Comparing the Developmental Toxicity Delay and Neurotoxicity of Benzothiazole and Its Derivatives (BTHs) in Juvenile Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Zebrafish Breeding and Embryo Collection
2.3. Embryos Exposed to Different BTH Solutions
2.4. Behavioral Experiments on Light and Dark Stimulation, Black and White Choice, and Tapping Stimulation of Zebrafish Larvae
2.4.1. Light and Dark Stimulation Behavioral Test
2.4.2. Vibration Startle Response Test (VSRA)
2.4.3. Phototaxis Selection Behavior Test
2.5. Image Observation of Transgenic Zebrafish
2.6. Quantitative qPCR Detection
2.7. Assessment of Oxidative Stress Levels
3. Results
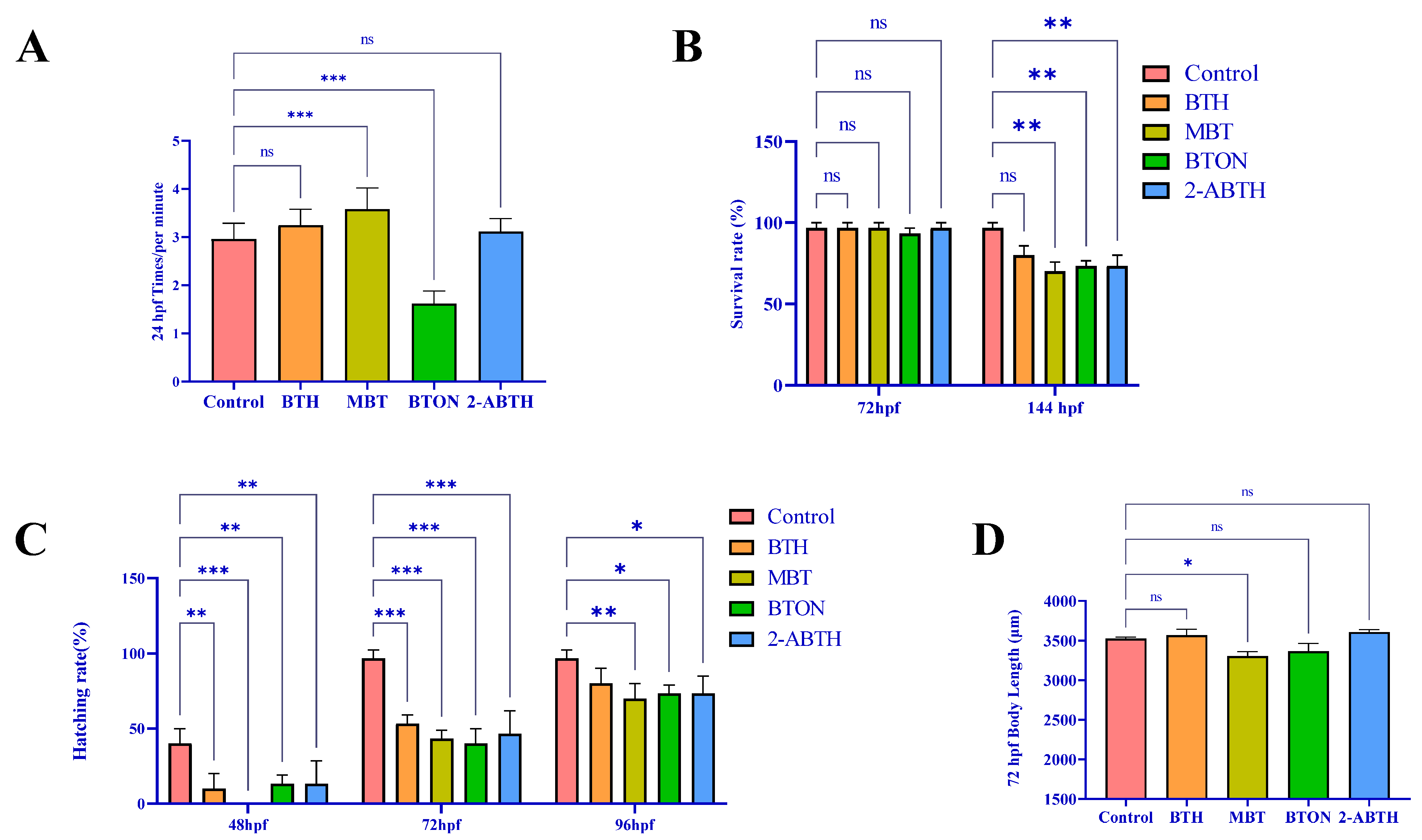
3.1. Developmental Toxicity of BTHs to Zebrafish Juveniles
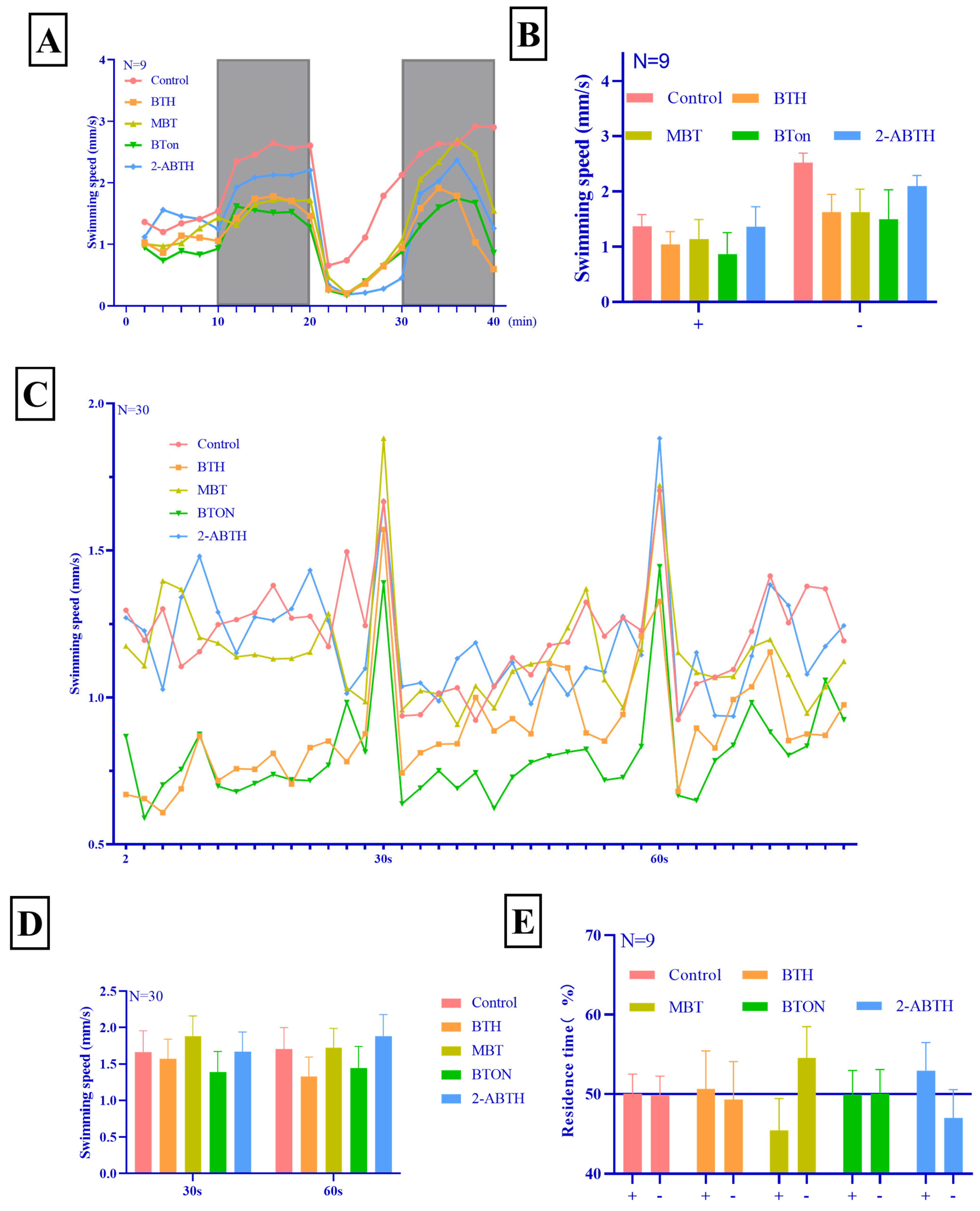
3.2. Behavioral Changes in Zebrafish Juveniles
3.2.1. Light and Dark Stimulation
3.2.2. Vibration Startle Response Test
3.2.3. Phototaxis Test
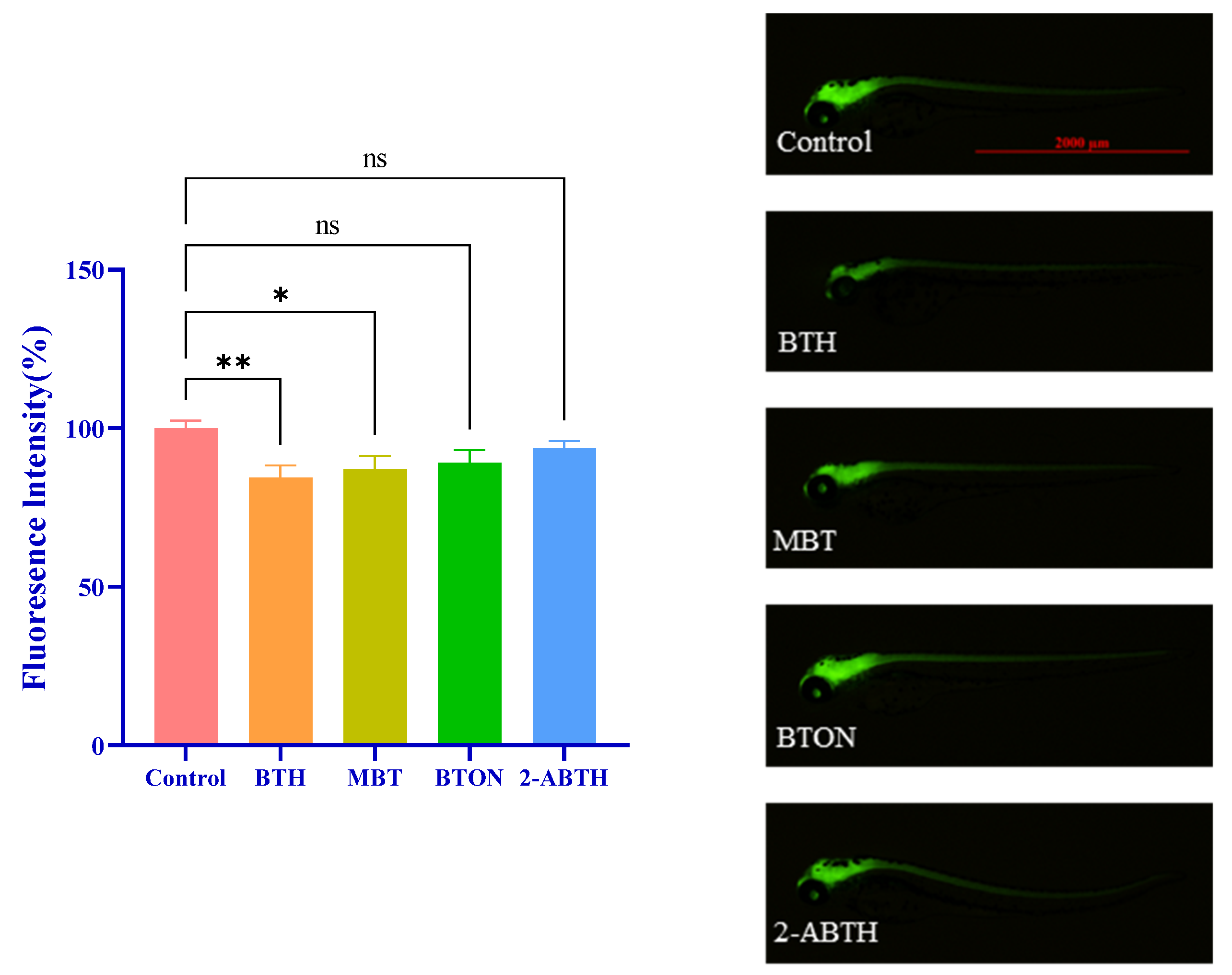
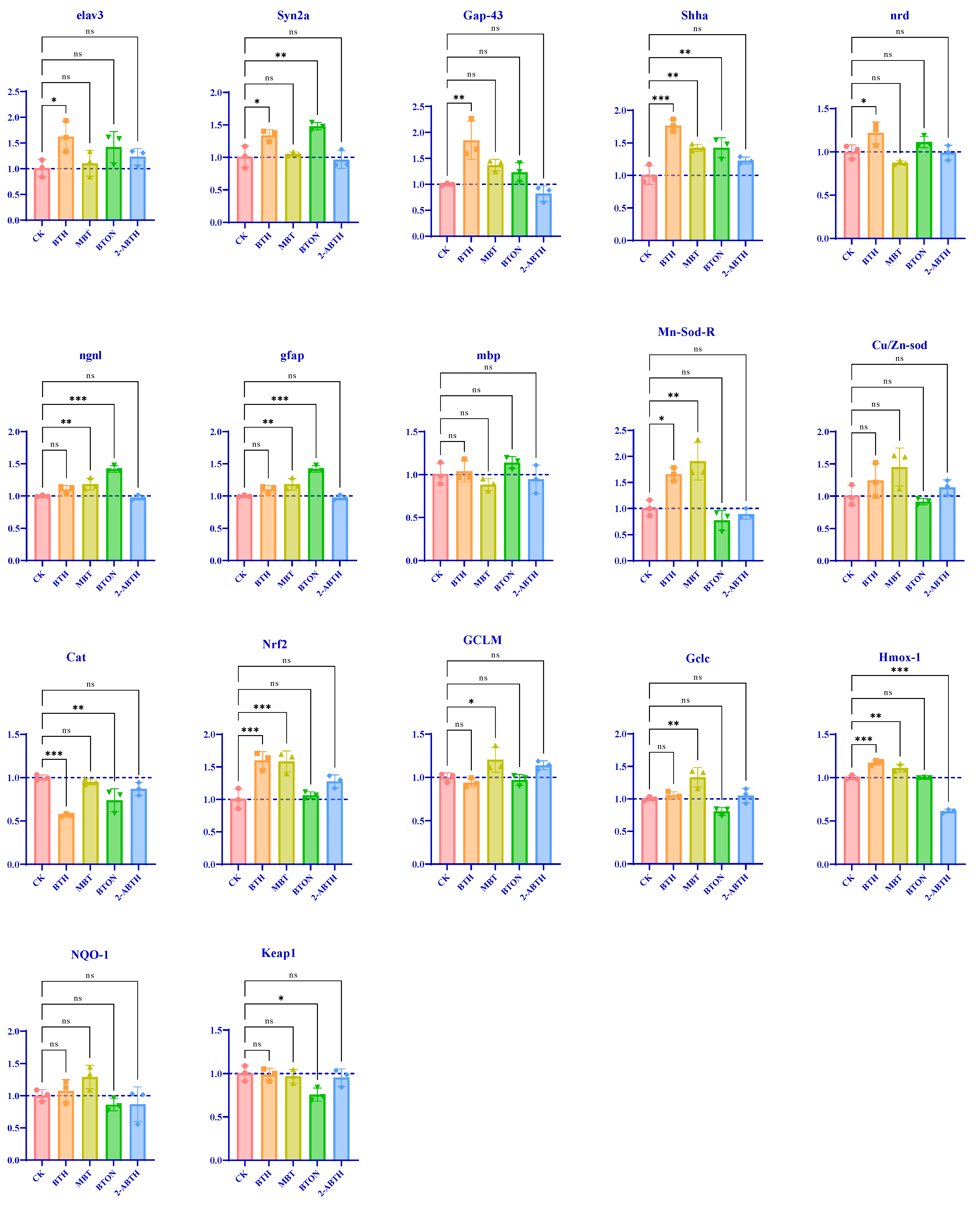
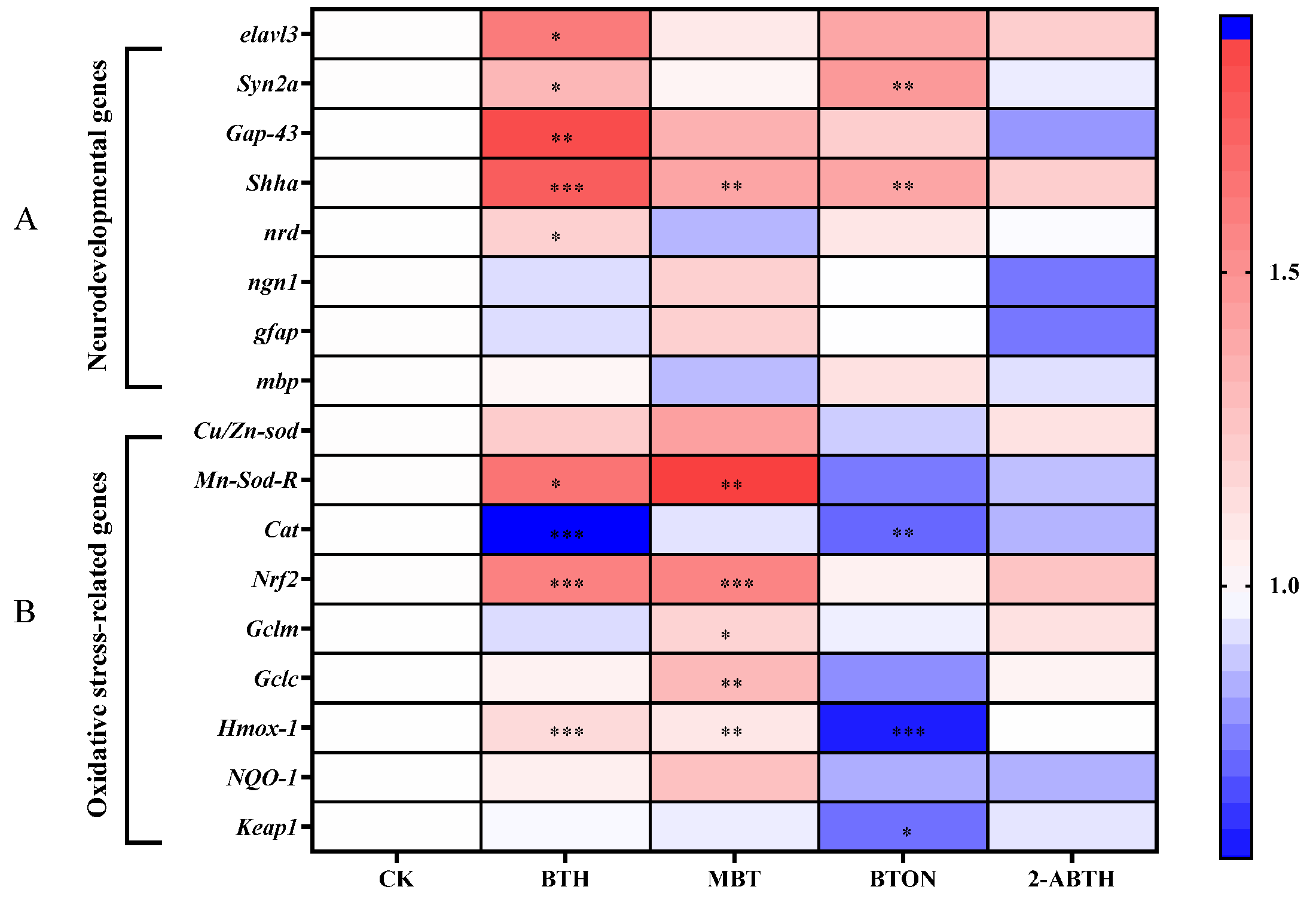
3.3. Influence on Central Nervous System Development
3.4. Effects on the Antioxidant Systems of Zebrafish
3.5. Gene Expression Related to Neurodevelopment in Zebrafish Larvae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Developmental toxicity: MBT > BTON ≈ 2-ABTH > BTH
- Neurotoxicity: BTH > MBT > BTON ≈ 2-ABTH
- Oxidative damage: MBT > BTH > BTON > 2-ABTH
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, Y.; Lee, S.; Woo, S.-H. Chemical Leaching from Tire Wear Particles with Various Treadwear Ratings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Zou, T.; Chen, M.; Song, Y.; Yang, C.; Qiu, B.; Chen, Z.-F.; Tsang, S.Y.; Qi, Z.; Cai, Z. Contamination profiles and health impact of benzothiazole and its derivatives in PM2.5 in typical Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Q. Widespread Occurrence of Benzotriazoles and Benzothiazoles in Tap Water: Influencing Factors and Contribution to Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Tian, L.; Mo, Y.; Yi, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Aquatic environmental fates and risks of benzotriazoles, benzothiazoles, and p-phenylenediamines in a catchment providing water to a megacity of China. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, G.; Toal, B.; Kurland, T. Benzothiazole Toxicity Assessment in Support of Synthetic Turf Field Human Health Risk Assessment. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2011, 74, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maceira, A.; Maria Marce, R.; Borrull, F. Occurrence of benzothiazole, benzotriazole and benzenesulfonamide derivates in outdoor air particulate matter samples and human exposure assessment. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wan, Y.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of benzotriazoles (BTRs) in indoor air from Albany, New York, USA, and its implications for inhalation exposure. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2017, 99, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancilla, D.A.; Holtkamp, A.; Matassa, L.; Fang, X. Isolation and characterization of Microtox®-active components from aircraft de-icing/anti-icing fluids. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 1997, 16, 430–434. [Google Scholar]
- Loos, R.; Locoro, G.; Comero, S.; Contini, S.; Schwesig, D.; Werres, F.; Balsaa, P.; Gans, O.; Weiss, S.; Blaha, L.; et al. Pan-European survey on the occurrence of selected polar organic persistent pollutants in ground water. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4115–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadaresta, F.; Manniello, M.D.; Östman, C.; Crescenzi, C.; Holmbäck, J.; Russo, P. Chemicals from textiles to skin: An in vitro permeation study of benzothiazole. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24629–24638. [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson, J.T.; Sydnes, M.O.; Raeder, E.M.; Schlenk, D.; Pampanin, D.M. Transcriptomic profiles of brains in juvenile Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) exposed to pharmaceuticals and personal care products from a wastewater treatment plant discharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, L.; Kim, H.; Lee, T.Y.; An, Y.J. Chemical toxicity screening of tire particle leachates from vehicles and their effects on organisms across three trophic levels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 114999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Schlichting, R.; Konig, M.; Scholz, S.; Krauss, M.; Escher, B.I. Monitoring Mixture Effects of Neurotoxicants in Surface Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents with Neurite Outgrowth Inhibition in SH-SY5Y Cells. ACS Environ. Au 2022, 2, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Jing, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yan, M.; Yi, X.; Liu, R. Acute toxicity of tire wear particles, leachates and toxicity identification evaluation of leachates to the marine copepod, Tigriopus japonicus. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Song, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Zhu, M. Benzothiazole-based ionic liquids (BIL)-induced acute toxicity attributed to damage to antioxidant enzyme system in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 49, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hornung, M.W.; Kosian, P.A.; Haselman, J.T.; Korte, J.J.; Challis, K.; Macherla, C.; Nevalainen, E.; Degitz, S.J. In Vitro, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Determination of Thyroid Hormone Modulating Activity of Benzothiazoles. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 146, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochs, S.D.; Souza, T.M.; Sobrinho, R.D.; de Oliveira, R.B.; Bernardes, M.C.; Netto, A.D.P. Simultaneous evaluation of benzotriazoles, benzothiazoles and benzenesulfonamides in water samples from the impacted urban Jacarepagua Lagoon System (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) by liquid chromatog- raphy coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, R.K.; Rawal, R.K.; Bariwal, J. Recent Advances in the Chemistry and Biology of Benzothiazoles. Arch. Pharm. 2015, 348, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avagyan, R.; Sadiktsis, I.; Bergvall, C.; Westerholm, R. Tire tread wear particles in ambient air—A previously unknown source of human exposure to the biocide 2-mercaptobenzothiazole. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11580–11586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, H.; Van Derpoorten, K.; Cacciaguerra, S.; Spampinato, S.; Stables, J.P.; Depovere, P.; Isa, M.; Masereel, B.; Delarge, J.; Poupaert, J.H. Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of 2(3H)-benzoxazolone and 2(3H)-benzothiazolone derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadmal, T.L.; Katre, S.D.; Mandewale, M.C.; Kumbhare, R.M. Contemporary progress in the synthesis and reactions of 2-aminobenzothiazole: A review. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 776–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.J.