Effect of Ozone Exposure on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease Mortality in the Elderly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Distributed Lag Nonlinear Model (DLNM)
- Yt: The number of deaths due to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease on day t.
- β0: The intercept.
- β: The vector of coefficients.
- cb.O3t: Cross-basis of O3 concentration at day t.
- cb.tempt: Cross-basis of temperature at day t.
- ns: Natural cubic spline.
- df: Degree of freedom.
- time: Time variable, to control long-term trend and seasonality.
- dow: The day of week and public holidays are represented as categorical variables to control short-term fluctuations.
2.3.2. Generalized Additive Model (GAM)
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Coefficients
3.2. The Association Between O3 and Mortality
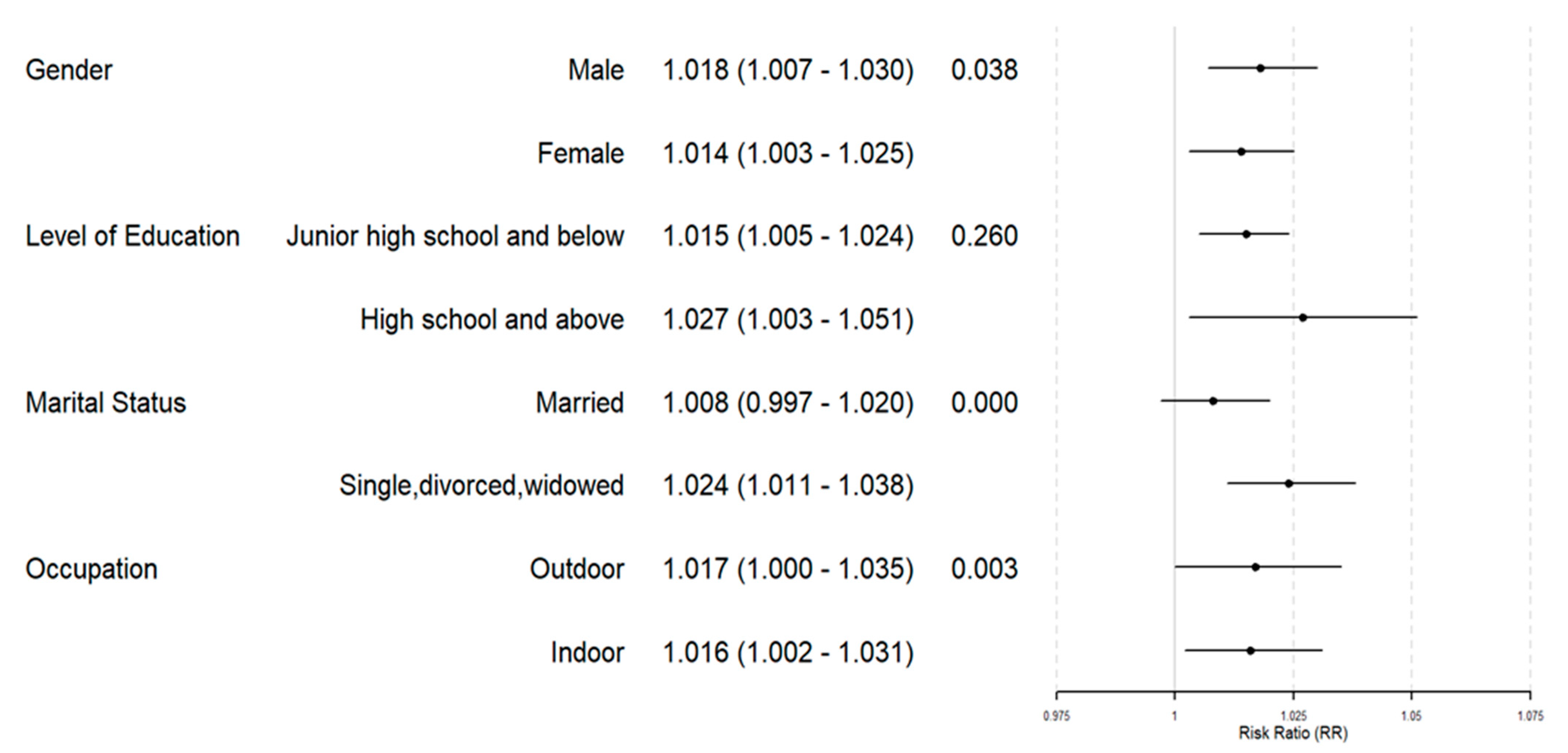
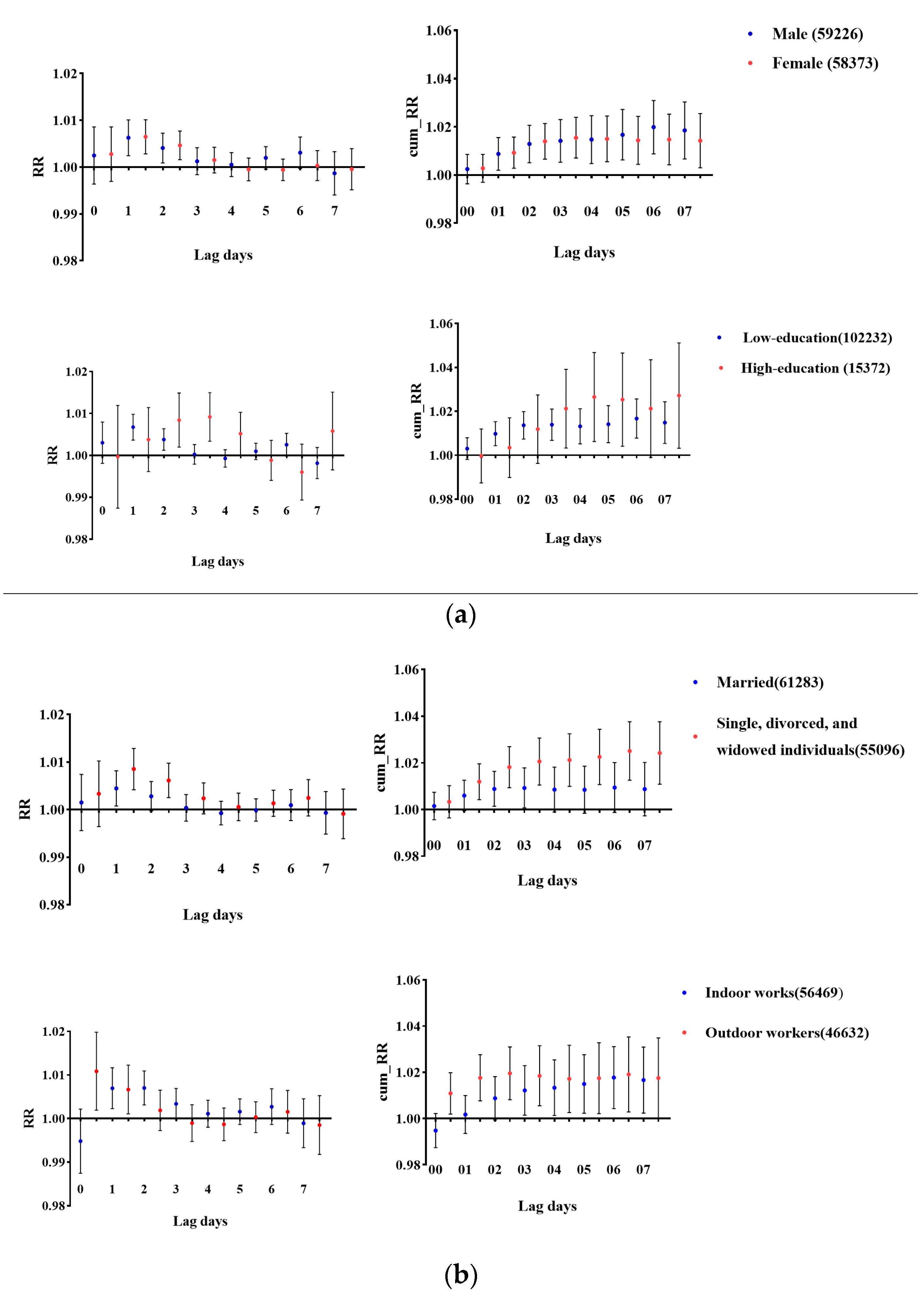
3.3. Subgroup Analysis of O3 Exposure
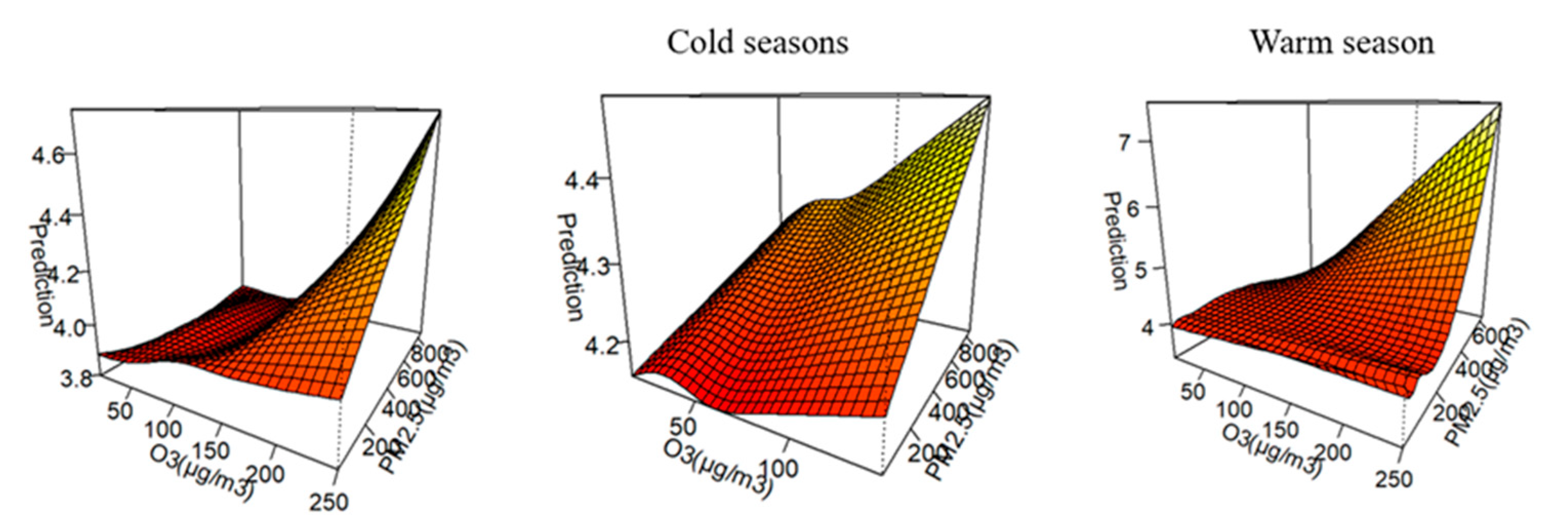
3.4. Joint Effect Between O3 and PM2.5
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Ozone on CVD and CEVD
4.2. Subgroups More Sensitive to O3
4.3. Synergy EFfect Between PM2.5 and O3
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, Y.; Ma, K.; He, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, S.; He, H. Urban Surface Ozone Concentration in Mainland China during 2015–2020: Spatial Clustering and Temporal Dynamics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzelli, G.; Suarez-Varela, M.M. Tropospheric Ozone: A Critical Review of the Literature on Emissions, Exposure, and Health Effects. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wu, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Gong, X.; Zhang, L. Surface ozone pollution in China: Trends, exposure risks, and drivers. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1131753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Zheng, P.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abdollahpour, I.; et al. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malashock, D.A.; Delang, M.N.; Becker, J.S.; Serre, M.L.; West, J.J.; Chang, K.-L.; Cooper, O.R.; Anenberg, S.C. Global trends in ozone concentration and attributable mortality for urban, peri-urban, and rural areas between 2000 and 2019: A modelling study. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e958–e967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Orellano, P.; Lin, H.; Jiang, M.; Guan, W. Short-term exposure to ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulphur dioxide and emergency department visits and hospital admissions due to asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 150, 106435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensor, K.B.; Raun, L.H.; Persse, D. A Case-Crossover Analysis of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest and Air Pollution. Circulation 2013, 127, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lu, K.; Fu, J. A Time-Series