Availability of Using Honeybees and Hive Products as Bioindicators of Ambient Pesticide Exposure in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
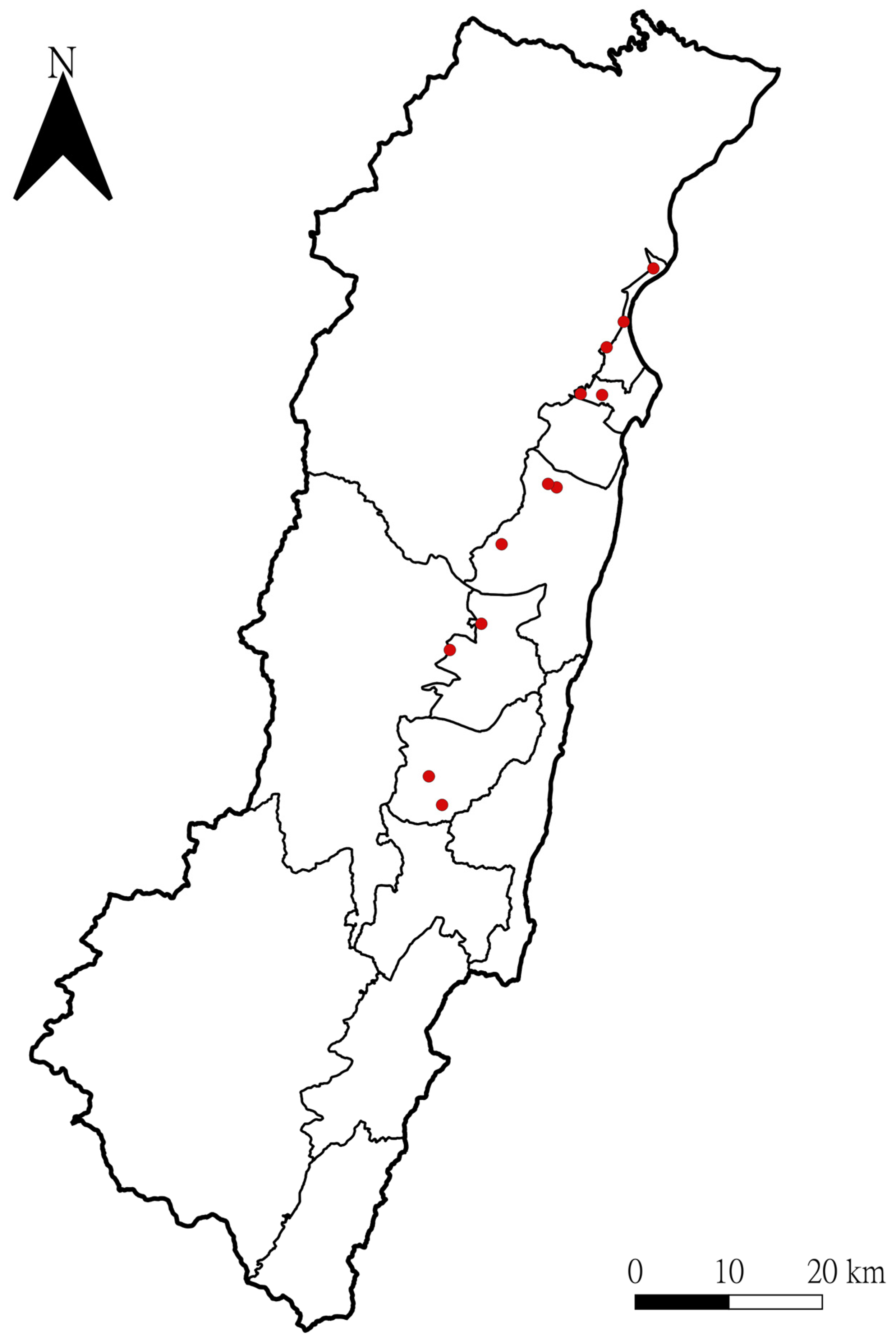
2.1. Participating Apiaries and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Treatment and Analysis
2.3. Data Management and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Girotti, S.; Ghini, S.; Ferri, E.; Bolelli, L.; Colombo, R.; Serra, G.; Porrini, C.; Sangiorgi, S. Bioindicators and biomonitoring: Honeybees and hive products as pollution impact assessment tools for the Mediterranean area. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2020, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargańska, Ż.; Ślebioda, M.; Namieśnik, J. Honey bees and their products: Bioindicators of environmental contamination. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkova, D.; Panayotova-Pencheva, M. Honey bees and their products as indicators of environmental pollution: A review. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2016, 8, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S. Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghini, S.; Fernandez, M.; Pico, Y.; Marin, R.; Fini, F.; Manes, J.; Girotti, S. Occurrence and distribution of pesticides in the province of Bologna, Italy, using honeybees as bioindicators. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 47, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurak, G.; Bosnir, J.; Racz, A.; Brkic, D.; Prskalo, I.; Kis, D.; Ozimec, S.; Kalambura, S. Bioindicator detection of pesticide residues in the environment using honey bees. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2021, 22, 458–466. [Google Scholar]
- Martinello, M.; Manzinello, C.; Dainese, N.; Giuliato, I.; Gallina, A.; Mutinelli, F. The honey bee: An active biosampler of environmental pollution and a possible warning biomarker for human health. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, P.; Della Sala, F.; Cavaliere, M.; Caputo, C.; Pecoraro, D.; Crispino, G.; Lettera, S.; Caioni, G.; Esposito, M.; Verre, A. Use of Honey Bees and Hive Products as Bioindicators to Assess Environmental Contamination in Targeted Areas of the Campania Region (Italy). Animals 2024, 14, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porrini, C.; Caprio, E.; Tesoriero, D.; Prisco, G.D. Using honey bee as bioindicator of chemicals in Campanian agroecosystems (South Italy). Bull. Insectology 2014, 67, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Porrini, C.; Sabatini, A.G.; Girotti, S.; Fini, F.; Monaco, L.; Celli, G.; Bortolotti, L.; Ghini, S. The death of honey bees and environmental pollution by pesticides: The honey bees as biological indicators. Bull. Insectology 2003, 56, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, R.C.; do Nascimento Queiroz, S.C.; da Luz, C.F.P.; Porto, R.S.; Rath, S. Bee pollen as a bioindicator of environmental pesticide contamination. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balayiannis, G.; Balayiannis, P. Bee honey as an environmental bioindicator of pesticides’ occurrence in six agricultural areas of Greece. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 55, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Waili, N.; Salom, K.