In Vitro Anti-Cholinesterase and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts of Moringa oleifera Plants from Rivers State, Niger Delta, Nigeria
Abstract
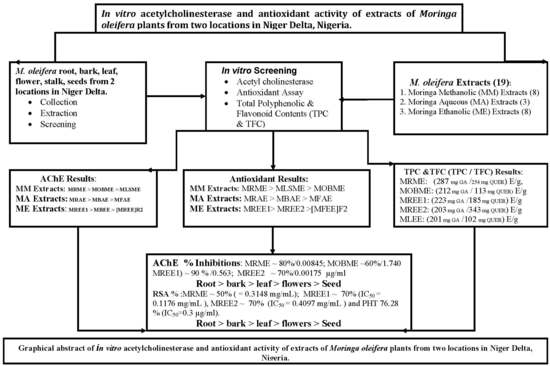
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Plant Materials Collection and Identification
2.2. Preparation of Methanolic, Ethanolic and Aqueous Extracts of Moringa oleifera
2.3. Chemicals
2.4. Animals
2.5. Assay for Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity
2.6. Determination of 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Radical Scavenging Effects
2.7. Reducing Power Capacity Assessment
2.8. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
2.9. Determination of Total Flavonoid Content
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Moringa Oleifera Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity
3.2. Moringa Oleifera DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.3. Moringa Oleifera Reducing (Antioxidant) Capacity
3.4. Moringa Oleifera Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Content
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rouch, I.; Dorey, J.-M.; Boublay, N.; Henaff, M.-A.; Dibie-Racoupeau, F.; Makaroff, Z.; Haston, S.; Benoit, M.; Barrellon, M.; Fedrico, D.; et al. Personality, Alzheimer’s disease and behavioural and cognitive symptoms of dementia: The PACO prospective cohort study protocol. BMC Geriatr. 2014, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Dementia; Fact Sheet 362; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer’s Disease International, World Alzheimer’s Report 2015: Global Impact of Dementia, 2015. Available online: http://www.alz.co.uk/research/world-report-2015 (accessed on 4 October 2016).
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2016, 12, 459–509. [Google Scholar]
- Borsje, P.; Hems, M.A.; Lucassen, P.L.; Bor, H.; Koopmans, R.T.; Pot, A.M. Psychological distress in informal caregivers of patients with dementia in primary care: Course and determinants. Fam. Pract. 2016, 33, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Hyman, B.T. Neuropathological Alterations in Alzheimer Disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006189. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.S.; Stachowiak, A.; Mamun, A.A.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; Takeda, S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Bergantin, L.B.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Stankiewicz, A.M. Autophagy and Alzheimer’s disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Implications. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, G.B.; El-Agnaf, O.M.; Shankar, G.M.; Walsh, D.M. Protein aggregation in the brain: The molecular basis for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-beta and tau: The trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowacek, A.; Kosloski, L.M.; Gendelman, H.E. Neurodegenerative disorders and nanoformulated drug development. Nanomedicine 2009, 4, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballard, C.; Gauthier, S.; Corbett, A.; Brayne, C.; Aarsland, D.; Jones, E. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2011, 377, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, P.I.; Smith, M.A.; Zhu, X.; Nunomura, A.; Castellani, R.J.; Perry, G. Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Jiang, L. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, C.; Scapagini, G.; Curro, D.; Giuffrida, S.A.M.; DeMarco, C.; Butterfield, D.A.; Calabrese, V. Mitochondrial dysfunction, free radical generation and cellular stress response in neurodegenerative disorders. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mufson, E.J.; Counts, S.E.; Perez, S.E.; Ginsberg, S.D. Cholinergic system during the progression of Alzheimer’s disease: Therapeutic implications. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2008, 8, 1703–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunomura, A.; Perry, G.; Aliev, G.; Hirai, K.; Takeda, A.; Balraj, E.K.; Jones, P.K.; Ghanbari, H.; Wataya, H.; Shimohama, S.; et al. Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, M.A.; Markesbery, W.R. Oxidative DNA Damage in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Late-Stage Alzheimer’s Disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7497–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chenm, G.; Zhang, C.; Wu, M.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q. Research progress of natural antioxidants in foods for the treatment of diseases. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2014, 3, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Brunton, N.P.; Barry-Ryan, C.; Martin-Diana, A.B.; Wilkinson, M. Antioxidant activity of spices extracts and phenolics in comparison to synthetic antioxidants. Rasayan J. Chem. 2008, 4, 751–756. [Google Scholar]
