Application of GIS Techniques in Identifying Artificial Groundwater Recharging Zones in Arid Regions: A Case Study in Tissamaharama, Sri Lanka
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. GIS Applications in Groundwater Studies
3. Case study Application
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Rainfall Data
3.3. Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
3.4. Soil and Land Use Data
4. Methodology
4.1. Developing the Thematic Layers
4.2. Weighted Overlay Analysis
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Average Annual Rainfall Variation in Thissamaharama DSD
5.2. Variation of Slope and Drainage Density
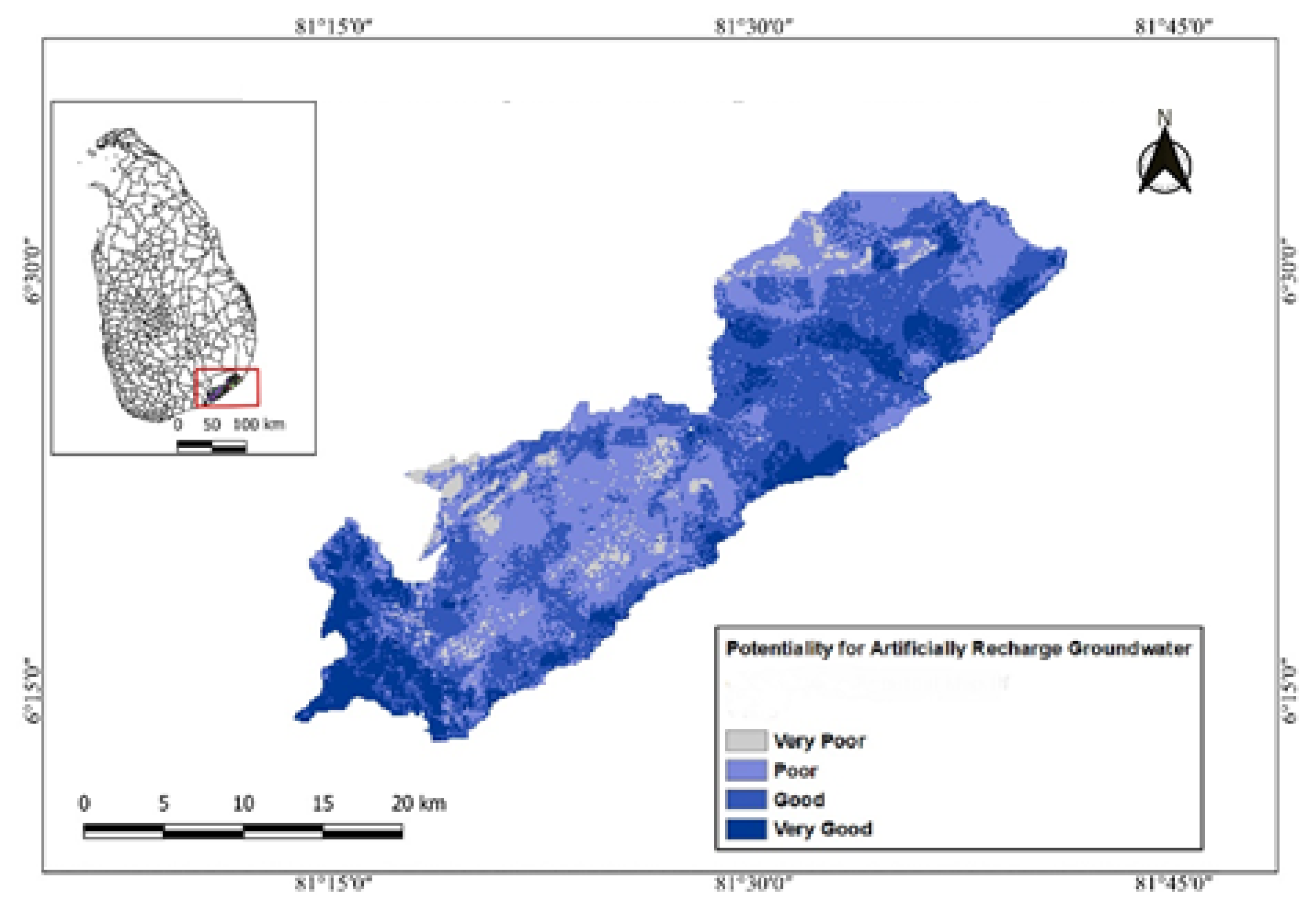
5.3. Groundwater Recharge Potential Zones
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Senanayake, I.P.; Dissanayake, D.M.D.O.K.; Mayadunna, B.B.; Weerasekera, W.L. An approach to delineate groundwater recharge potential sites in Ambalantota, Sri Lanka using GIS techniques. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouwer, H. Artificial recharge of groundwater: Hydrogeology and engineering. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCracken, M.; Wolf, A.T. Updating the Register of International River Basins of the world. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2019, 35, 732–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, R.; Nanthakumaran, A.; Senanayake, I.P. Identification of artificial groundwater recharge zones in Vavuniya district using remote sensing and GIS. AGRIEAST J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 13, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.V.; Venkateswaran, S. Delineation of Artificial Recharge Zones Using Geospatial Techniques in Sarabanga Sub Basin Cauvery River, Tamil Nadu. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brands, E.; Rajagopal, R.; Eleswarapu, U.; Li, P. Groundwater: Natural and physicalscience perspectives. Int. Encycl. Geogr. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhena, T.; Mochane, M.; Tshwafo, M.; Linganiso, L.; Thekisoe, O.; Songca, S. Groundwater Recharges Technology for Water Resource Management: A Case Study. In Groundwater; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Sophocleous, M. Interactions between groundwater and surface water: The state of the science. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, M.; Sudarsana Raju, G.; Sreenivasulu, Y.; Siddi Raju, R. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in semi-arid region of Jilledubanderu river basin, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India using fuzzy logic, AHP and integrated fuzzy-AHP approaches. HydroResearch 2019, 2, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Pal, S.C. Combination of GIS and fuzzy-AHP for delineating groundwater recharge potential zones in the critical Goghat-II block of West Bengal, India. HydroResearch 2019, 2, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abijith, D.; Saravanan, S.; Singh, L.; Jennifer, J.J.; Saranya, T.; Parthasarathy, K.S.S. GIS-based multi-criteria analysis for identification of potential groundwater recharge zones—A case study from Ponnaniyaru watershed, Tamil Nadu, India. HydroResearch 2020, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.A. Enhancing groundwater recharge in arid region- a case study from central Saudi Arabia. Sci. Res. Essays 2011, 6, 2757–2762. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyeye, O.A.; Ikpokonte, E.A.; Arabi, S.A. GIS-based groundwater potential mapping within Dengi area, North Central Nigeria. