Predictive Modeling and Analysis of Cu–Be Alloys: Insights into Material Properties and Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
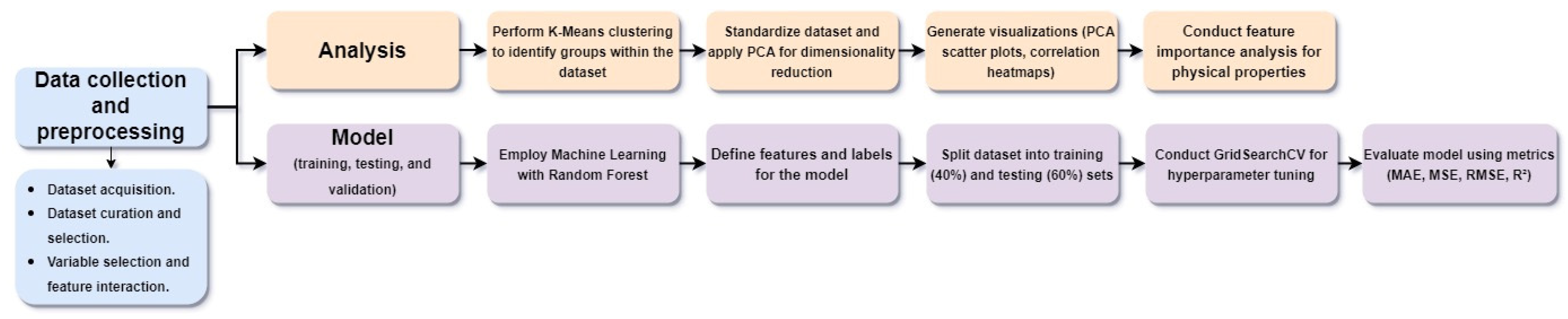
2.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.2. Model Training, Testing, and Validation
2.3. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance and Validation
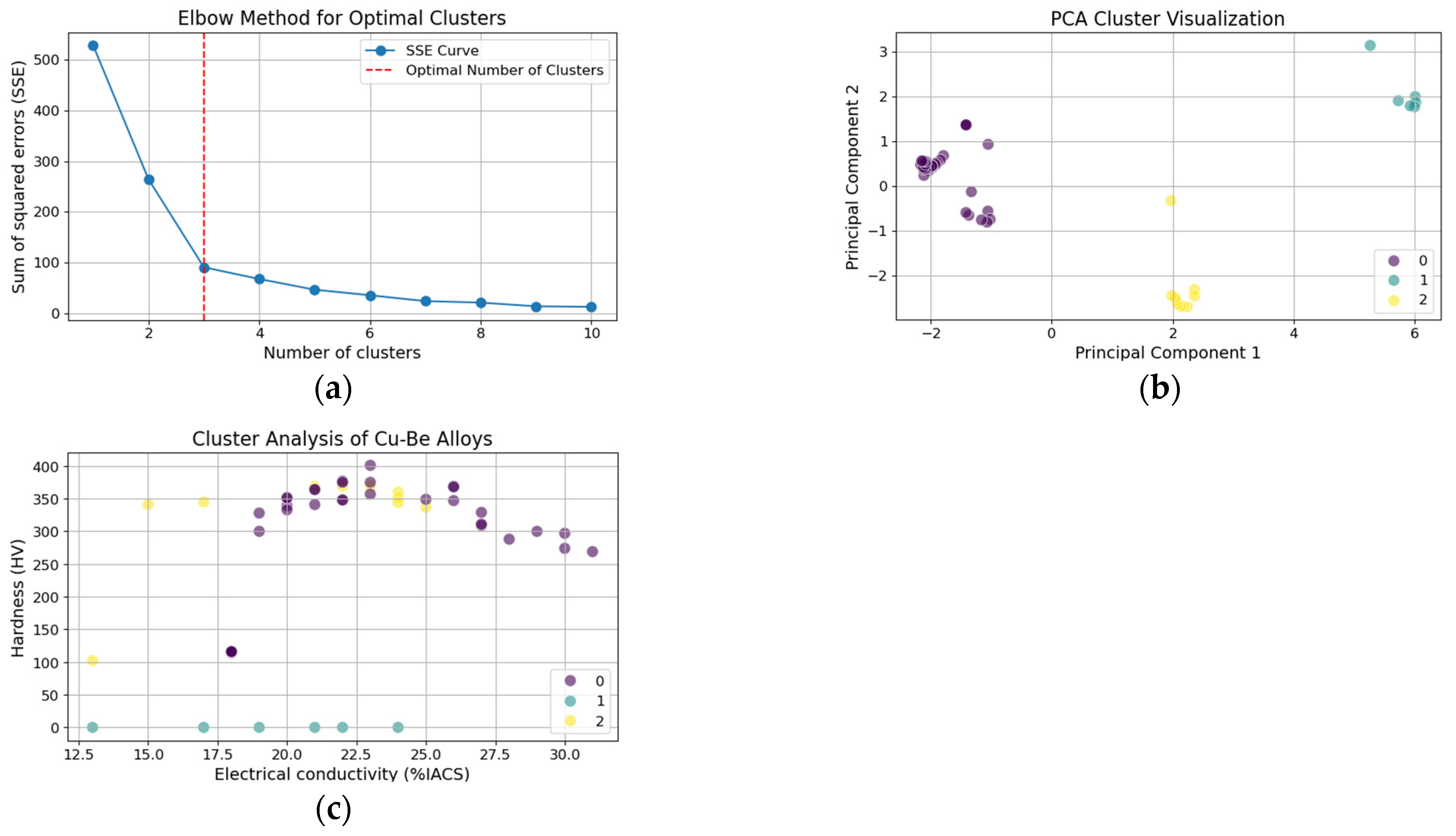
3.2. Cluster Analysis and Principal Component Insights
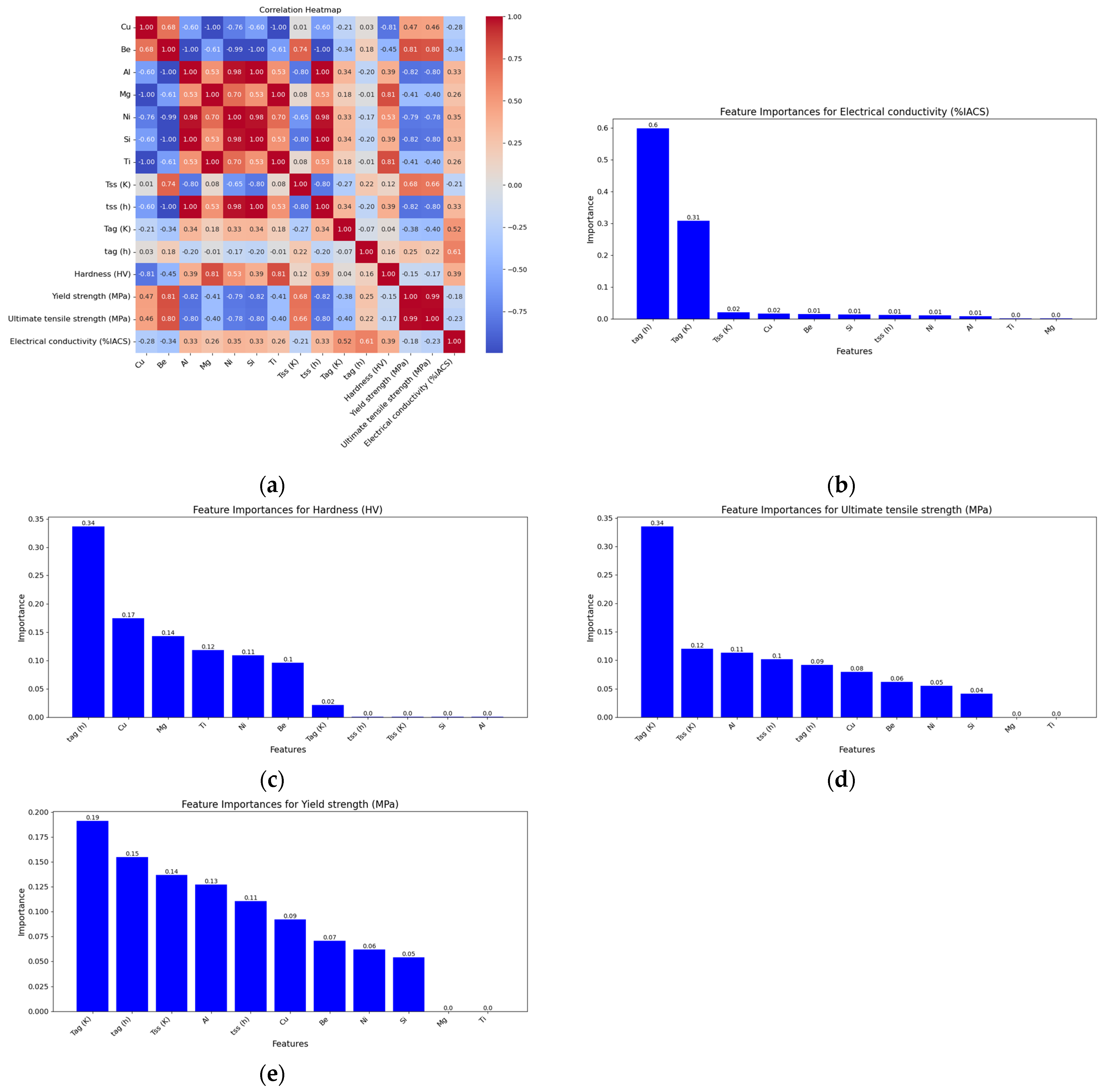
3.3. Feature Importance and Inter-Feature Relationships
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morshed-Behbahani, K.; Aliyu, A.; Bishop, D.P.; Nasiri, A. Additive Manufacturing of Copper-Based Alloys for High-Temperature Aerospace Applications: A Review. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 108395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.Q.; Wei, K.X.; Wei, W.; Alexandrov, I.V.; An, X.L.; Wang, D.D.; Liu, X.K. Simultaneously Enhancing Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Cu-0.5%Cr Alloy as 5G Connector Material. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 948, 169750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. A Review on Copper Alloys with High Strength and High Electrical Conductivity. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 990, 174456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, I.; de Prado, J.; Rosero-Romo, J.J.; Sánchez, M.; Salazar, D.; Ureña, A. Exploration and Optimization of Copper-Based Alloys Incorporating Amorphizing Elements for Heat Transfer Applications. Mater. Charact. 2024, 208, 113675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Yue, L. Precipitation Behavior, Microstructure and Properties of Aged Cu-1.7 Wt% Be Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoliang, X.; Qiangsong, W.; Xujun, M.; Baiqing, X.; Lijun, P. The Precipitation Behavior and Strengthening of a Cu–2.0wt% Be Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Fu, H.; Shao, L.; Hao, Z. The Influence of Precipitation Transformation on Young’s Modulus and Strengthening Mechanism of a Cu–Be Binary Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Lei, C.