Contemporary Long-Term Trends in Water Discharge, Suspended Sediment Load, and Erosion Intensity in River Basins of the North Caucasus Region, SW Russia
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Problem Formulation
1.2. Environmental Challenges for the North Caucasus Region
1.3. The Study’s Purposes
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Objects
2.2. Data and Their Sources
2.2.1. Hydrological Data
2.2.2. Climate Data
2.2.3. Land Use/Cover Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Hydrological Data Processing
2.3.2. Land Use/Cover Data Processing
2.3.3. Statistical Processing
3. Results
3.1. Contemporary Hydrological Changes in the Kalaus River Basin
3.1.1. Long-Term Trends in Water Discharge
3.1.2. Long-Term Trends in Suspended Sediment Load/Concentration
3.2. Contemporary Hydrological Changes in the Basins of Kuma River and the Additionally Studied Rivers of the North Caucasus Region
3.3. General Patterns of Contemporary Trend Changes in Discharge/Load of the North Caucasus Region’s Studied Rivers
4. Discussion
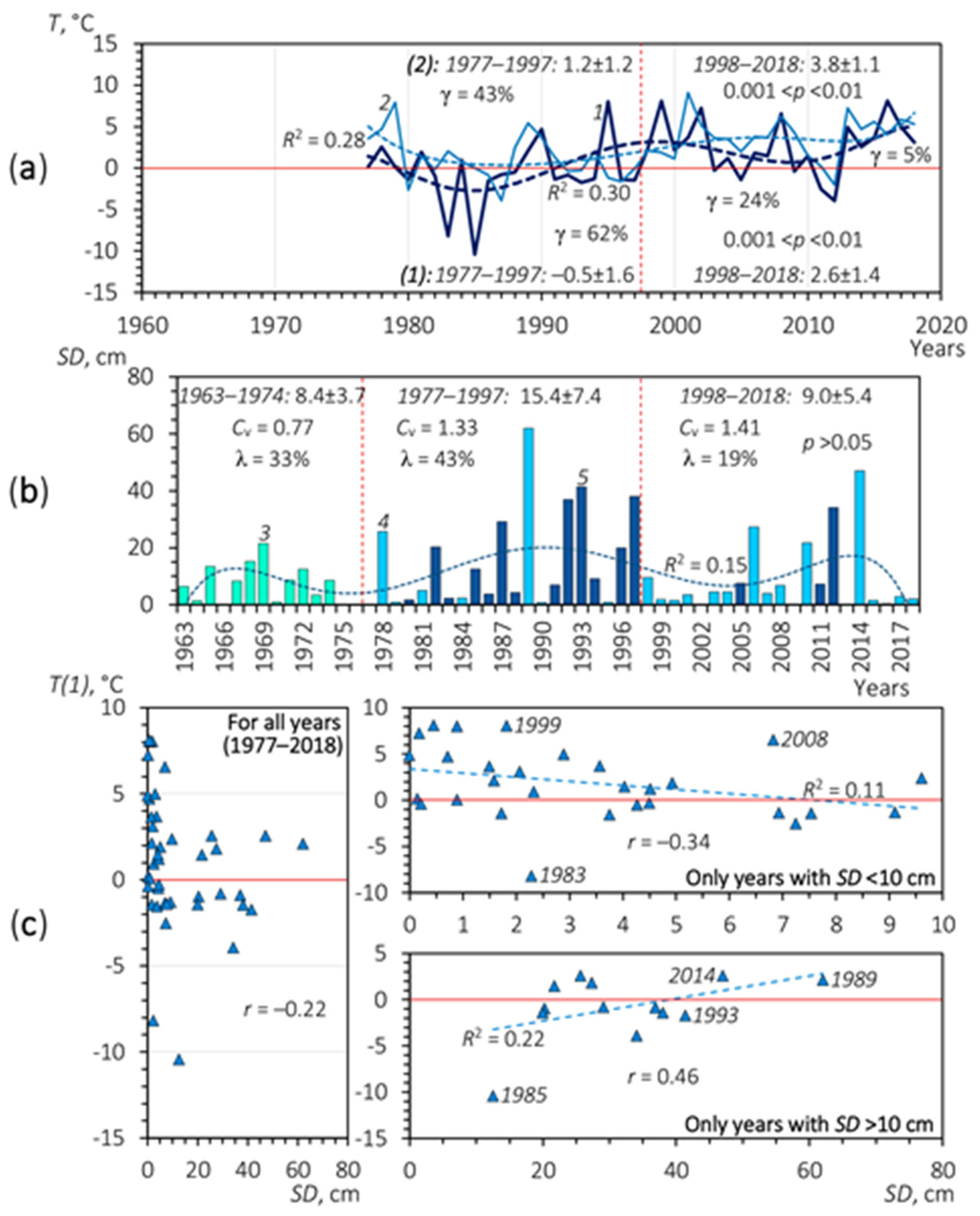
4.1. The Impact of Climate and Climate-Induced Changes
4.1.1. Changes in Surface Water/Sediment Runoff Formation during Snow Melting
4.1.2. Changes in Surface Water/Sediment Runoff Formation during the Warm (Rainy) Season
4.2. The Impact of Human Activities Changes
4.2.1. River Water Transfer
4.2.2. Cultivated Land Area Changes Impact
4.2.3. Livestock Changes Impact
4.3. Neighboring River Basins of the North Caucasus Region
4.4. Comparison with Neighboring Regions of Europe
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shmakin, A.B.; Popova, V.V. Dynamics of climate extremes in Northern Eurasia in the late 20th century. Izv. Atmos. Ocean Phys. 2006, 42, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulygina, O.N.; Razuvaev, V.N.; Korshunova, N.N.; Groisman, P.Y. Climate variations and changes in extreme climate events in Russia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2007, 2, 045020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, V.V.; Polyakova, I.A. Change of stable snow cover destruction dates in Northern Eurasia, 1936–2008: Impact of global warming and the role of largescale atmospheric circulation. Ice Snow 2013, 53, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zolina, O.; Simmer, C.; Belyaev, K.; Gulev, S.K.; Koltermann, P. Changes in the duration of European wet and dry spells during the last 60 years. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2022–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashabokov, B.A.; Tashilova, A.A.; Kesheva, L.A.; Taubekova, Z.A. Trends in precipitation parameters in the climate zones of southern Russia (1961–2011). Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2017, 42, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebnikova, E.I.; Rudakova, Y.L.; Shkolnik, I.M. Changes in Precipitation Regime over the Territory of Russia: Data of Regional Climate Modeling and Observations. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2019, 44, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostert, P.; Kuemmerle, T.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Sieber, A.; Lambin, E.F.; Radeloff, V.C. Rapid land use change after socio-economic disturbances: The collapse of the Soviet Union versus Chernobyl. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 045201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhin, G.D. Ecological-economic assessment of land use structure within the European territory of Russia during two recent decades. Vestn. Mosk. Univ. Ser. Geogr. 2012, 5, 19–28. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nefedova, T.G. Major trends for changes in the socioeconomic space of rural Russia. Reg. Res. Russ. 2012, 2, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prishchepov, A.V.; Radeloff, V.C.; Baumann, M.; Kuemmerle, T.; Müller, D. Effects of institutional changes on land use: Agricultural land abandonment during the transition from state-command to market-driven economies in post-Soviet Eastern Europe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 024021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prishchepov, A.V.; Müller, D.; Dubinin, M.; Baumann, M.; Radeloff, V.C. Determinants of agricultural land abandonment in post-Soviet European Russia. Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekrich, A.S.; Lyuri, D.I. Changes of the dynamic of agrarian lands of Russia in 1990–2014. Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk Seriya Geogr. 2019, 3, 64–77. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, S.V. Climate changes of the annual rivers’ run-off and its components in the European part of Russia. Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk Seriya Geogr. 2011, 6, 78–86. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Parajka, J.; Perdigão, R.A.; Merz, B.