Microarray and Functional Pathway Analyses Revealed Significantly Elevated Gene Expressions Associated with Metabolic Resistance to Oxamyl (Vydate) in Lygus lineolaris
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Colony and Field Population of the Tarnished Plant Bug (TPB, Lygus lineolaris)
2.2. cDNA Library Sequencing, Microarray Processing, and Functional and Pathway Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scatter Plot Comparison of Gene Expression Levels between LLMCK(S) and Vyd1515FF(R)
3.2. Identity, Abundance, and Potential Association of Upregulated Genes with Oxamyl Resistance
3.2.1. Gene Expression Patterns of Major Detoxification Enzymes
3.2.2. Hydrolysis Is a Key Detoxification Mechanism in the Survivors of Oxamyl-Treated TPBs
3.2.3. Other Enzyme Genes
3.2.4. Over Expressions of Digestive Enzyme Genes
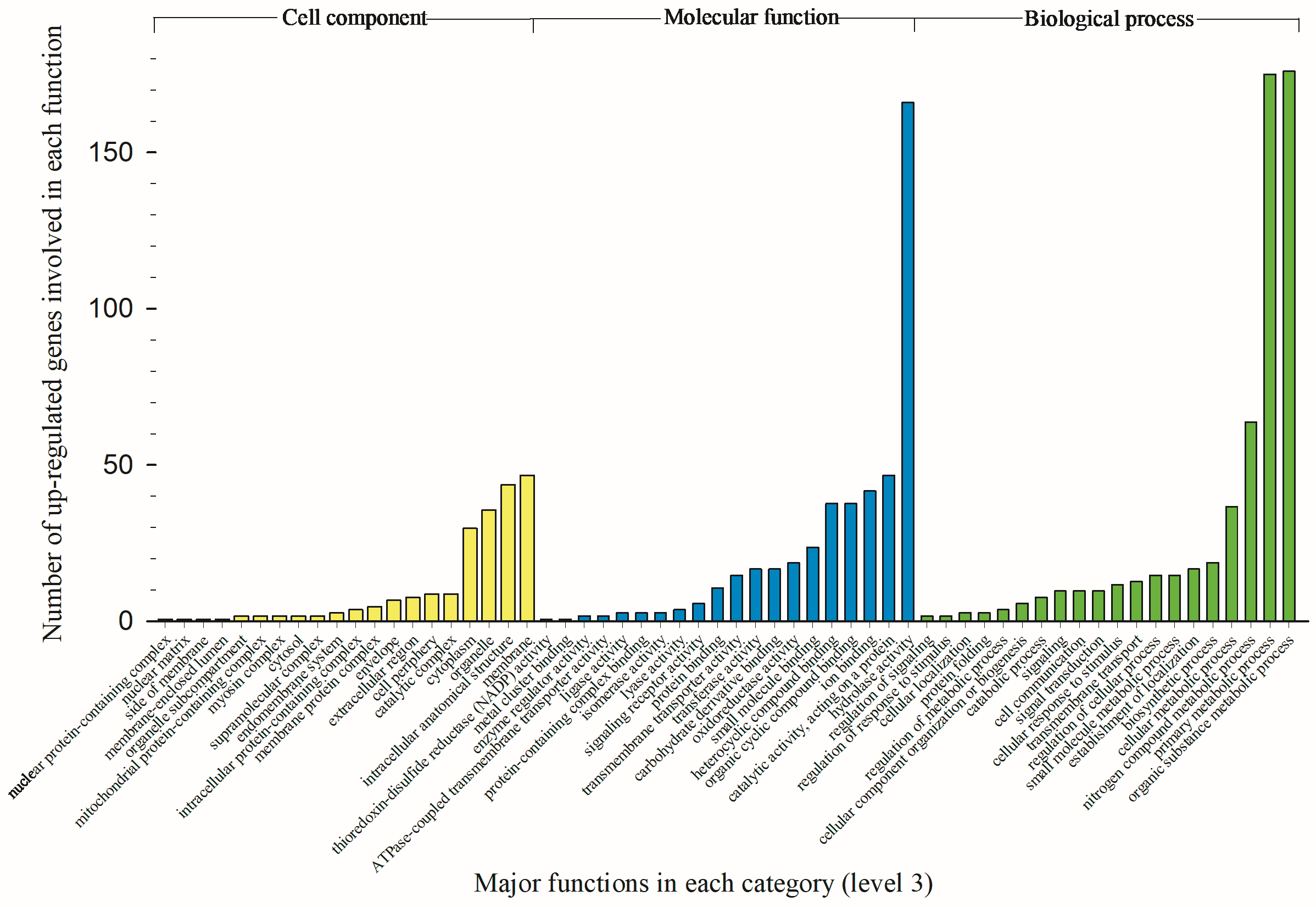
3.3. Modified Biological Processes, Molecular Functions, and Cellular Components
3.4. Pathway Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Y.C.; Yao, J.; Luttrell, R. Identification of genes potentially responsible for extra-oral digestion and overcoming plant defense from salivary glands of the tarnished plant bug (Lygus lineolaris) using cDNA sequencing. J. Insect Sci. 2016, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IRAC. Mode of Action Classification Scheme. Insecticide Resistance Action Committee. Version 8.0. 2020. Available online: www.irac-online.org (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Du, Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Portilla, M.; Zhang, M.; Reddy, G.V. The mechanisms of metabolic resistance to pyrethroids and neonicotinoids fade away without selection pressure in the tarnished plant bug Lygus lineolaris. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 3893–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingsworth, R.G.; Steinkraus, D.C.; Tugwell, N.P. Responses of Arkansas Populations of Tarnished Plant Bugs (Heteroptera: Miridae) to Insecticides, and Tolerance Differences Between Nymphs and Adults. J. Econ. Entomol. 1997, 90, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, G.L.; Scott, W.P. Seasonal changes in pyrethroid resistance in tarnished plant bug (Heteroptera: Miridae) populations during a three-year period in the Delta area of Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenheim, J.A. Control Failures Following Insecticide Applications in Commercial Agriculture: How Often Do They Occur? A Case Study of Lygus hesperus (Hemiptera: Miridae) Control in Cotton. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Snodgrass, G.L. Cytochrome P450 CYP6X1 cDNAs and mRNA expression levels in three strains of the tarnished plant bug Lygus lineolaris (Heteroptera: Miridae) having different susceptibilities to pyrethroid insecticide. Insect Mol. Biol. 2003, 12, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Snodgrass, G.L.; Chen, M.S. Enhanced esterase gene expression and activity in a malathion-resistant strain of the tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Snodgrass, G.L.; Chen, M.S. Comparative study on glutathione S-transferase activity, cDNA, and gene expression between