Study for Effects of Ozone on Respiratory Mortality and Cardiovascular Mortality in Nanchang, Jiangxi Province, China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 864537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, M.G.; Garcia-Esperon, C.; Tomari, Y.K.; Walker, R.; Saluja, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Boyle, A.; Levi, C.R.; Naidu, R.; Filippelli, G.; et al. Effect of short-term exposure to air pollution on daily cardio- and cerebrovascular hospitalisations in areas with a low level of air pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 102438–102445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, M.; Freedman, G.; Frostad, J.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Dentener, F.; Dingenen, R.V.; Estep, K.; Amini, H.; Apte, J.S.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution Exposure Estimation for the Global Burden of Disease 2013. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.C.; Jerrett, M.; Pope, C.A.; Krewski, D.; Gapstur, S.M.; Diver, W.R.; Beckerman, B.S.; Marshall, J.D.; Su, J.; Crouse, D.L.; et al. Long-Term Ozone Exposure and Mortality in a Large Prospective Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, D.L.; Peters, P.A.; Hystad, P.; Brook, J.R.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Jerrett, M.; Goldberg, M.S.; Pope, C.A.; et al. Ambient PM 2.5, O 3, and NO 2 Exposures and Associations with Mortality over 16 Years of Follow-Up in the Canadian Census Health and Environment Cohort (CanCHEC). Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, I.M.; Atkinson, R.W.; Kent, A.J.; Van Staa, T.; Cook, D.G.; Anderson, H.R. Mortality Associations with Long-Term Exposure to Outdoor Air Pollution in a National English Cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.W.; Butland, B.K.; Dimitroulopoulou, C.; Heal, M.R.; Stedman, J.R.; Carslaw, N.; Jarvis, D.; Heaviside, C.; Vardoulakis, S.; Walton, H.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient ozone and mortality: A quantitative systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence from cohort studies. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e009493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; Yin, P.; Meng, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Ji, J.S.; Qiu, Y.; Kan, H.; et al. Long-term exposure to ozone and cardiovascular mortality in China: A nationwide cohort study. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e496–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; You, X.; Wang, D.; Qiu, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X. Short-term effects of ambient ozone exposure on daily hospitalizations for circulatory diseases in Ganzhou, China: A time-series study. Chemosphere 2023, 327, 138513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, T.-Y.; Ting, H.-W.; Chan, C.-L.; Yang, N.-P.; Pan, R.-H.; Lai, K.; Hung, S.