An Arsenic Removal Technology and Its Application in Arsenic-Containing Copper
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current Status of ACC Minerals
2.1. Depletion of Cu Minerals
2.2. Hazards of ACC Minerals
3. Technical Process of As Removal in ACC Minerals
4. Pyrometallurgy
4.1. Reduction Pyrometallurgy
4.2. Oxidation Pyrometallurgy
4.3. Sulfate/Carbonate Roasting
5. Hydrometallurgy
5.1. Alkali Leaching
5.2. Acid Leaching
6. Biometallurgy
7. Industrial Arsenic Removal
7.1. EI Indio
7.2. CMI NESA Process
7.3. Ministro Hales
7.4. Others
8. Precipitation of Arsenic
8.1. Ferrihydrate Precipitation
8.2. Ferric Precipitation
9. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ybarra, I.; Gupta, G.V. Using a wafer backside spin process to eliminate contamination in copper applications. Micro-Santa Monica 2000, 18, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zuo, L.-s.; Hu, P.J.; Yao, H.L.; Zhu, H. Evaluation and simulation analysis of China’s copper security evolution trajectory. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.M.; Hammarstrom, J.M.; Zientek, M.L.; Dicken, C.L. Estimate of undiscovered copper resources of the world, 2013. In Center for Integrated Data Analytics Wisconsin Science Center; Fact Sheet; US Geological Survey: Reston, VI, USA, 2014; pp. 2014–3004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Z.; Lu, M.; Gu, F.; Liu, J.; Jiang, T. Recycling the domestic copper scrap to address the China’s copper sustainability. Munich Pers. RePEc Arch. 2020, 9, 2846–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausser, G.; Stuermer, M. A Dynamic Analysis of Collusive Action: The Case of the World Copper Market; IDEAS: Bloomington, MN, USA, 2020; pp. 1882–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Seck, G.S.; Hache, E.; Bonnet, C.; Simoën, M.; Carcanague, S. Copper at the crossroads: Assessment of the interactions between low-carbon energy transition and supply limitations. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 105072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villena, M.; Greve, F. On resource depletion and productivity: The case of the Chilean copper industry. Resour. Policy 2018, 59, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.Q.; Liu, G.Q.; Guo, S.X.; Mine, C.C.; Corporation, J.C. The Research on the Index Regulation of Copper Concentrate in Chengmenshan Copper Mine. Copp. Eng. 2017, 6, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Qing-Jun, H.U. Mining Loss and Depletion Management Practice in Fenghuangshan Copper Mine. World Nonferrous Met. 2019, 7, 201–202. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Xiao, K.Y.; Lou, D.B.; Ding, J.H.; Yin, J.N.; Xiang, J. On present situation and potential analysis of copper resources in China. J. Geol. 2013, 37, 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, R. Study of China’s current copper slag on the use of resources. Min. Metall. 2008, 17, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.T.; Qin, K.Z. Types, Metallogenic Environments and Characteristics of Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Copper Deposits in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 1989, 2, 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Cui, J.; Hu, S.; Huang, Y.; Jing, C. Arsenic Removal and Recovery from Copper Smelting Wastewater Using TiO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9094–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, M.; Mehrzad, J.; Mahmudy Gharaie, M.H.; Afshari, R.; Dadsetan, A.; Hami, S. High soil and groundwater arsenic levels induce high body arsenic loads, health risk and potential anemia for inhabitants of northeastern Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.W.; He, Y.H. Development and Prospect of Arsenic Removal Technology for Containing Arsenic Copper Minerals. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2023, 57, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soorani, L.Y.; Bafti, B.S.; Homam, S.M.; Abbasloo, Z.; Zanooghi, H.T. Hypogene enrichment in Miduk porphyry copper ore deposit, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1913. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciuttolo, C.; Atencio, E. Past, Present, and Future of Copper Mine Tailings Governance in Chile (1905–2022): A Review in One of the Leading Mining Countries in the World. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 13060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northey, S.; Mohr, S.; Mudd, G.M.; Weng, Z.; Giurco, D. Modelling future copper ore grade decline based on a detailed assessment of copper resources and mining. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, G.; Mudd, G.; Valero, A.; Valero, A. Decreasing ore grades in global metallic mining: A theoretical issue or a global reality? Resources 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schodde, R. The key drivers behind resource growth: An analysis of the copper industry over the last 100 years. In Proceedings of the MEMS Conference Mineral and Metal Markets over the Long Term, Joint Program with the SME Annual Meeting, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 28 February–3 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.K.; Bruckard, W.J. The separation of arsenic from copper in a Northparkes copper–gold ore using controlled-potential flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 84, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Tong, X.; Zhou, Q.H. Flotation Test of Some Sulphide Copper Ore Containing High Arsenic. Express Inf. Min. Ind. 2007, 10, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, M.; Rachamalla, M.; Niyogi, S.; Datusalia, A.K.; Flora, S.J.S. Molecular Mechanism of Arsenic-Induced Neurotoxicity including Neuronal Dysfunctions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradham, K.D.; Diamond, G.L.; Burgess, M.; Juhasz, A.; Klotzbach, J.M.; Maddaloni, M.; Nelson, C.; Scheckel, K.; Serda, S.M.; Stifelman, M.; et al. In vivo and in vitro methods for evaluating soil arsenic bioavailability: Relevant to human health risk assessment. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2018, 21, 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Speer, R.M.; Volk, L.; Hudson, L.G.; Liu, K.J. Arsenic co-carcinogenesis: Inhibition of DNA repair and interaction with zinc finger proteins. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 76, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barral-Fraga, L.; Barral, M.T.; Macneill, K.L.; Martiá-Prieto, D.; Morin, S.; Rodríguez-Castro, M.C.; Tuulaikhuu, B.A.; Guasch, H. Biotic and Abiotic Factors Influencing Arsenic Biogeochemistry and Toxicity in Fluvial Ecosystems: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Xue, X.M.; Kappler, A.; Rosen, B.P.; Meharg, A.A. Linking Genes to Microbial Biogeochemical Cycling: Lessons from Arsenic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7326–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcgrory, E.; Henry, T.; Conroy, P.; Morrison, L. Occurrence, Geochemistry and Speciation of Elevated Arsenic Concentrations in a Fractured Bedrock Aquifer System. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 414–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.P. Harm of Arsenic Pollution and Its Treated Technology. Environ. Prot. Xinjiang 1999, 21, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, Y.; Yang, W. Arsenic Pollution Status and Repair Technology: An Overview; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 300, p. 032094. [Google Scholar]