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Sp. Sci. 2019, 22, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V.; Reddy, V.K. Identification of Groundwater Potential Zones using GIS and Remote Sensing. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2018, 119, 3195–3210. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, R.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Krishnamurthy, J.; Saxena, R. Role of remote sensing and GIS techniques for generation of groundwater prospect zones towards rural development—An approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somartha, M.; Silva, R.P.; Chaminda, G.H.; Weragoda, G.G.T.; Kumar, S.K. Identifying groundwater recharge zones through MIKE modeling approach: A case study at mid Kelani river, Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Advances in Civil and Environmental Engineering Practices for Sustainable Development (ACEPS-2018), Galle, Sri Lanka, 15 March 2018; pp. 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Adimalla, N.; Taloor, A.K. Hydrogeochemical investigation of groundwater quality in the hard rock terrain of South India using Geographic Information System (GIS) and groundwater quality index (GWQI) techniques. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 10, 100–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, I.S.; Mohamed; Hiyama, T. Assessing groundwater quality using GIS. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 21, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nas, B.; Berktay, A. Groundwater quality mapping in urban groundwater using GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 160, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baalousha, H.M. Mapping groundwater contamination risk using GIS and groundwater modelling. A case study from the Gaza Strip, Palestine. Arab. J. Geosci. 2010, 4, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, J.W. GIS-based groundwater pollution hazard assessment: A critical review of the DRASTIC model. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1994, 60, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Zeddies, M.; Shankar, U.; Griffiths, G.A. Potential groundwater recharge zones within New Zealand. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagriti Tiwari, R.J.P.S.K.S. Gour River Sub-watersheds Prioritization using Morphometric Parameters: A Remote Sensing and GIS Based Approach. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. Res. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Maity, B.; Mallick, S.K.; Das, P.; Rudra, S. Comparative analysis of groundwater potentiality zone using fuzzy AHP, frequency ratio and Bayesian weights of evidence methods. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EarthExplorer. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Jie, F.; Fei, L.; Li, S.; Hao, K.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Liu, N. Quantitative effects of vadose zone thickness on delayed recharge of groundwater for an irrigation district in an arid area of Northwest China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Agriculture Sri lanka. Available online: https://doa.gov.lk/home-page/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Survey Department of SriLanka. Available online: https://survey.gov.lk/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Chen, X.; Yan, J.F.; Chen, Z.; Luo, G.P.; Song, Q.; Xu, W.Q. A spatial geostatistical analysis of impact of landuse development on groundwater resourcesin the Sangong Oasis Region using remotesensing imagery and data. J. Arid Land 2009, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Jacinth, J.J.; Singh, L.; Saranya, T.; Sivaranjani, S. Impact of land-use change on soil erosion in the Coonoor watershed, Nilgiris mountain range, Tamil Nadu, India. Adv. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2019, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Ahuja, A.; Vishwakarma, B.D.; Jain, K. Groundwater potential zone (GWPZ) for urban development site suitability analysis in Bhopal, India. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 1793–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Rainfall Gauging Station | Location Coordinates | |