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; Bonacci, O.; Borga, M.; et al. Changing climate shifts timing of European floods. Science 2017, 357, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, N.L.; Agafonova, S.A.; Kireeva, M.B.; Povalishnikova, E.S.; Pakhomova, O.M. Recent changes of annual flow distribution of the Volga basin rivers. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 10, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Viglione, A.; Perdigão, R.A.; Parajka, J.; Merz, B.; Lun, D.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; et al. Changing climate both increases and decreases European river floods. Nature 2019, 573, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, L.F.; Kiryukhina, Z.P.; Krasnov, S.F.; Dobrovol’skaya, N.G. Dynamics of agricultural soil erosion in European Russia. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2017, 50, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal’tsev, K.A.; Ivanov, M.A.; Sharifullin, A.G.; Golosov, V.N. Changes in the rate of soil loss in river basins within the southern part of European Russia. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusarov, A.V. The impact of contemporary changes in climate and land use/cover on tendencies in water flow, suspended sediment yield and erosion intensity in the northeastern part of the Don River basin, SW European Russia. Environ. Res. 2019, 175, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusarov, A.V.; Sharifullin, A.G. Contemporary erosion and suspended sediment yield within river basins in the steppe of the southeastern part of the Russian Plain: A case study of the Samara River basin. Izv. Akad. Nauk Seriya Geogr. 2019, 1, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gusarov, A.V. The response of water flow, suspended sediment yield and erosion intensity to contemporary long-term changes in climate and land use/cover in river basins of the Middle Volga Region, European Russia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 134770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedev, I.F.; Levitskaya, N.G.; Makarov, V.Z.; Nazarov, V.A. The results of monitoring of erosion processes on chernozems of the Volga Region. Agrar. Sci. J. 2016, 8, 29–34. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rysin, I.I.; Golosov, V.N.; Grigoryev, I.I.; Zaitseva, M.Y. Influence of climate change on the rates of gully growth in the Vyatka-Kama watershed. Geomorfologiya 2017, 1, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafurov, A.M.; Rysin, I.I.; Golosov, V.N.; Grigoryev, I.I.; Sharifullin, A.G. Estimation of the recent rate of gully head retreat on the southern megaslope of the East European Plain using a set of instrumental methods. Vestn. Mosk. Univ. Seriya Geogr. 2018, 5, 61–71. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Medvedeva, R.A. Trends of the gully erosion development in the territory of the Republic of Tatarstan. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 107, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, V.N. Erosion and Deposition Processes in River Basins of Cultivated Plains; GEOS Publ.: Moscow, Russia, 2006. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Markelov, M.V.; Golosov, V.N.; Belyaev, V.R. Changes in the sedimentation rates on the floodplains of small rivers in the Central Russian Plain. Vestn. Mosk. Univ. Ser. Geogr. 2012, 5, 70–76. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sharifullin, A.G.; Gusarov, A.V.; Golosov, V.N. Assessment of contemporary erosion/sedimentation trend within a small cultivated catchment in the Republic of Tatarstan (European Russia). Geomorfologiya 2018, 3, 93–108. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusarov, A.V.; Rysin, I.I.; Sharifullin, A.G.; Golosov, V.N. Assessment of contemporary erosion/sedimentation rates trend within a small cultivated catchment using the radiocaesium-137 as a chronomarker (a case study from the Udmurt Republic, European Russia). Geomorfologiya 2019, 2, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluzhina, A.S.; Begday, I.V. The ecological assessment status of the catchment area of the Kalaus River in Stavropol Region. Bull. Dagestan State Pedagog. Univ. Nat. Exact Sci. 2014, 4, 67–71. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bluzhina, A.S.; Begday, I.V.; Kharin, K.V. Ecological and geochemical assessment of the Kuma River basin in the Stavropol Krai. Sci. Innov. Technol. 2015, 4, 65–80. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dobrovolsky, A.D.; Zalogin, B.S. Seas of the USSR; Moscow State University Publ.: Moscow, Russia, 1982. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dzhamirzoyev, G.S.; Bukreyev, S.A. Kizlyar Bay/Wetlands of Russia. Russian program Wetlands International. 2016. Available online: http://www.fesk.ru/wetlands/347.html (accessed on 18 December 2020). (In Russian).