malathion susceptible and resistant strains of the tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2007, 87, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; West, S.; Snodgrass, G.; Luttrell, R. Variability in resistance-related enzyme activities in field populations of the tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 99, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Luttrell, R. Variation of acephate susceptibility and correlation with esterase and glutathione S-transferase activities in field populations of the tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 103, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Scheibener, S.; Portilla, M. Toxicity Assessment of Four Formulated Pyrethroid-Containing Binary Insecticides in Two Resistant Adult Tarnished Plant Bug (Lygus lineolaris) Populations. Insects 2023, 14, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Scheibener, S.; Zhu, Y.C.; Portilla, M.; Zhang, M. Resistance risk assessment of six pyrethroids and acephate toward the resistant adult tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris. Insect Sci. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Scheibener, S.; Zhu, Y.C.; Portilla, M.; Reddy, G.V. Biochemical and molecular characterization of neonicotinoids resistance in the tarnished plant bug; Lygus lineolaris. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 275, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Guo, Z.; He, Y.; Luttrell, R. Microarray analysis of gene regulations and potential association with acephate-resistance and fitness cost in Lygus lineolaris. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Luttrell, R. Altered gene regulation and potential association with metabolic resistance development to imidacloprid in the tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Du, Y.; Yao, J.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, Y. Detect Cytochrome C Oxidase- and Glutathione-S-Transferase-Mediated Detoxification in a Permethrin-Resistant Population of Lygus lineolaris. Toxics 2023, 11, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, G.L. Insecticide resistance in field populations of the tarnished plant bug (Heteroptera: Miridae) in cotton in the Mississippi Delta. J. Econ. Entomol. 1996, 89, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, M.; Malcolm, C.; Chandre, F.; Mogensen, K.; Berthomieu, A.; Marquine, M.; Raymond, M. The unique mutation in Ace-1 giving high insecticide resistance is easily detectable in mosquito vectors. Insect Mol. Biol. 2004, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aïkpon, R.; Sèzonlin, M.; Ossè, R.; Akogbéto, M. Evidence of multiple mechanisms providing carbamate and organophosphate resistance in field An. gambiae population from Atacora in Benin. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olé Sangba, M.L.; Sidick, A.; Govoetchan, R.; Dide-Agossou, C.; Ossè, R.A.; Akogbeto, M.; Ndiath, M.O. Evidence of multiple insecticide resistance mechanisms in Anopheles gambiae populations in Bangui, Central African Republic. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbel, V.; N’Guessan, R.; Brengues, C.; Chandre, F.; Djogbénou, L.; Martin, T.; Akogbéto, M.; Hougard, J.M.; Rowland, M. Multiple insecticide resistance mechanisms in Anopheles gambiae and Culex quinquefasciatus from Benin. West Afr. Acta Trop. 2007, 101, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S. Characterization of the role of esterases in the biodegradation of organophosphate, carbamate, and pyrethroid pesticides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Ndula, M.; Riveron, J.M.; Irving, H.; Wondji, C.S. The P450 CYP 6Z1 confers carbamate/pyrethroid cross-resistance in a major African malaria vector beside a novel carbamate-insensitive N485I acetylcholinesterase-1 mutation. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3436–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolstad, B.M.; Irizarry, R.A.; Astrand, M.; Speed, T.P. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyereisen, R. Insect CYP genes and P450 enzymes. In Insect Molecular Biology and Biochemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 236–316. [Google Scholar]
- Agosin, M. Role of microsomal oxidations in insecticide degradation. In Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pharmacology; Kerkut, G.A., Gilbert, L.I., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1985; Volume 12, pp. 647–712. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Nayak, B.; Xiong, L.; Xie, C.; Dong, Y.; You, M.; Yuchi, Z.; You, S. The role of insect cytochrome P450s in mediating insecticide resistance. Agriculture 2022, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. Molecular Mechanisms of Metabolic Resistance to Synthetic and Natural Xenobiotics. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Dowdy, A.K.; Baker, J.E. Differential mRNA expression levels and gene sequences of a putative carboxylesterase-like enzyme from two strains of the parasitoid Anisopteromalus calandrae (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruse, C.; Moural, T.W.; Zhu, F. Dynamic roles of insect carboxyl/cholinesterases in chemical adaptation. Insects 2023, 14, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, D.E.; Krishnan, N.; Catchot, A.L.; Musser, F.R. Susceptibility to insecticides and activities of glutathione S-transferase and esterase in populations of Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera: Miridae) in Mississippi. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Becnel, J.J.; Clark, G.G.; Linthicum, K.J. Permethrin induces overexpression of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 3 in Aedes aegypti. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Liu, N. Overexpression of the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene associated with a pyrethroid resistant strain of German cockroaches, Blattella germanica (L.). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 33, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Chandre, F.; Ochou, O.G.; Vaissayre, M.; Fournierd, D. Pyrethroid resistance mechanisms in the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from West Africa. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2002, 74, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmquist, M. Alpha Beta-Hydrolase Fold Enzymes Structures, Functions and Mechanisms. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2000, 1, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogorb, M.A.; Vilanova, E. Enzymes involved in the detoxification of organophosphorus, carbamate and pyrethroid insecticides through hydrolysis. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 128, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudderuddin, K.I.; Tan, K.H. Some hydrolases and their involvement in insecticide resistance. PANS Pest Artic. News Summ. 1973, 19, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celorio-Mancera, M.P.; Greve, L.C.; Teuber, L.R.; Labavitch, J.M. Identification of endo- and exo-polygalacturonase activity in Lygus hesperus (Knight) salivary glands. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 70, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, J.; Booth, R.E. Expression of Polygalacturonase from Lygus Hesperus. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 853.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.; Krishnan, N.; Musser, F. Polygalacturonase gene expression and enzymatic activity in salivary glands of laboratory reared and wild populations of Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera: Miridae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2017, 114, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.A.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Oliveira, M.G.A.; Ferreira, G.H. Enhanced proteolytic and cellulolytic activity in insecticide-resistant strains of the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2008, 44, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Bond, J.S. Proteases: Multifunctional Enzymes in Life and Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30433–30437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. Families of serine peptidases. Meth. Enzymol. 1994, 244, 19–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Chen, M.S.; Abel, C.A. Potential use of proteinase inhibitors, avidin, and other bio-reagents for synergizing Bt performance and delaying resistance development to Bt. In Recent Advances in Entomological Research: From Molecular Biology to Pest Management; Liu, T.X., Kang, L., Eds.; The High Education Press: Beijing, China, 2010; Volume 19, pp. 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- López-Zavala, A.A.; Quintero-Reyes, I.E.; Carrasco-Miranda, J.S.; Stojanoff, V.; Weichsel, A.; Rudiño-Piñera, E.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R. Structure of nucleoside diphosphate kinase from pacific shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in binary complexes with purine and pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphates. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2014, 70, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

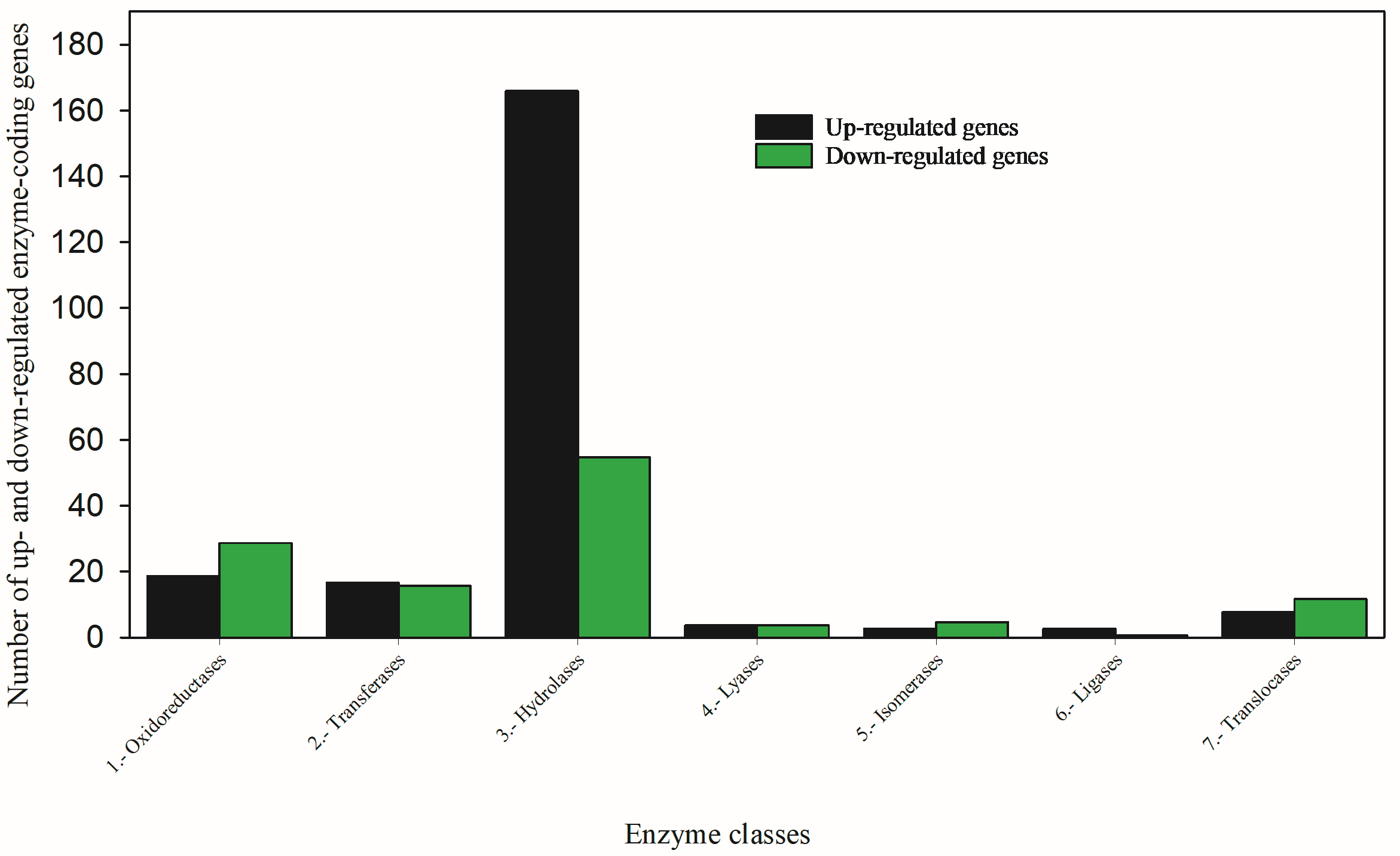

| 176 Upregulated Genes Code 30 Enzymes | 120 Downregulated Genes Code 29 Enzymes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Enzymes | No. of Coding Genes | No. | Enzymes | No. of Coding Genes |
| 1 | Esterase | 11 | 1 | Esterase | 1 |
| 2 | P450 | 6 * | P450 | 0 | |
| 3 | GST | 1 | GST | 0 | |
