Toxicity of Four Commercial Fungicides, Alone and in Combination, on the Earthworm Eisenia fetida: A Field Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Protection Products
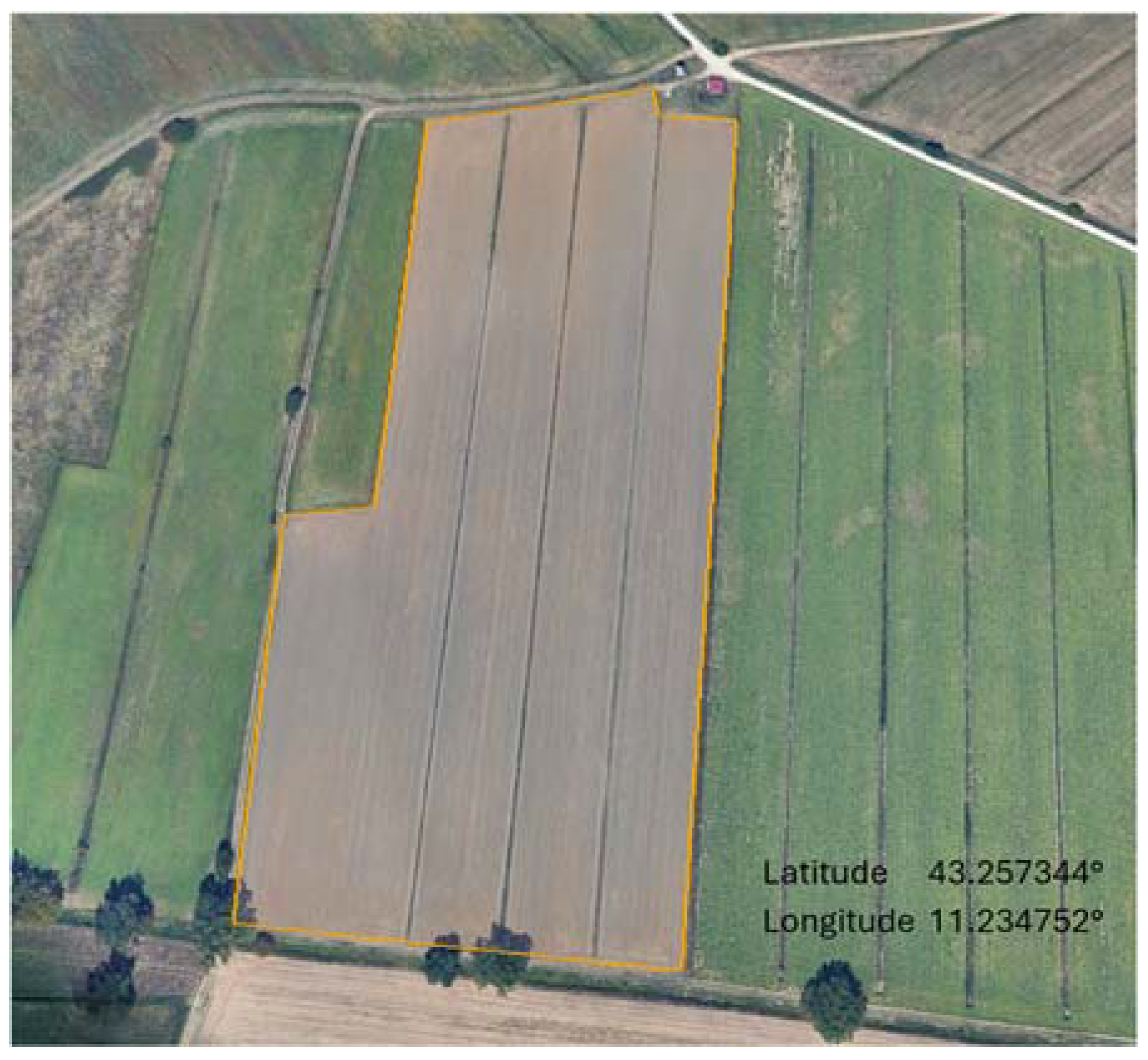
2.2. Plot Description
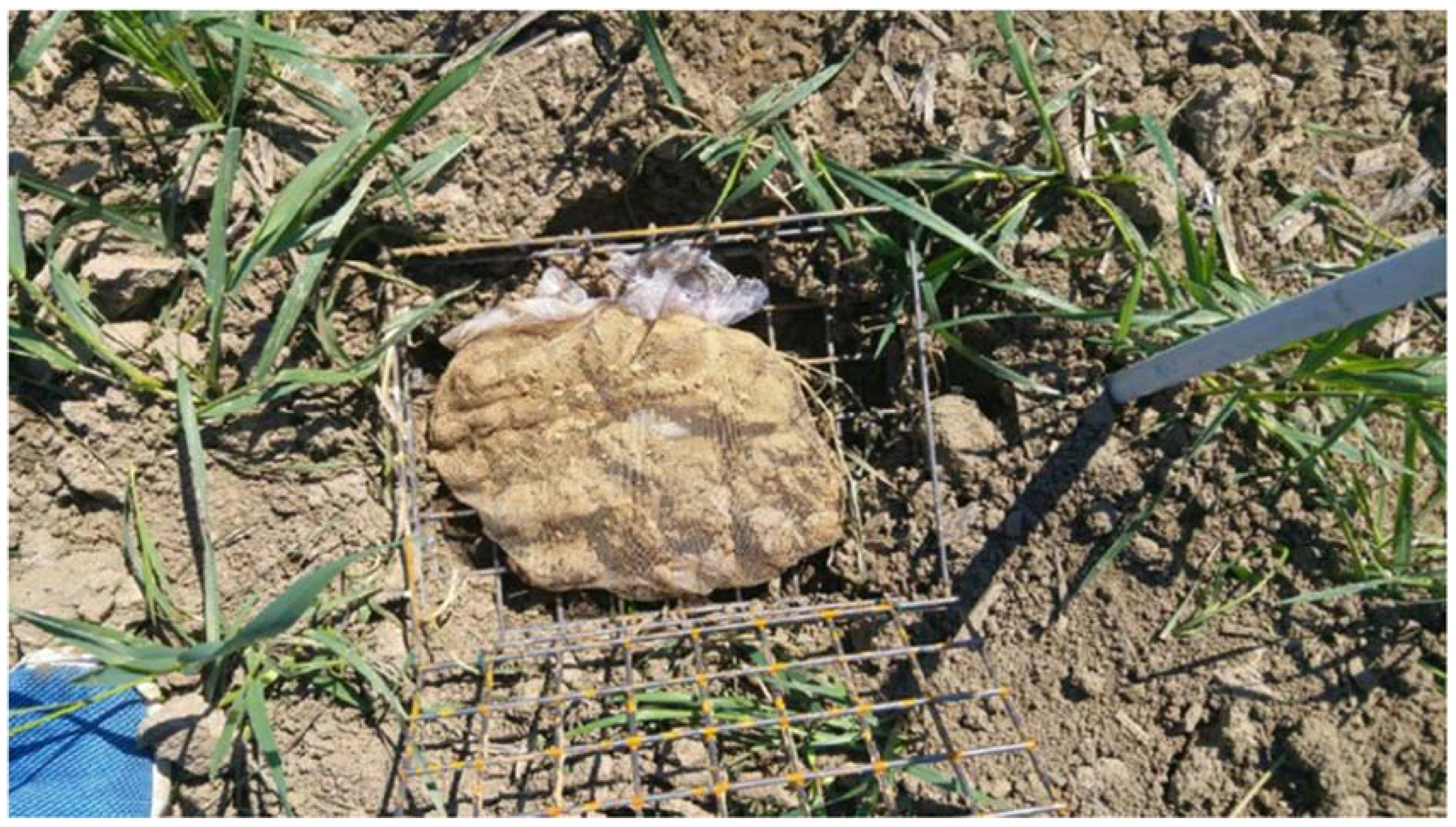
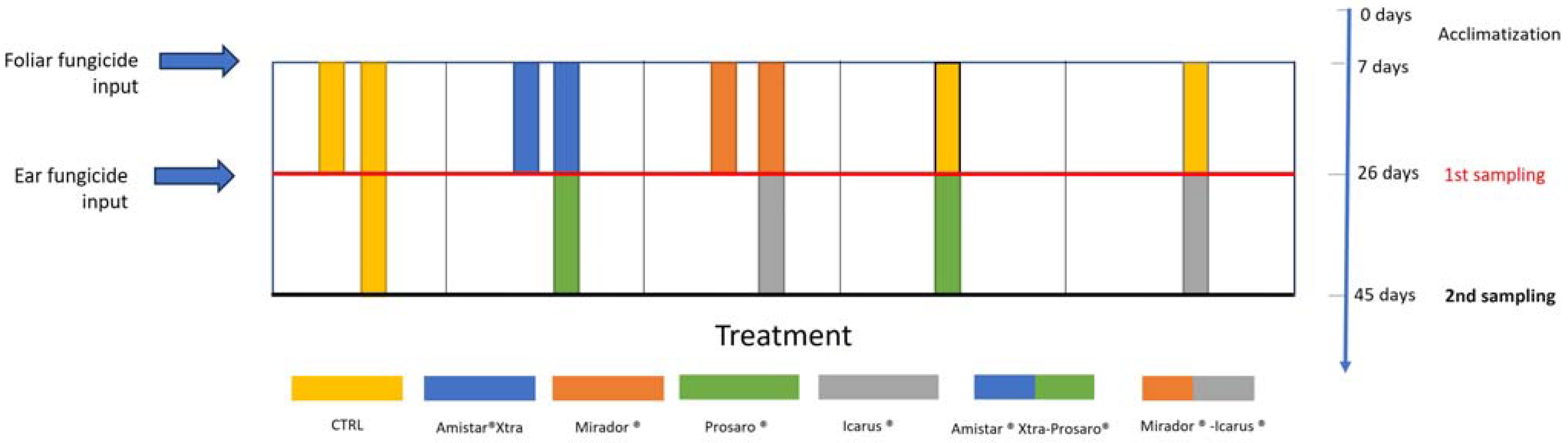
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Biomarkers Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
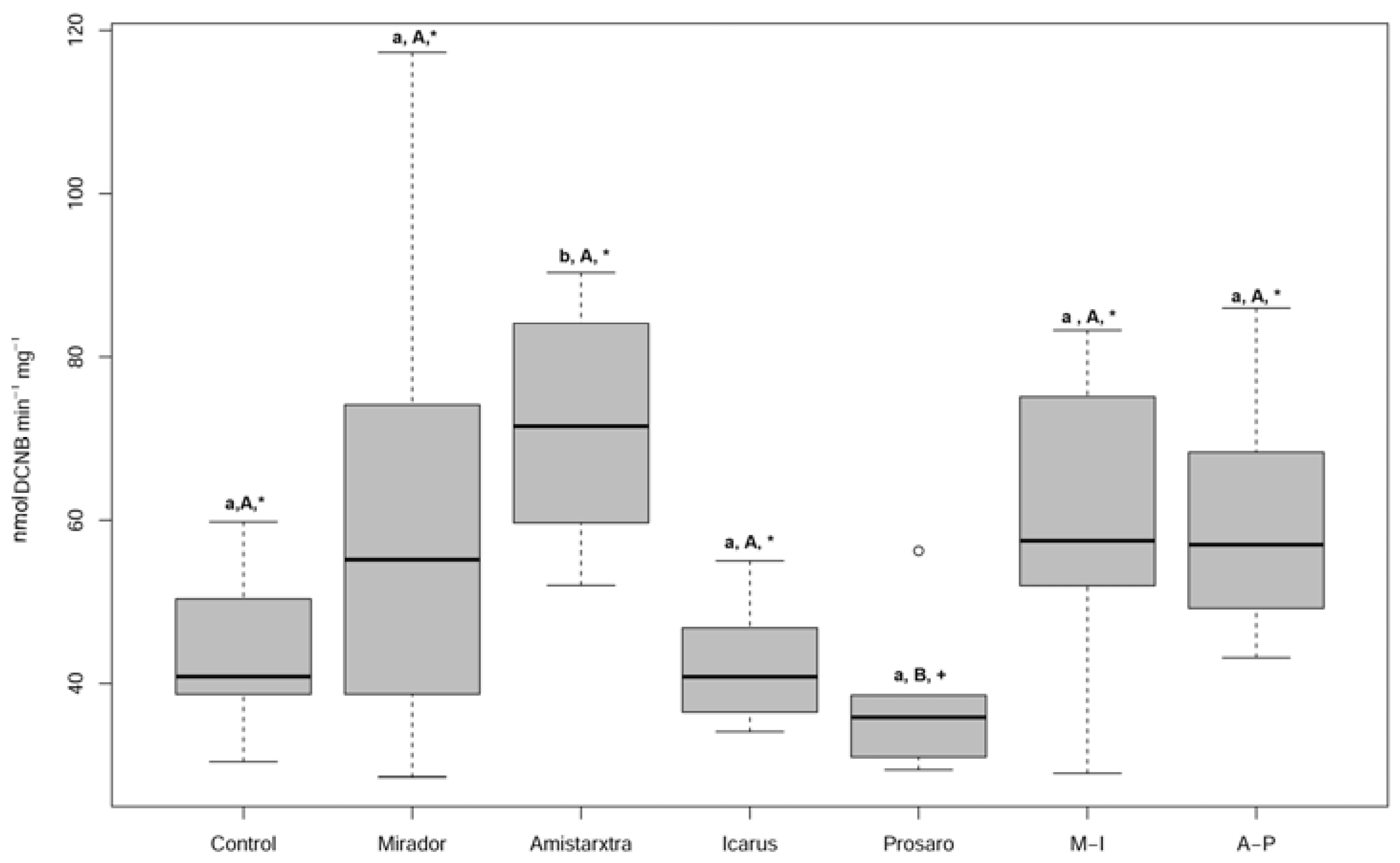
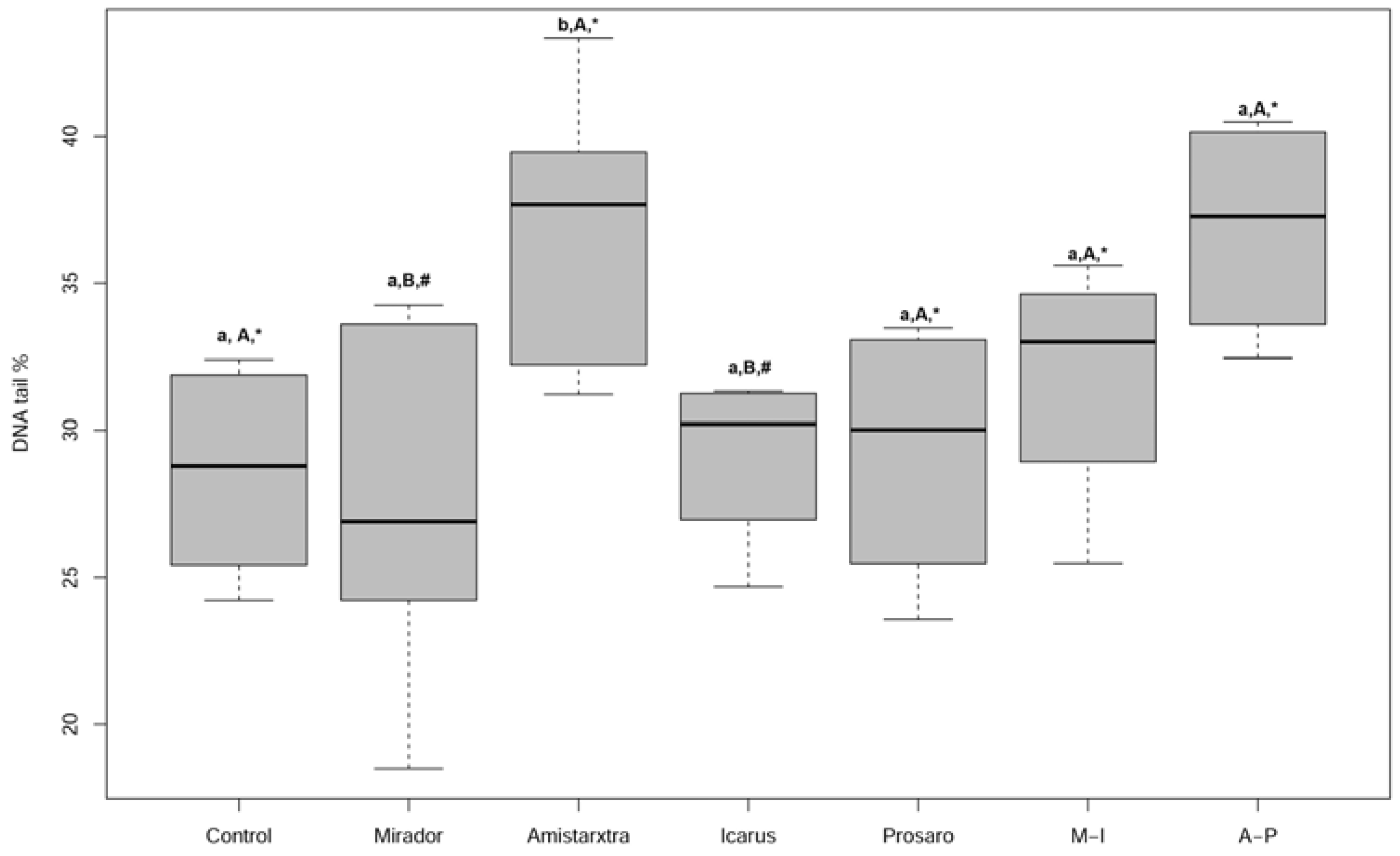
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Awika, J.M. Major Cereal Grains Production and Use around the World. In Advances in Cereal Science: Implications to Food Processing and Health Promotion; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 1–13. ISBN 1947-5918. [Google Scholar]
- Asensio, V.; Covelo, E.F.; Kandeler, E. Soil management of copper mine tailing soils—Sludge amendment and tree vegetation could improve biological soil quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.; Hodson, M.E.; Delgado, E.A.; Baker, G.; Brussaard, L.; Butt, K.R.; Dai, J.; Dendooven, L.; Pérès, G.; Tondoh, J. A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santadino, M.; Coviella, C.; Momo, F. Glyphosate sublethal effects on the population dynamics of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.G.; Pashanasi, B.; Villenave, C.; Patron, J.; Senapati, B.K.; Giri, S.; Barois, I.; Lavelle, P.; Blanchart, E.; Blakemore, R. Effects of earthworms on plant production in the tropics. Earthworm Manag. Trop. Agroecosystems 1999, 5, 87–147. [Google Scholar]
- Fishel, F.M. Pesticide Formulations: PI231/PI231, 6/2010. EDIS 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, A.; Guzmán, E. Emulsions containing essential oils, their components or volatile semiochemicals as promising tools for insect pest and pathogen management. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 287, 102330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge-Escudero, G.; Pérez Polanco, M.; Lagerlöf, J.E.; Pérez, C.A.; Míguez, D. Commercial fungicide toxic effects on terrestrial non-target species might be underestimated when based solely on active ingredient toxicity and standard earthworm tests. Toxics 2022, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderjan, E.; Wagenhoff, E.; Kandeler, E.; Moser, T. Natural soils in OECD 222 testing—Influence of soil water and soil properties on earthworm reproduction toxicity of carbendazim. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Lin, W.J.; Lu, T.P. Chapter 58—Biomarkers of Susceptibility: Pharmacogenomics and Toxicogenomics A2—Gupta, Ramesh, C. In Biomarkers in Toxicology; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 975–982. ISBN 978-0-12-404630-6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, C. Antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to 1,3,4, 6,7, 8-Hexahydro-4, 6,6, 7,8, 8-Hexamethyl-Cyclopenta-γ-2-Benzopyran. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 27, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cheng, C.; Du, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L. toxicological effects of pyraclostrobin on the antioxidant defense system and DNA Damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochron, S.; Choudhury, M.; Gomez, R.; Hussaini, S.; Illuzzi, K.; Mann, M.; Mezic, M.; Nikakis, J.; Tucker, C. temperature and body mass drive earthworm (Eisenia fetida) sensitivity to a popular glyphosate-based herbicide. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yan, B.; Martyniuk, C.J. A comprehensive review of strobilurin fungicide toxicity in aquatic species: Emphasis on mode of action from the zebrafish model. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, E.; Gerstle, V.; Schmitt, T.; Brühl, C.A. Co-formulants and adjuvants affect the acute aquatic and terrestrial toxicity of a cycloxydim herbicide formulation to European common frogs (Rana temporaria). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campani, T.; Casini, S.; Maccantelli, A.; Tosoni, F.; D’Agostino, A.; Caliani, I. Oxidative stress and DNA alteration on the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to four commercial pesticides. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 35969–35978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, K.; Duca, R.C.; Lovas, S.; Creta, M.; Scheepers, P.T.J.; Godderis, L.; Ádám, B. Systematic review of comparative studies assessing the toxicity of pesticide active ingredients and their product formulations. Environ. Res. 2020, 181, 108926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, P.M.C.; van Gestel, C.A. Comparative sensitivity of Eisenia andrei and Perionyx excavatus in earthworm avoidance tests using two soil types in the tropics. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghlami, R.I.; Toukabri, W.; Boudabbous, K.; Hechmi, S.; Barbouchi, M.; Oueriemmi, H.; Moussa, M.; Bahri, H. Assessment of earthworm viability and soil health after two years of raw and composted de-inking paper sludge amendment. Agriculture 2023, 13, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliani, I.; Campani, T.; Conti, B.; Cosci, F.; Bedini, S.; D’Agostino, A.; Ammendola, A.; Di Noi, A.; Gori, A.; Casini, S. Multi-biomarker approach and IBR index to evaluate the effects of different contaminants on the ecotoxicological status of Apis mellifera. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campani, T.; Caliani, I.; Pozzuoli, C.; Romi, M.; Fossi, M.C.; Casini, S. Assessment of toxicological effects of raw and bioremediated olive mill waste in the earthworm Eisenia fetida: A biomarker approach for sustainable agriculture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 119, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, W.; Porcher, J.M. Fish biomarkers for environmental monitoring within the water framework directive of the European Union. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, S.; Minguez, L.; Giamberini, L.; Geffard, A.; Boussetta, H.; Mouneyrac, C. Assessment of the health status of Donax trunculus from the Gulf of Tunis using integrative biomarker indices. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 32, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Xia, X. Effect of Different Exposure Times and Doses of Cyantraniliprole on Oxidative Stress and Genotoxicity in Earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 2023, 319, 138023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviraj, A.; Gupta, A. Biomarkers of type II synthetic pyrethroid pesticides in freshwater fish. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 928063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, C.; Barot, S.; Capowiez, Y.; Hedde, M.; Vandenbulcke, F. Pesticides and earthworms. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amossé, J.; Bart, S.; Brulle, F.; Tebby, C.; Beaudouin, R.; Nelieu, S.; Lamy, I.; Pery, A.R.; Pelosi, C. A two years field experiment to assess the impact of two fungicides on earthworm communities and their recovery. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 110979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyambe, G.S.; Goven, A.J.; Fitzpatrick, L.C.; Venables, B.J.; Cooper, E.L. A non-invasive technique for sequential collection of earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) leukocytes during subchronic immunotoxicity studies. Lab. Anim. 1991, 25, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.P.; Draper, H.H. [35] Comparative Studies on Different Methods of Malonaldehyde Determination. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984; Volume 105, pp. 299–305. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- Habig, W.; Pabst, M.; Jakoby, W. Biological assay kit measures total GST activity. WJ Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984; Volume 105, pp. 121–126. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, S.; Soares, A.M.; Guilhermino, L.; Peck, M.R. Biomarker responses of the estuarine brown shrimp Crangon crangon, L. to non-toxic stressors: Temperature, salinity and handling stress effects. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 335, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliani, I.; Cannicci, S.; Pretti, C.; Baratti, M.; Contini, G.; Vitale, M.; Casini, S.; Fossi, M.C.; Iannucci, A.; Fratini, S. A multidisciplinary integrated approach using pachygrapsus Marmoratus to assess the impact of port activities on Mediterranean Marine protected areas. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.M.; McClellan-Green, P.D.; Kucklick, J.R.; Keil, D.E.; Peden-Adams, M.M. Effects of organochlorine contaminants on loggerhead sea turtle immunity: Comparison of a correlative field study and in vitro exposure experiments. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core TeamR. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Dinno, A. Dinno A_dunn.Test: Dunn’s Test of Multiple Comparisons Using Rank Sums_R Package, Version 1.3.5; RDR, Inc.: Centreville, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, H.J.; Traa, A.; Van Raamsdonk, J.M. Beneficial and detrimental effects of reactive oxygen species on lifespan: A comprehensive review of comparative and experimental studies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 628157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Du, Z.; Li, B.; Juhasz, A.; Zhu, L. Oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by trifloxystrobin on earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in two soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Meng, Z.; Sun, W.; Wu, R.; Jia, M.; Yan, S.; Tian, S.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Z. Bioaccumulation and toxic effects of penconazole in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) following soil exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 38056–38063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, S. Integrated assessment of oxidative stress and DNA damage in Earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to azoxystrobin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 107, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, B.; Hou, K.; Du, Z.; Allen, S.C.; Zhu, L.; Li, W.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. ecotoxicity evaluation of azoxystrobin on Eisenia fetida in different soils. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.N.; Leung, M.C.; Rooney, J.P.; Sendoel, A.; Hengartner, M.O.; Kisby, G.E.; Bess, A.S. Mitochondria as a target of environmental toxicants. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 134, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Tamae, K. Earthworms and soil pollutants. Sensors 2011, 11, 11157–11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vischetti, C.; Casucci, C.; De Bernardi, A.; Monaci, E.; Tiano, L.; Marcheggiani, F.; Ciani, M.; Comitini, F.; Marini, E.; Taskin, E. Sub-lethal effects of pesticides on the DNA of soil organisms as early ecotoxicological biomarkers. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 536577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Liu, R. Mechanistic insights into phenanthrene-triggered oxidative stress-associated neurotoxicity, genotoxicity, and behavioral disturbances toward the brandling worm (Eisenia fetida) brain: The need for an ecotoxicological evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 131072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforzini, S.; Boeri, M.; Dagnino, A.; Oliveri, L.; Bolognesi, C.; Viarengo, A. Genotoxicity assessment in Eisenia andrei Coelomocytes: A study of the induction of DNA damage and micronuclei in earthworms exposed to B[a]P- and TCDD-spiked soils. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2012, 746, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muangphra, P.; Kwankua, W.; Gooneratne, R. Genotoxic effects of glyphosate or paraquat on earthworm Coelomocytes. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatoo, A.M.; Ali, M.N.; Zaheen, Z.; Baba, Z.A.; Ali, S.; Rasool, S.; Sheikh, T.A.; Sillanpää, M.; Gupta, P.K.; Hamid, B. Assessment of pesticide toxicity on earthworms using multiple biomarkers: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2573–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, W.J.; Collier, S. Apparent differences in pH optima among isozymes of Glycerol-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase, Hexokinase, and Lactate Dehydrogenase in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. 1991, 98, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, G.; Kachhwaha, N.; Dabi, I.; Bandooni, N. Temperature-dependent alterations in metabolic enzymes and proteins of three ecophysiologically different species of earthworms. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011, 54, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, A.; Sabater, C.; Castillo, M.