Quantitative Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Factors on Heavy Metals Pollution and Spatial Distribution in Surface Drinking Water Sources in the Upper Huaihe River Basin in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
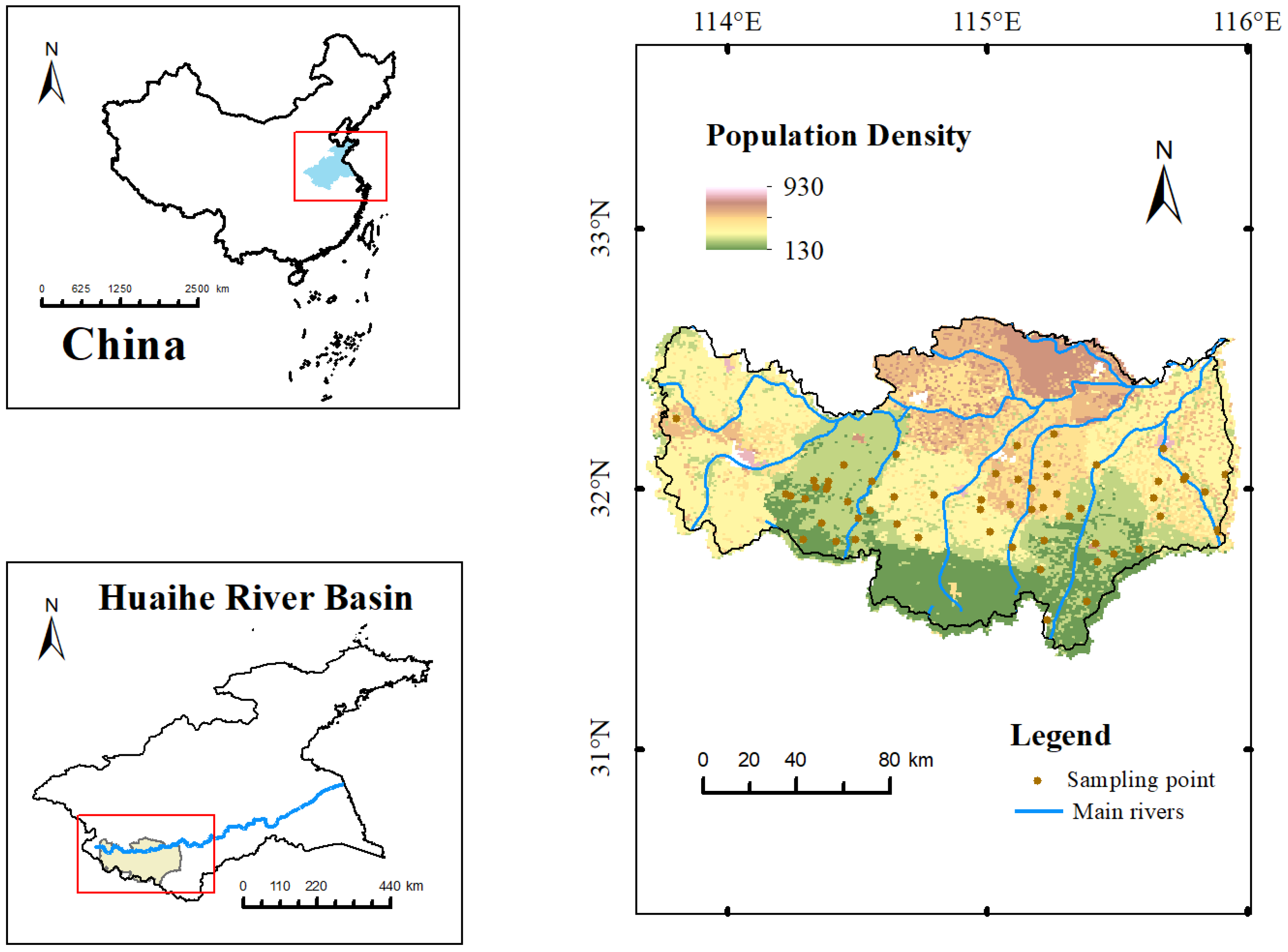
2.1. Study Area
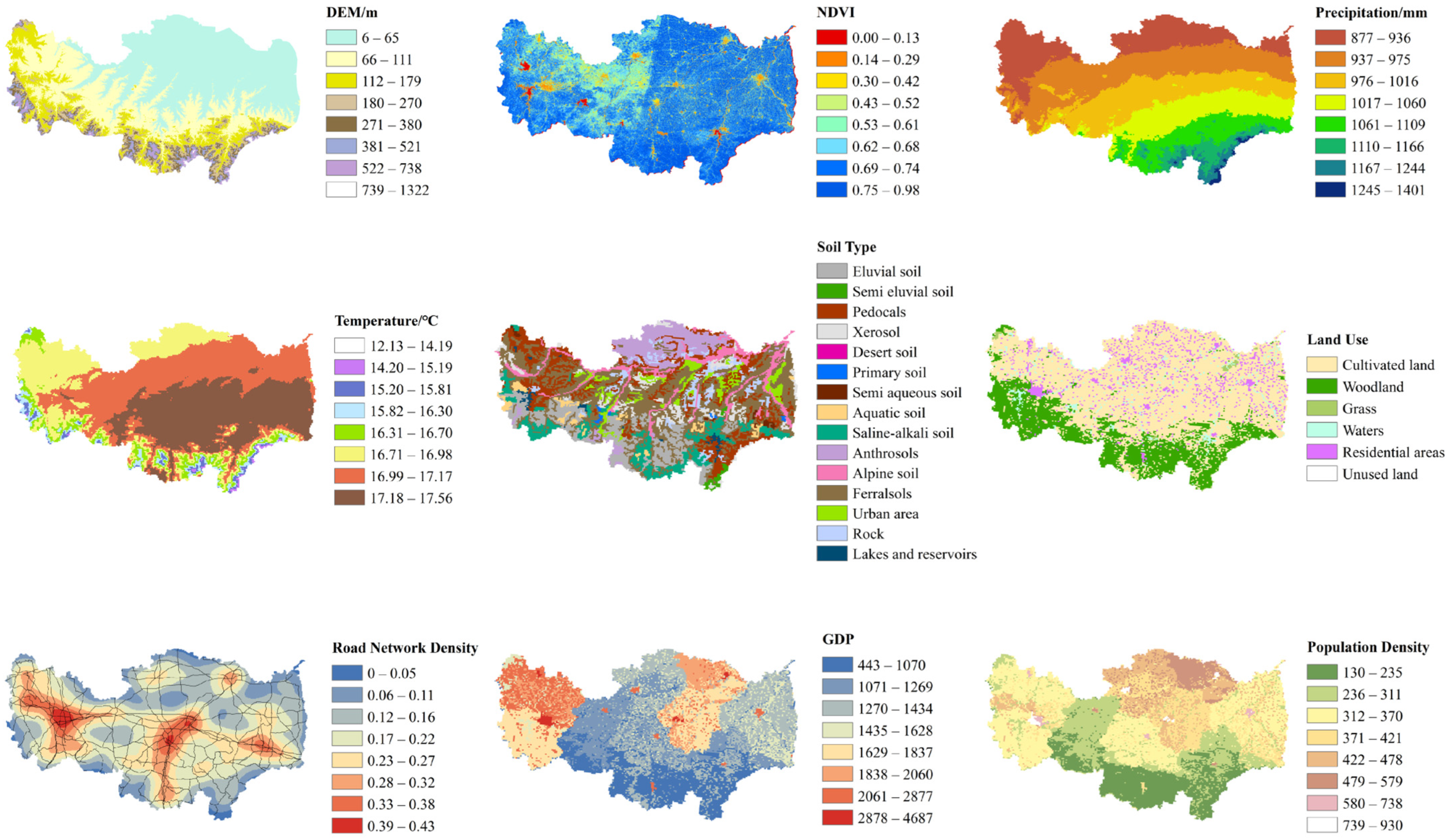
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Quality Assessment and Quality Control
2.5. Research Methods
2.5.1. Water Quality Index (WQI)
2.5.2. Universal Index Formula in the Form of a Logarithmic Power Function
2.5.3. Health Assessment
2.5.4. Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS)
2.5.5. Geodetector
- (1)
- Factor detection
- (2)
- Interaction detector
2.5.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assessment of Water Quality Pollution in Drinking Water Source Areas
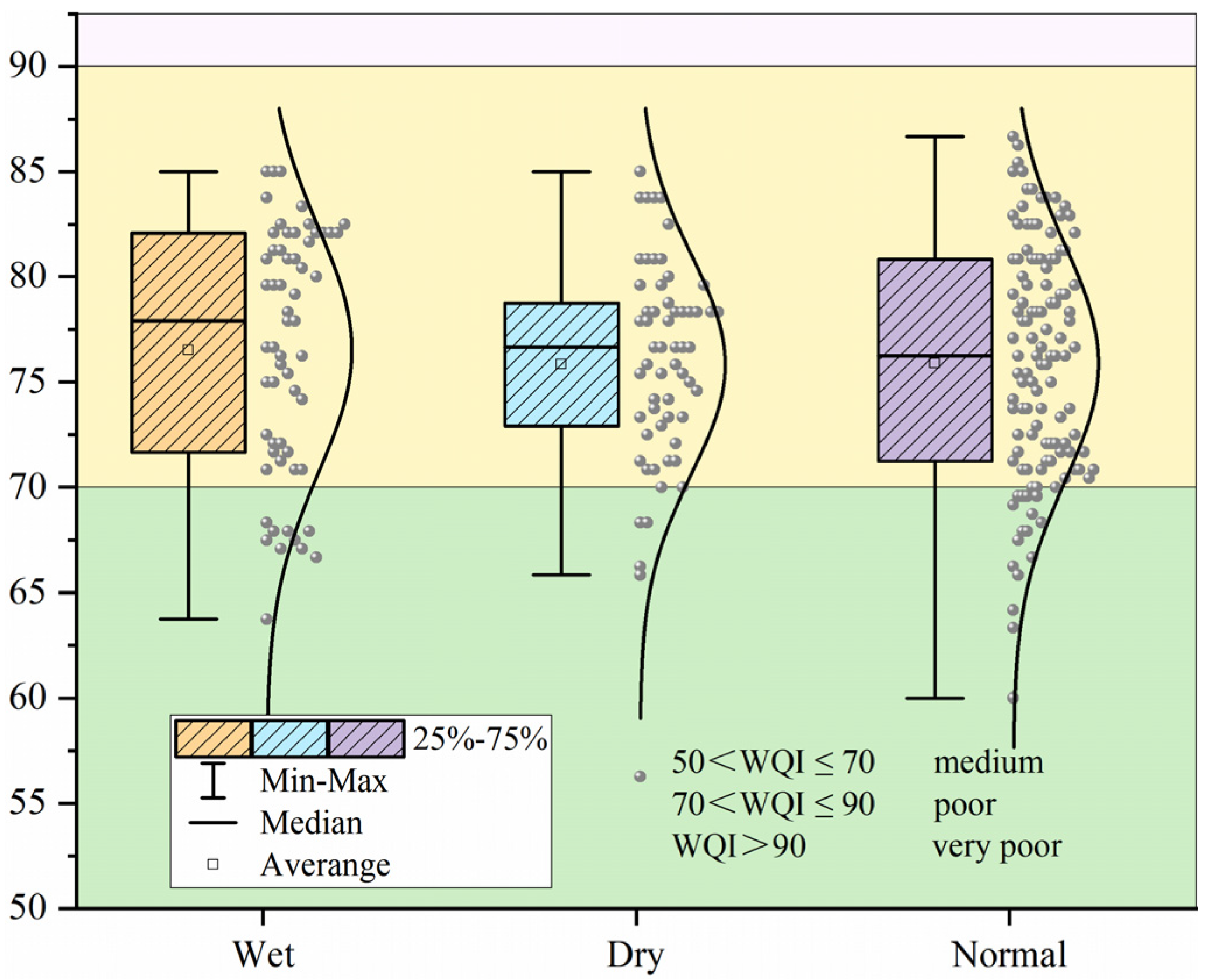
3.1.1. Comprehensive Index Evaluation of Water Quality
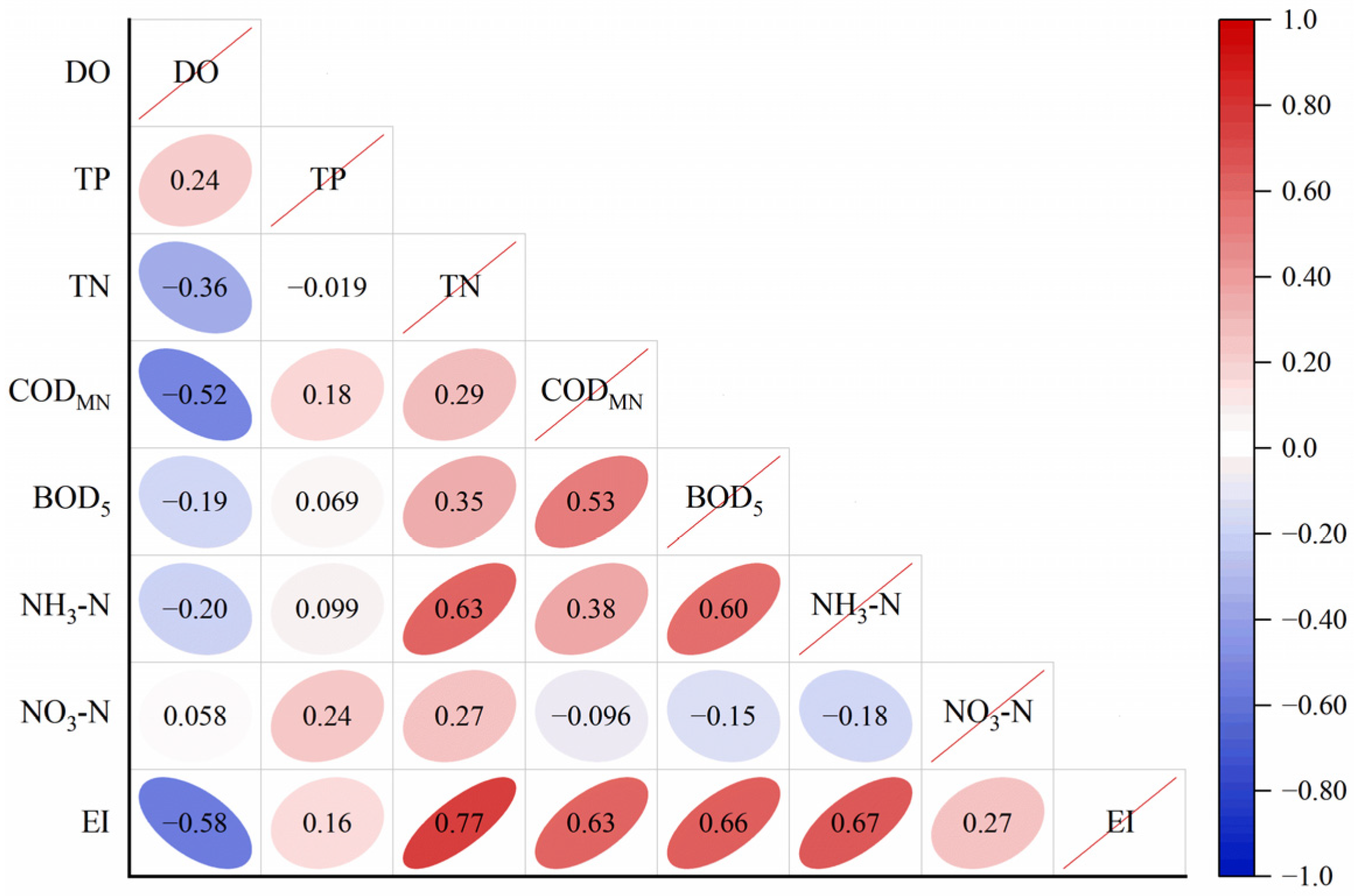
3.1.2. Water Eutrophication Assessment
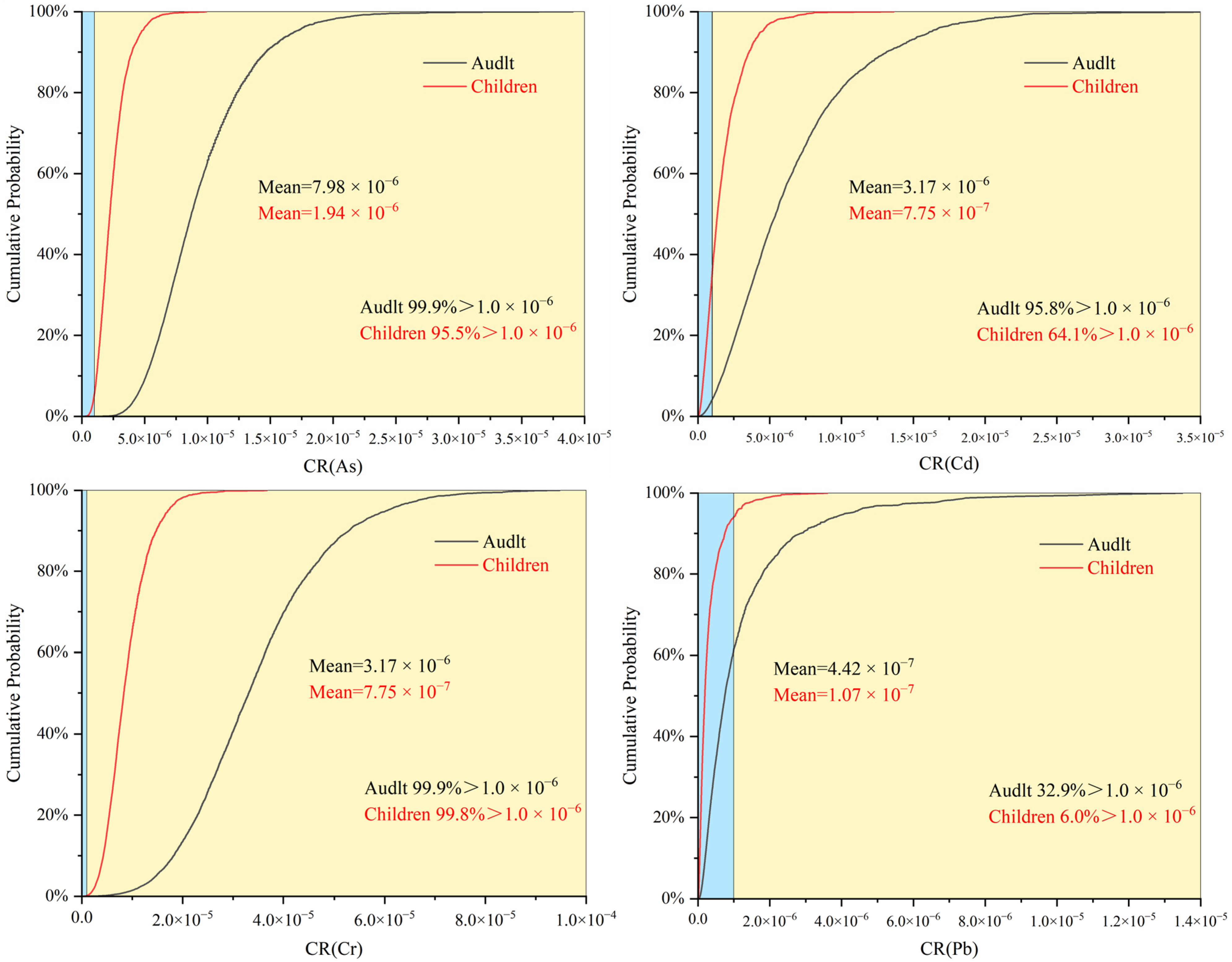
