Toxicity to the Male Reproductive System after Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics: A Macrogenomic and Metabolomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
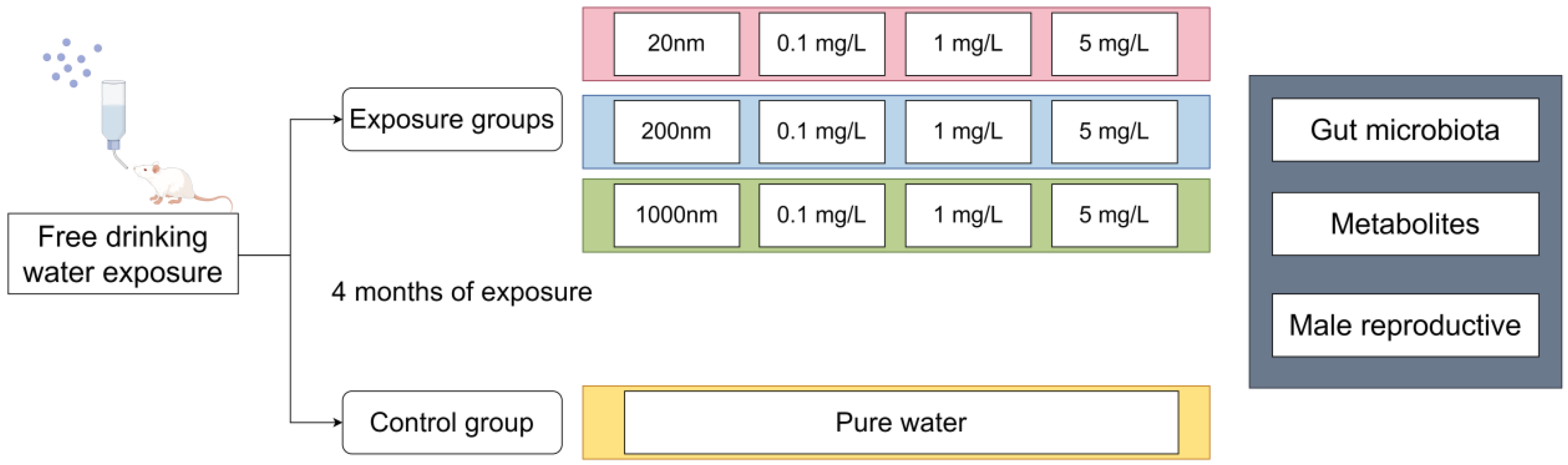
2.2. Exposure and Animals
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Sperm Quality Observation
2.5. Analysis of Inflammatory Factors, Testosterone, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone, and Oxidative Stress
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. Histopathological Assessment
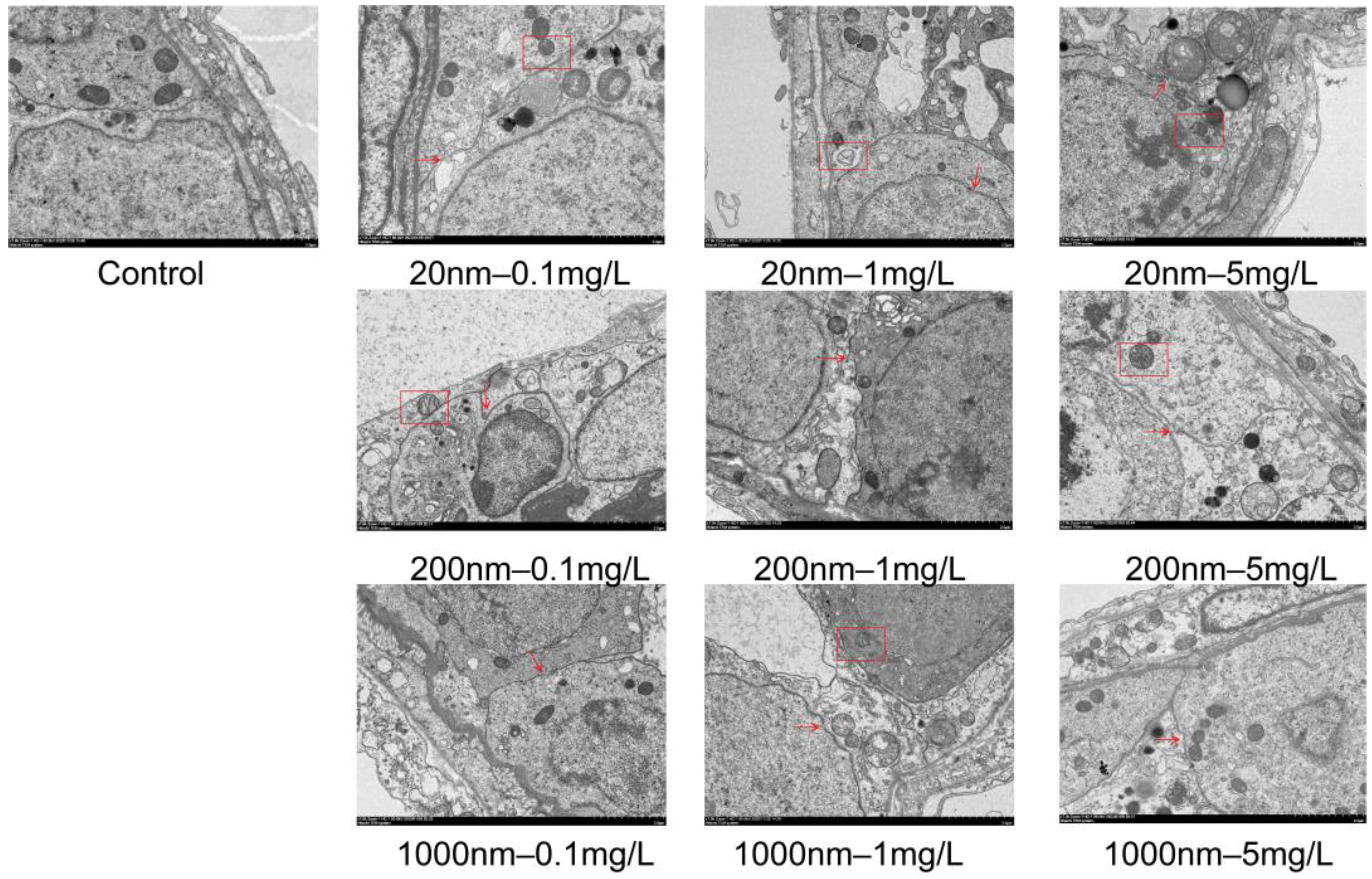
2.8. Electron Microscopy
2.9. Metagenomic Sequencing
2.10. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Untargeted Metabolomics
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Drinking Water Exposure to PS-NPs Induced Reproductive Dysfunction in Male Mice
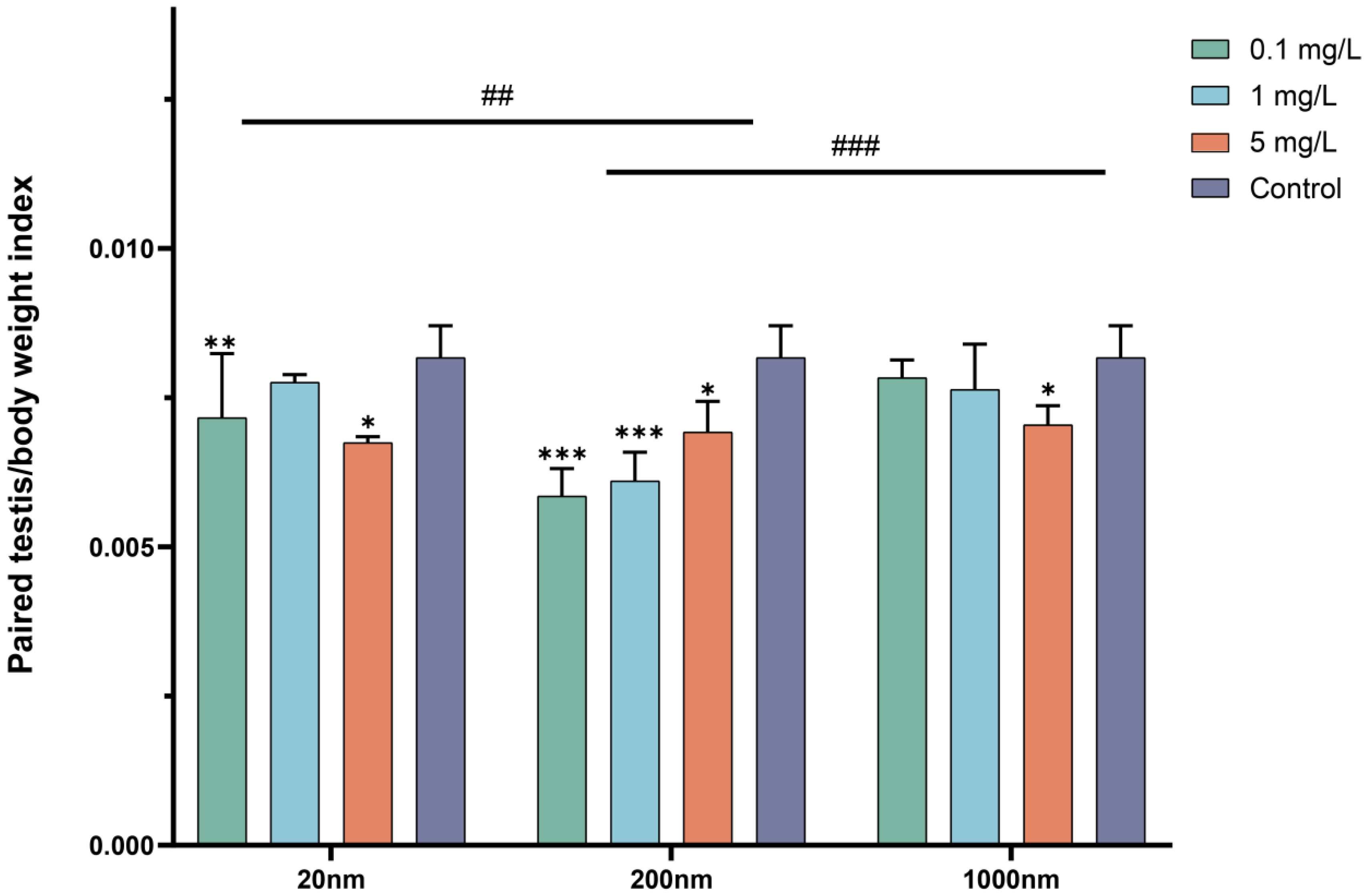
3.1.1. Body Weight and Changes in Testicular Organ Coefficients after Drinking Exposure to PS-NPs
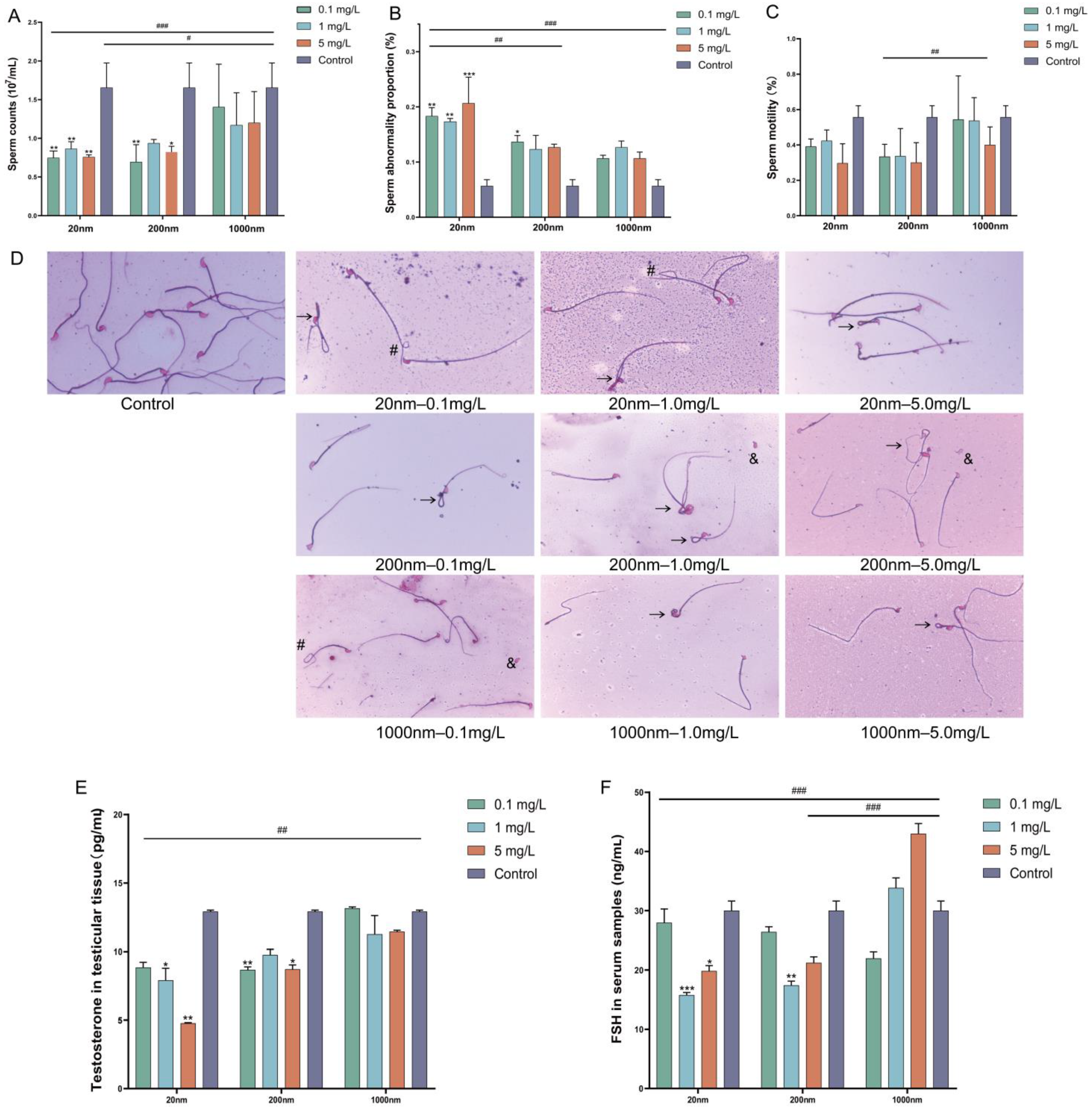
3.1.2. Changes in Sperm Quality and Sex Hormones after Drinking Water Exposure to PS-NPs
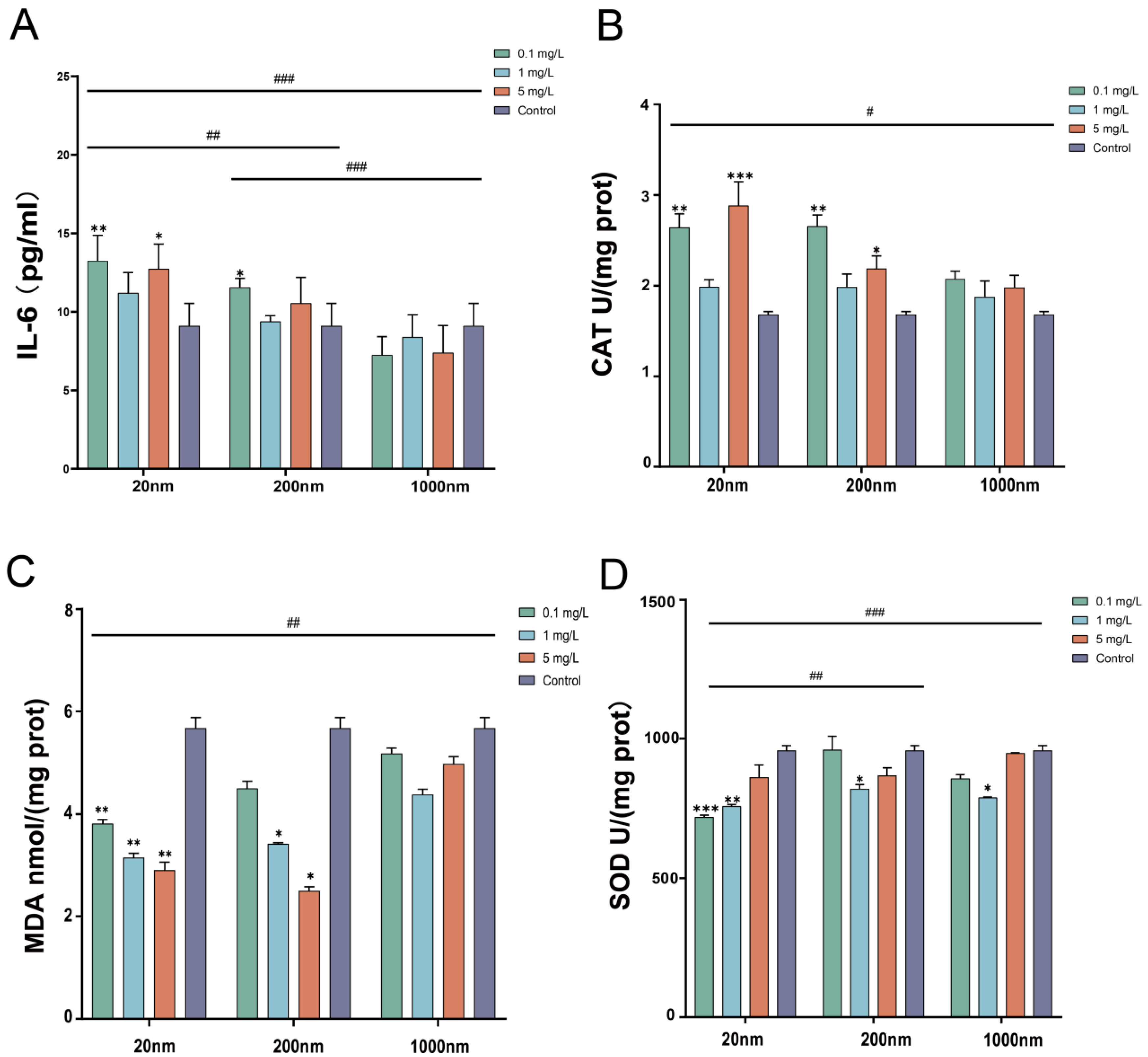
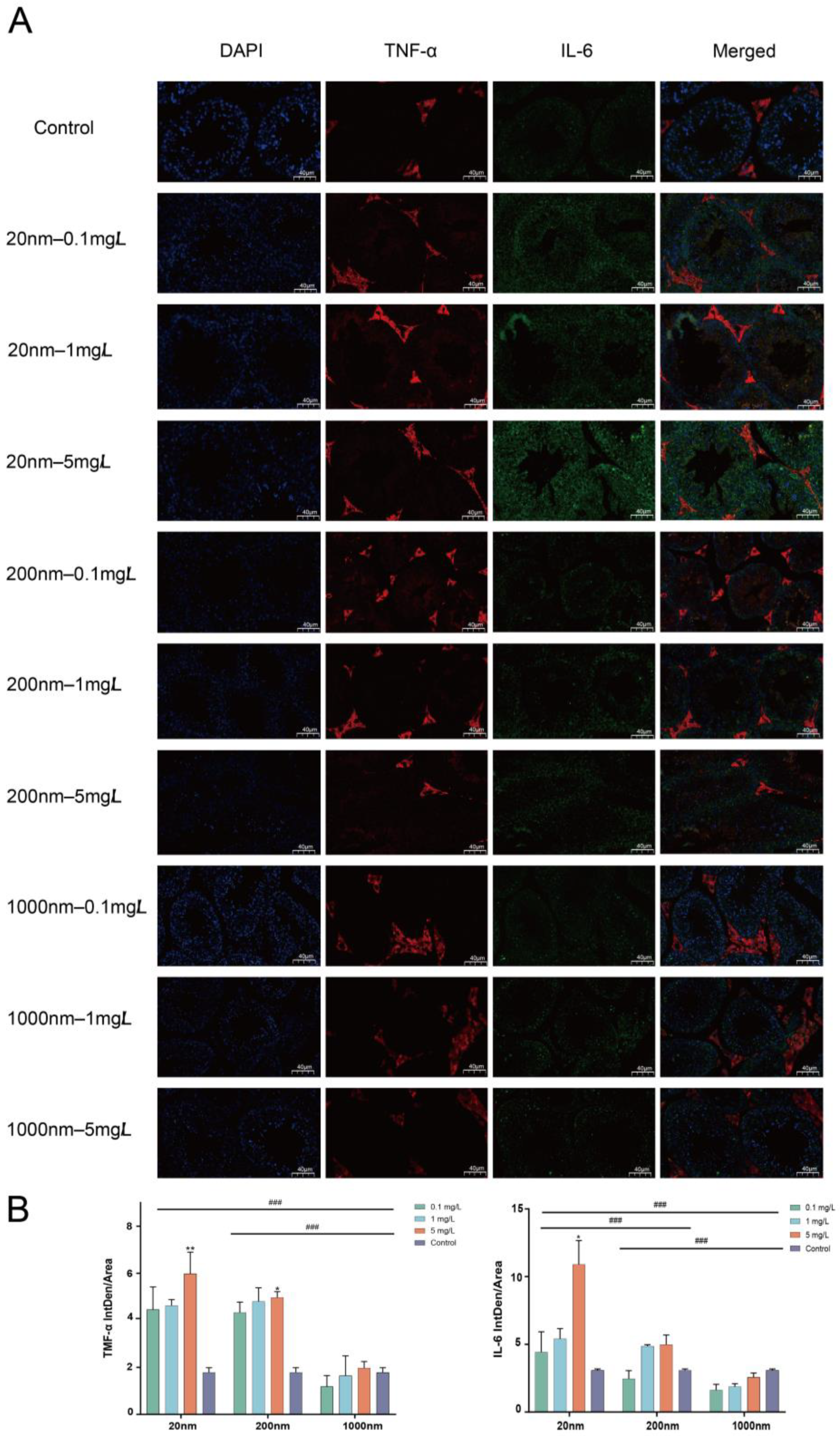
3.1.3. Changes in Inflammatory Factors and Oxidative Stress in Testicular Tissue after Exposure
3.1.4. IL-6 and TNF-α Expression in Mice Testes Detected by Immunofluorescence
3.1.5. Changes in Testicular Histological Structure after Exposure to NPs in Drinking Water
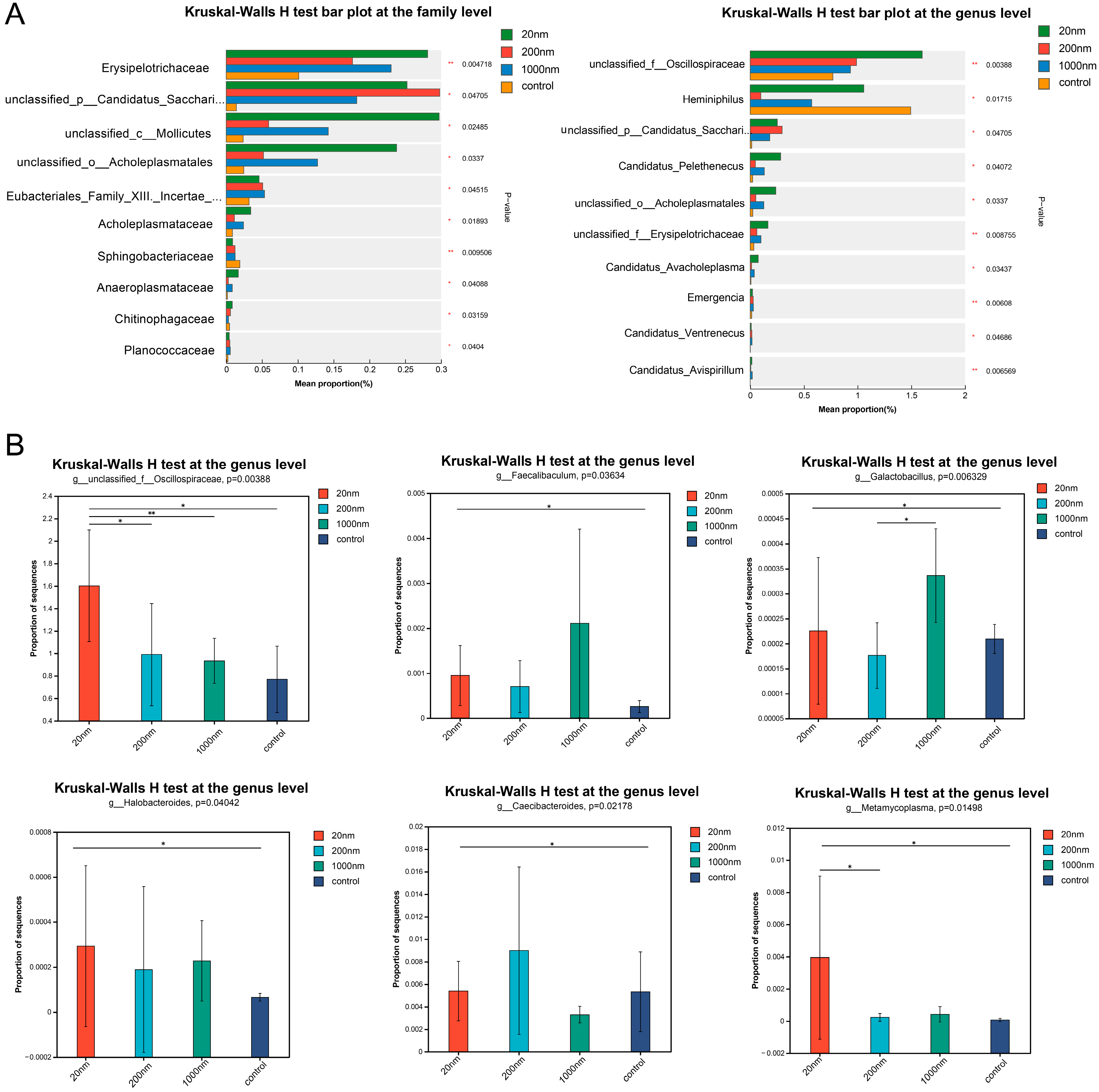
3.2. Macrogenomic Alterations after Drinking Water Exposure to PS-NPs
3.2.1. Macrogenomic Annotation Information Statistics
3.2.2. Changes in the Abundance of Gut Microbes Following Drinking Water Exposure to Polystyrene
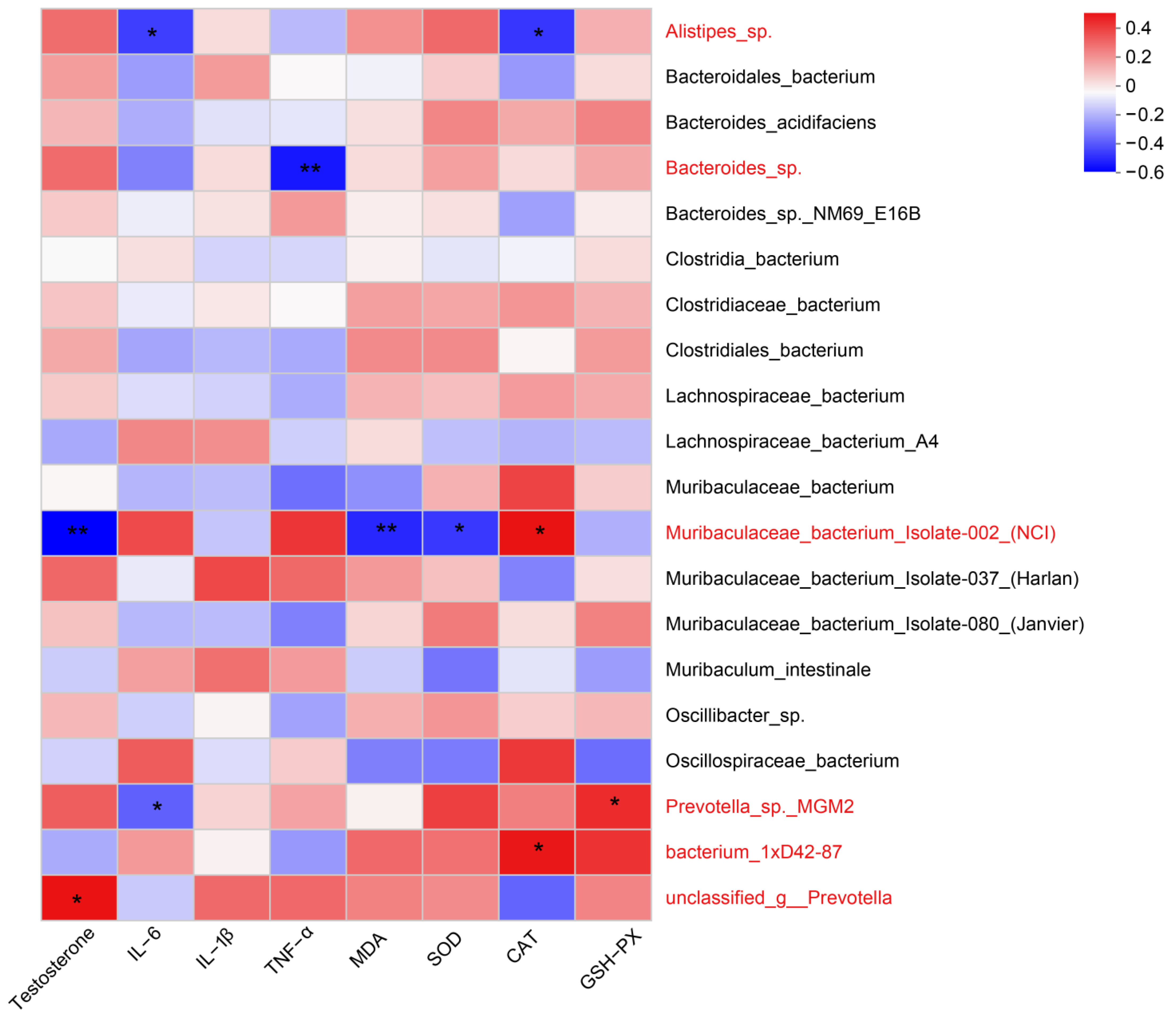
3.2.3. Correlation Analysis between Gut Microbial Abundance and Testicular Tissue Levels of Testosterone, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress
3.3. LC-MS Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
3.3.1. Metabolite Annotation Information
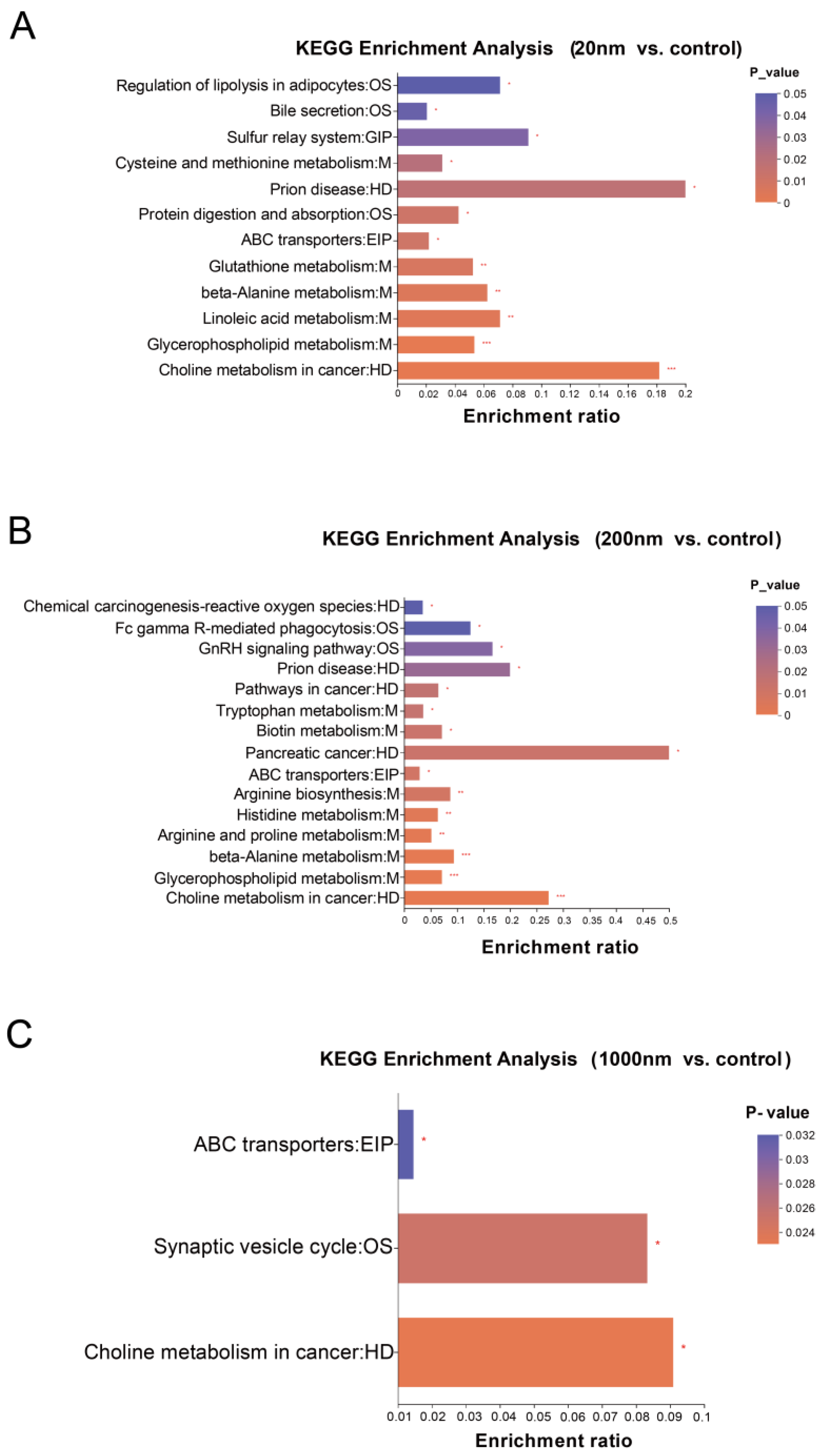
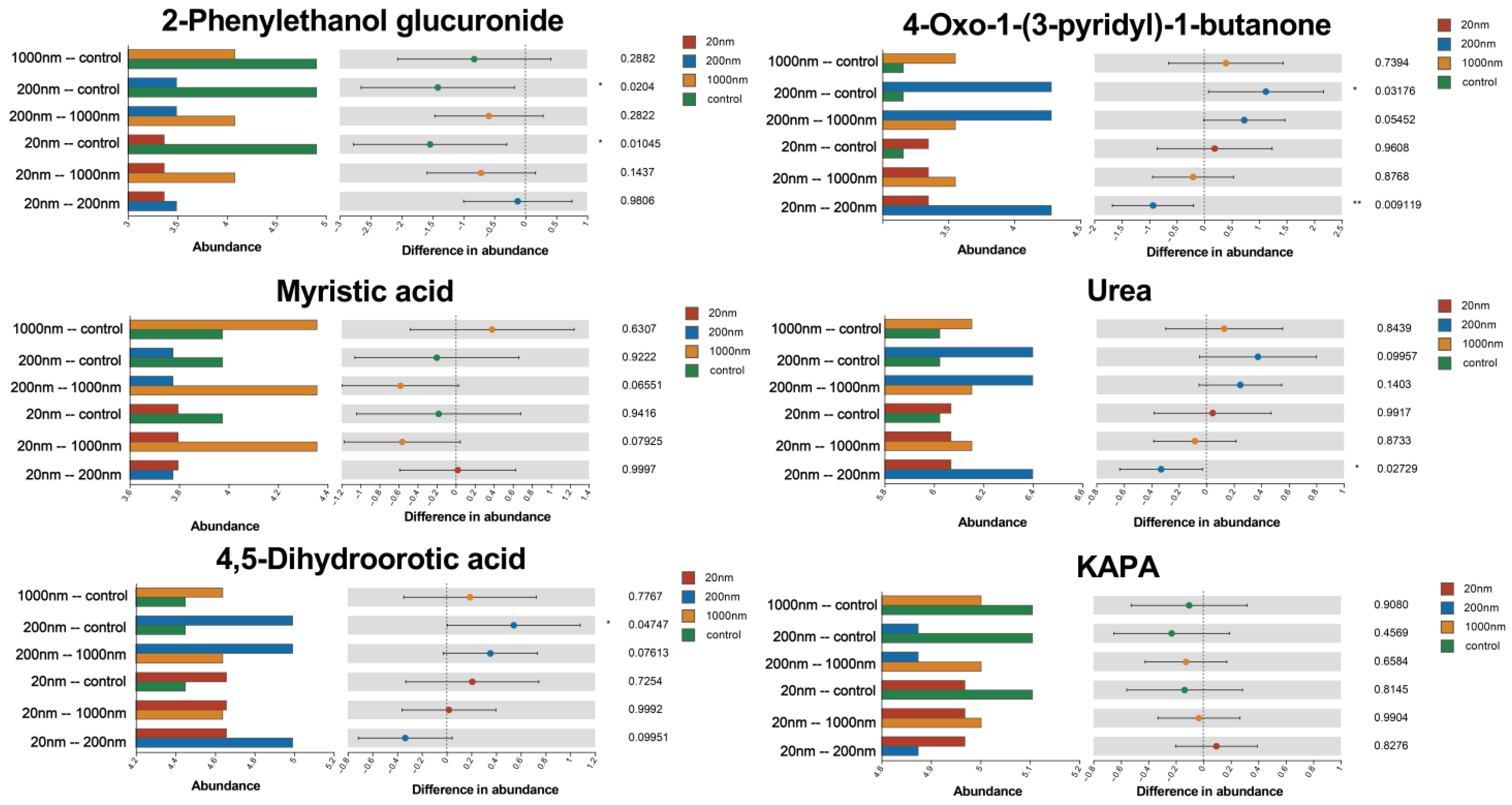
3.3.2. KEGG Differential Metabolite Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Exposure to PS-NPs Causes Reproductive Impairment in Male Mice
