Numerical Simulation of the Effect of Different Footwear Midsole Structures on Plantar Pressure Distribution and Bone Stress in Obese and Healthy Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
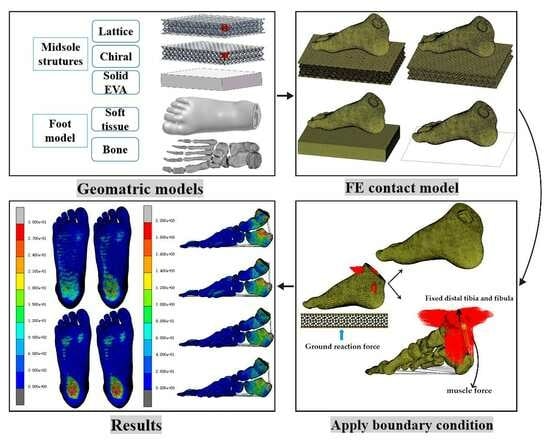
2. Materials and Methods
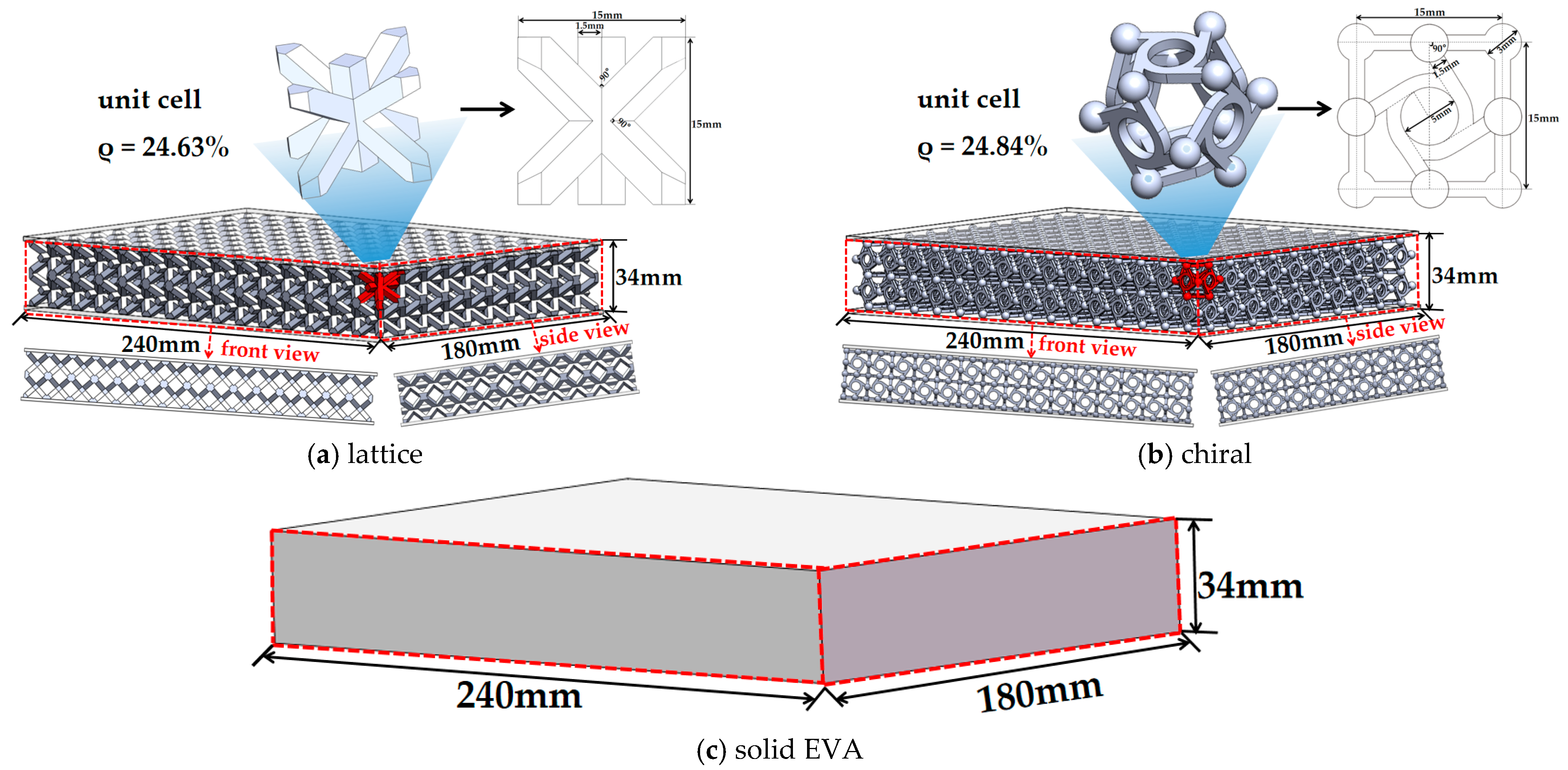
2.1. Structural Design of Midsole