3.2. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water Source Areas
3.3. Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water Sources
3.3.1. Factor Detection
3.3.2. Interaction Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, S.; Guo, J.; Xie, Y.; Bian, R.; Wang, N.; Qi, W.; Liu, H. Distribution, sources, and potential health risks of fluoride, total iodine, and nitrate in rural drinking water sources of north and east China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, J.; Meng, W.; Su, G. A critical review on organophosphate esters in drinking water: Analysis, occurrence, sources, and human health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoyong, S.; Guibin, J. Strengthen environmental and health research capacity to build a beautiful china. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2020, 35, 1317–1320. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, J.P. Water microbiology. Bacterial pathogens and water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3657–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ren, J.; Xu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Peng, Y. Priority screening of contaminant of emerging concern (CECs) in surface water from drinking water sources in the lower reaches of the Yangtze river based on exposure-activity ratios (ears). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Chen, Z. Heavy metal (loid) s and organic contaminants in groundwater in the Pearl River Delta that has undergone three decades of urbanization and industrialization: Distributions, sources, and driving forces. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, Z.; Qiao, H.; Liu, F. Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, A. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: A global assessment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gong, D.; Zhao, W.; Lin, L.; Yang, W.; Guo, W.; Tang, X.; Li, Q. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water of the three gorges reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 134883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchart, A.; Green, A.; Hoyo, C.; Mattingly, C.J. Heavy metal exposure and metabolic syndrome: Evidence from human and model system studies. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, C.; Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metal soil pollution: A case study in the Qixia mining area, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2012, 18, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Du, Q.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Shan, Y.; Shao, W. A Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of an oasis agricultural region in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Rickaby, R.E.M. Interactions of thallium with marine phytoplankton. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 276, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Hossain, M.B.; Matin, A.; Sarker, M.S.I. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and source apportionment in the sediment from Feni River estuary, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Y.; Cao, P.; Hua, P. Vehicular contribution of pahs in size dependent road dust: A source apportionment by PCA-MLR, PMF, and Unmix receptor models. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Hua, P.; Zhang, J.; Krebs, P. Ecological risk and machine learning based source analyses of trace metals in typical surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Xiao, R.; Ren, Z.; Lv, X. Contamination assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil through the synthesis of PMF and GeogDetector models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinfeng, W.; Chengdong, X. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KXReader/Detail?invoice=H9yMXjRru5Rgr8gzMKR9WAY3oV7g2cyiC5C8pqxNdmsa7Gqx3bJVwQuTCRv85UYAyPueqhOejTuf5QahcA3wQsUorxMr6dNP98ErilrWE1pugKJj3hlgTlXqB9Qy6638ZGh6PvAGTr3tP3WZhITjwXwAanfW07706tVfJtAoiXE%3D&DBCODE=CJFQ&FileName=DLXB201701011&TABLEName=cjfdlast2017&nonce=9C7A009C2E04460799FB364524756411&TIMESTAMP=1715952060138&uid= (accessed on 15 June 2024). (In Chinese).