- Bazelyuk, A.A. Changes in the hydrography and water flow of the rivers of the Kuma-Manych Depression under the influence of anthropogenic activity. Bull. High. Educ. Inst. North Cauc. Reg. Nat. Sci. 2017, 2, 89–91. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Stepanjan, O.V.; Startsev, A.V. Present state of the Kumo-Manych Depression’s water biota: Ust’-Manychskoye, Vesyolovskoye, Proletarskoye and Chograyskoye water reservoirs. Arid Ecosyst. 2014, 20, 56–69. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Surface Water Resources of the USSR. Hydrological Knowledge, Volume 8: The Northern Caucasus; Gidrometeoizdat Publ.: Leningrad, Russia, 1972. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, M.A.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Golosov, V.N.; Zalyaliev, R.R.; Efimov, K.V.; Kondrat’eva, A.A.; Kinyashova, A.D.; Ionova, Y.K. Changes of cropland area in the river basins of the European part of Russia for the period 1985–2015, as a factor of soil erosion dynamics. Sovrem. Probl. Distantsionnogo Zondirovaniya Zemli Kosm. 2017, 14, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Water Cadaster. The Main Hydrological Characteristics (for 1971–1975 and the Entire Observation Period), Volume 8. The Northern Caucasus; Gidrometeoizdat Publ.: Leningrad, Russia, 1980. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Surface Water Resources of the USSR. The Main Hydrological Characteristics, Volume 8: The Northern Caucasus; Gidrometeoizdat Publ.: Leningrad, Russia, 1966. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Surface Water Resources of the USSR. The Main Hydrological Characteristics (for 1963–1970 and the Entire Observation Period), Volume 8: The Northern Caucasus; Gidrometeoizdat Publ.: Leningrad, Russia, 1975. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- State Water Cadaster. Long-Term Surface Water Regime Data, Volume 1 (Iss. 1): The Northeast Coast of the Black Sea, and the Kuban River Basin; Gidrometeoizdat Publ.: Leningrad, Russia, 1986. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- State Water Cadaster. Long-Term Surface Water Regime Data, Volume 1 (Iss. 26): The Basins of the Terek, Kuma, Samur, Sulak Rivers; Gidrometeoizdat Publ.: Leningrad, Russia, 1987. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Karasev, I.F.; Kurdin, R.D.; Fedorov, N.N.; Kopylov, A.P.; Ivashenko, E.P.; Shestakova, R.A.; Dementiev, V.V.; Popova, L.A.; Ustyuzhanin, B.S.; Petukhova, G.A.; et al. Manual for Hydrometeorological Stations and Posts. Issue 6. Part I. Hydrological Observations and Work on Large and Medium-Sized Rivers, 3rd ed.; Revised and Enlarged; Main Directorate of the Hydrometeorological Service, Council of Ministers of the USSR: Moscow, Russia, 1977. (In Russian)
- Karaushev, A.V. Water erosion and sediment. In Sediment Yield, Its Study and Geographical Distribution; Karaushev, A.V., Ed.; Gidrometeoizdat Publ.: Leningrad, Russia, 1977; pp. 5–16. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Agriculture of the USSR. Statistical Bulletin (Crop Production); Goskomstat of the USSR Publ.: Moscow, Russia, 1988. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Report on the Current Situation in Agriculture of the Stavropol Krai for 11–15 March 2019. Available online: http://www.mshsk.ru/press-sluzhba/novosti_new_2/index.php?ELEMENT_ID=10988 (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Nefedova, T. Rural Stavropol Krai through the Eyes of a Moscow Geographer. A Variety of Regions in the South of Russia; Stavropol State University Publ.: Stavropol, Russia, 2012. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dedkov, A.P.; Mozzherin, V.I. Erosion and Sediment Yield on the Earth; Kazan University Publ.: Kazan, Russia, 1984. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bobrovitskaya, N.N. Long-term variations in mean erosion and sediment yield from the rivers of the former Soviet Union. IAHS AISH Publ. 1996, 236, 407–441. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, M.M.; Govers, G.; van Doorn, A.; Quetier, F.; Chouvardas, D.; Rounsevell, M. The response of soil erosion and sediment export to land-use change in four areas of Europe: The importance of landscape pattern. Geomorphology 2008, 98, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; van Dam, O.; Verstraeten, G.; van Huissteden, J. Changing sediment dynamics due to natural reforestation in the Dragonja catchment, SW Slovenia. Catena 2009, 78, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, M.; Will, M.; Kunert, E.; Kreutzer, S.; Fischer, M.; Reverman, R. The temporal and spatial quantification of Holocene sediment dynamics in a mesoscale catchment in northern Bavaria, Germany. Holocene 2011, 21, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Pappagallo, G.; Porto, A.L. Temporal variability of suspended sediment transport and rating curves in a Mediterranean river basin: The Celone (SE Italy). Catena 2015, 128, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yan, M.; Cai, Q.; Fang, H. Suspended sediment dynamics at different time scales in the Loushui River, south-central China. Catena 2016, 136, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.; Grabowski, R.C.; Rickson, R.J. Suspended sediment transport dynamics in rivers: Multi-scale drivers of temporal variation. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 166, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Meng, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Comprehensive evaluation of the effects of climate change and land use and land cover change variables on runoff and sediment discharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedkov, A. The relationship between sediment yield and drainage basin area. IAHS Publ. 2004, 288, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Baartman, J.E.; Masselink, R.; Keesstra, S.D.; Temme, A.J. Linking landscape morphological complexity and sediment connectivity. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 1457–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryirs, K.A. (Dis)Connectivity in catchment sediment cascades: A fresh look at the sediment delivery problem. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.; Heckmann, T.; Larsen, J.R.; Bork, H.-R. Gully catchments as a sediment sink, not just a source: Results from a long-term (~12,500 year) sediment budget. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2016, 41, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalov, R.S.; Golosov, V.N.; Sidorchuk, A.Y.; Litvin, L.F.; Alexeevsky, N.I.; Chernov, A.V.; Kovalev, S.N.; Krasnov, S.F.; Larionov, G.A.; Berkovich, K.M.; et al. Catchment Erosion-Fluvial Systems; INFRA-M Publ.: Moscow, Russia, 2017. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sidorchuk, A.Y. The fluvial system on the East European plain: Sediment source and sink. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 11, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabanov, A.T.; Dolgov, S.V.; Koronkevich, N.I. Effect of present-day climate changes and agricultural activities on spring overland runoff in forest-steppe and steppe regions of the Russian Plain. Water Resour. 2018, 45, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabanov, A.T.; Dolgov, S.V.; Koronkevich, N.I.; Panov, V.I.; Petel’ko, A.I. Surface Runoff and Snowmelt Infiltration into the Soil on Plowlands in the Forest-Steppe and Steppe Zones of the East European Plain. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2018, 51, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.M.; Landine, P.G.; Granger, R.J. Simulating infiltration into frozen prairie soils in streamflow models. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1985, 22, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; McKenzie, J.; Voss, C.; Wu, Q. Exchange of groundwater and surface-water mediated by permafrost response to seasonal and long-term air temperature variation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L14402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shi, H.; Flerchinger, G.N.; Akae, T.; Wang, C. Simulation of freezing and thawing soils in Inner Mongolia Hetao Irrigation District, China. Geoderma 2012, 173, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouli, Y.; Cade-Menun, B.J.; Cutforth, H.W. Freeze–thaw cycles and soil water content effects on infiltration rate of three Saskatchewan soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 93, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gaetano, A.T.; Cameron, M.D.; Wilks, D.S. Physical simulation of maximum seasonal soil freezing depth in the United States using routine weather observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, H.A.L. Climate change and soil freezing dynamics: Historical trends and projected changes. Clim. Chang. 2008, 87, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komissarov, M.A.; Gabbasova, I.M. Snowmelt-induced soil erosion on gentle slopes in the Southern Cis-Ural Region. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2014, 47, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernokulsky, A.; Kozlov, F.; Zolina, O.; Bulygina, O.; Mokhov, I.I.; Semenov, V.A. Observed changes in convective and stratiform precipitation in Northern Eurasia over the last five decades. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, V.; Gusarov, A.; Litvin, L.; Yermolaev, O.; Chizhikova, N.; Safina, G.; Kiryukhina, Z. Evaluation of soil erosion rates in the southern half of the Russian Plain: Methodology and initial results. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2017, 375, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzherin, V.I.; Kurbanova, S.G. Human Activity and Erosion-Riverbed Systems of the Middle Volga Region; ART Design Publ.: Kazan, Russia, 2004. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Grazhdankin, A.I.; Kara-Murza, S.G. White Book of Russia. Construction, Reconstruction and Reforms: 1950–2013; Nauchniy Ekspert Publ.: Moscow, Russia, 2015. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hammerová, A.; Jandák, J.; Brtnický, M.; Hladký, J.; Hrabovská, B. Physical Parameters of Chernozem Lands Affected by Water Erosion. In Proceedings of the MendelNet-2013, Brno, Czech Republic, 20–21 November 2013; pp. 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Mulholland, B.; Fullen, M.A. Cattle trampling and soil compaction on loamy sands. Soil Use Manag. 1991, 7, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, N.T.; Gedir, J.V.; Hudson, R.J.; Bork, E.W.; Chanasyk, D.S.; Naeth, M.A. Impacts of grazing systems on soil compaction and pasture production in Alberta. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2002, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyba, J.; Kroulík, M.; Krištof, K.; Misiewicz, P.A.; Chaney, K. Influence of soil compaction by farm machinery and livestock on water infiltration rate on grassland. Agron. Res. 2014, 12, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmenkova, N.V.; Ivanov, M.M.; Alexandrin, M.Y.; Grachev, A.M.; Rozhkova, A.K.; Zhizhin, K.D.; Grabenko, E.A.; Golosov, V.N. Use of natural and artificial radionuclides to determine the sedimentation rates in two North Caucasus lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyplenkov, A.; Vanmaercke, M.; Golosov, V. Contemporary suspended sediment yield of Caucasus mountains. Proc. IAHS 2019, 381, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavaev, V.A.; Seminozhenko, S.S. Terrain Morphometry and Mudflow Features in the Northern Slope of the Great Caucasus. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2019, 487, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, V.N.; Gennadiev, A.N.; Olson, K.R.; Markelov, M.V.; Zhidkin, A.P.; Chendev, Y.G.; Kovach, R.G. Spatial and temporal features of soil erosion in the forest-steppe zone of the East-European Plain. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2011, 44, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apukhtin, A.V.; Kumani, M.V. Recent changes in the conditions of spring floods of rivers in the Kursk region. Elec. Sci. J. Kursk St. Univ. 2012, 1, 300–311. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sarauskiene, D.; Kriauciuniene, J.; Reihan, A.; Klavins, M. Flood pattern changes in the rivers of the Baltic countries. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2015, 23, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arheimer, B.; Lindström, G. Climate impact on floods: Changes in high flows in Sweden in the past and the future (1911–2100). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, Z. The impact of climate variability on flood risk in Poland. Risk Anal. 2003, 23, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ni, J.; Chang, F.; Yue, Y.; Frolova, N.; Magritsky, D.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Ciais, P.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, C.; et al. Global trends in water and sediment fluxes of the world’s large rivers. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



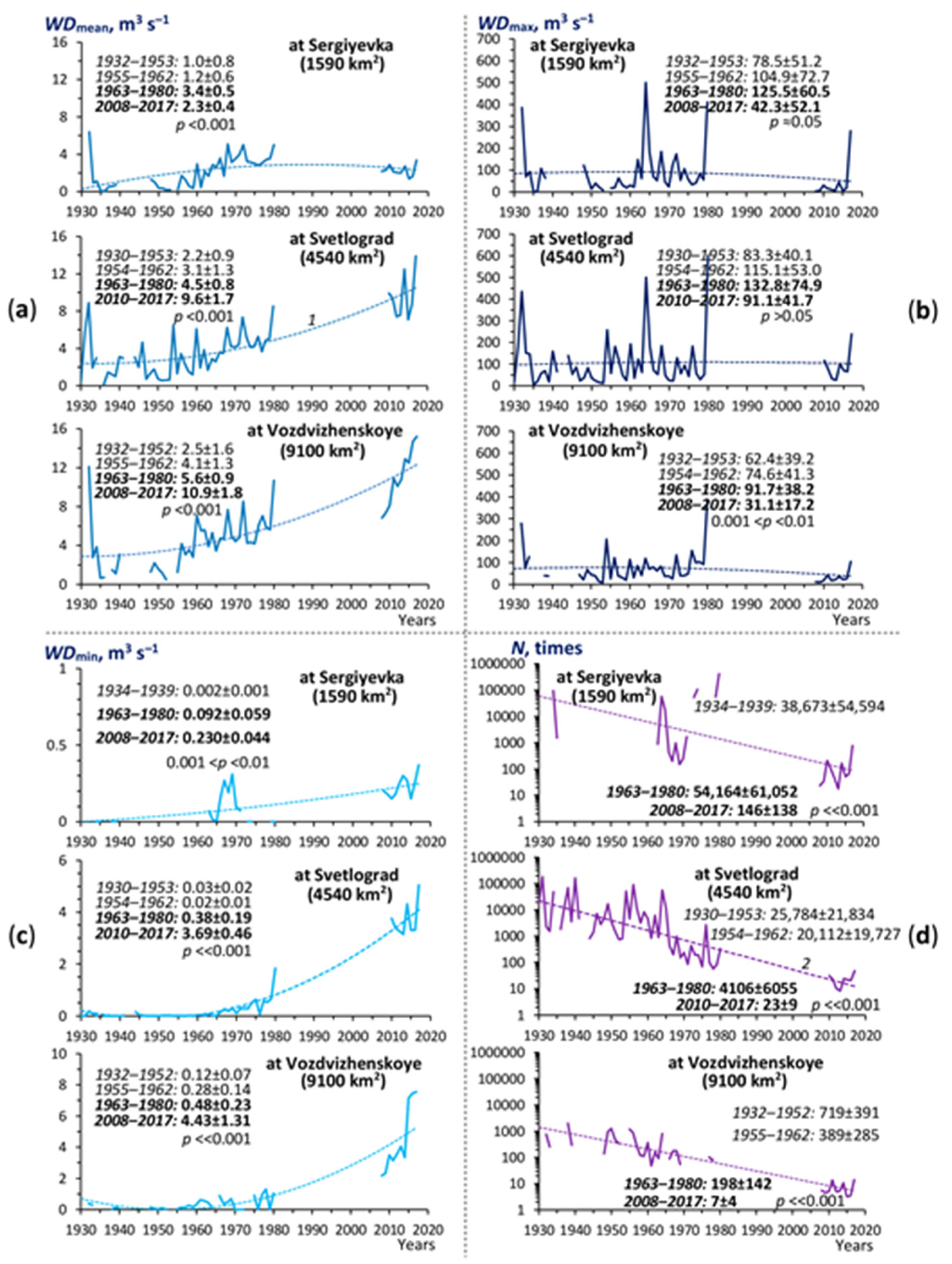









| Rivers/Hydrological Stations (see Figure 1) (Geographic Coordinates of the Stations) | Characteristics: | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S, km2 | A, m | I, ‰ | L, % | F, % | P, % | WDmean | M(WDmean) | |
| Kalaus River basin: | ||||||||
| 1. Kalaus River/Sergiyevka (44°57′ N, 42°43′ E) | 1590 | 380 | 1.6 | 0.01 | <5 | 60 | 3.13 | 1.97 |
| 2. Kalaus River/Svetlograd (45°13′ N, 42°30′ E) | 4540 | 340 | 1.2 | 0.11 | <5 | 60 | 6.07 | 1.34 |
| 3. Kalaus River/Vozdvizhenskoye (45°49′ N, 43°40′ E) | 9100 | 190 | 0.7 | 0.06 | <5 | 60 | 7.50 | 0.82 |
| 4. Ula River/Staromarievka (45°03′ N, 42°08′ E) | 273 | 440 | 11 | ND | 5 | 35 | 1.89 | 6.92 |
| Kuma River basin: | ||||||||
| 5. Kuma River/Bekeshevskaya (44.07° N, 42.27° E) | 434 | 1290 | 23 | ND | 15 | <5 | 2.51 | 5.78 |
| 6. Kuma River/Aleksandriyskaya (44.13° N,43.22° E) | 3630 | 740 | 4.8 | 0.36 | 5 | 20 | 7.07 | 1.95 |
| 7. Kuma River/Novozavedennoye (44.15° N, 43.38° E) | 6360 | 1000 | 3.3 | 0.23 | 5 | 20 | 15.9 | 2.51 |
| 8. Kuma River/Zelenokumsk (44.25° N, 43.53° E) | 9960 | 820 | 2.0 | 0.17 | <5 | 25 | 15.1 | 1.51 |
| 9. Kuma River/Budyonnovsk (44.46° N, 44.11° E) | 15,000 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 16.1 | 1.08 |
| 10. Kuma River/Vladimirovka (44.45° N, 44.47° E) | 20,000 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 9.28 | 0.46 |
| 11. Zolka River/Mikhailovsky (44.14° N, 43.42° E) | 717 | 770 | 8.4 | 0.30 | <5 | 25 | 0.38 | 0.66 |
| 12. Tomuzlovka River/Novoselitskoye (44.45° N, 43.27° E) | 815 | 360 | 4.0 | ND | 5 | 45 | 1.21 | 1.56 |
| 13. Podkumok River/Lysogorskaya (44.11° N, 43.29° E) | 1960 | 1250 | 10 | 0.09 | 5 | 10 | 9.47 | 4.83 |
| Terek River basin: | ||||||||
| 14. Terek River/Kotlyarevskaya (43.35° N, 44.05° E) | 8920 | 1800 | 13 | 0.01 | 20 | 5 | 128.8 | 14.4 |
| 15. Kambileyevka River/Olginskoye (43.10° N, 44.42°E) | 359 | 1260 | 13 | ND | 40 | 5 | 3.89 | 15.0 |
| 16. Malka River/Prokhladnaya (43.44° N, 44.03° E) | 9820 | 1900 | 11 | 0.01 | 15 | 5 | 99.8 | 10.2 |
| 17. Chegem River 1/Nijny Chegem (43.30° N, 43.17° E) | 739 | 2500 | 29 | 0.01 | 10 | ND | 14.4 | 19.4 |
| 18. Cherek Balkarsky River/Babugent (43.16° N, 43.33° E) | 695 | 2590 | 28 | 0.02 | 5 | ND | 27.1 | 39.0 |
| Kuban River basin: | ||||||||
| 19. Belaya River/Kamenny Most (44.17° N, 40.11° E) | 1850 | 1330 | 9.9 | 0.01 | 80 | <5 | 25.0 | 26.5 |
| 20. Urup River/Steblitsky (44.55° N, 41.09° E) | 3190 | 910 | 4.2 | 0.03 | 30 | 20 | 19.5 | 6.10 |
| 21. Fars River/Dondukovskaya (44.53° N, 40.21° E) | 1240 | 400 | 3.9 | 0.01 | 50 | 11 | 2.42 | 4.00 |
| River/Hydrological Station (River Basin Area) | Variables | Monitoring Periods: | ∆, % | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1963–1980 | 2008–2017 | ||||