- Satyanarayana, U.; Kumar, A.N.; Naidu, J.N.; Prasad, D.K.V. Antioxidant Supplementation for Health—A Boon or a Bane? J. Dr. NTR Univ. Health Sci. 2014, 3, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Huy, L.A.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C. Free Radicals, Antioxidants in Disease and Health. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2008, 4, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perry, E.K.; Pickering, A.T.; Wang, W.W.; Houghton, P.J.; Perry, N.S. Medicinal plants and Alzheimer’s disease: From ethno botany to phytotherapy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1999, 51, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.S.; Mamun, A.A.; Iqbal, M.A.; Islam, A.; Hossain, M.F.; Khanum, S.; Rashid, M. Analyzing Nootropic Effect of Phyllanthus reticulatus Poir. on Cognitive Functions, Brain Antioxidant Enzymes and Acetylcholinesterase Activity against Aluminium-Induced Alzheimer’s Model in Rats: Applicable for Controlling the Risk Factors of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Alzh Dis. 2016, 5, 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-E.; Wu, F.; Zhao, A.; Ge, H.; Zhan, H. Protection Efficacy of the Extract of Ginkgo biloba against the Learning and Memory Damage of Rats under Repeated High Sustained +Gz Exposure. Evid-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, S.; Borowski, T. Neuropharmacological Review of the Nootropic Herb Bacopa monnieri. Rejuv. Res. 2013, 16, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, A.K.; Naithani, V.; Bangar, O.P. Medicinal Plants with a Potential to Treat Alzheimer and Associated Symptoms. Int. J. Nutr. Pharmacol. Neurol. Dis. 2012, 2, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, C.; Peter, K.V.; Gopalakrishnan, P.K. Drumstick (Moringa oleifera): A multipurpose Indian vegetable. Econ. Bot. 1980, 34, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, A.K. Indian Materia Medica; Popular Prakashan: Bombay, India, 1976; pp. 810–816. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, F.; Latif, S.; Ashraf, M.; Gilani, A.H. Moringa oleifera: A food plant with multiple medicinal uses. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokkhasmit, M.; Swasdimongkol, K.; Ngarmwathana, W.; Permphiphat, U. Pharmacological evaluation of Thai medicinal plants. J. Med. Assoc. Thailand 1971, 54, 490–504. [Google Scholar]
- Kooltheat, N.; Sranujit, R.P.; Chumark, P.; Potup, P.; Laytragoon-Lewin, N.; Usuwanthim, K. An ethyl acetate fraction of Moringa oleifera Lam. inhibits human macrophage cytokine production induced by cigarette smoke. Nutrients 2014, 6, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, M.T.; Arulselvan, P.; Karthivashan, G.; Adam, S.K.; Fakurazi, S. Bioactive extract from Moringa oleifera inhibits the pro-inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide stimulated macrophages. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, S556–S563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arulselvan, P.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Muniandy, K.; Fakurazi, S.; Esa, N.M.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Kumar, S.S. Anti-inflammatory potential of ethyl acetate fraction of Moringa oleifera in downregulating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Molecules 2016, 21, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacoppo, S.; Rajan, T.S.; De Nicola, G.R.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The isothiocyanate isolated from Moringa oleifera shows potent anti-inflammatory activity in the treatment of murine subacute Parkinson’s disease. Rejuv. Res. 2017, 20, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, J.R.; Silva, G.C.; Costa, R.A.; de Sousa, F.J.; Vieira, G.H.; Filho, A.A.; Dos, F.V.R. In vitro antibacterial effect of aqueous and ethanolic Moringa leaf extracts. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumark, P.; Khunawat, P.; Sanvarinda, Y.; Phornchirasilp, S.; Morales, N.P.; Phivthong-Ngam, L.; Ratanachamnong, P.; Srisawat, S.; Pongrapeeporn, K.U. The in vitro and ex vivo antioxidant properties, hypolipidaemic and antiatherosclerotic activities of water extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 116, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Asmari, A.K.; Albalawi, S.M.; Athar, M.T.; Khan, A.Q.; Al-Shahrani, H.; Islam, M. Moringa oleifera as an anti-cancer agent against breast and colorectal cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifudin, S.A.; Fakurazi, S.; Hidayat, M.T.; Hairuszah, I.; Moklas, M.A.; Arulselvan, P. Therapeutic potential of Moringa oleifera extracts against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Arya, P.V.; Aggarwal, V.P.; Gupta, R.S. Evaluation of antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves in carbon tetrachloride-intoxicated rats. Antioxidants (Basel) 2014, 3, 569–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutalangka, C.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Thukham-mee, W. Moringa oleifera mitigates memory impairment and neurodegeneration in animal model of age-related dementia. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, M.A.; Kang, J.Y.; Mohibbullah, M.; Hong, Y.K.; Lee, H.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, I.S.; Moon, I.S. Moringa oleifera with promising neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth promoting potentials. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekong, M.B.; Ekpo, M.M.; Akpanyung, E.O.; Nwaokonko, D.U. Neuroprotective effect of Moringa oleifera leaf extract on aluminium-induced temporal cortical degeneration. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, L.K.; Balaraman, R.; Amin, A.H.; Bafna, P.A.; Gulati, O.D. Effects of fruits of Moringa oleifera on the lipid profile of normal and hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 86, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeamuzle, I.C.; Ambadederomo, A.W.; Shode, F.O.; Ekwebelem, S.C. Antiinflammatory effects of Moringa oleifera root extract. Int. J. Pharmacogn. 1996, 34, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atawodi, S.E.; Atawodi, J.C.; Idakwo, G.A.; Pfundstein, B. Evaluation of the polyphenol content and antioxidant properties of methanol extracts of the leaves, stem, and root barks of Moringa oleifera Lam. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddhuraju, P.; Becker, K. Antioxidant properties of various solvent extracts of total phenolic constituents from three different agroclimatic origins of drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera Lam.) leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensah, J.K.; Ikhajiagbe, B.; Edema, N.E.; Emokhor, J. Phytochemical, nutritional and antibacterial properties of dried leaf powder of Moringa oleifera (Lam.) from Edo Central Province, Nigeria. J. Nat. Prod. Plant Resour. 2012, 2, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Omodanisi, E.; Aboua, Y.G.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Assessment of the Anti-Hyperglycaemic, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of the Methanol Extract of Moringa oleifera in Diabetes-Induced Nephrotoxic Male Wistar Rats. Molecules 2017, 22, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.C.; Bannerji, R.; Mirra, G.; Nigam, S.K. Nutritional value of Moringa. Curr. Sci. 1976, 45, 769–771. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, B.R.; Agrawal, B.B.; Goyal, R.K.; Mehta, A.A. Phyto-pharmacology of Moringa oleifera Lam. 6 An overview. Nat. Prod. Radiance 2007, 6, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Adedapo, A.A.; Mogbojuri, O.M.; Emikpe, B.O. Safety evaluations of the aqueous extract of the leaves of Moringa oleifera in rats. J. Med. Plants Res. 2009, 3, 586–591. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, R.J.; Lee, K.S.; Hyacinth, H.I.; Hibbert, J.M.; Reid, M.E.; Wheatley, A.O.; Asemota, H.N. An investigation of the Antioxidant Capacity in Extracts from Moringa oleifera Plants Grown in Jamaica. Plant 2017, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Bhanger, M.I. Effect of season and production location on antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera leaves grown in Pakistan. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreelatha, S.; Padma, P.R. Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolic Content of Moringa oleifera Leaves in Two Stages of Maturity. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2009, 64, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, W.G.; Tarhoni, M.; Rathbone, A.J.; Ray, D.E. Differential protein adduction by seven organophosphorus pesticides in both brain and thymus. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2007, 26, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarhoni, M.H.; Vigneswara, V.; Smith, M.; Anderson, S.; Wigmore, P.; Lees, J.; Ray, D.E.; Carter, W.G. Detection, quantification, and microlocalisation of targets of pesticides using microchannel plate autoradiographic imagers. Molecules 2011, 16, 8535–8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwidu, L.L.; Elmorsy, E.; Thornton, J.; Wijamunige, B.; Wijesekara, A.; Tarbox, R.; Warren, A.; Carter, W.G. Antiacetylcholinesterase activity and antioxidant properties of extracts and fractions of Carpolobia lutea. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganguly, R.; Guha, D. Alteration of brain monoamines & EEG wave pattern in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease & protection by Moringa oleifera. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 744–751. [Google Scholar]
- Obulesu, M.; Rao, D.M. Effect of plant extracts on Alzheimer’s disease: An insight into therapeutic avenues. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2011, 2, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igado, O.O.; Olopade, J.O. A Review on the Possible Neuroprotective Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract. Niger J. Physiol. Sci. 2017, 31, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.; Li, B.; Olayanju, J.B.; Drake, J.M.; Chen, N. Nutraceutical or Pharmacological Potential of Moringa oleifera Lam. Nutrients 2018, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirisattayakul, W.; Wattanathorn, J.; Tong-Un, T.; Muchimapura, S.; Wannanon, P.; Jittiwat, J. Cerebroprotective effect of Moringa oleifera against focal ischemic stroke induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, H.; Cornelius, K. Use of Cholinesterase inhibitors in Dementia. Adv. Psychiatr. Treat. 2002, 8, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, V.; Priya Jennifer, M.H. Anticholinesterases and anticholinergic drugs. Oxford J. 2004, 4, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.L.; Farlow, M.R.; Doody, R.S.; Mohs, R.; Friedhoff, L.T.; Donepezil Sudy Group. A 24-week, double blind, placebo-controlled trial of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1998, 50, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, M.; Abdu, A.; Marwan, S. New Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Intern. J. Alzheimer Dis. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, W.M.; Barros, M.L.; Cunha, P.E.L.; Santana, M.V.A.; Stevam, C.S.; Leopoldo, P.T.G.; Fernandes, R.P.M. Evaluation of acetylcholinesterase inhibition by extracts from medicinal plants. Rev. Bras. Plant. Med. 2012, 14, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharayu, R.; Asmita, M. Screening of acetylcholinestereases inhibitors by Moringa oleifera. Int. J. Life Sci. 2016, 4, 302–305. [Google Scholar]
- Pontual, E.V.; Napoleao, T.H.; Dias de Assis, C.R.; Bezerra, R.S.; Xavier, H.S.; Navarro, D.M.; Coelho, L.C.; Paiva, P.M. Effect of Moringa oleifera flower extract or larval trypsin and acetylcholinesterase activities in Aedes aegypti. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 79, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, T.; Kaden, B.; Fischer, J.P.; Bickel, U.; Barz, H.; Gusztony, G.; Cervos-Navarro, J.; Kewitz, H. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity in human brain tissue and erythrocytes by galanthamine, physostigmine and tacrine. Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1991, 29, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triggle, D.J.; Mitchell, J.M.; Filler, R. The pharmacology of physostigmine. CNS Drug Rev. 1998, 4, 87–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, N.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G.; Tijburg, L.; Bolwell, G.P.; Rice-Evans, C. Polyphenolic flavanols as scavengers of aqueous phase radicals and as chain-breaking antioxidants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 322, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brilhante, R.S.N.; Jamille Sales, J.A.; Pereira, V.S.; Castelo-Branco, D.S.C.M.; Cordeiro, R.A.; Sampaio, C.M.S.; Paiva, M.A.N.; dos Santos, J.B.F.; Sidrim, J.J.C.; Rocha, M.F.G. Research advances on the multiple uses of Moringa oleifera: A sustainable alternative for socially neglected population. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhakmani, F.; Kumar, S.; Khan, S.A. Estimation of total phenolic content, in-vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of flowers of Moringa oleifera. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.; Miller, N.; Paganga, G. Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauconneau, B.; Waffo-Teguo, P.; Huguet, F.; Barrier, L.; Decendit, A.; Merillon, J.M. Comparative study of radical scavenger and antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds from Vitis vinifera cell cultures using in vitro tests. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Foo, L.Y. Antioxidant activities of polyphenols from sage (Salvia officinalis). Food Chem. 2001, 75, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloff, N.J. Which extractant should be used for the screening and isolation of antimicrobial components from plants? J. Ethnopharmacol. 1998, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmir, J.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Sharif, K.M.; Mohamed, A.; Sahena, F.; Jahurul, M.H.A.; Ghafoor, K.; Norulaini, N.A.N.; Omar, A.K.M. Techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials: A review. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Moringa oleifera Extracts | Yield (%) | IC50 Concentrations (mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AChE | DPPH Radical Scavenging (×10−3) | ||
| Methanolic | |||
| MOBME | 2.67 | 0.1740 | 0.1419 |
| MOFME | 8.88 | 0.2750 | 0.04767 |
| MOSME | 3.44 | 0.3425 | 0.04902 |
| MOFPME | 14.71 | 0.4335 | 0.02579 |
| MOSME (h) | 6.83 | 0.3863 | 0.04561 |
| MOLME | 4.78 | 0.2615 | 0.02517 |
| MOSME (c) | 3.68 | 0.08723 | 0.08723 |
| MORME | 9.84 | 0.00845 | 0.3148 |
| Aqueous | |||
| MOFAE | 39.1 | 0.3784 | 0.1313 |
| MOBAE | 26.2 | 0.2185 | 0.08298 |
| MORAE | 14.3 | 0.2764 | 0.1574 |
| Ethanolic | |||
| MOLEE | 5.3 | 0.2105 | 0.4638 |
| MOREE2 | 1.1 | 0.00175 | 0.4097 |
| MOREE1 | 6.3 | 0.0563 | 0.1176 |
| MOFEE1 | 14.4 | 0.2756 | 0.6819 |
| MOFEE2 | 3.1 | 0.2654 | 0.6819 |
| MOBEE | 10.2 | 0.0173 | 0.6709 |
| MOSEE1 | 7.1 | 0.2864 | 3.168 |
| MOSEE2 | 10.3 | 0.2464 | 0.1653 |
| Moringa oleifera Extracts | Total Phenolic Content (mg GAE/g) | Total Flavonoid Content (mg QUER E/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Methanolic | ||
| MOBME | 212.3 ± 2.30 | 112.5 ± 2.40 |
| MOFME | 175.6 ± 0.09 | 84.3 ± 2.30 |
| MOSME | 187.4 ± 2.00 | 52.0 ± 0.60 |
| MOFPME | 100.4 ± 0.08 | 7.3 ± 1.90 |
| MOSME (h) | 123.2 ± 1.10 | 57.0 ± 3.30 |
| MOLME | 113.3 ± 1.90 | 91.2 ± 0.90 |
| MOSME (c) | 94.5 ± 0.90 | 18.0 ± 0.09 |
| MORME | 287.1 ± 0.00 | 254.3 ± 2.30 |
| Aqueous | ||
| MOFAE | 165.2 ± 0.80 | 27.0 ± 3.00 |
| MOBAE | 153.3 ± 0.08 | 87.2 ± 3.60 |
| MORAE | 187.0 ± 1.90 | 67.2 ± 2.00 |
| Ethanolic | ||
| MOLEE | 201.0 ± 2.30 | 102.2 ± 1.50 |
| MOREE2 | 203.2 ± 0.02 | 342.5 ± 1.70 |
| MOREE1 | 223.2 ± 1.01 | 185.4 ± 2.70 |
| MOFEE1 | 186.3 ± 2.00 | 75.0 ± 0.30 |
| MOFEE2 | 176.3 ± 0.30 | 69.7 ± 1.70 |
| MOBEE | 187.2 ± 2.00 | 202.3 ± 3.10 |
| MOSEE1 | 146.3 ± 0.20 | 95.3 ± 2.5 |
| MOSEE2 | 109.2 ± 0.80 | 87.2 ± 3.60 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nwidu, L.L.; Elmorsy, E.; Aprioku, J.S.; Siminialayi, I.; Carter, W.G. In Vitro Anti-Cholinesterase and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts of Moringa oleifera Plants from Rivers State, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Medicines 2018, 5, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030071
Nwidu LL, Elmorsy E, Aprioku JS, Siminialayi I, Carter WG. In Vitro Anti-Cholinesterase and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts of Moringa oleifera Plants from Rivers State, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Medicines. 2018; 5(3):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030071
Chicago/Turabian StyleNwidu, Lucky Legbosi, Ekramy Elmorsy, Jonah Sydney Aprioku, Iyeopu Siminialayi, and Wayne Grant Carter. 2018. "In Vitro Anti-Cholinesterase and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts of Moringa oleifera Plants from Rivers State, Niger Delta, Nigeria" Medicines 5, no. 3: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030071
APA StyleNwidu, L. L., Elmorsy, E., Aprioku, J. S., Siminialayi, I., & Carter, W. G. (2018). In Vitro Anti-Cholinesterase and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts of Moringa oleifera Plants from Rivers State, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Medicines, 5(3), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030071