| 4 | Oxidase | 2 | 2 | Oxidase | 10 |
| 5 | Hydrolase | 14 | 3 | Hydrolase | 2 |
| 6 | Reductase | 6 | 4 | Reductase | 1 |
| 7 | Transferase | 7 | 5 | Transferase | 4 |
| 8 | Dehydrogenase | 4 | 6 | Dehydrogenase | 14 |
| 9 | Kinase | 7 | 7 | Kinase | 8 |
| 10 | Synthase | 7 | 8 | Synthase | 5 |
| 11 | ATPase | 2 | 9 | ATPase | 1 |
| 12 | Lyase | 1 | 10 | Lyase | 2 |
| 13 | Isomerase | 1 | 11 | Isomerase | 4 |
| Ligase | 0 | 12 | Ligase | 3 | |
| 14 | Translocase | 1 | Translocase | 0 | |
| 15 | Thio-Esterase | 1 | Thio-Esterase | 0 | |
| Phospho-Est | 0 | 13 | Phospho-Est | 1 | |
| 16 | Deoxyribonuclease | 1 | Deoxyribonuclease | 0 | |
| 17 | Phosphatase | 3 | 14 | Phosphatase | 9 |
| 18 | lysozyme | 2 | lysozyme | 0 | |
| 19 | Polymerase | 1 | 15 | Polymerase | 3 |
| Nucleotidase | 0 | 16 | Nucleotidase | 1 | |
| 20 | Amidase | 1 | Amidase | 0 | |
| Chitinase | 0 | 17 | Chitinase | 1 | |
| Ovochymase | 0 | 18 | Ovochymase | 1 | |
| 21 | Amylase | 1 | 19 | Amylase | 2 |
| 22 | Carboxypeptidase | 4 | 20 | Carboxypeptidase | 6 |
| 23 | Cathepsin | 3 | 21 | Cathepsin | 1 |
| CysProtease | 0 | 22 | CysProtease | 2 | |
| Dismutase | 0 | 23 | Dismutase | 6 | |
| 24 | Glucosidase | 4 | 24 | Glucosidase | 1 |
| 25 | Lipase | 13 | 25 | Lipase | 2 |
| 26 | Peptidase | 1 | 26 | Peptidase | 11 |
| 27 | Polygalacturonase | 35 | 27 | Polygalacturonase | 1 |
| 28 | Protease | 24 | 28 | Protease | 15 |
| 29 | Trypsin | 11 | 29 | Trypsin | 2 |
| 30 | Transcriptase | 1 | Transcriptase | 0 | |
| Pathway | Pathway ID | Seqs | Gene Sequences ID | Coded Enzyme |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug metabolism—other enzymes | ko00983 | 11 | LL_2770; LL-223; LL_5104; LL_6522; LL_2244; LL_2193; LL_2639; LL_2508; LL_1233; LL_2520; LL_2600 | Esterase |
| 1 | LL_2533 | Synthase | ||
| Xenobiotics | R-MMU-211981 | 1 | LL-39 * | P450 |
| R-GGA-211981 | 1 | LL_4087 * | P450 | |
| Detoxification of reactive oxygen species | R-DME-3299685 | 1 | LL_3600 | Reductase |
| Aflatoxin activation and detoxification | R-GGA-5423646 | 2 | LL_4087; LL-39 | P450 |
| Oxidative phosphorylation | ko00190 | 1 | LL_547 | Oxidase |
| 2 | LL_5277; LL_1710 | Synthase | ||
| 1 | LL_2370 | Dehydrogenase | ||
| Respiratory electron transport | R-DME-611105 | 1 | LL_74 | Oxidase |
| Neurotransmitter clearance | R-DME-112311 | 1 | LL_6522 | Esterase |
| Eicosanoids | R-RNO-211979 | 1 | LL_4510 | P450 |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | ko00590 | 1 | LL_4510 | P450 |
| 3 | LL_5131; LL_5648; LL_4347 | Reductase | ||
| Biosynthesis of maresin-like SPMs | R-MMU-9027307 | 1 | LL-39 | P450 |
| R-GGA-9027307 | 1 | LL_4087 | P450 | |
| Endogenous sterols | R-MMU-211976 | 1 | LL_3822 | P450 |
| Synthesis of leukotrienes (LT) and eoxins (EX) | R-RNO-2142691 | 1 | LL_4510 | P450 |
| Phase I—functionalization of compounds | R-HSA-211945 | 1 | LL_2193 | Esterase |
| R-DME-211945 | 1 | LL_6522 | Esterase | |
| R-SSC-211945 | 2 | LL_5131; LL_4347 | Reductase | |
| R-CFA-211945 | 1 | LL_5648 | Reductase | |
| Cholinergic synapse | ko04725 | 2 | LL_6522; LL_2193 | Esterase |
| Cytoprotection by HMOX1 | R-DME-9707564 | 1 | LL_74 | Oxidase |
| Fatty acids | R-RNO-211935 | 1 | LL_4510 | P450 |
