Effect of O3 Dose on the O3/UV Treatment Process for the Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Secondary Effluent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Experimental Setting and Operational Conditions
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Sample Preparation and Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antibiotics
3.2. Analgesics
3.3. Antiarrhythmic Agents
3.4. Anticonvulsants
3.5. Vasodilators
3.6. Lipid-Modifying Agents
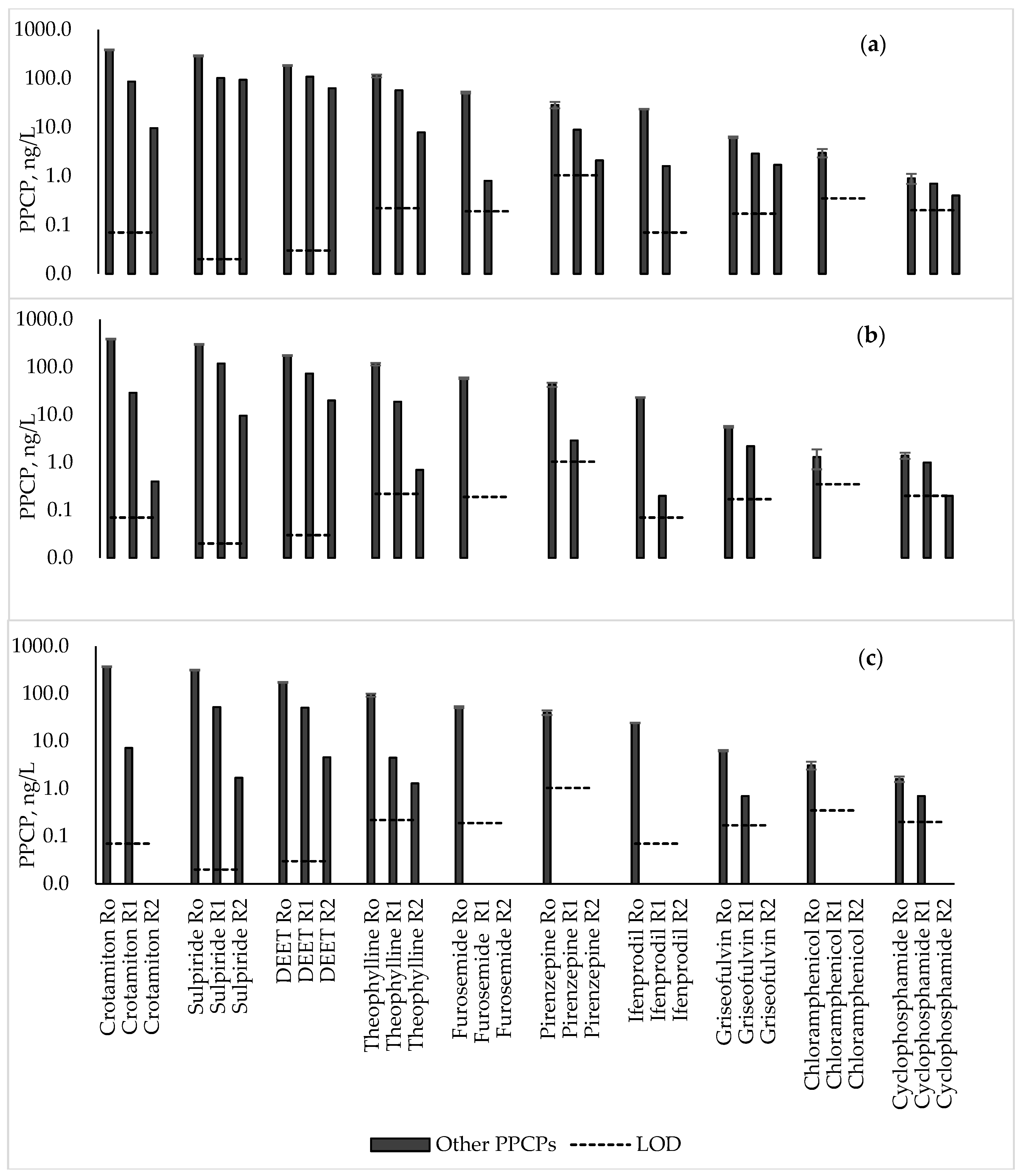
3.7. Other PPCPs
3.8. Relative Degradability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suárez, S.; Carballa, M.; Omil, F.; Lema, J.M. How are pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) removed from Urban Wastewaters? Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs). 2011. Available online: http//epa.gov/ppcp (accessed on 26 May 2016).