- Qiao, P.; Yang, S.; Lei, M.; Chen, T.; Dong, N. Quantitative analysis of the factors influencing spatial distribution of soil heavy metals based on geographical detector. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 392–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Liao, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhu, G.; Cassidy, D.P. Quantifying in fluences of interacting anthropogenic-natural factors on trace element accumulation and pollution risk in karst soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Gao, Y.; He, X.; Liu, T.; Jiang, B.; Shao, H.; Yao, Y. Spatial-temporal pattern evolution and driving force analysis of ecological environment vulnerability in Panzhihua City. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 7151–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, L. Interactive effects of natural and anthropogenic factors on heterogenetic accumulations of heavy metals in surface soils through geodetector analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhongqing, Y.; Zhongmin, W.; Junjie, Z.; Pan, X.; Hua, J.; Xiaohong, G. Example of water quality upgrading project of a municipal sewage plant in Huaihe River Basin, Anhui province. Technol. Water Treat. 2023, 49, 132–136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zihang, Z.; Juanjuan, Z.; Yu, L. For the sake of a clear river. China Youth News, 22 February 2023; p. 3. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, T. Huaihe River, anlan runs the central plains. Henan Daily Newspaper, 21 December 2022; p. 2. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-F.; Wu, L.-J.; Zhou, H.-S. Assessment and trend analysis of water quality in the Huaihe River Basin. J. Hydroecol. 2022, 43, 15–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Qiuhong, T.; Yongyong, Z. Spatiotemporal changes of water quality in Huai River Basin (Henan section) and its correlation with land use patterns. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1519–1530. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, L.; Pan, R. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments from a source water reservoir. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2016, 28, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zuo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X. Phytoplankton Community Structure and Nutrition Status Evaluation in the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Huaihe River. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2019, 1–6. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KXReader/Detail?invoice=t0BZ2Jx5txWr5mzFBwwtcHGH31TaviYBhFzZErOH2hvbqlp7eBFh%2F6Fv4H9YiJdRtnO4bDjL9qMjWvWxFx2Sox3V4GuWGeDj%2Bim%2BJqjTu%2BuARtRl6OkFdtL1XyFjFN77s2CHgMkl1%2BRLQdvZqTy35UHtK%2FjT%2FwGM8ZltD3fayqo%3D&DBCODE=CJFQ&FileName=ZNSD201902001&TABLEName=cjfdlast2019&nonce=72F7CEAC64984D7687F3071FB50F9705&TIMESTAMP=1720665361951&uid= (accessed on 16 June 2024).
- Fenf, D.; Xie, R.; Xu, Y.; Shen, D.; Jia, K.; Lv, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metals metalloid in drinking water in a region of Huaihe river basin from 2015 to 2019. J. Hyg. Res. 2023, 52, 721–725. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcher, M.; Bormann, H. On the transferability of the concept of drinking water protection zones from EU to Latin American countries. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1803–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinyin, Y.; Yong, H.; Chunli, Z.; Zuxiang, Y. Spatial-temporal variations of climate change of the Huaihe river basin during recent 50 years. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 25, 84–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Na, W.; Chen, W. Renovation practice of beautiful rural residential environment under the background of rural revitalization: Taking the pilot construction of Xiajiachong in Xinyang city as an example. Constr. Econ. 2022, 43, 516–520. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyu, L. Make every effort to shape the brand of “looking at Xinyang for a better life”. China Enterprise News, 14 March 2023; p. 2. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. State Environmental Protection Administration; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of China. 2002. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=FruxrO_GJXKojmBabj00ByRdzkLqeN091Rv0K9ORq5IxpGGiTVpEEV6aDqvcBspqkmNUrscxW98QZUKSLHQ1dENgpONXKid_lngGS2ipHfjnLMOHYeUtT-9b92OQi-obwMdXNadWXcw=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 17 June 2024). (In Chinese).