|---|---|---|
| Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | |
| Tissamaharama Irrigation | 81.293988 | 6.292839 |
| Weerawila | 81.228772 | 6.370483 |
| Map Layer | Class | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Average annual rainfall (mm) | 975–1000 | 2 |
| 1000–1025 | 3 | |
| 1025–1050 | 4 | |
| 1050–1075 | 6 | |
| 1075–1100 | 8 | |
| Slope (°) | 0–0.5 | 9 |
| 0.5–1 | 8 | |
| 1–3 | 6 | |
| 3–5 | 4 | |
| 5–10 | 3 | |
| 10–15 | 1 | |
| Landuse/Land cover | Built up area | 2 |
| Barren land | 5 | |
| Open forest | 3 | |
| Dense forest | 3 | |
| Grassland | 3 | |
| Mangrove | 6 | |
| Marsh land | 7 | |
| Forest plantation | 3 | |
| Scrubland | 5 | |
| Sparsely used croplands | 5 | |
| Forest unclassified | 3 | |
| Cemetery | 2 | |
| Coconut | 6 | |
| Paddy | 7 | |
| Other cultivation | 5 | |
| Water bodies | 8 | |
| Rock | 2 | |
| Sand | 8 | |
| Homesteads/garden | 2 | |
| Quarry | 2 | |
| Soil cover | Alluvial soils of variable drainage and texture | 5 |
| Erosional remnants | 2 | |
| Reddish-brown earths and low humic gley soils; undulating terrain | 6 | |
| Reddish-brown earths and Solodized Solonetz; undulating terrain | 4 | |
| Reddish-brown earths with a high amount of gravel in the subsoil and low humic gley soils; undulating terrain | 6 | |
| Regosols on recent beach and dune sands; flat terrain | 8 | |
| Rock knob plain | 2 | |
| Solodized Solonetz and Solonchaks; flat terrain | 4 | |
| Alluvial soils of variable drainage and texture | 5 | |
| Drainage density (km/km2) | 0–0.5 | 1 |
| 0.5–1 | 2 | |
| 1–2 | 3 | |
| 2–3 | 5 | |
| 3–5 | 6 | |
| 5–7 | 8 |
| PGWR (Weighted Overlay Value) | Potential Groundwater Recharge Classes |
|---|---|
| >40 | Very good |
| 30–40 | Good |
| 20–30 | Poor |
| <20 | Very poor |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kariyawasam, T.; Basnayake, V.; Wanniarachchi, S.; Sarukkalige, R.; Rathnayake, U. Application of GIS Techniques in Identifying Artificial Groundwater Recharging Zones in Arid Regions: A Case Study in Tissamaharama, Sri Lanka. Hydrology 2022, 9, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9120224
Kariyawasam T, Basnayake V, Wanniarachchi S, Sarukkalige R, Rathnayake U. Application of GIS Techniques in Identifying Artificial Groundwater Recharging Zones in Arid Regions: A Case Study in Tissamaharama, Sri Lanka. Hydrology. 2022; 9(12):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9120224
Chicago/Turabian StyleKariyawasam, Tiran, Vindhya Basnayake, Susantha Wanniarachchi, Ranjan Sarukkalige, and Upaka Rathnayake. 2022. "Application of GIS Techniques in Identifying Artificial Groundwater Recharging Zones in Arid Regions: A Case Study in Tissamaharama, Sri Lanka" Hydrology 9, no. 12: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9120224
APA StyleKariyawasam, T., Basnayake, V., Wanniarachchi, S., Sarukkalige, R., & Rathnayake, U. (2022). Application of GIS Techniques in Identifying Artificial Groundwater Recharging Zones in Arid Regions: A Case Study in Tissamaharama, Sri Lanka. Hydrology, 9(12), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9120224










