 1 + 5 | 24 | 32 | 52 | 80 | 108 | 136 | 4 + 5 + 6 | 32 | 52 | 114 | 250 | 394 | 598 |
| 1 + 6 | 18 | 36 | 120 | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 | 10 | 14 | 30 | 64 | 96 | 140 |
| 2 + 3 | 2 | 4 | 12 | 26 | 40 | 62 | 1 + 2 + 3 + 5 | 12 | 18 | 36 | 72 | 108 | 156 |
| 2 + 4 | 10 | 14 | 28 | 56 | 84 | 120 | 1 + 2 + 3 + 6 | 5 | 9 | 28 | 88 | 174 | 324 |
| 2 + 5 | 12 | 18 | 34 | 64 | 92 | 126 | 1 + 2 + 4 + 5 | 10 | 16 | 38 | 88 | 144 | 224 |
| 2 + 6 | 4 | 10 | 32 | 102 | 202 | 380 | 1 + 2 + 4 + 6 | 6 | 12 | 34 | 99 | 186 | 332 |
| 3 + 4 | 6 | 12 | 50 | 184 | 396 | 804 | 1 + 2 + 5 + 6 | 8 | 12 | 24 | 50 | 78 | 116 |
| 3 + 5 | 8 | 16 | 56 | 192 | 394 | 760 | 1 + 3 + 4 + 5 | 4 | 12 | 58 | 254 | 598 | 1312 |
| 3 + 6 | 1 | 2 | 18 | 102 | 272 | 672 | 1 + 3 + 4 + 6 | 1 | 4 | 40 | 376 | 1393 | 4661 |
| 4 + 5 | 12 | 20 | 36 | 64 | 88 | 116 | 1 + 3 + 5 + 6 | 2 | 8 | 48 | 294 | 842 | 2214 |
| 4 + 6 | 30 | 80 | 428 | 2278 | 6054 | 14,896 | 1 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 2 | 8 | 110 | 1431 | 6415 | 25,568 |
| 5 + 6 | 6 | 16 | 76 | 350 | 850 | 1918 | 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 | 6 | 12 | 30 | 70 | 114 | 180 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 | 4 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 38 | 54 | 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 | 2 | 6 | 20 | 62 | 124 | 232 |
| 1 + 2 + 4 | 8 | 12 | 28 | 64 | 100 | 154 | 2 + 3 + 5 + 6 | 3 | 6 | 17 | 55 | 107 | 199 |
| 1 + 2 + 5 | 20 | 30 | 54 | 98 | 138 | 190 | 2 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 4 | 8 | 27 | 91 | 186 | 360 |
| 1 + 2 + 6 | 6 | 12 | 28 | 62 | 100 | 154 | 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 | 8 | 14 | 38 | 100 | 172 | 284 |
| 1 + 3 + 4 | 2 | 6 | 40 | 228 | 630 | 1610 | 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 | 2 | 6 | 22 | 74 | 150 | 286 |
| 1 + 3 + 5 | 10 | 20 | 66 | 214 | 426 | 802 | 1 + 2 + 3 + 5 + 6 | 4 | 8 | 22 | 56 | 96 | 158 |
| 1 + 3 + 6 | 2 | 6 | 38 | 218 | 602 | 1532 | 1 + 2 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 4 | 9 | 30 | 106 | 220 | 431 |
| 1 + 4 + 5 | 34 | 56 | 126 | 282 | 454 | 702 | 1 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 2 | 6 | 42 | 290 | 886 | 2470 |
| 1 + 4 + 6 | 31 | 55 | 147 | 394 | 699 | 1187 | 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 8 | 12 | 22 | 40 | 56 | 78 |
| 1 + 5 + 6 | 20 | 40 | 168 | 684 | 1548 | 3288 | 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 2 | 6 | 24 | 100 | 228 | 482 |
| Combination Index Values at Different Effective Concentrations (Based on the Effective Concentration) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC10 | EC20 | EC50 | EC80 | EC90 | EC95 | |
| 1 + 2 | 2.14 | 1.30 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.42 |
| 1 + 3 | 2.11 | 1.67 | 1.17 | 0.75 | 0.59 | 0.48 |