| Kuma River basin: | |||||
| Zolka River/Mikhailovsky (717 km2) | WDmean: | 0.52 ± 0.09 a | 0.40 ± 0.05 | −23% | 0.01 < p < 0.05 |
| SSLmean: | 0.13 ± 0.04 b | 0.008 ± 0.002 | −94% | <0.001 | |
| SSYmean: | 5.7 b | 0.35 | |||
| Tomuzlovka River/Novoselitskoye (815 km2) | WDmean: | 1.20 ± 0.34 c | 1.22 ± 0.09 | +1.7% | >>0.05 |
| SSLmean: | 0.98 ± 0.40 c | 0.33 ± 0.07 | −66% | 0.001 < p < 0.01 | |
| SSYmean: | 38 c | 13 | |||
| Podkumok River/Lysogorskaya (1960 km2) | WDmean: | 7.85 ± 1.21 | 12.40 ± 1.91 | +58% | <0.001 |
| SSLmean: | 12.0 ± 4.7 | 7.0 ± 2.4 | −42% | ≈0.05 | |
| SSYmean: | 193 | 113 | |||
| Terek River basin: | |||||
| Terek River/Kotlyarevskaya (8920 km2) | WDmean: | 124.0 ± 6.1 | 138.4 ± 5.9 | +12% | 0.001 < p < 0.01 |
| SSLmean: | 114.5 ± 21.2 | 43.0 ± 5.6 | −62% | <0.001 | |
| SSYmean: | 405 | 152 | |||
| Kambileyevka River/Olginskoye (359 km2) | WDmean: | 3.93 ± 0.50 d | 3.83 ± 0.31 | −2.5% | 0.001 < p < 0.01 |
| SSLmean: | 1.17 ± 0.58 d | 0.97 ± 0.33 | −17% | >>0.05 | |
| SSYmean: | 103 d | 85 | |||
| Malka River/Prokhladnaya (9820 km2) | WDmean: | 93.8 ± 6.3 d | 107.6 ± 5.2 | +15% | 0.001 < p < 0.01 |
| SSLmean: | 120.4 ± 61.3 d | 63.4 ± 11.2 | −47% | ≈0.05 | |
| SSYmean: | 387 d | 204 | |||
| Chegem River 1/Nijny Chegem (739 km2) | WDmean: | 14.0 ± 0.5 d | 14.9 ± 1.1 | +6.4% | >0.05 |
| SSLmean: | 6.8 ± 2.7 d | 4.2 ± 1.12 | −38% | >0.05 | |
| SSYmean: | 290 d | 179 | |||
| Cherek Balkarsky River/Babugent (695 km2) | WDmean: | 27.3 ± 1.2 d | 26.8 ± 1.5 | −1.8% | >>0.05 |
| SSLmean: | 16.7 ± 9.8 d | 6.1 ± 1.9 | −63% | >0.05 | |
| SSYmean: | 758 d | 277 | |||
| Kuban River basin: | |||||
| Belaya River/Kamenny Most (1850 km2) | WDmean: | 49.1 ± 3.9 | 48.9 ± 5.7 | −0.4% | >>0.05 |
| SSLmean: | 11.0 ± 2.3 | 16.3 ± 6.8 | +48% | >0.05 | |
| SSYmean: | 188 | 278 | |||
| Urup River/Steblitsky (3190 km2) | WDmean: | 18.4 ± 1.8 | 21.4 ± 1.9 | +16% | 0.01 < p < 0.05 |
| SSLmean: | 28.9 ± 7.7 | 32.7 ± 9.3 | +13% | >>0.05 | |
| SSYmean: | 286 | 323 | |||
| Fars River/Dondukovskaya (1240 km2) | WDmean: | 4.6 ± 0.6 | 5.6 ± 1.6 | +22% | >0.05 |
| SSLmean: | 6.1 ± 1.6 | 8.1 ± 3.3 | +33% | >0.05 | |
| SSYmean: | 155 | 206 | |||
| Calendar Months: | Ja | F | Mr | Ap | Ma | Jn | Jl | Ag | S | O | N | D | Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stavropol (45°07′ N; 42°07′ E) | ||||||||||||||
| Air temperature | ||||||||||||||
| 1963–1980 | Mean, °C | −4.2 | −2.4 | 1.8 | 9.8 | 15.4 | 19.1 | 21.9 | 20.8 | 16.1 | 9.3 | 4.8 | −0.2 | 9.3 |
| 2008–2017 | Mean, °C | −3.1 | −1.7 | 3.6 | 10 | 15.7 | 20.4 | 23.3 | 23.2 | 17.2 | 9.7 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 10.2 |
| d, °C | 1.1 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 2.4 | 1.1 | 0.4 | −0.2 | 0.6 | 0.9 | |
| p | >0.05 | >0.05 | ≈0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.01 | |
| Precipitation | ||||||||||||||
| 1966–1980 a | ∑, mm | 23 | 29.8 | 33 | 46.9 | 64.1 | 72.1 | 50.9 | 63.9 | 42.6 | 49.1 | 38.6 | 44.6 | 558.7 |
| Cv | 0.47 | 0.66 | 0.37 | 0.65 | 0.41 | 0.7 | 0.59 | 0.52 | 0.37 | 0.58 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.15 | |
| 2008–2017 | ∑, mm | 30.6 | 23.3 | 43.9 | 35.4 | 98.9 | 72.2 | 72.6 | 29 | 53.1 | 44.7 | 34.6 | 38.4 | 576.6 |
| Cv | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.62 | 0.39 | 0.48 | 0.38 | 0.98 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.53 | 0.72 | 0.12 | |
| d, mm | 7.6 | −6.5 | 10.9 | −11.5 | 34.8 | 0.1 | 21.7 | −34.9 | 10.5 | −4.4 | −4.0 | −6.2 | 17.9 | |
| ∆, % | 33 | −21.8 | 33 | −24.5 | 54.3 | 0.1 | 42.6 | −54.6 | 24.6 | −9.0 | −10.3 | −13.9 | 3.2 | |
| p | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | |
| Budyonnovsk (44°47′ N; 44°08′ E) | ||||||||||||||
| Air temperature | ||||||||||||||
| 1963–1980 | Mean, °C | −5.0 | −3.2 | 2.4 | 10.8 | 17.5 | 21.6 | 24.5 | 23.5 | 18 | 10.1 | 4.8 | −0.5 | 10.5 |