2.1.1. Geometry Model of Midsole
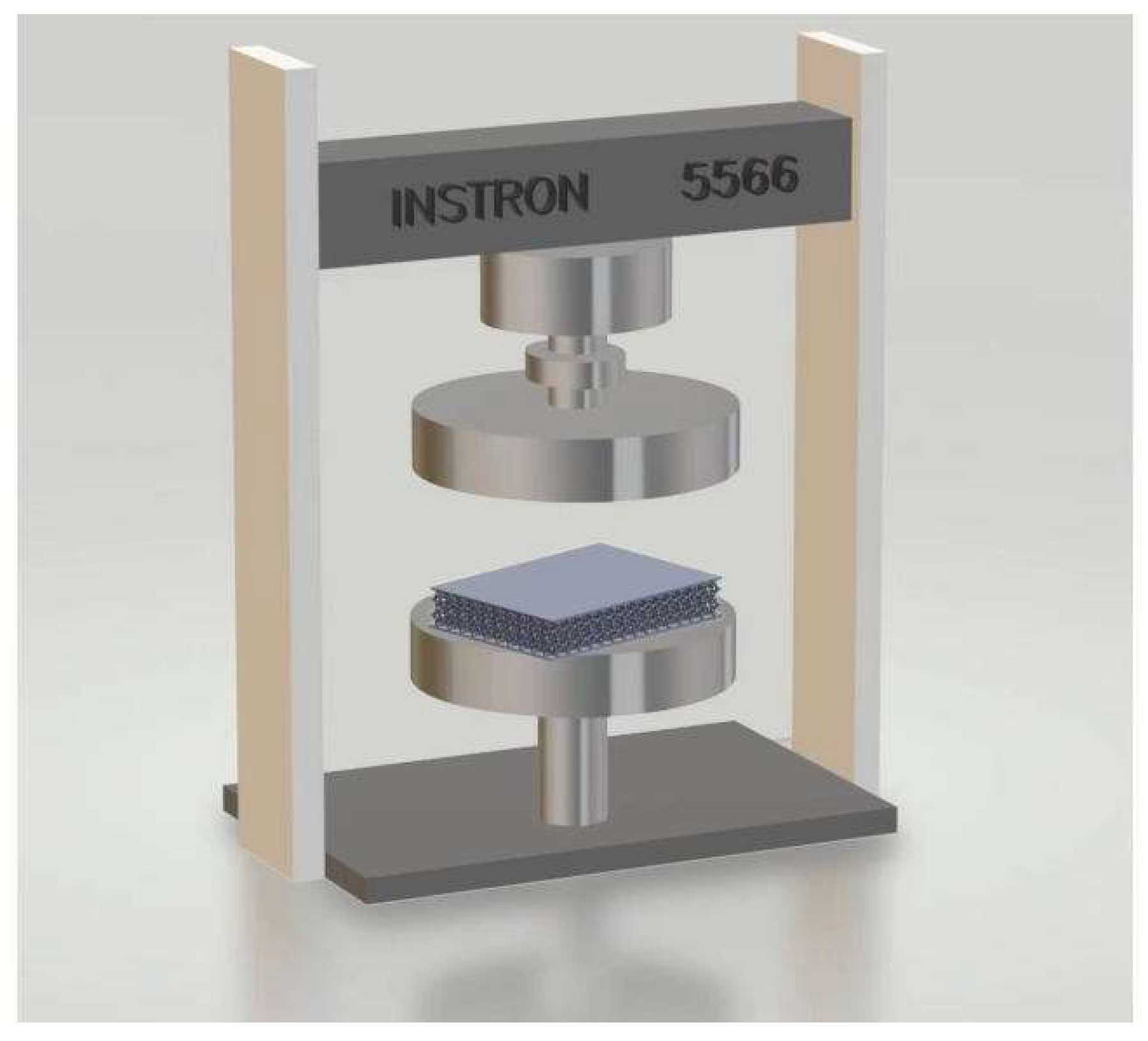
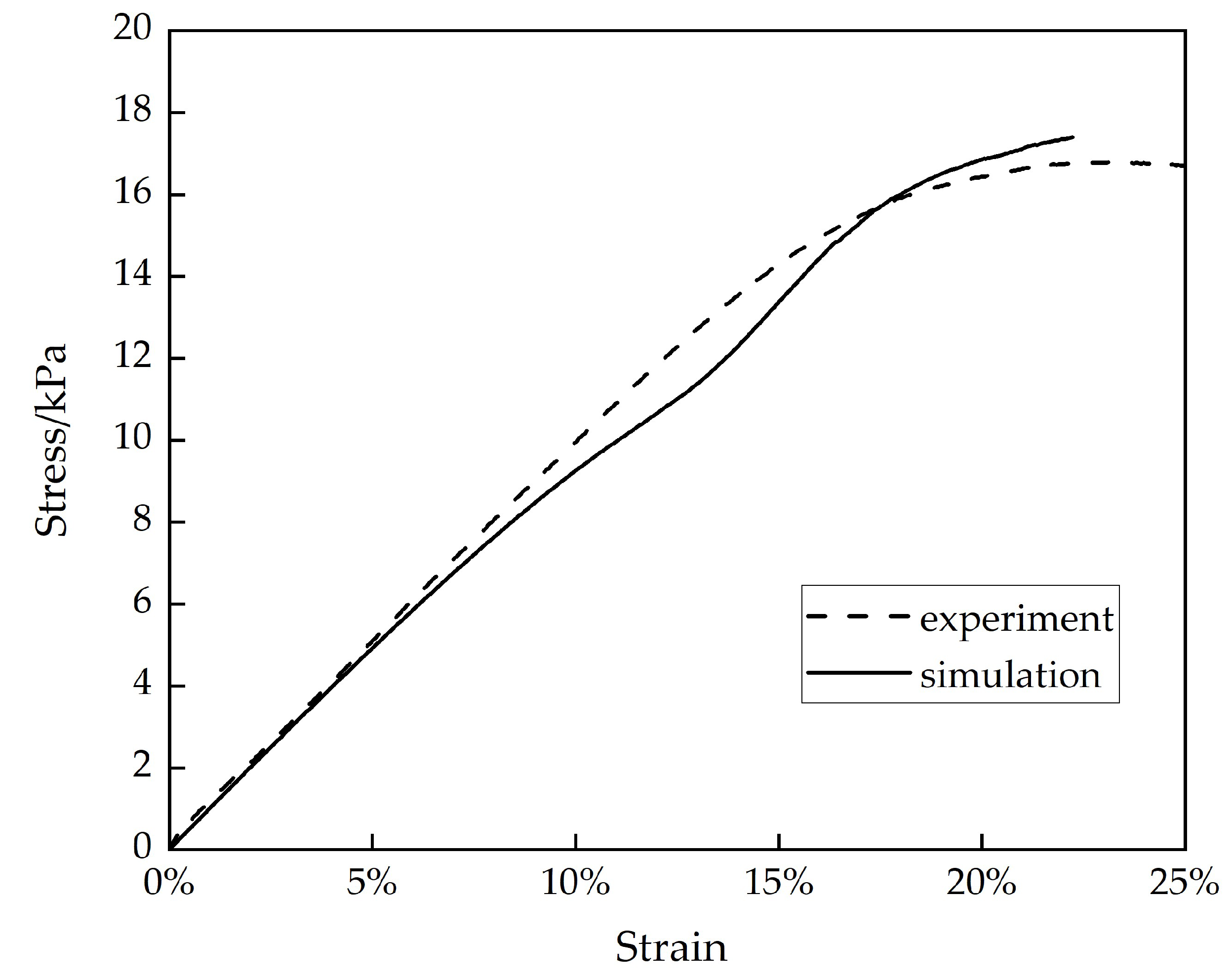
2.1.2. Compressive Behavior and Simulation