- Westerhoff, P.; Yoon, Y.; Snyder, S.; Wert, E. Fate of endocrine-disruptor, pharmaceutical, and personal care product chemicals during simulated drinking water treatment processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6649–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, C.G.; Ternes, T.A. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: Agents of subtle change? Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickenson, E.R.V.; Snyder, S.A.; Sedlak, D.L.; Drewes, J.E. Indicator compounds for assessment of wastewater effluent contributions to flow and water quality. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1199–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhang, K.; Cui, J.; Peng, X. Occurrence and behavior of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and lipid regulators in wastewater and urban river water of the Pearl River Delta, South China. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Banks, E.; Grover, D.; Jiang, J.Q. Pharmaceutical residues in wastewater treatment works effluents and their impact on receiving river water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Nors Nielsen, S.; Lanzky, P.F.; Ingerslev, F.; Holten Lützhøft, H.C.; Jørgensen, S.E. Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—A review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 357–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.M.; Canonica, S.; Park, G.Y.; von Gunten, U. Oxidation of pharmaceuticals during ozonation and advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Hernando, M.D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of pharmaceutical residues in environmental samples: A review. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1067, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Q.; Huang, J.; Lu, S.; Deng, S.; Wang, B.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, G. Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products by sequential ultraviolet and ozonation process in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenović, J.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Fate and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and sewage sludge of the conventional activated sludge (CAS) and advanced membrane bioreactor (MBR) treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosal, R.; Rodríguez, A.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Petre, A.; García-Calvo, E.; Gómez, M.J.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Occurrence of emerging pollutants in urban wastewater and their removal through biological treatment followed by ozonation. Water Res. 2010, 44, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternes, T.A.; Stüber, J.; Herrmann, N.; McDowell, D.; Ried, A.; Kampmann, M.; Teiser, B. Ozonation: A tool for removal of pharmaceuticals, contrast media and musk fragrances from wastewater? Water Res. 2003, 37, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollender, J.; Zimmermann, S.G.; Koepke, S.; Krauss, M.; McArdell, C.S.; Ort, C.; Singer, H.; von Gunten, U.; Siegrist, H. Elimination of organic micropollutants in a municipal wastewater treatment plant upgraded with a full-scale post-ozonation followed by sand filtration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7862–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.C.; Boxall, A.B.A. Occurrence and fate of human pharmaceuticals in the environment. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 202, 53–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snyder, S.A.; Wert, E.C.; Rexing, D.J.; Zegers, R.; Drury, D.D. Ozone oxidation of endocrine disruptors and pharmaceuticals in surface water and wastewater. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2006, 28, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.B.; Keefe, S.H.; Kolpin, D.W.; Schnoebelen, D.J.; Flynn, J.L.; Brown, G.K.; Furlong, E.T.; Glassmeyer, S.T.; Gray, J.L.; Meyer, M.T.; et al. Lagrangian Sampling of Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent in Boulder Creek, Colorado, and Fourmile Creek, Iowa, during the Summer of 2003 and Spring of 2005—Hydrological and Chemical Data; Open-File Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011; pp. 1054–1084.