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Ansari, M.J. Antibiotic, pesticide, and microbial contaminants of honey: Human health hazards. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 930849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubik, M.; Nowacki, J.; Pidek, A.; Warakomska, Z.; Michalczuk, L.; Goszczyñski, W.; Dwużpnik, B. Residues of captan (contact) and difenoconazole (systemic) fungicides in bee products from an apple orchard. Apidologie 2000, 31, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubik, M.; Nowacki, J.; Pidek, A.; Warakomska, Z.; Michalczuk, L.; Goszczyñski, W. Pesticide residues in bee products collected from cherry trees protected during blooming period with contact and systemic fungicides. Apidologie 1999, 30, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-C.; Yiin, L.-M. Availability of using honeybees as bioindicators of pesticide exposure in the vicinity of agricultural environments in Taiwan. Toxics 2023, 11, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, K.; Baert, N.; McArt, S. Pesticide contamination of beeswax from managed honey bee colonies in New York State. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2023, 35, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmart, O.; Legrève, A.; Scippo, M.-L.; Reybroeck, W.; Urbain, B.; de Graaf, D.C.; Spanoghe, P.; Delahaut, P.; Saegerman, C. Honey bee exposure scenarios to selected residues through contaminated beeswax. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolomeo, B.; Cilurzob, F.; Cristianob, M.C.; Cifelli, R.; Locatelli, M. Recent procedures for organic and inorganic toxics extraction in Honey, Propolis, and Royal Jelly: A review. AFSH 2014, 9, 51–72. [Google Scholar]
- Karazafiris, E.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Thrasyvoulou, A. New multiresidue method using solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography–micro-electron-capture detection for pesticide residues analysis in royal jelly. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1209, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.T.; Joshi, N.K.; Rajotte, E.G.; Zhu, F.; Peter, K.A.; López-Uribe, M.M.; Biddinger, D.J. Systemic pesticides in a solitary bee pollen food store affect larval development and increase pupal mortality. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.M.; Ramos, M.J.G.; Vázquez, P.P.; Galiano, F.J.D.; Valverde, M.G.; López, V.G.; Flores, J.M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Distribution of chemical residues in the beehive compartments and their transfer to the honeybee brood. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidance for Quality Assurance Project Plans (EPA QA/G-5), U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-06/documents/g5-final.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Migdal, P.; Murawska, A.; Berbeć, E.; Plotnik, M.; Skorus, A.; Latarowski, K. Selected Biochemical Markers Change after Oral Administration of Pesticide Mixtures in Honey Bees. Toxics 2022, 10, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawislak, J.; Adamczyk, J.; Johnson, D.R.; Lorenz, G.; Black, J.; Hornsby, Q.; Stewart, S.D.; Joshi, N. Comprehensive survey of area-wide agricultural pesticide use in southern United States row crops and potential impact