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | ko00564 | 2 | LL_6522; LL_2193 | Esterase |
| LDL clearance | R-DME-8964038 | 1 | LL_6522 | Esterase |
| Metabolism of angiotensinogen to angiotensins | R-HSA-2022377 | 1 | LL_2193 | Esterase |
| Miscellaneous substrates | R-RNO-211958 | 1 | LL_4510 | P450 |
| R-GGA-211958 | 1 | LL_4087 | P450 | |
| Platelet activation | ko04611 | 1 | LL_4510 | P450 |
| Synthesis of (16–20)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETE) | R-RNO-2142816 | 1 | LL_4510 | P450 |
| Synthesis of PC | R-DME-1483191 | 1 | LL_6522 | Esterase |
| R-MMU-1483191 | 1 | LL_2133 | kinase | |
| The canonica+6:42l retinoid cycle in rods (twilight vision) | R-MMU-2453902 | 1 | LL_3822 | P450 |
| Pathway | Pathway ID | Seqs | cDNA Sequence ID | Coded Enzymes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidative phosphorylation | ko00190 | 1 | LL_2757 | ATPase |
| 2 | LL_725; LL_1114 | Cytochrome b | ||
| 4 | LL_1370; LL_1608; LL_1489; LL_2446 | Dehydrogenase | ||
| 2 | LL_6245; LL_3052 | Hypothetical protein | ||
| 9 | LL_119; LL_128; LL_3927; LL_222; LL_3845; LL_791; LL_5019; LL_317; LL_2260 | Oxidase | ||
| 4 | LL_1620; LL_1695; LL_2225; LL_6173 | Synthase | ||
| Respiratory electron transport | R-DME-611105 | 12 | LL_725; LL_317; LL_119; LL_128; LL_2260; LL_3927; LL_222; LL_1114; LL_3845; LL_1531; LL_791; LL_5019 | Oxidase |
| TP53 regulates metabolic genes | R-DME-5628897 | 9 | LL_317; LL_119; LL_128; LL_3927; LL_222; LL_3845; LL_1531; LL_791; LL_5019 | Oxidase |
| Detoxification of reactive oxygen species | R-DRE-3299685 | 4 | LL_2080; LL-34; LL_6623; LL_3138 | Superoxide dismutase |
| 2 | LL_1663; LL_164 | Phosphatase | ||
| Drug metabolism—other enzymes | ko00983 | 1 | LL_1672 | Kinase |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.-C.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Portilla, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y. Microarray and Functional Pathway Analyses Revealed Significantly Elevated Gene Expressions Associated with Metabolic Resistance to Oxamyl (Vydate) in Lygus lineolaris. Toxics 2024, 12, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030188
Zhu Y-C, Du Y, Liu X, Portilla M, Chen J, Wang Y. Microarray and Functional Pathway Analyses Revealed Significantly Elevated Gene Expressions Associated with Metabolic Resistance to Oxamyl (Vydate) in Lygus lineolaris. Toxics. 2024; 12(3):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030188
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yu-Cheng, Yuzhe Du, Xiaofen Liu, Maribel Portilla, Jian Chen, and Yanhua Wang. 2024. "Microarray and Functional Pathway Analyses Revealed Significantly Elevated Gene Expressions Associated with Metabolic Resistance to Oxamyl (Vydate) in Lygus lineolaris" Toxics 12, no. 3: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030188
APA StyleZhu, Y.-C., Du, Y., Liu, X., Portilla, M., Chen, J., & Wang, Y. (2024). Microarray and Functional Pathway Analyses Revealed Significantly Elevated Gene Expressions Associated with Metabolic Resistance to Oxamyl (Vydate) in Lygus lineolaris. Toxics, 12(3), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030188