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Klesius, P.H. In vivo and in vitro effects of benzothiazole on sheepshead minnow (Cyprinodon variegatus). Mar. Environ. Res. 2000, 50, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephensen, E.; Adolfsson-Erici, M.; Hulander, M.; Parkkonen, J.; Förlin, L. Rubber additives induce oxidative stress in rainbow trout. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinckens, E.; Vergauwen, L.; Schroeder, A.L.; Maho, W.; Blackwell, B.R.; Witters, H.; Blust, R.; Ankley, G.T.; Covaci, A.; Villeneuve, D.L.; et al. Impaired anterior swim bladder inflation following exposure to the thyroid peroxidase inhibitor 2-mercaptobenzothiazole part II: Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 173, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, T.; Kim, J.; Ko, D.H.; Kim, C.; Hwang, J.; Ahn, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.; Yoon, T. Zebrafish as a new model for phenotype-based screening of melanogenic regulatory compounds. Pigment Cell Res. 2007, 20, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Guo, L.; Chen, C.; Ji, G.; Wang, L. Neurobehavioral toxic effects and mechanisms of 2-aminobenzothiazole exposure on zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Amora, M.; Giordani, S. The Utility of Zebrafish as a Model for Screening Developmental Neurotoxicity. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, Y.; Trengove, M.C.; Ward, A.C. Zebrafish As a Genetic Model in Pre-Clinical Drug Testing and Screening. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2458–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Freeman, J.L. Zebrafish as a Model for Developmental Neurotoxicity Assessment: The Application of the Zebrafish in Defining the Effects of Arsenic, Methylmercury, or Lead on Early Neurodevelopment. Toxics 2014, 2, 464–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, M.; Arena, C.; Cioni, C.; Tedeschi, G. Temperature- and chemical-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1276941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiper, K.G.; Freeman, J.L. Zebrafish as a Tool to Assess Developmental Neurotoxicity. In Cell Culture Techniques; Aschner, M., Costa, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 169–193. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.-Y.; Cowden, J.; Simmons, S.O.; Padilla, S.; Ramabhadran, R. Gene expression changes in developing zebrafish as potential markers for rapid developmental neurotoxicity screening. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St John, J.A.; Key, B. HuC–eGFP mosaic labelling of neurons in zebrafish enables in vivo live cell imaging of growth cones. J. Mol. Histol. 2012, 43, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffioli, E.; Angiulli, E.; Nonnis, S.; Grassi Scalvini, F.; Negri, A.; Tedeschi, G.; Arisi, I.; Frabetti, F.; D’Aniello, S.; Alleva, E.; et al. Brain Proteome and Behavioural Analysis in Wild Type, BDNF+/− and BDNF−/− Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Exposed to Two Different Temperatures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fero, K.; Yokogawa, T.; Burgess, H.A. The Behavioral Repertoire of Larval Zebrafish. In Zebrafish Models in Neurobehavioral Research; Kalueff, A.V., Cachat, J.M., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 249–291. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyberghs, J.; Bars, C.; Ayuso, M.; Van Ginneken, C.; Foubert, K.; Van Cruchten, S. DMSO Concentrations up to 1% are Safe to be Used in the Zebrafish Embryo Developmental Toxicity Assay. Front. Toxicol. 2021, 3, 804033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Fukushima, N.; Hasumi, A. Standardized Method for the Assessment of Behavioral Responses of Zebrafish Larvae. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Guo, M.; Yin, X.; Huang, C.; Qian, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Ji, G. A systematic comparison of neurotoxicity of bisphenol A and its derivatives in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.; Prats, E.; Novoa-Luna, K.A.; Bedrossiantz, J.; Gómez-Canela, C.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; Raldúa, D. Development of a vibrational startle response assay for screening environmental pollutants and drugs impairing predator avoidance. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650 Pt 1, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhou, B. Acute exposure to DE-71 causes alterations in visual behavior in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vliet, S.M.; Ho, T.C.; Volz, D.C. Behavioral screening of the LOPAC1280 library in zebrafish embryos. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 329, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fraga, J.; Dipp-Alvarez, V.; Bardullas, U. Quantification of Spontaneous Tail Movement in Zebrafish Embryos Using a Novel Open-Source MATLAB Application. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dou, J.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, X. Bioeffects of Inhaled Nanoplastics on Neurons and Alteration of Animal Behaviors through Deposition in the Brain. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Ueshima, E.; Muraoka, O.; Tanaka, H.; Yeo, S.Y.; Huh, T.L.; Miki, N. Zebrafish elav/HuC homologue as a very early neuronal marker. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 216, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Shao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, Z. Effects of Di-n-butyl Phthalate and Diethyl Phthalate on Acetylcholinesterase Activity and Neurotoxicity Related Gene Expression in Embryonic Zebrafish. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 91, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Jia, Y.; Dai, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Yu, L. Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate disrupts axonal growth, cholinergic system and motor behavior in early life zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 192, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprara, G.A.; Perni, S.; Morabito, C.; Mariggiò, M.A.; Guarnieri, S. Specific association of growth-associated protein 43 with calcium release units in skeletal muscles of lower vertebrates. Eur. J. Histochem. 2014, 58, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Dechlorane Plus exposure on axonal growth, musculature and motor behavior in embryo-larval zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Sun, H.; Xu, Z.; Hong, H.; Lin, H.; Gao, P. 3-Bromocarbazole-Induced Developmental Neurotoxicity and Effect Mechanisms in Zebrafish. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, C.Y.; Song, J.; Oh, H.; Kim, C.-H.; Park, J.-H. Trimethyltin chloride inhibits neuronal cell differentiation in zebrafish embryo neurodevelopment. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 54, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, Q.; Kim, K.J.; Dardashti, F.D.; Kim, J.; He, F.; Sun, Y. Ngn1 inhibits astrogliogenesis through induction of miR-9 during neuronal fate specification. eLife 2015, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, T.; Wullimann, M.F. Expression domains of neuroD (nrd) in the early postembryonic zebrafish brain. Brain Res. Bull. 2002, 57, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochocinska, M.J.; Hitchcock, P.F. NeuroD regulates proliferation of photoreceptor progenitors in the retina of the zebrafish. Mech. Dev. 2009, 126, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Bauer, N.; Schäfer, I.; White, R. Making myelin basic protein—From mRNA transport to localized translation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruvot, B.; Curé, Y.; Djiotsa, J.; Voncken, A.; Muller, M. Developmental defects in zebrafish for classification of EGF pathway inhibitors. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 274, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, F.; Botta, D.; White, C.C.; Schmuck, S.C.; Winfough, M.; Schaupp, C.M.; Gallagher, E.P.; Brooks, B.W.; Williams, E.S.; Coish, P.; et al. Kinetics of Glutathione Depletion and Antioxidant Gene Expression as Indicators of Chemical Modes of Action Assessed in Vitro in Mouse Hepatocytes with Enhanced Glutathione Synthesis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, L.G.; Kelleher, M.O.; Eggleston, I.M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayes, J.D. Transcription factor Nrf2 mediates an adaptive response to sulforaphane that protects fibroblasts in vitro against the cytotoxic effects of electrophiles, peroxides and redox-cycling agents. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 237, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korashy, H.M.; Brocks, D.R.; El-Kadi, A.O.S. Induction of the NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 by ketoconazole and itraconazole: A mechanism of cancer chemoprotection. Cancer Lett. 2007, 258, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.-H.; Jain, A.K.; Papusha, V.; Jaiswal, A.K. An Auto-regulatory Loop between Stress Sensors INrf2 and Nrf2 Controls Their Cellular Abundance. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 36412–36420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Park, J.-S.; Leem, Y.-H.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, H.-S. NQO1 mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of nootkatone in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation by modulating the AMPK signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 164, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilkaya, S.; Akpinar, G.; Sesal, N.C.; Kasap, M.; Gokalsin, B.; Kayhan, F.E. Using proteomics, q-PCR and biochemical methods complementing as a multiapproach to elicit the crucial responses of zebrafish liver exposed to neonicotinoid pesticide. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 47, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Primer Sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Reverse | |