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, H.; Ling, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H. Predicting the Property Contour-Map and Optimum Composition of Cu-Co-Si Alloys via Machine Learning. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 30, 103138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.-H.; Yin, H.-Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.-F.; Xu, B.; Yang, G.-Q.; Zhang, T.; Wu, M.; Qu, X.-H. Machine-Learning-Assisted Prediction of the Mechanical Properties of Cu-Al Alloy. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, D.; Jain, A.; Glensk, A.; Curtin, W.A. Machine Learning for Metallurgy I. A Neural-Network Potential for Al-Cu. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2020, 4, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fu, H.; Jiang, L.; Xue, D.; Xie, J. A Property-Oriented Design Strategy for High Performance Copper Alloys via Machine Learning. Npj Comput. Mater. 2019, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, M. A Novel Approach to Predict the Effect of Chemical Composition and Thermo-Mechanical Processing Parameters on Cu–Ni–Si Alloys Using a Hybrid Deep Learning and Ensemble Learning Model. Compos. Commun. 2024, 48, 101903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, D.N.; Miller, C.; Mier, R.; Osborn, C.; Thomas, S.M.; Tegtmeier, E.L.; Winter, W.P.; Carpenter, J.S.; Hunter, A. Predicting Electrical Conductivity in Cu/Nb Composites: A Combined Model-Experiment Study. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 132, 045105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Han, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Accelerated Discovery of High-Performance Cu-Ni-Co-Si Alloys through Machine Learning. Mater. Des. 2021, 209, 109929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsse, S.; Gouné, M.; Lin, W.