| 2008–2017 | Mean, °C | −3.7 | −1.9 | 4.5 | 11 | 17.7 | 23.2 | 26.1 | 25.5 | 19 | 10.9 | 4.7 | 0.4 | 11.5 |
| d, °C | 1.3 | 1.3 | 2.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 2 | 1 | 0.8 | −0.1 | 0.9 | 1 | |
| p | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.01 | |
| Precipitation | ||||||||||||||
| 1966–1980 a | Mean, mm | 19.8 | 21 | 22.7 | 32.5 | 44 | 51.5 | 43.5 | 54.2 | 32 | 20.5 | 18.4 | 30.9 | 387.9 |
| Cv | 0.47 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.48 | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.89 | 0.5 | 0.66 | 0.76 | 0.53 | 0.2 | |
| 2008–2017 | Mean, mm | 31.2 | 20.5 | 40 | 33.5 | 66.2 | 45 | 41.5 | 33 | 40.6 | 38.6 | 22.8 | 33.4 | 446.5 |
| Cv | 0.59 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.67 | 0.35 | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.99 | 0.86 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.63 | 0.06 | |
| d, mm | 11.4 | −0.5 | 17.3 | 1 | 22.2 | −6.5 | −2.0 | −21.2 | 8.6 | 18.1 | 4.4 | 2.5 | 58.6 | |
| ∆, % | 57.6 | −2.4 | 76.2 | 3.1 | 50.5 | −12.6 | −4.6 | −39.1 | 26.9 | 88.3 | 23.9 | 8.1 | 15.1 | |
| p | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | |
| PD, mm | Monitoring Periods | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1966–1980 a | 2008–2017 | |||||
| ∑P | μ | η | ∑P | μ | η | |
| Stavropol | ||||||
| <10 | 3825.3 | 2154.3 | 1.8 | 3405.3 | 1466.0 | 2.3 |
| 10–20 | 1106.8 | 82.9 | 13.4 | 1296.1 | 95.0 | 13.6 |
| 20–30 | 376.2 | 16.4 | 22.9 | 484.5 | 20.0 | 24.2 |
| 30–40 | 144.7 | 4.3 (May–2; June–2; September–1; October–1) | 33.7 | 373.8 | 11.0 (May–3; June–2; July–3; August–1; September–1; October–1) | 34.0 |
| 40–50 | 68.4 | 1.4 (June–1; August–1) | 48.9 | 88.3 | 2.0 (June–2) | 44.2 |
| >50 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 67.2 | 1.0 (June–1) | 67.2 |
| Budyonnovsk | ||||||
| <10 | 2850.5 | 2502.7 | 1.1 | 2832.1 | 1851.0 | 1.5 |
| 10–20 | 614.1 | 45.5 | 13.5 | 988.6 | 72.0 | 13.7 |
| 20–30 | 277.3 | 11.8 | 23.5 | 290.5 | 10.9 | 26.7 |
| 30–40 | 97.5 | 2.7 (August–2; September–1) | 36.1 | 135.5 | 4.0 (May–2; June–1; August–1) | 33.9 |
| 40–50 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 124.3 | 3.0 (September–2; October–1) | 41.4 |
| >50 | 50.9 | 1.0 (July–1) | 50.9 | 53.3 | 1.0 (August–1) | 53.3 |
| Variables | Periods | ∆, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1970–1975 | 2007–2019 | ||
| F(T), ×103 ha | 4080.3 | 3001.5 | −26.4 |
| Tractors, units | 31,518 | 19,594 | −37.8 |
| τ, units per 103 ha | 7.7 a | 6.5 | −15.6 |
| F(G), ×103 ha | 2223.4 | 2141.8 | −3.7 |
| Grain combine harvesters, units | 7834 | 6414 | −18.1 |
| τ, units per 103 ha | 3.5 | 3.0 | −14.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gusarov, A.V.; Sharifullin, A.G.; Komissarov, M.A. Contemporary Long-Term Trends in Water Discharge, Suspended Sediment Load, and Erosion Intensity in River Basins of the North Caucasus Region, SW Russia. Hydrology 2021, 8, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology8010028
Gusarov AV, Sharifullin AG, Komissarov MA. Contemporary Long-Term Trends in Water Discharge, Suspended Sediment Load, and Erosion Intensity in River Basins of the North Caucasus Region, SW Russia. Hydrology. 2021; 8(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology8010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleGusarov, Artyom V., Aidar G. Sharifullin, and Mikhail A. Komissarov. 2021. "Contemporary Long-Term Trends in Water Discharge, Suspended Sediment Load, and Erosion Intensity in River Basins of the North Caucasus Region, SW Russia" Hydrology 8, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology8010028
APA StyleGusarov, A. V., Sharifullin, A. G., & Komissarov, M. A. (2021). Contemporary Long-Term Trends in Water Discharge, Suspended Sediment Load, and Erosion Intensity in River Basins of the North Caucasus Region, SW Russia. Hydrology, 8(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology8010028