-I. Does the Short-Term Effect of Air Pollution Influence the Incidence of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Different Patient Groups? Big Data Analysis in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2017, 14, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Li, J.W.; Sun, B.; Chen, Y.L.; Shen, S.Q.; Yuan, C. Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases Induced by Air Pollution. Acta Acad. Med. Sin. 2022, 44, 318–323. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Zheng, H.; Xia, P.; Cheng, X.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhu, G.; Xu, T.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Long-term ambient PM2.5 exposure associated with cardiovascular risk factors in Chinese less educated population. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, J.; Ng, Y.; Yeo, K.K.; Sahlén, A.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lee, V.; Ma, S. Particulate air pollution on cardiovascular mortality in the tropics: Impact on the elderly. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.-J.; Heinrich, J.; Bloom, M.S.; Zhao, T.-Y.; Shi, T.-X.; Feng, W.-R.; Sun, Y.; Shen, J.-C.; Yang, Z.-C.; Yang, B.-Y.; et al. Ambient air pollution and depression: A systematic review with meta-analysis up to 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Peng, X.; Cheng, H.; Ma, C. Temporal and Spatial Features of the Correlation between PM2.5 and O3 Concentrations in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Duan, Z.; Wei, J.; Wang, F.; Han, D.; Zhang, K.; Jing, Y.; Wen, W.; Qin, W.; Yang, X. Associations of long-term exposure to ambient ozone with hypertension, blood pressure, and the mediation effects of body mass index: A national cross-sectional study of middle-aged and older adults in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Gasparrini, A.; Hajat, S.; Smeeth, L.; Armstrong, B. Time series regression studies in environmental epidemiology. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, S.; Yu, Z.; Jiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, B. A study on the short-term impact of fine particulate matter pollution on the incidence of cardiovascular diseases in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 215, 116889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Z.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y. The acute health effects of ozone and PM2.5 on daily cardiovascular disease mortality: A multi-center time series study in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, C.; Niu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Qi, J.; et al. Ambient Ozone Pollution and Daily Mortality: A Nationwide Study in 272 Chinese Cities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Liu, X.; Liang, J.; Lin, H.; Shen, P.; Zhang, J.; Lu, P.; Tang, X.; et al. Long-term exposure to ozone and cardiovascular mortality in a large Chinese cohort. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-C.; Chuang, K.-J.; Chien, L.-C.; Chen, W.-J.; Chang, W.-T. Urban air pollution and emergency admissions for cerebrovascular diseases in Taipei, Taiwan. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Sun, B.; Yu, L.; Chen, J.; Han, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, J. The Gender-Based Differences in Vulnerability to Ambient Air Pollution and Cerebrovascular Disease Mortality: Evidences Based on 26781 Deaths. Glob. Heart 2020, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, L.; He, G.; Zeng, W.; Rong, Z.; et al. Joint Associations of Short-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollutants with Hospital Admission of Ischemic Stroke. Epidemiology 2023, 34, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, N.; Dai, J.; Gong, J.; Xiang, H. Ambient air pollution and cerebrovascular disease mortality: An ecological time-series study based on 7-year death records in central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 27299–27307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Di, Q.; Sofer, T.; Awad, Y.A.; Schwartz, J. Inverse probability weighted distributed lag effects of short-term exposure to PM2.5 and ozone on CVD hospitalizations in New England Medicare participants—Exploring the causal effects. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, D.B.; Xiang, J.; Mo, J.; Li, F.; Chung, M.; Gong, J.; Weschler, C.J.; Ohman-Strickland, P.A.; Sundell, J.; Weng, W.; et al. Association of Ozone Exposure With Cardiorespiratory Pathophysiologic Mechanisms in Healthy Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, A.; Liu, M.; Dong, J.; Chen, R.; Tian, T.; Liu, T.; Ma, L.; Ruan, Y. Association Between Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease Hospitalizations in Lanzhou City, 2013–2020: A Time Series Analysis. GeoHealth 2024, 8, e2022GH000780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, M.; Zou, P.; Wang, J. Pollution Characteristics of PM2.5 Aerosol during Haze Periods in Changchun, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, J.J.; Neas, L.M.; Devlin, R.B.; Case, M.W.; Schmitt, M.T.; Madden, M.C.; Diaz-Sanchez, D. Interaction Effects of Temperature and Ozone on Lung Function and Markers of Systemic Inflammation, Coagulation, and Fibrinolysis: A Crossover Study of Healthy Young Volunteers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dong, H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, W.; Zare Sakhvidi, M.J.; Li, L.; Lin, G.; Yang, J. Association between ambient ozone pollution and mortality from a spectrum of causes in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo-Ojo, T.C.; Wichmann, J.; Arowosegbe, O.O.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Schindler, C.; Künzli, N. Short-Term Effects of PM10, NO2, SO2 and O3 on Cardio-Respiratory Mortality in Cape Town, South Africa, 2006–2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Dong, X.; He, G.; Pu, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhong, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Z.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient ozone and cardiovascular diseases: Evidence from two national cohort studies in China. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 62, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S. Long-term exposure to ambient fine particles associated with asthma: A cross-sectional study among older adults in six low- and middle-income countries. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S. Cigarette smoking increases deaths associated with air pollution in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Knibbs, L.D.; Zhou, Y.; Ou, Y.; Dong, G.-H.; Dong, H. The role of lifestyle in the association between long-term ambient air pollution exposure and cardiovascular disease: A national cohort study in China. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, H.; London, S.J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Song, G.; Zhao, N.; Jiang, L.; Chen, B. Season, Sex, Age, and Education as Modifiers of the Effects of Outdoor Air Pollution on Daily Mortality in Shanghai, China: The Public Health and Air Pollution in Asia (PAPA) Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, D.; Greisenegger, S.; Auff, E.; Lang, W.; Lalouschek, W. The Relation Between Knowledge About Hypertension and Education in Hospitalized Patients With Stroke in Vienna. Stroke 2007, 38, 1304–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cho, J.; Isehunwa, O.; Noh, J.; Noh, Y.; Oh, S.S.; Koh, S.-B.; Kim, C. Marriage as a social tie in the relation of depressive symptoms attributable to air pollution exposure among the elderly. J. Affect. Disord. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, D.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Feng, W.; Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; et al. Association of Depressive Symptoms With Incident Cardiovascular Diseases in Middle-Aged and Older Chinese Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1916591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Yang, T. Health Effects of Air Pollution in China. Int. J. Envrion. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jbaily, A. Air pollution exposure disparities across US population and income groups. Nature 2022, 601, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Ho, H.C.; Su, H.; Huang, C.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, W.; Tao, J.; Hossain, M.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, K.; et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of intraday effects of ambient air pollution and temperature on cardiorespiratory morbidities: First few hours of exposure matters to life. eBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.Z.; Liu, K.; Shirai, K.; Hu, K.; Qiu, C.; Liu, X.; et al. Ambient PM2.5, ozone and mortality in Chinese older adults: A nationwide cohort analysis (2005–2018). J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Lavigne, E.; Correa, P.M.; Ortega, N.V.; Achilleos, S.; et al. Interactive effects of ambient fine particulate matter and ozone on daily mortality in 372 cities: Two stage time series analysis. BMJ 2023, 383, e075203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mølhave, L.; Kjaergaard, S.K.; Sigsgaard, T.; Lebowitz, M. Interaction between ozone and airborne particulate matter in office air. Indoor Air 2005, 15, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Guo, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Cummings-Vaughn, L.A.; Rigdon, S.E.; Vaughn, M.G.; Sun, S.; et al. Ambient PM2.5 and O3 and their combined effects on prevalence of presbyopia among the elderly: A cross-sectional study in six low- and middle-income countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Overall (n = 117,604) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 80.3 ± 7.85 | |
| Gender | Male | 59,226 (50.4) |
| Female | 58,373 (49.6) | |
| Level of education | Junior high school and below | 102,232 (86.9) |
| High school and above | 15,372 (13.1) | |
| Marital status | Married | 61,283 (52.1) |
| Single, divorced and widowed | 55,096 (46.8) | |
| Unknow | 1225 (1.0) | |
| Occupation | Indoor | 56,469 (48.0) |
| Outdoor | 46,632 (39.6) | |
| Unknow | 14,503 (12.3) | |
| Cause of deaths | CVD (I05~I52) | 72,724 (61.8) |
| CEVD (I60~I69) | 44,880 (38.2) |
| Mean | SD | Min | Max | P25 | P50 | P75 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3 (μg/m3) O3-warm O3-cold | 66.7 84.7 41.9 | 40.3 40.5 22.2 | 9 10 9 | 250 250 140 | 35 56 24 | 59 79 37 | 88 107 54 |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) PM2.5-warm PM2.5-cold | 56.5 41.6 77.6 | 47.3 31.7 56.7 | 4 4 10 | 848 632 848 | 28 24 41 | 43 35 65 | 72 51 101 |
| SO2 (μg/m3) SO2-warm SO2-cold | 47.9 19.8 87.6 | 55.1 12.0 66.6 | 3 3 10 | 527 120 527 | 15 11 39 | 27 17 70 | 57 26 114 |
| NO2 (μg/m3) NO2-warm NO2-cold | 41.8 36.3 49.7 | 17.1 14.0 18.0 | 12 12 14 | 125 109 125 | 29 27 36 | 39 34 48 | 51 43 61 |
| Temperature (°C) Temperature-warm Temperature-cold | 9.1 18.5 −4.2 | 13.1 6.7 7.2 | −23 −5 −23 | 32 32 16 | −3 14 −9 | 11 20 −5 | 21.2 24 1 |
| RH (%) RH-warm RH-cold | 59.9 62.9 55.6 | 16.3 17.0 14.2 | 15 15 22 | 98 98 91 | 47.8 52 45 | 61 66 55 | 72 75 66 |
| PM2.5 | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | CO | O3-8 h | T | Rh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rh (%) | −0.04 | −0.10 * | −0.22 | −0.03 | 0.16 * | −0.08 * | 0.32 * | 1 |
| T (°C) | −0.39 * | −0.28 * | −0.068 * | −0.41 * | −0.22 * | 0.69 * | 1 | |
| O3-8 h (μg/m3) | −0.16 * | −0.06 * | −0.39 * | −0.35 * | −0.2 * | 1 | ||
| CO (mg/m3) | 0.8 * | 0.65 * | 0.63 * | 0.73 * | 1 | |||
| NO2 (μg/m3) | 0.74 * | 0.63 * | 0.71 * | 1 | ||||
| SO2 (μg/m3) | 0.71 * | 0.52 * | 1 | |||||
| PM10 (μg/m3) | 0.89 * | 1 | ||||||
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 1 |
| O3 (RR) | Warm Season O3 (RR) | Cold Season O3 (RR) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | 1.027 (1.019~1.034) | 1.032 (1.024~1.040) | 1.005 (0.988~1.023) |
| Model 2 | 1.008 (1.000~1.016) | 1.016 (1.007~1.025) | 1.015 (0.993~1.037) |