- Radjenovic, J.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Analysis of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and removal using a membrane bioreactor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Flowers, R.C.; Weinberg, H.S.; Singer, P.C. Ocurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in an advanced wastewater reclamation plant. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5218–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.M.; Korhone, S.; Ternes, T.A.; von Gunten, U. Oxidation of pharmaceuticals during water treatment with chlorine dioxide. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3607–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lester, Y.; Avisar, D.; Gozlan, I.; Mamane, H. Removal of pharmaceuticals using combination of UV/H2O2/O3 advanced oxidation process. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarchem Environmental Systems. Chemistry of advanced oxidation. In The UV/Oxidation Handbook; Solarchem Environmental Systems: Markham, ON, Canada; Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1994; Chapter 2; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Epold, I.; Dulova, N.; Veressinina, V.; Trapido, M. Application of ozonation, UV photolysis, fenton treatment and other related processes for degradation of ibuprofen and sulfamethoxazole in different aqueous matrices. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2012, 15, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavarioti, M.; Mantzavinos, D.; Kassinos, D. Removal of residual pharmaceuticals from aqueous systems by advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 402–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Meisenheimer, M.; McDowell, D.; Sacher, F.; Brauch, H.J.; Gulden, B.H.; Preuss, G.; Wilme, U.; Seibert, N.Z. Removal of pharmaceuticals during drinking water treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3855–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiener, C.; Frimmel, F.H. Oxidative treatment of pharmaceuticals in water. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1881–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esplugas, S.; Bila, D.M.; Krause, L.G.T.; Dezotti, M. Ozonation and advanced oxidation technologies to remove endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in water effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoma, T.; Umamaheshwar, S.K.; Mumper, A. Removal of sulfadiazine, sulfamethizole, sulfamethoxazole, and sulfathiazole from aqueous solution by ozonation. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paucar, N.E.; Kim, I.; Tanaka, H.; Sato, C. Ozone treatment process for the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Yamashita, N.; Park, C.; Shimono, T.; Takeuchi, D.M.; Tanaka, H. Removal characteristics of pharmaceuticals and personal care products: Comparison between membrane bioreactor and various biological treatment processes. Chemosphere 2017, 179, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijnen, W.A.M.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Medema, G.J. Inactivation credit of UV radiation for viruses, bacteria and protozoan (00) Cysts in water: A review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water and Wastewater Treatment, 1st ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chiou, C.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Juang, R.S. Influence of operating parameters on photocatalytic degradation of phenol in UV/TiO2 process. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoigne, J.; Bader, H. Role of Hydroxyl radical reactions in ozonation processes in aqueous-solutions. Water Res. 1976, 10, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyton, G.R.; Glaze, W.H. Destruction of pollutants in water with ozone in combination with ultraviolet-radiation. 3. Photolysis of aqueous ozone. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1988, 22, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poyatos, J.M.; Muñio, M.M.; Almecija, M.C.; Torres, J.C.; Hontoria, E.; Osorio, F. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: State of the Art. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 205, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; Baulch, D.L.; Cox, R.A.; Hampson, R.F.; Kerr, J.A.; Rossi, M.J.; Troe, J. Evaluated kinetic and photochemical data for atmospheric chemistry: Supplement VI. IUPAC subcommittee on gas kinetic data evaluation for atmospheric chemistry. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1997, 26, 1329–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šojić, D.; Despotović, V.; Orčić, D.; Szabó, E.; Arany, E.; Armaković, S.; Illé, E.; Gajda-Schrantz, K.; Dombi, A.; Alapi, T.; et al. Degradation of thiamethoxam and metoprolol by UV, O3 and UV/O3 hybrid processes: Kinetics, degradation intermediates and toxicity. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehelin, J.; Hoigné, J. Decomposition of ozone in water in the presence of organic solutes acting as promoters and inhibitors of radical chain reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1985, 19, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmehmet, B.I.; Ötker, M. Pre-treatment of antibiotic formulation wastewater by O3, O3/H2O2 and O3/UV processes. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2004, 28, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, Y.; Wang, W.; Shen, Y.S. Reaction Behaviors of Decomposition of Monocrotophos in Aqueous Solution by UV and UV/O3 Processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 72, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallas, J.; Munter, R. Post treatment of pulp and paper industry wastewaters using oxidation and adsorption processes. Water. Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Ozone Treatment of Municipal Wastewater Effluent for Oxidation of Emerging Contaminants and Disinfection. Master’s Thesis, University of Windsor, Windsor, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transportation, and Tourism. The Study on Endocrine Disruptors in Sewerage; Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transportation, and Tourism: Tokyo, Japan, 2001.