Á. Lethal and sub-lethal effects of five pesticides used in rice farming on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 127, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammertyn, S.; Masín, C.E.; Zalazar, C.S.; Fernandez, M.E. Biomarkers response and population biological parameters in the earthworm Eisenia fetida after short term exposure to atrazine herbicide. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Analysis | Unit of Measure | Value |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.95 | |
| Total Nitrogen | N (g/kg) | 1.35 |
| Plant-available phosphorus | P2O (mg/kg) | 14.5 |
| Exchangeable potassium | K2O (mg/kg) | 147.5 |
| Exchangeable calcium | Ca (mg/kg) | 3850.5 |
| Exchangeable magnesium | Mg (mg/kg) | 143 |
| Available iron | Fe (mg/kg) | 19.5 |
| Organic matter | % | 2.28 |
| C/N | 9.75 | |
| Total lime | % | 16.25 |
| Active lime | % | 3.5 |
| C.E.C. | meq/100 g | 20.8 |
| Clay | % | 28 |
| Silt | % | 34.4 |
| Sand | % | 37.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campani, T.; Caliani, I.; Di Noi, A.; Casini, S. Toxicity of Four Commercial Fungicides, Alone and in Combination, on the Earthworm Eisenia fetida: A Field Experiment. Toxics 2025, 13, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030209
Campani T, Caliani I, Di Noi A, Casini S. Toxicity of Four Commercial Fungicides, Alone and in Combination, on the Earthworm Eisenia fetida: A Field Experiment. Toxics. 2025; 13(3):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030209
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampani, Tommaso, Ilaria Caliani, Agata Di Noi, and Silvia Casini. 2025. "Toxicity of Four Commercial Fungicides, Alone and in Combination, on the Earthworm Eisenia fetida: A Field Experiment" Toxics 13, no. 3: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030209
APA StyleCampani, T., Caliani, I., Di Noi, A., & Casini, S. (2025). Toxicity of Four Commercial Fungicides, Alone and in Combination, on the Earthworm Eisenia fetida: A Field Experiment. Toxics, 13(3), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030209