| 1 + 4 | 1.96 | 1.40 | 0.71 | 0.39 | 0.30 | 0.24 |
| 1 + 5 | 4.17 | 2.42 | 1.14 | 0.62 | 0.48 | 0.37 |
| 2 + 3 | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.33 |
| 2 + 4 | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.55 |
| 2 + 5 | 1.51 | 1.43 | 1.24 | 1.07 | 0.98 | 0.88 |
| 3 + 4 | 1.48 | 1.27 | 1.25 | 1.11 | 1.04 | 1.00 |
| 3 + 5 | 2.39 | 2.20 | 2.18 | 2.33 | 2.52 | 2.77 |
| 4 + 5 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.48 | 0.40 | 0.33 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 | 1.11 | 0.73 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.20 |
| 1 + 2 + 4 | 1.00 | 0.69 | 0.53 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.49 |
| 1 + 2 + 5 | 3.17 | 2.36 | 1.53 | 1.16 | 1.01 | 0.90 |
| 1 + 3 + 4 | 0.48 | 0.58 | 0.83 | 1.06 | 1.25 | 1.47 |
| 1 + 3 + 5 | 2.75 | 2.35 | 1.99 | 1.87 | 1.91 | 2.02 |
| 1 + 4 + 5 | 4.14 | 3.01 | 2.00 | 1.59 | 1.47 | 1.43 |
| 2 + 3 + 4 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.78 |
| 2 + 3 + 5 | 2.43 | 2.40 | 2.14 | 2.12 | 2.22 | 2.37 |
| 2 + 4 + 5 | 0.54 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.47 |
| 3 + 4 + 5 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.82 | 1.52 | 2.21 | 3.20 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 | 2.13 | 1.31 | 0.78 | 0.54 | 0.45 | 0.40 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 + 5 | 2.86 | 1.97 | 1.18 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.64 |
| 1 + 2 + 4 + 5 | 1.24 | 0.99 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.82 |
| 1 + 3 + 4 + 5 | 0.84 | 1.09 | 1.36 | 1.75 | 2.13 | 2.62 |
| 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 | 1.12 | 1.11 | 0.92 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.74 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 | 1.56 | 1.25 | 1.03 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.95 |
| EC10 | EC20 | EC50 | EC80 | EC90 | EC95 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxicity enhancement by terbuthylazine (%) in the mixtures | ||||||
| 1 + 6 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. |
| 2 + 6 | 85 | 81 | 70 | 49 | 34 | 11 |
| 3 + 6 | 100 | 90 | 80 | 73 | 69 | 64 |
| 4 + 6 | 86 | 80 | 60 | 20 | n.e. | n.e. |
| 5 + 6 | 81 | 71 | 41 | −18 | −77 | −155 |
| 1 + 2 + 6 | 78 | 67 | 56 | 45 | 37 | 27 |
| 1 + 3 + 6 | 85 | 78 | 58 | 19 | −16 | −63 |
| 1 + 4 + 6 | 14 | 23 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 |
| 1 + 5 + 6 | 63 | 44 | −44 | −280 | −537 | −975 |
| 2 + 3 + 6 | 56 | 56 | 48 | 35 | 24 | 18 |
| 2 + 4 + 6 | 88 | 81 | 65 | 35 | 6 | −33 |
| 2 + 5 + 6 | 27 | 31 | 33 | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| 3 + 4 + 6 | 88 | 82 | 70 | 45 | 22 | −8 |
| 3 + 5 + 6 | 61 | 58 | 60 | 61 | 61 | 61 |
| 4 + 5 + 6 | −19 | −16 | −41 | −74 | −99 | −129 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 + 6 | 30 | 18 | −30 | −107 | −157 | −237 |