4.2. Exposure to PS-NPs Causes Reproduction-Associated Gut Microbiological Disturbances
4.3. Exposure to PS-NPs Causes Reproduction-Related Metabolic Disorders
4.4. There Are Grain Size Differences in the Reproductive Damage Caused by PS-NPs
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, N.; Jiang, S.; Jin, H. Microplastics in polystyrene-made food containers from China: Abundance, shape, size, and human intake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 40084–40093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco, J.; Corsi, I.; Matranga, V. Particles in the oceans: Implication for a safe marine environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, K.; Hansson, L.A.; Cedervall, T. Nano-plastics in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2015, 17, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, M.; Khan, B.; Iqbal, J.; Nauman Ahmad, M.; Khan, A.A.; Haq, T.-U.; Aziz, T.; Albekairi, T.H. Evidence of microplastic contamination in the food chain: An assessmen t of their presence in the gastrointestinal tract of native fish. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2024, 36, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuth, M.; Mason, S.A.; Wattenberg, E.V. Anthropogenic contamination of tap water, beer, and sea salt. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, N.; Gao, X.; Lang, X.; Deng, H.; Bratu, T.M.; Chen, Q.; Stapleton, P.; Yan, B.; Min, W. Rapid single-particle chemical imaging of nanoplastics by SRS microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2300582121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oßmann, B.E.; Sarau, G.; Holtmannspötter, H.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Christiansen, S.H.; Dicke, W. Small-sized microplastics and pigmented particles in bottled mineral water. Water Res. 2018, 141, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Yang, C.; Jiang, C.; Li, L.; Pan, M.; Li, D.; Han, X.; Ding, J. Evaluation of Neurotoxicity in BALB/c Mice following Chronic Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Xiong, S.; Jing, Q.; van Gestel, C.A.M.; van Straalen, N.M.; Roelofs, D.; Sun, L.; Qiu, H. Maternal exposure to polystyrene nanoparticles retarded fetal growth and triggered metabolic disorders of placenta and fetus in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Chen, Q.; Qiu, W.; Ma, C.; Gao, Z.; Chu, W.; Shi, H. Concurrent water- and foodborne exposure to microplastics leads to differential microplastic ingestion and neurotoxic effects in zebrafish. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, B.N.; Ullah, H.; Ashfaq, Y.; Hussain, N.; Atique, U.; Aziz, T.; Alharbi, M.; Albekairi, T.H.; Alasmari, A.F. Elucidating the effects of heavy metals contamination on vital organ of fish and migratory birds found at fresh water ecosystem. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, X.; Xiong, T.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Bioremediation of co-contaminated soil with heavy metals and pesticide s: Influence factors, mechanisms and evaluation methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotova, N.; Kosyreva, A.; Dzhalilova, D.; Fokichev, N.; Makarova, O. Harmful effects of the microplastic pollution on animal health: A literature review. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussarellu, R.; Suquet, M.; Thomas, Y.; Lambert, C.; Fabioux, C.; Pernet, M.E.; Le Goïc, N.; Quillien, V.; Mingant, C.; Epelboin, Y.; et al. Oyster reproduction is affected by exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Ma, T.; Sha, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Ding, J. Polystyrene microplastics induced male reproductive toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Tian, Y.; Cheng, C.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, L.; Yuan, Y.; Li, D.; Zheng, L.; Luo, T. Oral exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics reduced male fertility and even caused male infertility by inducing testicular and sperm toxicities in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueimonde, M.; Collado, M.C. Metagenomics and probiotics. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18 (Suppl. S4), 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Liu, L.; Han, H.; Li, Y.; Si, S.; Xu, B.; Dai, W.; Yang, H.; He, T.; Du, X.; et al. Integrated fecal microbiome and metabolome analysis explore the link between polystyrene nanoplastics exposure and male reproductive toxicity in mice. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 1277–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, L.; Tu, W.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z. Impacts of polystyrene microplastic on the gut barrier, microbiota and metabolism of mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Z. Exploring the role of gut microbiome in male reproduction. Andrology 2022, 10, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Reproductive toxicity of polystyrene microplastics: In vivo experimental study on testicular toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Du, Y.; He, X.; Wang, H.; Pu, L.; Pan, D.; He, S.; Liu, X.; et al. Effects of oral exposure to leachate from boiled-water treated plastic products on gut microbiome and metabolomics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, X.; Pan, D.; Shi, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Pu, L.; et al. Effects of thermal exposure to disposable plastic tableware on human gut microbiota and metabolites: A quasi-experimental study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Lam, T.W.; Yiu, S.M.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP2: An improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1966–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, C.E.; Wu, S.; Bhattacharjee, A.S.; Hamilton, J.J.; McMahon, K.D.; Goel, R.; Noguera, D.R. Metabolic network analysis reveals microbial community interactions in anammox granules. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagat, J.; Zang, L.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. Zebrafish: An emerging model to study microplastic and nanoplastic toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vethaak, A.D.; Legler, J. Microplastics and human health. Science 2021, 371, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, D.; Xiao, F. Keap1-Nrf2 pathway up-regulation via hydrogen sulfide mitigates polystyrene microplastics induced-hepatotoxic effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Li, T.; Chen, K.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, H.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, J. PS-NPs Induced Neurotoxic Effects in SHSY-5Y Cells via Autophagy Activation and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, T.; Ehrlich, L.; Henrich, W.; Koeppel, S.; Lomako, I.; Schwabl, P.; Liebmann, B. Detection of Microplastic in Human Placenta and Meconium in a Clinical Setting. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, M.; Jiang, J.; Dai, M.; Wang, B.; et al. Underestimated health risks: Polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics jointly induce intestinal barrier dysfunction by ROS-mediated epithelial cell apoptosis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcelino, R.C.; Cardoso, R.M.; Domingues, E.; Gonçalves, R.V.; Lima, G.D.A.; Novaes, R.D. The emerging risk of microplastics and nanoplastics on the microstructure and function of reproductive organs in mammals: A systematic review of preclinical evidence. Life Sci. 2022, 295, 120404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; He, Q. Reproductive toxicity and related mechanisms of micro(nano)plastics in terrestrial mammals: Review of current evidence. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 279, 116505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, S.; Guo, X.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, S.; Nabi, G.; Wanghe, K. A review of the endocrine disrupting effects of micro and nano plastic and their associated chemicals in mammals. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1084236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Shen, M.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.; Li, R.; Dorj, G.; Gombojav, E.; Du, J.; Ren, L. A meta-analysis-based adverse outcome pathway for the male reproductive toxicity induced by microplastics and nanoplastics in mammals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marana, M.H.; Poulsen, R.; Thormar, E.A.; Clausen, C.G.; Thit, A.; Mathiessen, H.; Jaafar, R.; Korbut, R.; Hansen, A.M.B.; Hansen, M.; et al. Plastic nanoparticles cause mild inflammation, disrupt metabolic pathways, change the gut microbiota and affect reproduction in zebrafish: A full generation multi-omics study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424 Pt D, 127705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolla, R.P. Sperm biology and male reproductive health. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Deng, T.; Duan, J.; Xie, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Gu, W.; Li, X.; Han, Z.