- Nong, X.; Shao, D.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J. Evaluation of water quality in the south-to-north water diversion project of China using the water quality index (WQI) method. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sener, S.; Sener, E.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.M.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Xue, L.; Fan, T.T. Pollution status of the yellow river tributaries in middle and lower reaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocer, M.A.T.; Sevgili, H. Parameters selection for water quality index in the assessment of the environmental impacts of land-based trout farms. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhao, F.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Hao, W. Water quality evaluation of Daheiting reservoir based on principal component analysis and wqimin. J. Henan Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 49, 52–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, P.; Shang, X.; Randy, D.; Zhang, M. Study on diurnal variation of wetland water quality in city. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2013, 39, 18–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wanf, J.; Guo, C. A universal index formula for eutrophic evaluation using a logarithmic power function. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2010, 30, 664–672. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Xu, T. A universal index formula for evaluating eutrophication level using a power function of weighted sums. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2008, 392–400. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Sun, T.; Fan, H.; Wu, B.; Li, M.; Qian, L. Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater quality and human health risk assessment of nitrate in the largest peninsula of China based on high-density sampling: A case study of Weifang. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omonona, O.V.; Okogbue, C.O. Hydrochemical evolution, geospatial groundwater quality and potential health risks associated with intake of nitrate via drinking water: Case of Gboko agricultural district, central Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H. Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, south India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Peng, J.; Yan, X.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in drinking water of rural schools in Henan province. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2023, 44, 307–310. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Z. Effects of agriculture and animal husbandry on heavy metal contamination in the aquatic environment and human health in Huangshui river basin. Water 2022, 14, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorennec, P.; Bemrah, N.; Tard, A.; Robin, A.; Le Bot, B.; Bard, D. Probabilistic modeling of young children’s overall lead exposure in France: Integrated approach for various exposure media. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zeng, M.; Peng, H.; Huang, C.; Sun, H.; Hou, Q.; Pi, P. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of Hainan island using the Monte Carlo simulation coupled with the APCS/MLR model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, M.; Han, Q.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Sun, A.; Mao, P.; Xiong, Q.; et al. Health risk assessment of PM2.5 heavy metals in county units of northern China based on Monte Carlo simulation and APCS-MLR. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Lin, Y.; Luo, Y. Influence of coastal groundwater salinization on the distribution and risks of heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S. Industrial metal pollution in water and probabilistic assessment of human health risk. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 185, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, C.; Wang, M.; Sun, A.; Han, Q.; Chen, C.; Liu, D.; Mao, P.; Feng, X.; Wang, M. Quantitative effects of anthropogenic and natural interactions on heavy metal pollution and spatial distribution in sediment of Qinhe river. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 43, 176–186. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.-X.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Dong, H.; Liu, J.-F.; Wang, D.-W.; Yan, B.-Q.; Chen, Y. Spatial differentiation and influencing factor analysis of soil heavy metal content at town level based on geographic detector. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4566–4577. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Peng, K.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, Y. Emission of methane from a key lake in the eastern route of the south-to-north water transfer project and the corresponding driving factors. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 1958–1965. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, L. Current situation and prevention and control measures of rural environmental pollution in Xinyang city. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 161–162. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KXReader/Detail?invoice=SHlgzhJP6%2FBHTazj9027%2Bi6oBqLo9VLY6xJ4%2Fb7UmNoIQBKdZCPTTpNSI3E%2FdzylMSeDtewmgSGspcJaMYlWo4Cwc4I%2BlDCU52gcT%2FSl1WkfFBlWXAOBmQ97FebBt8e8o6Tm1lGh%2FXXsymP2lidGg1%2BDwaNbVysbCHB1X4NBbu8%3D&DBCODE=CJFQ&FileName=ANHE201905093&TABLEName=cjfdlast2019&nonce=8D6E3DC31B2549F89AA1E7A017404B97&TIMESTAMP=1715952032449&uid= (accessed on 9 June 2024). (In Chinese).