| 1 + 2 + 4 + 6 | 58 | 46 | 32 | 13 | −5 | −21 |
| 1 + 2 + 5 + 6 | 78 | 78 | 75 | 71 | 68 | 66 |
| 1 + 3 + 4 + 6 | 69 | 60 | 44 | 7 | −24 | −63 |
| 1 + 3 + 5 + 6 | 89 | 78 | 59 | 23 | −11 | −55 |
| 1 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 97 | 92 | 51 | −185 | −695 | −1898 |
| 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 | 72 | 58 | 49 | 46 | 41 | 37 |
| 2 + 3 + 5 + 6 | 84 | 85 | 82 | 79 | 77 | 75 |
| 2 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 64 | 44 | 25 | −22 | −59 | −107 |
| 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 44 | 16 | 33 | 42 | 45 | 48 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 | 87 | 73 | 53 | 26 | n.e. | −31 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 + 5 + 6 | 79 | 72 | 61 | 50 | 43 | 35 |
| 1 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 68 | 68 | 54 | 27 | 5 | −20 |
| 1 + 2 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 73 | 66 | 49 | 23 | 2 | −23 |
| 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 15 | 36 | 53 | 63 | 69 | 72 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 | 83 | 70 | 56 | 31 | 8 | −18 |
| PERMANOVA (999 Permutations) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | Sum Sq | R2 | F-Model | p-Value | ||
| Tebuconazole | 1 | 3.9289 | 0.21950 | 17.0848 | 0.001 | *** |
| Ibuprofen | 1 | 1.9133 | 0.10689 | 8.3198 | 0.009 | ** |
| Diclofenac | 1 | 0.9145 | 0.05109 | 3.9768 | 0.033 | * |
| S-Metolachlor | 1 | 1.4574 | 0.08142 | 6.3375 | 0.009 | ** |
| Carbamazepine | 1 | 0.8052 | 0.04498 | 3.5012 | 0.056 | |
| Tebuconazole: ibuprofen | 1 | 0.2668 | 0.01491 | 1.1603 | 0.335 | |
| Tebuconazole: diclofenac | 1 | 0.2318 | 0.01295 | 1.0082 | 0.374 | |
| Ibuprofen: diclofenac | 1 | 1.8906 | 0.10562 | 8.2211 | 0.006 | ** |
| Tebuconazole: S-metolachlor | 1 | 1.0758 | 0.06011 | 4.6783 | 0.027 | * |
| Tebuconazole: carbamazepine | 1 | 0.1992 | 0.01113 | 0.8661 | 0.394 | |
| S-metolachlor: carbamazepine | 1 | 0.6547 | 0.03657 | 2.8468 | 0.072 | |
| Ibuprofen: S-metolachlor | 1 | 0.1790 | 0.01000 | 0.7783 | 0.464 | |
| Diclofenac: S-metolachlor | 1 | 0.3924 | 0.02192 | 1.7064 | 0.219 | |
| Tebuconazole: ibuprofen: diclofenac | 1 | 0.2695 | 0.01505 | 1.1718 | 0.339 | |
| Tebuconazole: S-metolachlor: carbamazepine | 1 | 1.0217 | 0.05708 | 4.4430 | 0.028 | * |
| Ibuprofen: diclofenac: S-metolachlor | 1 | 0.6288 | 0.03513 | 2.7345 | 0.091 | |
| Residual | 9 | 2.0697 | 0.11563 | |||
| Total | 25 | 17.8992 | 1.00000 | |||
| df | Sum Sq | R2 | F-Model | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | 1 | 52.68 | 0.09762 | 90.4915 | 0.002 | ** |
| Diclofenac | 1 | 64.30 | 0.11917 | 110.4598 | 0.003 | ** |
| Tebuconazole | 1 | 9.42 | 0.01746 | 16.1814 | 0.009 | ** |
| S-metolachlor | 1 | 2.21 | 0.00409 | 3.7916 | 0.112 | |
| Carbamazepine | 1 | 36.87 | 0.06832 | 63.3309 | 0.001 | *** |