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Su, Z. Continuous oral exposure to micro- and nanoplastics induced gut microbiota dysbiosis, intestinal barrier and immune dysfunction in adult mice. Environ. Int. 2023, 182, 108353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, A.; Sun, J.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Mei, Y.; Liang, Y. Lactobacillus rhamnosus and L. plantarum Combination Treatment Ameliorated Colitis Symptoms in a Mouse Model by Altering Intestinal Microbial Composition and Suppressing Inflammatory Response. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2200340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, S.B.; Sarsour, N.; Salehi, M.; Schroering, A.; Mell, B.; Joe, B.; Hill, J.W. Prenatal androgen exposure causes hypertension and gut microbiota dysbiosis. Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 400–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrageta, D.F.; Guerra-Carvalho, B.; Spadella, M.A.; Yeste, M.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G. Animal models of male reproductive ageing to study testosterone production and spermatogenesis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.J.; Wearsch, P.A.; Veloo, A.C.M.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. The Genus Alistipes: Gut Bacteria with Emerging Implications to Inflammation, Cancer, and Mental Health. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lin, S.; Zheng, B.; Cheung, P.C.K. Short-chain fatty acids in control of energy metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; White, J.C.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, L.; Duan, M.; Wu, F. Polystyrene Nanoplastics Toxicity to Zebrafish: Dysregulation of the Brain-Intestine-Microbiota Axis. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8190–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, Q.; Su, S.; Zhuang, J.; Qiao, D. Polystyrene micro- and nanoparticles exposure induced anxiety-like behaviors, gut microbiota dysbiosis and metabolism disorder in adult mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 259, 115000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, W.; Zhang, J.; Lan, Z.; Deepak, R.; Liu, C.