Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Road-Deposited Sediments and Correlation Distribution of DOM and Heavy Metals in Beijing, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Heavy Metal Evaluation Methods
2.4. DOM Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Heavy Metal Content and Pollution Characteristics
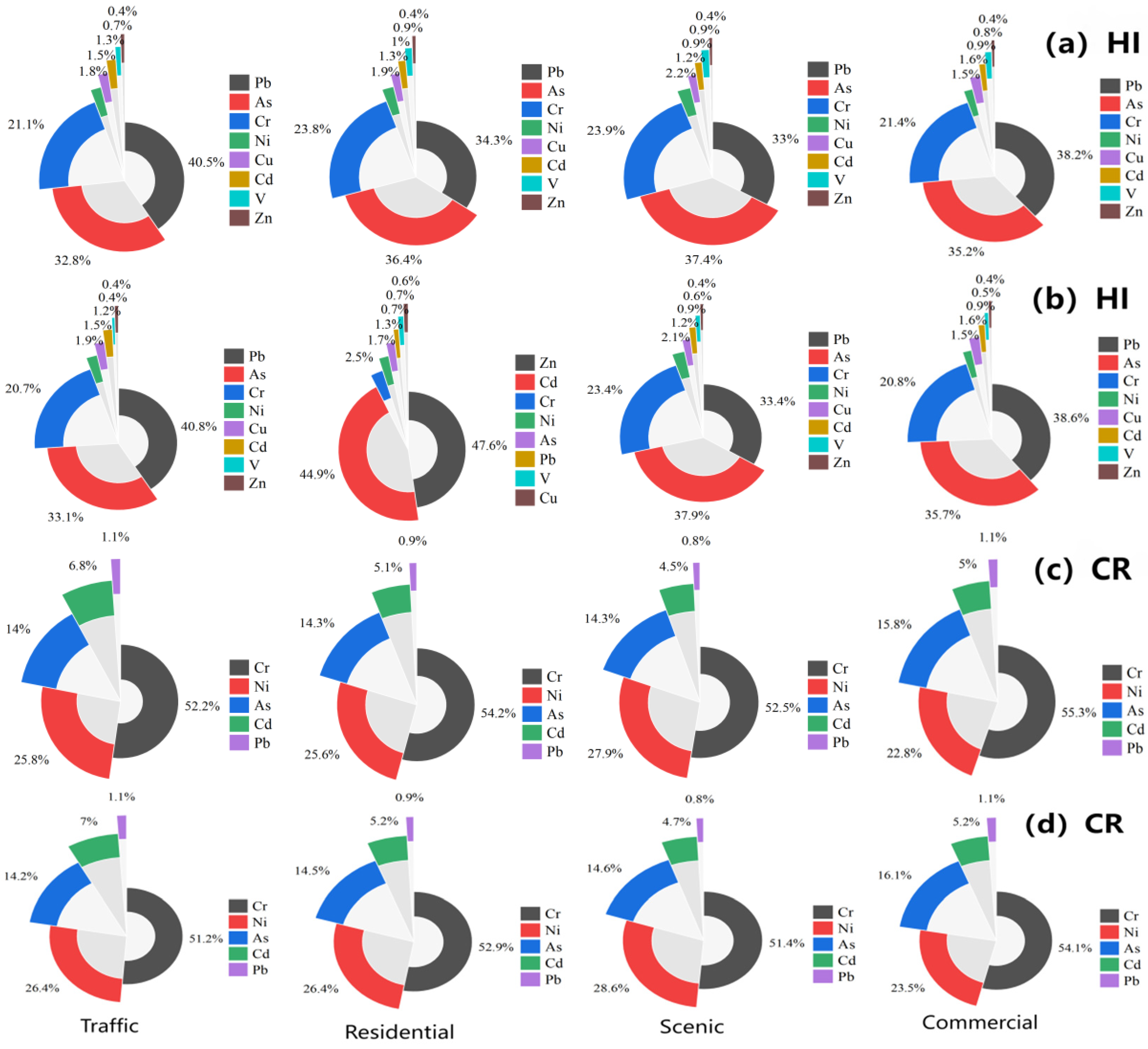
3.2. Ecological Risk Evaluation of Heavy Metals and the Extent of Contamination
3.3. Changes in DOM Quantity and Quality
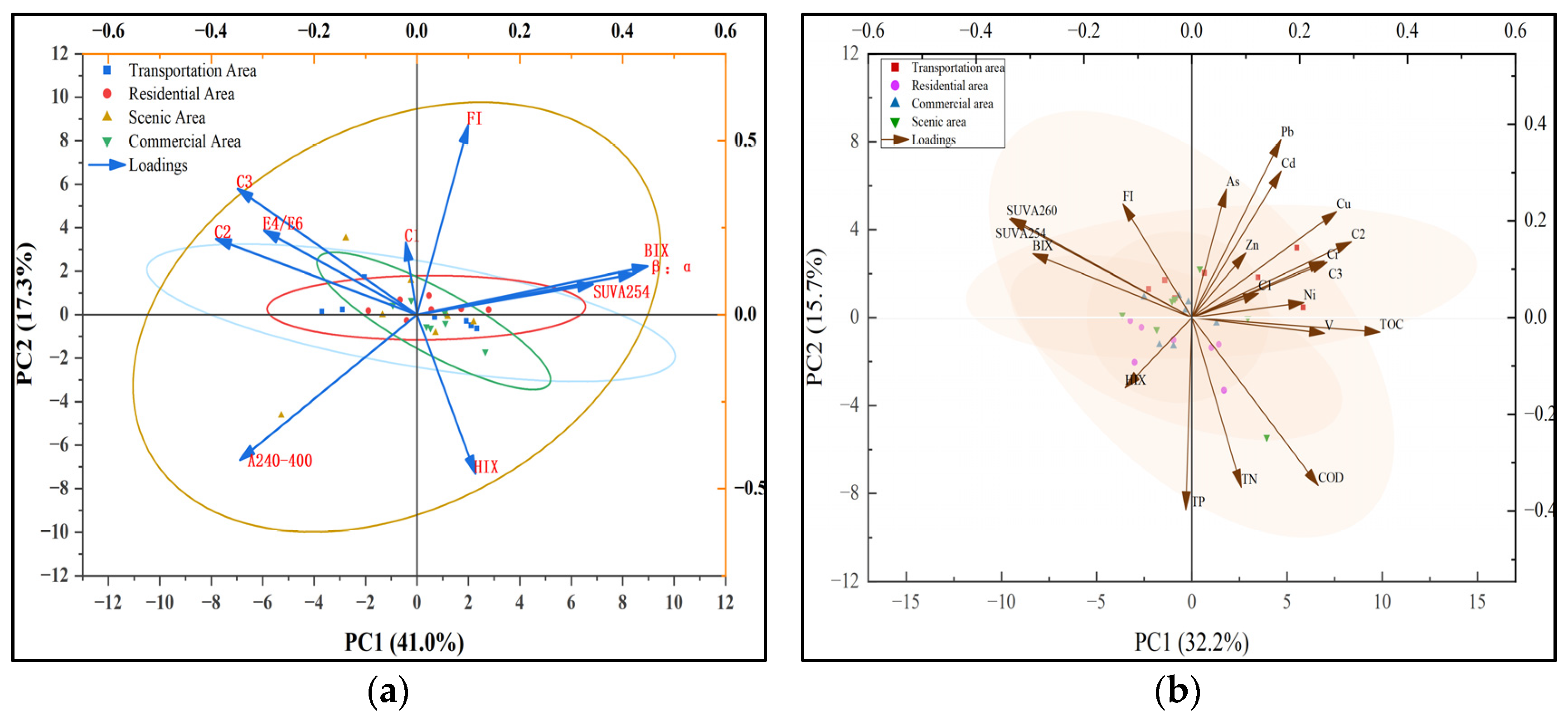
3.4. Correlation Between DOM and Heavy Metals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P.; Cao, C.; Wang, Y.H.; Yu, K.; Liu, C.X.; He, C. Chemodiversity of water-extractable organic matter in sediment columns of a polluted urban river in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, M.; Wolfe, A.; Burke, M.; Krekeler, M.P.S. The first pollution investigation of road sediment in Gary, Indiana: Anthropogenic metals and possible health implications for a socioeconomically disadvantaged area. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.R.; Wang, Y.S.; Guo, S.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yan, L.; Tan, C.; Yang, Z.; Guo, X. Concentration and speciation of trace metals and metalloids from road-deposited sediments in urban and rural areas of Beijing, China. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 3487–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.M.; Xu, F.; Wang, Q.R.; Guo, L.J.; Shen, Z.Y. Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommel, S.H.; Stinshoff, P.; Helmreich, B. Sequential extraction of heavy metals from sorptive filter media and sediments trapped in stormwater quality improvement devices for road runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahandari, A. Pollution status and human health risk assessments of selected heavy metals in urban dust of 16 cities in Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23094–23107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardana, C.; Goonetilleke, A.; Egodawatta, P.; Dawes, L.; Kokot, S. Source characterisation of road dust based on chemical and mineralogical composition. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, X.C.; Ge, Y. Size distributions and heavy metal pollution of urban road-deposited sediments (RDS) related to traffic types. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 34199–34210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanad, A.; Alolayan, M. Heavy metals in road-deposited sediments and pollution indices for different land activities. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lim, J.; Shim, W.J.; Kim, Y.O.; Ra, K. Characterization of the contribution of road deposited sediments to the contamination of the close marine environment with trace metals: Case of the port city of Busan (South Korea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordez, A.; Loredo, J.; De Miguel, E.; Charlesworth, S. Distribution of Heavy Metals in the Street Dusts and Soils of an Industrial City in Northern Spain. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 44, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, S.; Sivarethinamohan, R. A critical review of Cr(VI) ion effect on mankind and its amputation through adsorption by activated carbon. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Ji, H.B.; Shi, C.J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Ding, H.; Tang, L.; Xing, Y. Distribution of heavy metals and metalloids in bulk and particle size fractions of soils from coal-mine brownfield and implications on human health. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.D.; Hou, X.; Shi, Y.; Huang, T.; Yang, H.; Huang, C.C. Rapid photodegradation of terrestrial soil dissolved organic matter (DOM) with abundant humic-like substances under simulated ultraviolet radiation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.F.; Yang, X.M.; Liu, G.B.; Liang, C.T.; Xue, S.; Chen, H.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Response of soil dissolved organic matter to microplastic addition in Chinese loess soil. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Huang, D.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, S. Intrinsic linkage mechanisms of DOM properties to organic phosphorus in lake sediments: Evidence from coupled molecular weight ultrafiltration and spectral analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.P.; Wang, H.R. Grey clustering assessment of level of service for urban expressway segments. In Proceedings of the 7th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Washington, WA, USA, 3–6 October 2004; pp. 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- HJ/T 166-2004; Technical Specifications for Soil Environmental Monitoring. State Environmental Protection Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Cui, X.; Li, H.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y. Bioaccessibility, sources and health risk assessment of trace metals in urban park dust in Nanjing, Southeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, X.; Pan, H. Analysis of heavy metals in the re-suspended road dusts from different functional areas in Xi’an, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 19838–19846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Sun, X.; Shi, G.; Xu, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, L. Quantitative spatial characteristics and environmental risk of toxic heavy metals in urban dusts of Shanghai, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, K.A.; Meuser, H.; Usman, A.R.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Al-Farraj, A.S. A comparison of two digestion methods for assessing heavy metals level in urban soils influenced by mining and industrial activities. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coufalík, P.; Zvěřina, O.; Mikuška, P.; Komárek, J. Seasonal Variability of Mercury Contents in Street Dust in Brno, Czech Republic. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 93, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Graiti, T.; Jakab, G.; Ujházy, N.; Vancsik, A.; Fodor, N.; Árendás, T.; Madarász, B.; Barcza, Z.; Márialigeti, K.; Szalai, Z. The Composition of Dissolved Organic Matter in Arable Lands: Does Soil Management Practice Matter? Agronomy 2022, 12, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Willett, V.B. Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, M.; Bhogal, A.; Barrett, G.; Dyer, C. Dissolved organic nitrogen in agricultural soils: Effects of sample preparation on measured values. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 1523–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Gao, B.; Wei, X.; Xu, D.; Gao, L. Spatial distribution, health risk assessment, and isotopic composition of lead contamination of street dusts in different functional areas of Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3247–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, A.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Malik, R.N.; Ahmed, Z. Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah—Feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake Reservoir, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Yadav, S. Sources apportionment and spatio-temporal changes in metal pollution in surface and sub-surface soils of a mixed type industrial area in India. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zuo, Q.; Feng, F.; Jia, H.; Ji, Y. Pollution characteristics, bioavailability, and risk assessment of heavy metals in urban road dust from Zhengzhou, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control. a sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusin, F.M.; Rahman, M.S.A.; Madzin, Z.; Jusop, S.; Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Ariffin, M.; Z, M.S.M. The occurrence and potential ecological risk assessment of bauxite mine-impacted water and sediments in Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 24, 1306–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, J.; Barbieri, M.; Agnan, Y.; Sellami, A.; Braham, A.; Dhaha, F.; Charef, A. Trace element contamination in the mine-affected stream sediments of Oued Rarai in north-western Tunisia: A river basin scale assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4027–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsogtbaatar, U.; Huo, L.; Jiao, L.; Dalantai, S.; An, Y.; Batsaikhan, B.; Jugnee, U.; Natsagdorj, B.; Batsaikhan, T.; Munkhchuluun, B. Ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals based on hyperspectral: A case study of rice paddy soil in xiangtan county, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudhevan, P.; Pu, S.; Ayyamperumal, R.; Manikandan, E.; Sujitha, S.B.; Singh, S.; Ponniah, J.M.; Dixit, S.; Thangavel, P. Pollution assessment, ecological risk and source identifcation of heavy metals in paddy soils and rice grains from Salem, South India. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100526. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuyan, M.S.; Haider, S.M.B.; Meraj, G.; Bakar, M.A.; Islam, M.T.; Kunda, M.; Bhat, M.A. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in beach sediments of eastern St. Martin’s island, Bangladesh: Implications for environmental and human health risks. Water 2023, 15, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Song, J.; Abeysekara, S.D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Jiang, B. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in Upstream Bailang River, Eastern China: Spatial Analysis, Health Risks, and Pollution Source Identification. Soil Sediment Contam. 2024, 34, 559–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Exposure Factors Handbook 2011 Edition (Final). 2022. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/risk/recordisplay.cfm?deid=236252 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites OSWER, 2002. 9355.4-24. Available online: https://semspub.epa.gov/work/HQ/175878.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk-Based Concentration Table; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Kalipci, E.; Cüce, H.; Ustaoglu, F.; Dereli, M.A.; Türkmen, M. Toxicological health risk analysis of hazardous trace elements accumulation in the edible fish species of the Black Sea in Türkiye using multivariate statistical and spatial assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 97, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Cancer, Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Bro, R. Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: A tutorial. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2008, 6, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.R.; Yan, C.X.; Nie, M.H.; Ju, M.; Ding, M.J.; Huang, X.; Chen, J. The partitioning behavior of PAHs between settled dust and its extracted water phase: Coefficients and effects of the fluorescent organic matter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cai, G.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, W.; Cheng, H.; Lin, C. Contents and chemical forms of heavy metals in school and roadside topsoils and road-surface dust of Beijing. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xia, D.; Liu, X.; Chen, F.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, A. Spatial and temporal variation in magnetic properties of street dust in Lanzhou City, China. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Liang, S.; Li, X. A novel in situ method for sampling urban soil dust: Particle size distribution, trace metal concentrations, and stable lead isotopes. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Markert, B.; Chen, W.; Peng, C.; Ouyang, Z. Identification of heavy metal pollutants using multivariate analysis and effects of land uses on their accumulation in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 5889–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Tan, J. Atmospheric heavy metals and Arsenic in China: Situation, sources and control policies. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, L.; Dubs, F.; Gignoux, J.; Lata, J.C.; Lerch, T.Z.; Mathieu, J.; Nold, F.; Nunan, N.; Raynaud, X.; Abbadie, L.; et al. Trace element concentrations along a gradient of urban pressure in forest and lawn soils of the Paris region (France). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Gui, H.; Wang, Y.; Peng, W. Pollution characteristics, source apportionment, and health risk of heavy metals in street dust of Suzhou, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 24, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, B.; Dong, L.; Hu, W.; Akhtar, M.S.; Qu, M. Accumulation, sources and health risks of trace metals in elevated geochemical background soils used for greenhouse vegetable production in southwestern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, J.; Lv, M. Spatial Distribution, Sources Apportionment and Health Risk of Metals in Topsoil in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardyjak, E.R.; Speckart, S.O.; Yin, F.; Veranth, J.M. Near source deposition of vehicle generated fugitive dust on vegetation and buildings: Model development and theory. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6442–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, M.; Peng, C.; Alatalo, J.M. Impacts of urbanization on the distribution of heavy metals in soils along the Huangpu River, the drinking water source for Shanghai. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 5222–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Tsou, M.C.M.; Chien, H.L.C. Oral and inhalation bioaccessibility of mercury in contaminated soils and potential health risk to the kidneys and neurodevelopment of children in Taiwan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6267–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, B.R.; Pai, B.J.; Salmataj, S.A.; Naik, N. Assessment of Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk indices of heavy metal exposure in different age groups using Monte Carlo Simulation Approach. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyimah, E.; Gyimah, G.N.W.; Stemn, E.; Ndur, S.; Amankwaa, G.; Fosu, S. Ecological and human risk assessments of heavy metal contamination of surface soils of auto-mechanic shops at bogoso junction, tarkwa, ghana. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coble, P.G. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy. Mar. Chem. 1996, 51, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.J.; Yamashita, Y.; Wilson, H.F.; Jaffé, R.; Xenopoulos, M.A. Unraveling the role of land use and microbial activity in shaping dissolved organic matter characteristics in stream ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coble, P.G. Marine Optical Biogeochemistry: The Chemistry of Ocean Color. Chemosphere Rev. 2007, 107, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, C.C.; Li, J.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, P.; Pei, Z.J. Dissolved organic matter in urban stormwater runoff at three typical regions in Beijing: Chemical composition, structural characterization and source identification. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 73490–73500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.D.; Yang, C.H.; Yu, J.L.; Zhuang, H.F.; Fang, C.R. Coadsorption of heavy metal and antibiotic onto humic acid from Polder River sediment. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 2856–2867. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Jiang, Z.; He, M.; Ye, B.; Wei, S. Relating Cd2+ binding by humic acids to molecular weight: A modeling and spectroscopic study. Environ. Sci. 2018, 70, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Lin, S.; Wang, W.C.; Huang, Z.W.; Zeng, H.L.; Chen, X.L.; Zeng, F.; Fan, Z. Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of the Xiashan stream, eastern Guangdong Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25908–25924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.Y.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Y.Y.; Guo, X.J.; Li, Y.Z.; Dai, B.L.; Huang, T. Study on the complexation of heavy metals onto biogas slurry DOM using two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy combined with the log-transformed synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22878–22885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, D.; Li, P.; Yan, C.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, C.; Kou, Y. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Road-Deposited Sediments and Correlation Distribution of DOM and Heavy Metals in Beijing, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040308
Yuan D, Li P, Yan C, Wang J, Bai X, Wei Y, Wang C, Kou Y. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Road-Deposited Sediments and Correlation Distribution of DOM and Heavy Metals in Beijing, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040308
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Donghai, Pengmiao Li, Chenling Yan, Jinggang Wang, Xiaochen Bai, Yuhang Wei, Chen Wang, and Yingying Kou. 2025. "Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Road-Deposited Sediments and Correlation Distribution of DOM and Heavy Metals in Beijing, China" Toxics 13, no. 4: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040308
APA StyleYuan, D., Li, P., Yan, C., Wang, J., Bai, X., Wei, Y., Wang, C., & Kou, Y. (2025). Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Road-Deposited Sediments and Correlation Distribution of DOM and Heavy Metals in Beijing, China. Toxics, 13(4), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040308