| Ibuprofen: diclofenac | 1 | 74.09 | 0.13730 | 127.2731 | 0.005 | ** |
| Ibuprofen: tebuconazole | 1 | 23.52 | 0.04360 | 40.4110 | 0.002 | ** |
| Diclofenac: tebuconazole | 1 | 30.66 | 0.05681 | 52.6622 | 0.006 | ** |
| Ibuprofen: S-metolachlor | 1 | 5.21 | 0.00966 | 8.9548 | 0.038 | * |
| Diclofenac: S-metolachlor | 1 | 2.38 | 0.00442 | 4.0967 | 0.123 | |
| Tebuconazole: S-metolachlor | 1 | 5.88 | 0.01090 | 10.1014 | 0.013 | * |
| Ibuprofen: carbamazepine | 1 | 11.54 | 0.02139 | 19.8274 | 0.009 | ** |
| Diclofenac: carbamazepine | 1 | 38.95 | 0.07218 | 66.9076 | 0.002 | ** |
| S-metolachlor: carbamazepine | 1 | 1.23 | 0.00228 | 2.1170 | 0.191 | |
| Ibuprofen: diclofenac: tebuconazole | 1 | 59.17 | 0.10965 | 101.6437 | 0.003 | ** |
| Ibuprofen: diclofenac: S-metolachlor | 1 | 3.75 | 0.00695 | 6.4437 | 0.087 | . |
| Ibuprofen: tebuconazole: S-metolachlor | 1 | 0.24 | 0.00044 | 0.4069 | 0.642 | |
| Diclofenac: tebuconazole: S-metolachlor | 1 | 1.81 | 0.00335 | 3.1090 | 0.070 | . |
| Ibuprofen: diclofenac: carbamazepine | 1 | 87.93 | 0.16295 | 151.0464 | 0.001 | *** |
| Ibuprofen: S-metolachlor: carbamazepine | 1 | 6.01 | 0.01114 | 10.3296 | 0.033 | * |
| Diclofenac: S-metolachlor: carbamazepine | 1 | 6.97 | 0.01291 | 11.9692 | 0.026 | * |
| Ibuprofen: diclofenac: S-metolachlor: carbamazepine | 1 | 11.29 | 0.02092 | 19.3925 | 0.023 | * |
| Residual | 6 | 3.49 | 0.00647 | |||
| Total | 28 | 539.61 | 1.00000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Göbölös, B.; Sebők, R.E.; Szabó, G.; Tóth, G.; Szoboszlay, S.; Kriszt, B.; Kaszab, E.; Háhn, J. The Cocktail Effects on the Acute Cytotoxicity of Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals Frequently Detected in the Environment. Toxics 2024, 12, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030189
Göbölös B, Sebők RE, Szabó G, Tóth G, Szoboszlay S, Kriszt B, Kaszab E, Háhn J. The Cocktail Effects on the Acute Cytotoxicity of Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals Frequently Detected in the Environment. Toxics. 2024; 12(3):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030189
Chicago/Turabian StyleGöbölös, Balázs, Rózsa E. Sebők, Gyula Szabó, Gergő Tóth, Sándor Szoboszlay, Balázs Kriszt, Edit Kaszab, and Judit Háhn. 2024. "The Cocktail Effects on the Acute Cytotoxicity of Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals Frequently Detected in the Environment" Toxics 12, no. 3: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030189
APA StyleGöbölös, B., Sebők, R. E., Szabó, G., Tóth, G., Szoboszlay, S., Kriszt, B., Kaszab, E., & Háhn, J. (2024). The Cocktail Effects on the Acute Cytotoxicity of Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals Frequently Detected in the Environment. Toxics, 12(3), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030189