on honey bee colonies. Insects 2019, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calatayud-Vernich, P.; Calatayud, F.; Simó, E.; Picó, Y. Pesticide residues in honey bees, pollen and beeswax: Assessing beehive exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, R. Chemical residues in beebread, honey, pollen and wax samples collected from bee hives placed on canola crops in Western Australia. J. Apic. Res. 2018, 57, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaad, E.; Fracheboud, M.; Droz, B.; Kast, C. Quantitation of pesticides in bee bread collected from honey bee colonies in an agricultural environment in Switzerland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 56353–56367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type and Name | Analytical Method | Retention Time (min) | Main Use (Agriculture, Environmental Sanitation, or Both) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insecticide | |||
| Acetamiprid | LC-MS | 2.31 | Agriculture |
| Chlorpyrifos | GC-MS | 8.62 | Both |
| Cypermethrin | GC-MS | 22.71 | Agriculture |
| Dinotefuran | LC-MS | 6.41 | Both |
| Fipronil | GC-MS | 6.31 | Both |
| Indoxacarb | LC-MS | 3.36 | Agriculture |
| Herbicide | |||
| Ametryn | LC-MS | 4.51 | Agriculture |
| Glyphosate | LC-MS | 1.13 | Agriculture |
| Oxadiazon | LC-MS | 8.81 | Agriculture |
| Paraquat | LC-MS | 3.29 | Agriculture |
| Pendimethalin | LC-MS | 2.79 | Agriculture |
| Fungicide | |||
| Dimethomorph | GC-MS | 15.45 | Agriculture |
| Famoxadone | LC-MS | 6.75 | Agriculture |
| Tebuconazole | LC-MS | 6.49 | Agriculture |
| All | Healthy Bees | Sick Bees | Dead Bees | Broods | Pollen | Beeswax | Honey | Royal Jelly | Dust 0–50 m | Dust 50–150 m | Dust 150–500 m | Dust 0.5–1.5 km | Dust 1.5–2.5 km | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insect. | ||||||||||||||
| Healthy bees | 0.909 ** | 0.832 ** | 0.385 | 0.776 ** | 0.895 ** | 0.622 * | 0.510 | 0.559 | 0.839 ** | 0.319 | 0.469 | 0.839 ** | ||
| Sick bees | 0.394 | 0.867 ** | 0.336 | 0.874 ** | 0.853 ** | 0.462 | 0.566 | 0.538 | 0.734 ** | 0.238 | 0.273 | 0.671 * | ||
| Dead bees | 0.480 | 0.704 * | 0.077 | 0.734 ** | 0.839 ** | 0.455 | 0.371 | 0.455 | 0.811 ** | 0.490 | 0.364 | 0.671 * | ||
| Broods | 0.631 * | 0.708 ** | 0.624 * | 0.329 | 0.182 | 0.671 * | 0.755 ** | 0.350 | 0.294 | 0.186 | −0.119 | 0.224 | ||
| Pollen | 0.393 | 0.396 | 0.706 * | 0.653 * | 0.853 ** | 0.448 | 0.566 | 0.741 ** | 0.664 * | 0.287 | 0.287 | 0.364 | ||
| Beeswax | 0.393 | 0.623 * | 0.790 ** | 0.641 * | 0.942 ** | 0.469 | 0.273 | 0.538 | 0.769 ** | 0.259 | 0.434 | 0.615 * | ||
| Honey | 0.480 | 0.708 * | 0.734 ** | 0.650 * | 0.517 | 0.601 * | 0.699 * | 0.483 | 0.643 * | 0.711 ** | 0.503 | 0.594 * | ||
| Royal jelly | 0.498 | 0.574 | 0.761 ** | 0.774 ** | 0.805 ** | 0.769 ** | 0.471 | 0.531 | 0.441 | 0.480 | 0.224 | 0.343 | ||
| Dust 0–50 m | −0.044 | 0.392 | 0.566 | 0.386 | 0.629 * | 0.629 * | 0.448 | 0.740 ** | 0.664 * | 0.385 | 0.259 | 0.203 | ||
| Dust 50–150 m | 0.218 | 0.778 ** | 0.853 ** | 0.624 * | 0.545 | 0.615 * | 0.559 | 0.776 ** | 0.706 * | 0.455 | 0.476 | 0.650 * | ||
| Dust 150–500 m | 0.306 | 0.357 | 0.406 | 0.725 ** | 0.378 | 0.294 | 0.35 | 0.558 | 0.441 | 0.469 | 0.469 | 0.368 | ||
| Dust 0.5–1.5 km | 0.218 | 0.473 | 0.434 | 0.532 | 0.573 | 0.483 | 0.664 * | 0.428 | 0.385 | 0.294 | 0.406 | 0.545 | ||