-C.; Girard, L. Dataset of Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Copper-Based Alloys. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsse, S.; Gouné, M.; Lin, W.-C.; Girard, L. Dataset of mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of copper-based alloys. Figshare, 2023; collection. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C. Alloying Element Distributions of Precipitates in Cu–Cr Alloys Aided by Machine Learning. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, M. COF-RF-Tool: A Python Software for Predicting the Coefficient of Friction of Open-Cell AlSi10Mg-SiC Composites Using Random Forest Model. Softw. Impacts 2023, 17, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, C.; Casavola, C.; Pappalettera, G.; Paramsamy Kannan, V. Laplacian Score and K-Means Data Clustering for Damage Characterization of Adhesively Bonded CFRP Composites by Means of Acoustic Emission Technique. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 185, 108425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanasopoulos, N.; Singh, A.; Hadjidoukas, P. Machine Learning-Based Modelling, Feature Importance and Shapley Additive Explanations Analysis of Variable-Stiffness Composite Beam Structures. Structures 2024, 62, 106206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
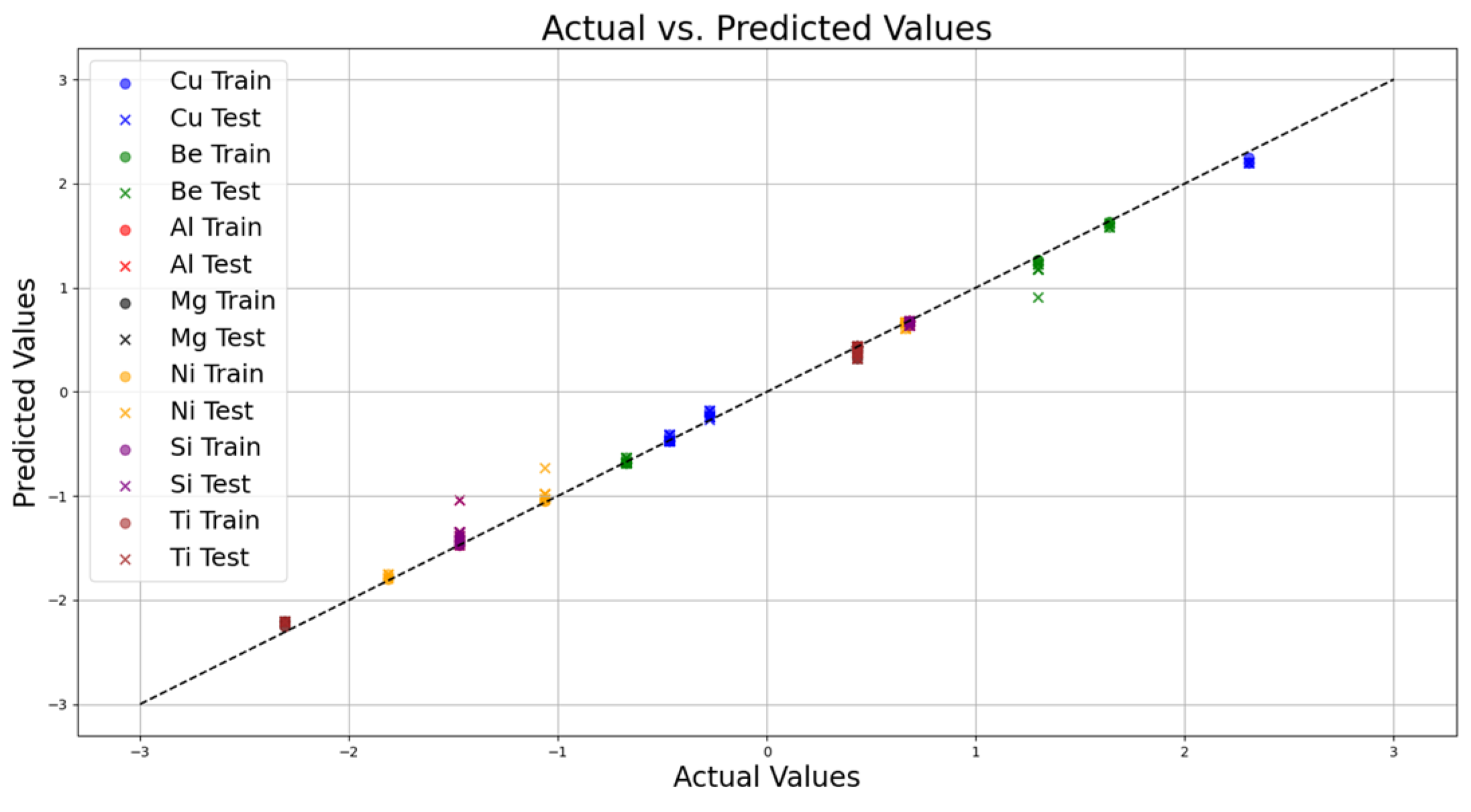
| Metric | Testing Set | Training Set |
|---|---|---|
| MAE | 0.01997 | 0.01591 |
| MSE | 0.00206 | 0.00183 |
| RMSE | 0.04542 | 0.04275 |
| R2 | 0.99375 | 0.99858 |
| Predicted | Actual | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Be | Al | Mg | Ni | Si | Ti | Cu | Be | Al | Mg | Ni | Si | Ti |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 97.80 | 1.99 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 98.00 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 93.03 | 1.93 | 0.01 | 1.96 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 2.94 | 92.95 | 1.95 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 3.00 |