| β-actin | ACAGGGAAAAGATGACACAGATCA | CAGCCTGGATGGCAACGTA |
| elavl3 | AGACAAGATCACAGGCCAGAGCTT | TGGTCTGCAGTTTGAGACCGTTGA |
| Syn2a | GTGACCATGCCAGCATTTC | TGGTTCTCCACTTTCACCTT |
| Gap-43 | TTAACGGAGGACCAGTGCAA | GACGGAGGTCTGAGTCCTGA |
| Shha | AGACCGAGACTCCACGACGC | TGCAGTCACTGGTGCGAACG |
| nrd | CAGCAAGTGCTTCCTTTTCC | TAAGGGGTCCGTCAAATGAG |
| ngn1 | TGCACAACCTTAACGACGCATTGG | TGCCCAGATGTAGTTGTGAGCGAA |
| gfap | GGATGCAGCCAATCGTAAT | TTCCAGGTCACAGGTCAG |
| mbp | AATCAGCAGGTTCTTCGGAGGAGA | AAGAAATGCACGACAGGGTTGACG |
| Cu/Zn-Sod | GTCGTCTGGCTTGTGGAGTG | TGTCAGCGGGCTAGTGCTT |
| Mn-Sod | GTCCGCACTTCAACCCTCA | TCCTCATTGCCACCCTTCC |
| Cat | TGATCTTAGCAAATGCAACACTGA | TGCAAAGGCCCCCATTTT |
| Nrf2 | GACAAAATCGGCGACAAAAT | TTAGGCCATGTCCACACGTA |
| Gclm | AAGCCAGACACTGACACACC | ATCTGGAGGCATCACACAGC |
| Gclc | CTCCTCACAGTCACGGCATT | TGAATGGAGACGGGGTGTTG |
| Hmox-1 | ACGCTTACACCCCGCTACCTC | ATCCCCTTGTTTCCAGTCAG |
| NQO-1 | CCTGCCATTCTGAAAGGCTGGT | GTGGTGATGGAAAGCACTGCCT |
| Keap1 | CCAACGGCATAGAGGTAGTTAT | CCTGTATGTGGTAGGAGGGTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, X.; Wang, L.; Mao, L. Comparing the Developmental Toxicity Delay and Neurotoxicity of Benzothiazole and Its Derivatives (BTHs) in Juvenile Zebrafish. Toxics 2024, 12, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12050341
Yin X, Wang L, Mao L. Comparing the Developmental Toxicity Delay and Neurotoxicity of Benzothiazole and Its Derivatives (BTHs) in Juvenile Zebrafish. Toxics. 2024; 12(5):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12050341
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Xiaogang, Lei Wang, and Lianshan Mao. 2024. "Comparing the Developmental Toxicity Delay and Neurotoxicity of Benzothiazole and Its Derivatives (BTHs) in Juvenile Zebrafish" Toxics 12, no. 5: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12050341
APA StyleYin, X., Wang, L., & Mao, L. (2024). Comparing the Developmental Toxicity Delay and Neurotoxicity of Benzothiazole and Its Derivatives (BTHs) in Juvenile Zebrafish. Toxics, 12(5), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12050341