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, G. Causes of excessive use of chemical fertilizer and its impacts on China’s water environment security. South-North. Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 104–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Zhang, M.; Lou, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Hou, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhao, F. Evolution and control strategies of eutrophication in water source reservoirs: A case study of Laohutan reservoir in Zhejiang province. J. Hydroecol. 2024, 1–12. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1785.x.20240628.1047.003.html (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Shan, K.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Z.; Lou, G.; Huang, Y. Study on spatial distribution characteristics and diversity of phytoplankton community structure in Sanmenxia reservoir of the yellow river. Yellow River 2023, 45, 78–83. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KXReader/Detail?invoice=ZU2iainvlbaIfV7U3jcGJ9Mm2j7HIRcnjyX2aInyysIP0W0PSPGoNIv%2BzKdF1WfuqV86KTkrIC%2FZbTI4Pt3ptPskdFKSoVaKhufwQ0H1jhO9YLQKEbkeszjbxYLrKhTSjJOUxbKI8v2ZdMcf1jutcgNdQKfkgje1bwhdcHRKIjg%3D&DBCODE=CJFQ&FileName=RMHH202310014&TABLEName=cjfdlast2023&nonce=F69F352AE50A45CDBA5204AD51BD3FE0&TIMESTAMP=1720770811399&uid= (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Xiao, M.; Guo, C.; Zou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Mechanisms and countermeasures of water quality risks in reservoirs using as drinking water sources in China. J. Lake Sci. 2024, 36, 1–16. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KXReader/Detail?invoice=nnN5ZvJ19XM7BqJeW2spaIXq%2BIz3R1KiNu1StjDQiVgr2DzeqxWax1C7CmOfgTREbDyLWTMPooEIqFK%2FQ09hNz59rulhIHr60jSnNoHmwfweb4yieYDzq9Z2ZPOLTyvuViRs4LkY6XcmVMubIpe1ydE2MWUnAKDJa1FOqXXbsEE%3D&DBCODE=CJFQ&FileName=FLKX202401001&TABLEName=cjfdlast2024&nonce=EC6241063F8349309175A92D60D28700&TIMESTAMP=1720774040267&uid= (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Ma, J.; Dong, W.; Ruan, X. Health risk assessment of heavy metal accumulation in soil and groundwater in a typical high cancer incidence area of Huai River Basin. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2016, 36, 4537–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, G.; Jin, Z.; Yang, M. Spatial differentiation and influencing factors of heavy metal content in soils of typical river valley city. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 30, 1276–1285. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Research on Source Landscape Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals at County Scale. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2023; 131p. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27158/d.cnki.ghznu.2023.000048 (accessed on 30 June 2024). (In Chinese).
- Wagn, H.; Zhagn, J.; Ding, S.; Guo, T.; Fu, X. Distribution characteristics, sources identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of urban rivers in Kaifeng. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2016, 36, 4520–4530. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wang, J.; Qu, L. Review on textile industry wastewater pollutants and their treatment technologies. Wool. Text. J. 2023, 51, 125–131. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ding, L.; Tang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, X.; Jin, G.; Yuan, S. Distribution and variation of pollutants in main stream of Huaihe river. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 48, 29–38. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KXReader/Detail?invoice=PVOYSu2%2FlH8LueznHLHJ8bEEQJcw1PudOnHnHbfqXm2dmqXXo62o7fQI%2FZfMZjLZiSp9vR3HOvkedc6k7arRXuUfCcbpJCtoCYBEl1IYPx1dbhI2Dv2ADcKtwr%2BDHQs%2BwaVni%2FneWlVYt992kSaxZuySHCAgXOXMx3XHwp2afOs%3D&DBCODE=CJFQ&FileName=HHDX202001006&TABLEName=cjfdlast2020&nonce=FBEC9DFC571F4B63AD301AF44F9802BE&TIMESTAMP=1720778338631&uid= (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Ding, P.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Shen, P.; Li, X.; Huang, C.; Wu, H.; Song, X.; Xiang, C.; Hu, G. Pollution characteristics, potential sources, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Jiangsu section of Huaihe river. Environ. Chem. 2023, 42, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Zhang, F.; Jia, L.; Ma, W.; Sui, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, M. Quantitative Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Factors on Heavy Metals Pollution and Spatial Distribution in Surface Drinking Water Sources in the Upper Huaihe River Basin in China. Toxics 2024, 12, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12070517
Liu T, Wang M, Zhang C, Yang S, Zhang F, Jia L, Ma W, Sui S, Liu Q, Wang M. Quantitative Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Factors on Heavy Metals Pollution and Spatial Distribution in Surface Drinking Water Sources in the Upper Huaihe River Basin in China. Toxics. 2024; 12(7):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12070517
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tong, Mingya Wang, Chunhui Zhang, Shili Yang, Fan Zhang, Luhao Jia, Wanqi Ma, Shaobo Sui, Qingwei Liu, and Mingshi Wang. 2024. "Quantitative Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Factors on Heavy Metals Pollution and Spatial Distribution in Surface Drinking Water Sources in the Upper Huaihe River Basin in China" Toxics 12, no. 7: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12070517
APA StyleLiu, T., Wang, M., Zhang, C., Yang, S., Zhang, F., Jia, L., Ma, W., Sui, S., Liu, Q., & Wang, M. (2024). Quantitative Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Factors on Heavy Metals Pollution and Spatial Distribution in Surface Drinking Water Sources in the Upper Huaihe River Basin in China. Toxics, 12(7), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12070517