| Model 3 | 1.007 (0.999~1.015) | 1.016 (1.007~1.025) | 1.016 (0.993~1.038) |
| Model 4 | 1.007 (1.000~1.015) | 1.016 (1.007~1.025) | 1.007 (0.986~1.029) |
| Lag | O3 | Warm Season O3 | Cold Season O3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| lag0 | 1.002 (0.998–1.006) | 1.002 (0.997–1.006) | 1.003 (0.994–1.012) |
| lag1 | 1.005 (1.002–1.007) | 1.007 (1.004–1.010) | 1.003 (0.997–1.010) |
| lag2 | 1.002 (1.000–1.004) | 1.005 (1.002–1.007) | 0.999 (0.994–1.005) |
| lag3 | 0.999 (0.997–1.001) | 1.001 (0.999–1.004) | 0.996 (0.991–1.001) |
| lag4 | 0.998 (0.997–1.000) | 1.000 (0.998–1.002) | 0.997 (0.992–1.002) |
| lag5 | 1.001 (0.999–1.002) | 1.000 (1.000–1.003) | 1.001 (0.997–1.006) |
| lag6 | 1.002 (1.000–1.005) | 1.002 (1.000–1.005) | 1.005 (0.999–1.011) |
| lag7 | 0.998 (0.995–1.002) | 0.998 (0.995–1.002) | 1.002 (0.994–1.009) |
| lag00 | 1.002 (0.998–1.006) | 1.002 (0.997–1.006) | 1.003 (0.993–1.012) |
| lag01 | 1.007 (1.002–1.011) | 1.008 (1.003–1.014) | 1.006 (0.994–1.018) |
| lag02 | 1.009 (1.003–1.014) | 1.013 (1.007–1.019) | 1.005 (0.991–1.020) |
| lag03 | 1.007 (1.001–1.013) | 1.015 (1.008–1.021) | 1.001 (0.985–1.018) |
| lag04 | 1.006 (1.000–1.013) | 1.014 (1.007–1.022) | 0.998 (0.980–1.017) |
| lag05 | 1.006 (1.000–1.014) | 1.015 (1.007–1.023) | 1.000 (0.980–1.020) |
| lag06 | 1.009 (1.001–1.016) | 1.017 (1.009–1.026) | 1.005 (0.985–1.023) |
| lag07 | 1.007 (1.000–1.015) | 1.016 (1.007–1.025) | 1.007 (0.986–1.002) |
| Model | Pollutants | RR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Single-pollutant analysis | O3 (PM2.5low) | 0.998 (0.995–1.004) |
| O3 (PM2.5high) | 1.006 (1.000–1.007) | |
| Two-pollutant analysis | O3-PM2.5low | 0.998 (0.992–1.003) |
| O3-PM2.5high | 1.001 (1.000–1.004) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Deng, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Peng, W.; Cui, Y.; He, M. Effect of Ozone Exposure on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease Mortality in the Elderly. Toxics 2025, 13, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030184
Wang T, Wang J, Sun L, Deng Y, Xiang Y, Wang Y, Chen J, Peng W, Cui Y, He M. Effect of Ozone Exposure on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease Mortality in the Elderly. Toxics. 2025; 13(3):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030184
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tianyun, Junlong Wang, Li Sun, Ye Deng, Yuting Xiang, Yuting Wang, Jiamei Chen, Wen Peng, Yuanyao Cui, and Miao He. 2025. "Effect of Ozone Exposure on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease Mortality in the Elderly" Toxics 13, no. 3: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030184
APA StyleWang, T., Wang, J., Sun, L., Deng, Y., Xiang, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, J., Peng, W., Cui, Y., & He, M. (2025). Effect of Ozone Exposure on Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease Mortality in the Elderly. Toxics, 13(3), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030184