- Lombard, M.A.; Bryan, M.S.; Jones, D.K.; Bulka, C.; Bradley, P.M.; Backer, L.C.; Focazio, M.J.; Silverman, D.T.; Toccalino, P.; Argos, M. Machine Learning Models of Arsenic in Private Wells Throughout the Conterminous United States As a Tool for Exposure Assessment in Human Health Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5012–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Seto, E.; Eskenazi, B.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Hua, J. A Comprehensive Review of Arsenic Exposure and Risk from Rice and a Risk Assessment among a Cohort of Adolescents in Kunming, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alka, S.; Shahir, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Ndejiko, M.J.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Abd Manan, F. Arsenic removal technologies and future trends: A mini review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckard, W.J.; Davey, K.J.; Jorgensen, F.R.A.; Wright, S.; Brew, D.R.M.; Haque, N.; Vance, E.R. Development and evaluation of an early removal process for the beneficiation of arsenic-bearing copper ores. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devia, M.; Wilkomirsky, I.; Parra, R. Roasting kinetics of high-arsenic copper concentrates: A review. Min. Metall. Explor. 2012, 29, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Peng, Y.; Bradshaw, D. A review of copper-arsenic mineral removal from copper concentrates. Miner. Eng. 2012, 36, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarzadeh, M.S.; Miller, J.D. The pyrometallurgy of enargite: A literature update. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 157, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, A.; Takasaki, Y.; William, T.; Yamatodani, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Sunagawa, S.; Ono, E. Treatment of smelting residue for arsenic removal and recovery of copper using pyro–hydrometallurgical process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.C.; Liu, Q.J.; Liang, Y.Q.; Jiang, X.; Ji, H.C. Optimization Arsenic Removal from Copper Concentrate through Alkali Leaching Based on Response Surface. Nonferrous Met. Eng. 2019, 9, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.H.; Paredes, E. How St. Joe Gold’s El Indio mine has become a major producer of high quality crude arsenic trioxide. Arsen. Metall. Fundam. Appl. 1988, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Secco, A.C.; Riveros, G.A.; Luraschi, A.A. Thermal decomposition of enargite and phase relations in the system copper-arsenic-sulfur. At Copper 1987, 87, 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, R.; Fan, Y.; Wilkomirsky, I. Thermal Decomposition of Enargite. Canad. Metallurgic. Quart. 2001, 40, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindkvist, G.; Holmström, Ǻ. Roasting of complex concentrates with high arsenic content. Metall. Soc. 1983, 2, 451–472. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.Z.; Smith, R.W. Arsenic removal from high arsenic bearing gold sulphide concentrate. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2004, 113, 189–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkomirsky, I.; Parra, R.; Parada, F.; Balladares, E. Mineralochemichal characterization of calcines and flue dusts during neutral roasting of arsenic copper concentrates in the pilot plant of University of Concepcion. In Proceedings of the Conference of Metallurgists (COM 2014), Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 28 September–1 October 2014; p. 8643. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkomirsky, I. Dynamic simulation of processing high-arsenic copper concentrates in a fluidized bed roaster. In Proceedings of the SME Annual Meeting/Exhibit, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 27 February–2 March 2014; pp. 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura, Z. The Fundamental Investigation of Dearsenising Roasting of Copper Concentrates and its Industrial Practices. J. MMIJ 1962, 78, 447–453. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, R.; Aracena, A.; Ruiz, M.C. In Decomposition/volatilization of enargite in nitrogen-oxygen atmosphere. In Proceedings of the TMS 2010-139th Annual Meeting and Exhibition, Seattle, WD, USA, 14–18 February 2010; pp. 497–504. [Google Scholar]
- Adham, K.; Harris, C.T. In two-stage fluid bed reactor for arsenic removal and fixation. In Proceedings of the COM 2014—Conference of Metallurgists, Conference of Metallurgists, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 28 September–1 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhen, C. Thermodynamics Evaluation and Verification of High-Sulfur Copper Slag Composite Agglomerate in Oxidation-Roasting-Separation-Leaching Process. Materials 2023, 16, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, B.; Pickles, C.A.; Peacey, J.G. 2012. Thermodynamic analysis of the sulfation roasting of enargite concentrates. High Temp. Mater 2012, 31, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, T.A.R. Arsenic removal from enargite with sodium carbonate using complete and partial oxidized roasting. In Dissertations & Theses Gradworks; Colorado School of Mines: Golden, CO, USA, 2013; p. 3595462. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, J.; Han, H.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y.; Wang, T.Y.L.; Yang, Y.; Cao, X.; Tang, H. Arsenic removal from arsenic-containing copper and cobalt slag using alkaline leaching technology and MgNH4 AsO4 precipitation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, L.; Li, L. Removal of arsenic from arsenate complex contained in secondary zinc oxide. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.J.; Lin, B.Q.; Wang, Y.G. Study on arsenic removal from high arsenic copper ore by sodium sulfide sodium hydroxide leaching. Nonferrous Metal. 1983, 4, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Grandon, L.; Padilla, R. Selective arsenic removal from enargite by alkaline digestion and water leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 150, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongamp, W.; Takasaki, Y.; Shibayama, A. Arsenic removal from copper ores and concentrates through alkaline leaching in NaHS media. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Qiu, G.Z.; Xu, J. Thermodynamic analysis of FeAsS, FeS2, Au in NaClO-NaOH solution and one step leaching of gold. Nonferrous Metal 1998, 50, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Viñals, J.; Roca, A.; Hernández, M.C.; Benavente, O. Topochemical transformation of enargite into copper oxide by hypochlorite leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 68, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, J.; Liu, W.; Jiao, F.; Wang, H.; Qin, W. Separation of arsenic from lead smelter ash by acid leaching combined with pressure oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 273, 118988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, G.W. Study on the Removal of Arsenic in Pyrite Cinder by Acid Leaching. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 781–784, 2114–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.F.; Du, A.L. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Diagram of Oxygen-Chlorine-Titanium System. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 233–235, 2068–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M. An Investigation into the Leaching of Enargite Under Atmospheric Conditions; Queen’s University: Belfast, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Vasquez, B.F.; Dixon, D. Rapid atmospheric leaching of enargite in acidic ferric sulfate media. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 152, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarlagadda, S.; Gude, V.G.; Camacho, L.M.; Pinappu, S.; Deng, S. Potable water recovery from As, U, and F contaminated ground waters by direct contact membrane distillation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, P.; Manna, A.K. Removal of arsenic from contaminated groundwater by solar-driven membrane distillation using three different commercial membranes. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5750–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaiah, P.; Guerra, E.; Choi, Y.; Ye, Z. Pressure oxidation leaching of an enargite concentrate in the presence of polytetrafluoroethylene beads. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 157, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.S.; Qin, W.Q.; Yang, C.R.; Zhang, Y.S. Study on Bacterial Leaching of High Arsenic-bearing Primary Copper Sulfide Ore. Min. Metall. Eng. 2011, 31, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.F.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, A.X. Experimental Study on Bioleaching of Copper Sulfide Tailings under Alkaline Conditions. Min. Metall. Eng. 2011, 31, 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, G.A.; Risopatron, C.; Pease, J. Processing of Complex Materials in the Copper Industry: Challenges and Opportunities Ahead. Jom 2020, 72, 3447–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
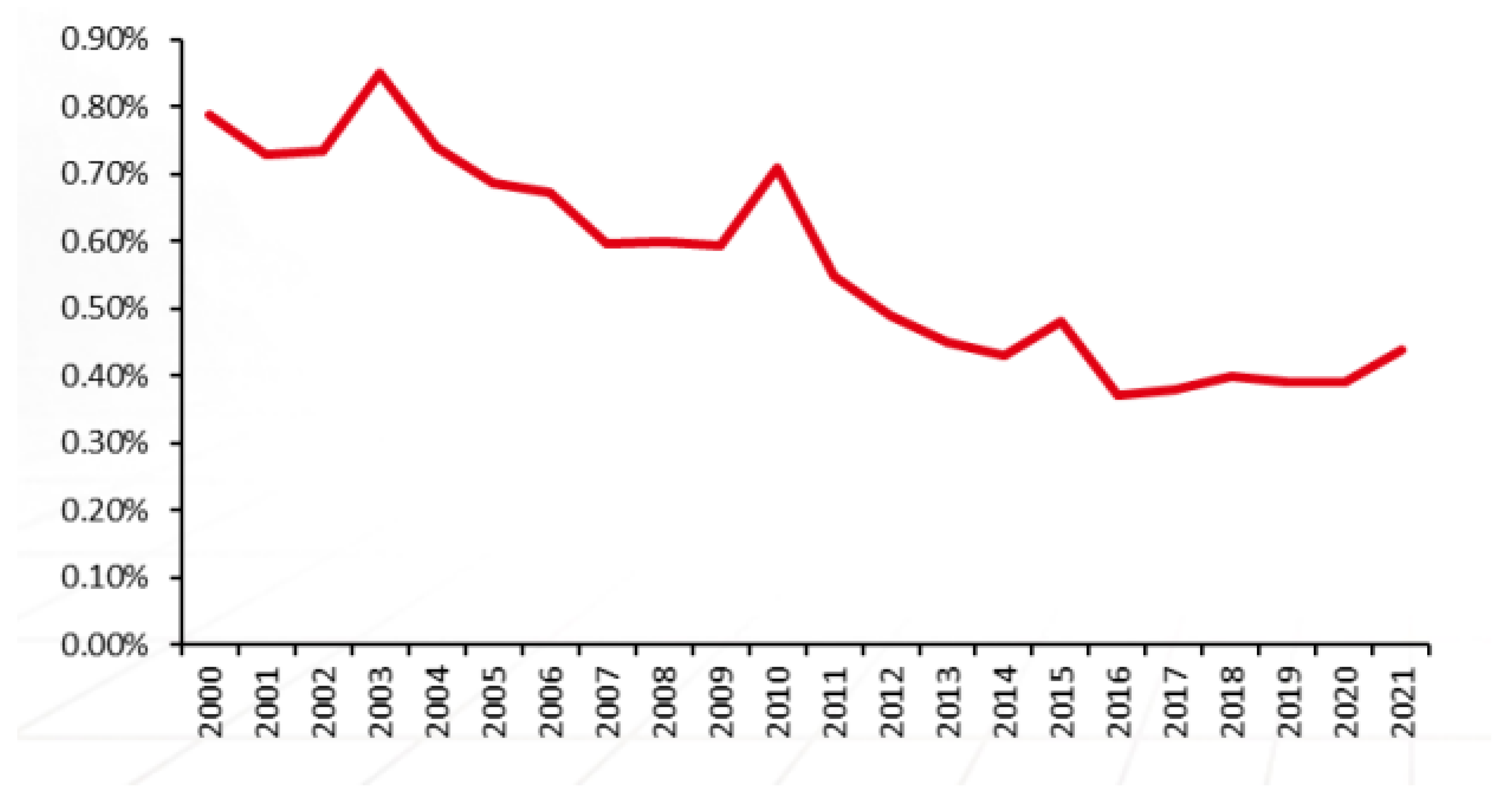
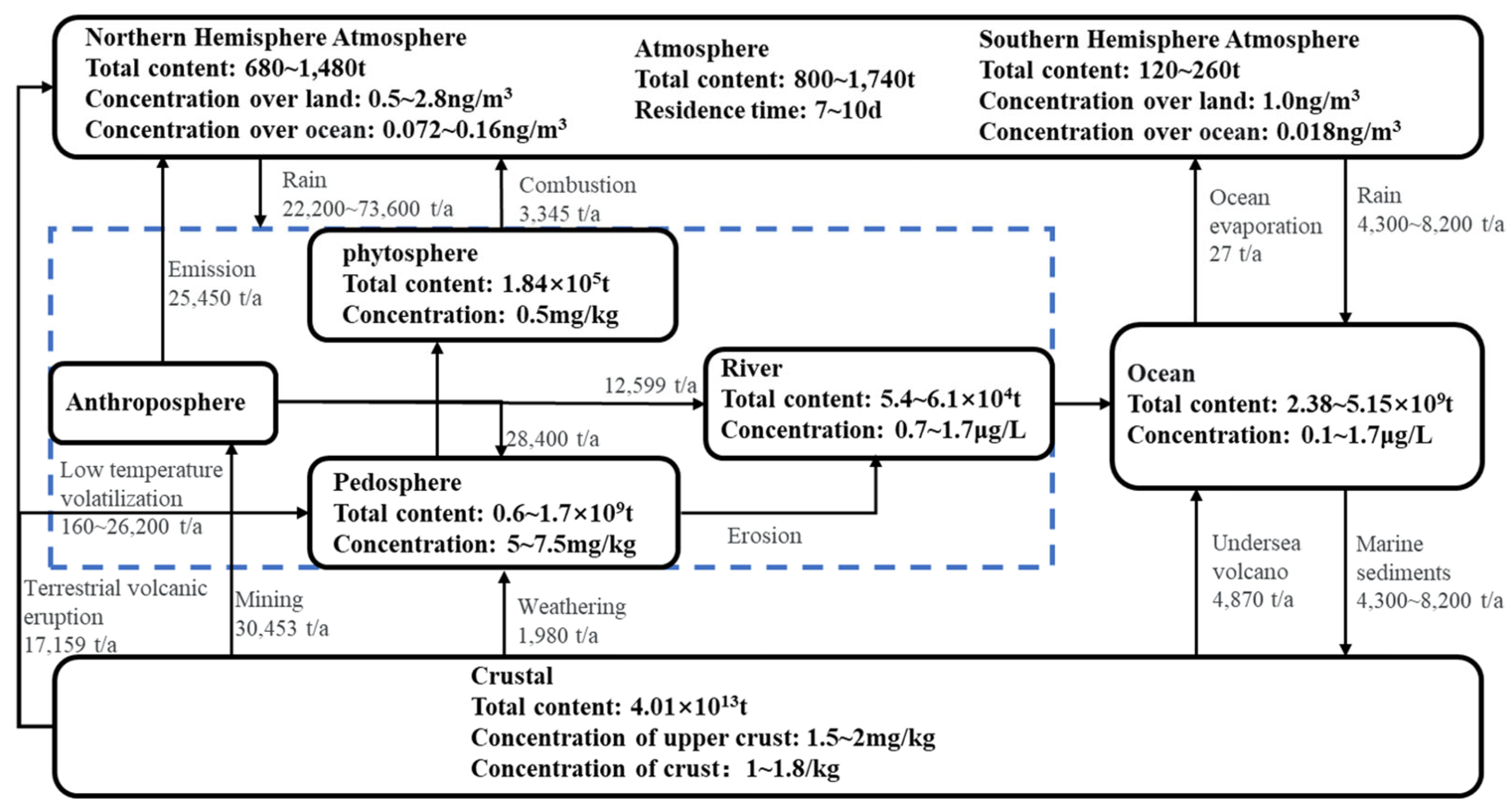


| Country or Locality | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | Production | 36,500 | 37,000 | 37,000 | 33,400 | 32,300 | 60,000 | 59,000 |
| China | Import | 4.03 | 0.45 | 3.15 | 16.98 | 3.31 | 35.68 | 21.1 |
| Export | 2345 | 2672 | 3555 | 2275 | 2008 | 1966 | 2601 | |
| U.S.A | Import | 5920 | 5320 | 5980 | 5540 | 7090 | 7780 | 6000 |
| Export | 1670 | 1760 | 698 | 107 | 56 | 29 | 40 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; He, Y. An Arsenic Removal Technology and Its Application in Arsenic-Containing Copper. ChemEngineering 2024, 8, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8030056
Tang X, He Y. An Arsenic Removal Technology and Its Application in Arsenic-Containing Copper. ChemEngineering. 2024; 8(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xiaowei, and Yuehui He. 2024. "An Arsenic Removal Technology and Its Application in Arsenic-Containing Copper" ChemEngineering 8, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8030056
APA StyleTang, X., & He, Y. (2024). An Arsenic Removal Technology and Its Application in Arsenic-Containing Copper. ChemEngineering, 8(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8030056