| Dust 1.5–2.5 km | 0.480 | 0.704 * | 0.566 | 0.486 | 0.573 | 0.727 ** | 0.545 | 0.609 * | 0.378 | 0.448 | 0.287 | 0.727 ** | ||
| Herb. | Healthy Bees | Sick Bees | Dead Bees | Broods | Pollen | Beeswax | Honey | Royal Jelly | Dust 0–50 m | Dust 50–150 m | Dust 150–500 m | Dust 0.5–1.5 km | Dust 1.5–2.5 km | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fung. | ||||||||||||||
| Healthy bees | 0.888 ** | 0.713 ** | 0.531 | 0.629 * | 0.350 | 0.210 | 0.455 | 0.566 | 0.881 ** | 0.322 | 0.056 | 0.245 | ||
| Sick bees | 0.895 ** | 0.839 ** | 0.587 * | 0.727 ** | 0.476 | 0.154 | 0.497 | 0.469 | 0.713 ** | 0.322 | −0.032 | 0.203 | ||
| Dead bees | 0.776 ** | 0.860 ** | 0.245 | 0.580 * | 0.573 | −0.084 | 0.315 | 0.203 | 0.469 | 0.490 | 0.203 | 0.196 | ||
| Broods | 0.814 ** | 0.860 ** | 0.796 ** | 0.882 ** | 0.787 ** | 0.784 ** | 0.680 * | 0.462 | 0.608 * | −0.105 | −0.501 | 0.140 | ||
| Pollen | 0.839 ** | 0.741 ** | 0.594 * | 0.721 ** | 0.727 ** | 0.077 | 0.469 | 0.664 * | 0.615 * | 0.280 | 0.077 | 0.147 | ||
| Beeswax | 0.734 ** | 0.783 ** | 0.839 ** | 0.690 * | 0.570 | −0.294 | 0.427 | 0.322 | 0.392 | 0.259 | −0.056 | 0.287 | ||
| Honey | 0.881 ** | 0.846 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.550 | 0.776 ** | 0.699 * | 0.524 | 0.594 * | 0.427 | −0.007 | −0.011 | −0.042 | ||
| Royal jelly | 0.690 * | 0.620 * | 0.400 | −0.039 | 0.560 | 0.230 | 0.669 * | 0.755 ** | 0.622 * | 0.273 | −0.081 | −0.007 | ||
| Dust 0–50 m | 0.470 | 0.692 * | 0.550 | 0.560 | 0.490 | 0.430 | 0.490 | 0.420 | 0.804 ** | 0.168 | −0.032 | −0.063 | ||
| Dust 50–150 m | 0.430 | 0.657 * | 0.748 ** | 0.709 ** | 0.480 | 0.629 * | 0.450 | 0.250 | 0.776 ** | 0.231 | −0.039 | 0.273 | ||
| Dust 150–500 m | 0.615 * | 0.734 ** | 0.643 * | 0.667 * | 0.804 ** | 0.832 ** | 0.615 * | 0.200 | 0.550 | 0.671 * | 0.858 ** | −0.196 | ||
| Dust 0.5–1.5 km | 0.825 ** | 0.888 ** | 0.748 ** | 0.761 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.748 ** | 0.734 ** | 0.520 | 0.678 * | 0.692 * | 0.825 ** | −0.158 | ||
| Dust 1.5–2.5 km | 0.797 ** | 0.790 ** | 0.790 ** | 0.667 * | 0.601 * | 0.530 | 0.916 ** | 0.577 * | 0.440 | 0.380 | 0.470 | 0.685 * | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, C.-C.; Chang, W.-C.; Hsueh, C.-W.; Yiin, L.-M. Availability of Using Honeybees and Hive Products as Bioindicators of Ambient Pesticide Exposure in Taiwan. Toxics 2024, 12, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12090639
Hung C-C, Chang W-C, Hsueh C-W, Yiin L-M. Availability of Using Honeybees and Hive Products as Bioindicators of Ambient Pesticide Exposure in Taiwan. Toxics. 2024; 12(9):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12090639
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Chien-Che, Wei-Cheng Chang, Chung-Wen Hsueh, and Lih-Ming Yiin. 2024. "Availability of Using Honeybees and Hive Products as Bioindicators of Ambient Pesticide Exposure in Taiwan" Toxics 12, no. 9: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12090639
APA StyleHung, C.-C., Chang, W.-C., Hsueh, C.-W., & Yiin, L.-M. (2024). Availability of Using Honeybees and Hive Products as Bioindicators of Ambient Pesticide Exposure in Taiwan. Toxics, 12(9), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12090639