- Tainaka, T. The sewerage system in the Lake Biwa Basin. In Proceedings of the TAAL 2007: The 12th World Lake Conference, Jaipur, India, 28 October–2 November 2007; pp. 1417–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.H.; Yamashita, N.; Kato, Y.; Tanaka, H. Discussion on the application of UV/H2O2, O3 and O3/UV processes as technologies for sewage reuse considering the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, C.; Kim, I.; Tanaka, H. Effect of H2O2 on UV photo-oxidation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, H.; Hoigne, J. Determination of ozone in water by the indigo method. Water Res. 1981, 15, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, D.T.C.; Thi, K.Q.V.; Thanh, T.N.; Xuan, T.B. Performance of Ozonation process as advanced treatment for antibiotics removal in membrane permeate. Geosci. Eng. 2016, 62, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.O.; Howe, K.J.; Thomson, B.M. Ozone and biofiltration as an alternative to reverse osmosis for removing PPCPs and micropollutants from treated wastewater. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaar, H.; Clara, M.; Gans, O.; Kreuzinger, N. Micropollutant removal during biological wastewater treatment and a subsequent ozonation step. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickenson, E.R.V.; Drewes, J.E.; Sedlak, D.L.; Wert, E.C.; Snyder, S.A. Applying surrogates and indicators to asses removal efficiency of trace organic chemicals during chemical oxidation of wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6242–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, R.R.; Ozaki, H.; Ota, S.; Takanami, R.; Taniguchi, S. Degradation of common pharmaceuticals and personal care products in mixed solutions by advanced oxidation techniques. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, R.; Raffaele, M.; Nicklas, P. Pharmaceuticals in STP effluents and their solar photodegradation in aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, C.; Lajeunesse, A.; Cejka, P.; Gagne, F.; Hausler, R. Degradation of selected acidic and neutral pharmaceutical products in a primary treated wastewater by disinfection processes. Ozone Sic. Eng. 2008, 30, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reungoat, J.; Macova, M.; Escher, B.I.; Carswell, S.; Mueller, J.F.; Keller, J. Removal of micropollutants and reduction of biological activity in a full scale reclamation plant using ozonation and activated carbon filtration. Water Res. 2010, 44, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, N.; Shinohara, H.; Murata, A.; Kiri, K.; Managaki, S.; Sato, N.; Takada, H. Removal of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) during sand filtration and ozonation at a municipal sewage treatment plant. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4373–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, K.; Jodeiri Naghashkar, N.; Gamal El-Din, M. Degradation of aqueous pharmaceuticals by ozonation and advanced oxidation processes: A review. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2006, 2, 353–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Run | Injected O3 Concentration (mg L−1) | O3 Dose per UV Reactor (mg L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 HRT (R1) = 5 min | R2 HRT (R1 + R2) = 10 min | ||
| 1 | 14 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 28 | 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 42 | 3 | 6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paucar, N.E.; Kim, I.; Tanaka, H.; Sato, C. Effect of O3 Dose on the O3/UV Treatment Process for the Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Secondary Effluent. ChemEngineering 2019, 3, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3020053
Paucar NE, Kim I, Tanaka H, Sato C. Effect of O3 Dose on the O3/UV Treatment Process for the Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Secondary Effluent. ChemEngineering. 2019; 3(2):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3020053
Chicago/Turabian StylePaucar, N. Evelin, IIho Kim, Hiroaki Tanaka, and Chikashi Sato. 2019. "Effect of O3 Dose on the O3/UV Treatment Process for the Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Secondary Effluent" ChemEngineering 3, no. 2: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3020053
APA StylePaucar, N. E., Kim, I., Tanaka, H., & Sato, C. (2019). Effect of O3 Dose on the O3/UV Treatment Process for the Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Secondary Effluent. ChemEngineering, 3(2), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3020053