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, X.; Meng, X.; Wang, W.; et al. SLC22A14 is a mitochondrial riboflavin transporter required for sperm oxidative phosphorylation and male fertility. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.S.M.; Giribabu, N.; Yelumalai, S.; Shahzad, H.; Kilari, E.K.; Salleh, N. Myristic acid defends against testicular oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis: Restoration of spermatogenesis, steroidogenesis in diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.; Jiang, D.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Ling, W.; An, X.; Ji, C.; Li, S.; et al. Spermidine suppresses oxidative stress and ferroptosis by Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 and Akt/FHC/ACSL4 pathway to alleviate ovarian damage. Life Sci. 2023, 332, 122109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakshinamurti, K. Biotin—A regulator of gene expression. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Han, X.; Guo, W.; Wu, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Disturbed Gut-Liver axis indicating oral exposure to polystyrene microplastic potentially increases the risk of insulin resistance. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Benson, M.; Han, X.; Li, D. Roles of piRNAs in microcystin-leucine-arginine (MC-LR) induced reproductive toxicity in testis on male offspring. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 105, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkl, M.; Ertl, R.; Handschuh, S.; Aurich, C.; Schäfer-Somi, S. The cholesterol transporter ABCA1 is expressed in stallion spermatozoa and reproductive tract tissues. Theriogenology 2016, 85, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Ye, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, F.; Shen, Y.; Chang, D.; You, Y. Integrative proteomics and metabolomics approach to identify the key roles of icariin-mediated protective effects against cyclophosphamide-induced spermatogenesis dysfunction in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1040544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llavanera, M.; Mateo-Otero, Y.; Bonet, S.; Barranco, I.; Fernández-Fuertes, B.; Yeste, M. The triple role of glutathione S-transferases in mammalian male fertility. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2331–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Hu, D.; Wen, X.; Ren, X. Recent advances in toxicological research of nanoplastics in the environment: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252 Pt A, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Q.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Yan, C. Combined effects of micro-/nano-plastics and oxytetracycline on the intestinal histopathology and microbiome in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


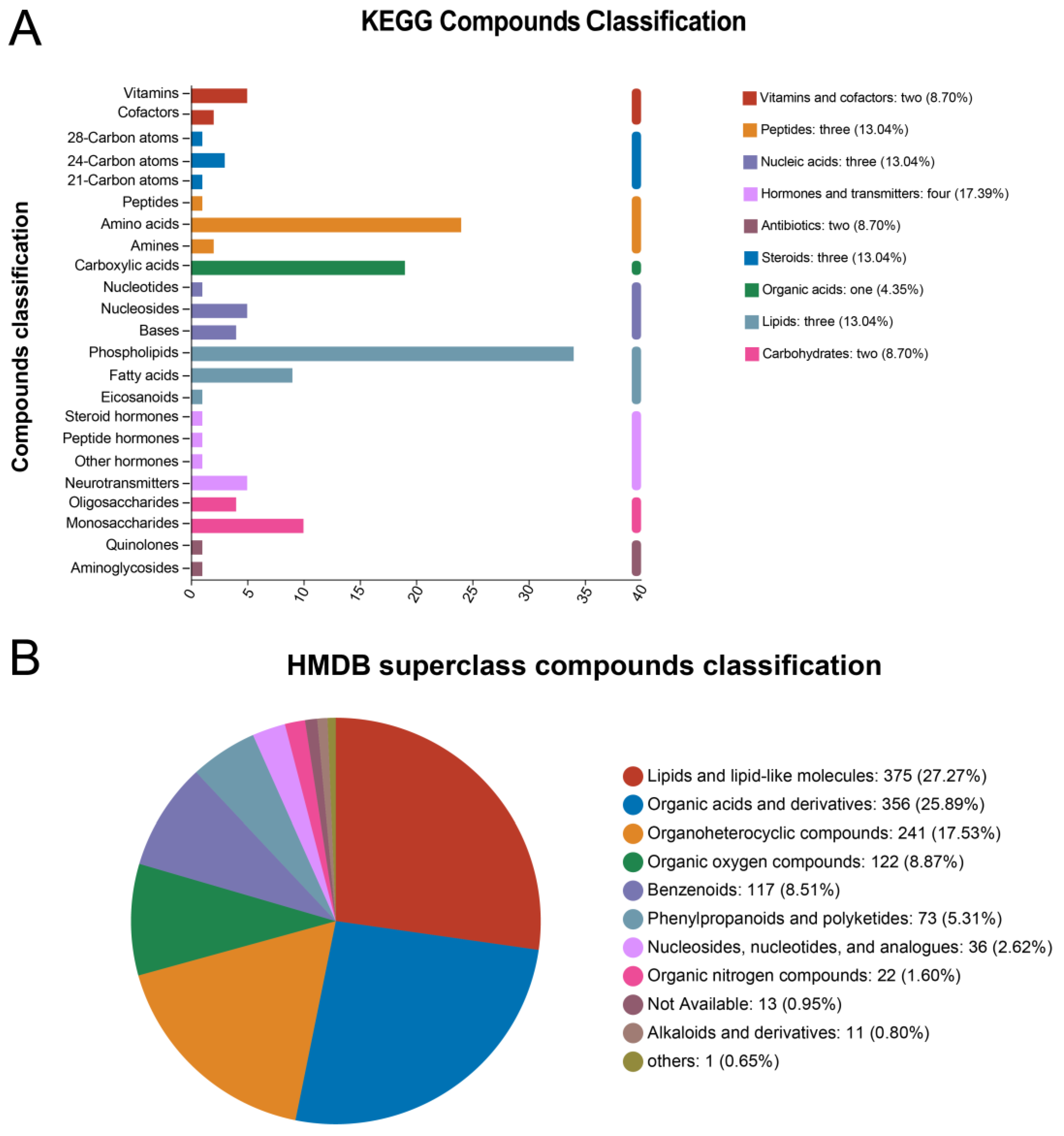
| Ion Mode | All Peaks | Identified Metabolites | Metabolites in Library | Metabolites in KEGG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pos | 4138 | 943 | 884 | 528 |
| neg | 3825 | 531 | 508 | 293 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Fu, X.; He, S.; Shi, L.; Xu, H.; Shi, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Toxicity to the Male Reproductive System after Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics: A Macrogenomic and Metabolomic Analysis. Toxics 2024, 12, 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080531
Zhang X, Wu Y, Fu X, He S, Shi L, Xu H, Shi X, Yang Y, Zhu Y, Wang Y, et al. Toxicity to the Male Reproductive System after Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics: A Macrogenomic and Metabolomic Analysis. Toxics. 2024; 12(8):531. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080531
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xue, Yueping Wu, Xufeng Fu, Shulan He, Liping Shi, Haiming Xu, Xiaojuan Shi, Yue Yang, Yongbin Zhu, Yanrong Wang, and et al. 2024. "Toxicity to the Male Reproductive System after Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics: A Macrogenomic and Metabolomic Analysis" Toxics 12, no. 8: 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080531
APA StyleZhang, X., Wu, Y., Fu, X., He, S., Shi, L., Xu, H., Shi, X., Yang, Y., Zhu, Y., Wang, Y., Qiu, H., Li, H., & Li, J. (2024). Toxicity to the Male Reproductive System after Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics: A Macrogenomic and Metabolomic Analysis. Toxics, 12(8), 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080531