| 92.68 | 1.67 | 0.13 | 1.96 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 2.94 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 93.14 | 1.94 | 0.00 | 1.92 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 2.88 | 92.95 | 1.95 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 3.00 |
| 93.03 | 1.93 | 0.01 | 1.96 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 2.94 | 92.95 | 1.95 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 3.00 |
| 93.03 | 1.93 | 0.01 | 1.96 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 2.94 | 92.95 | 1.95 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.68 | 1.67 | 0.13 | 1.96 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 2.94 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.68 | 1.67 | 0.13 | 1.96 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 2.94 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 97.79 | 1.99 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 98.00 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 93.14 | 1.94 | 0.01 | 1.92 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 2.88 | 92.95 | 1.95 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 97.79 | 1.99 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 98.00 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 92.98 | 1.89 | 0.02 | 1.96 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 2.94 | 92.95 | 1.95 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| 93.03 | 1.93 | 0.01 | 1.96 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 2.94 | 92.95 | 1.95 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 3.00 |
| 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 | 92.57 | 1.66 | 0.13 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 3.00 |
| Composition | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.86534 | 0.48476 |
| Be | 0.95893 | −0.24863 |
| Al | −0.92657 | 0.33246 |
| Mg | −0.81893 | −0.55009 |
| Ni | −0.98749 | 0.13823 |
| Si | −0.92657 | 0.33246 |
| Ti | −0.81893 | −0.55009 |
| Hardness (HV) | −0.64410 | −0.67264 |
| Yield strength (MPa) | 0.79962 | −0.51454 |
| Ultimate tensile strength (MPa) | 0.79339 | −0.50089 |
| Electrical conductivity (%IACS) | −0.39655 | −0.11634 |
| Composition | Cluster 0 | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 92.57 | 98.00 | 92.95 |
| Al | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Be | 1.66 | 2.00 | 1.95 |
| Mg | 2.00 | 0.00 | 2.00 |
| Ni | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.10 |
| Si | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Ti | 3.00 | 0.00 | 3.00 |
| Tss (K) | 1053.00 | 1073.00 | 1193.00 |
| tss (h) | 0.17 | NaN | NaN |
| Tag (K) | 610.50 | 593.00 | 593.00 |
| tag (h) | 4.31 | 5.17 | 7.30 |
| Hardness (HV) | 310.13 | NaN | 328.80 |
| Yield strength (MPa) | 149.16 | 984.50 | 1051.10 |
| Ultimate tensile strength (MPa) | 216.50 | 1185.50 | 1247.10 |
| Electrical conductivity (%IACS) | 23.19 | 19.33 | 20.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolev, M. Predictive Modeling and Analysis of Cu–Be Alloys: Insights into Material Properties and Performance. ChemEngineering 2024, 8, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8040070
Kolev M. Predictive Modeling and Analysis of Cu–Be Alloys: Insights into Material Properties and Performance. ChemEngineering. 2024; 8(4):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8040070
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolev, Mihail. 2024. "Predictive Modeling and Analysis of Cu–Be Alloys: Insights into Material Properties and Performance" ChemEngineering 8, no. 4: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8040070
APA StyleKolev, M. (2024). Predictive Modeling and Analysis of Cu–Be Alloys: Insights into Material Properties and Performance. ChemEngineering, 8(4), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8040070