2.2. FE Model of Foot Structure
2.2.1. Geometric Modeling
2.2.2. Material Properties
2.2.3. Loading and Boundary Conditions
3. Results
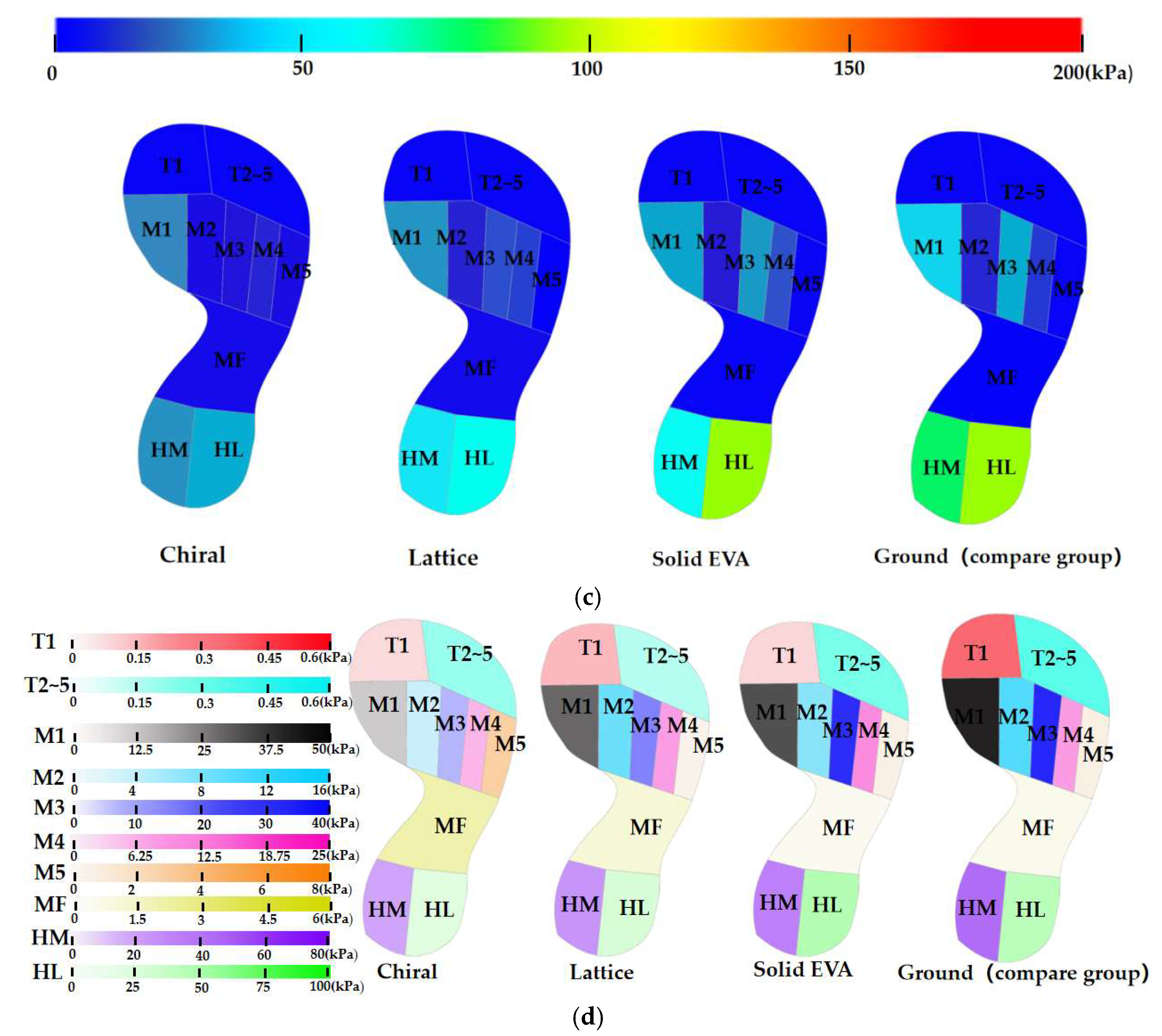
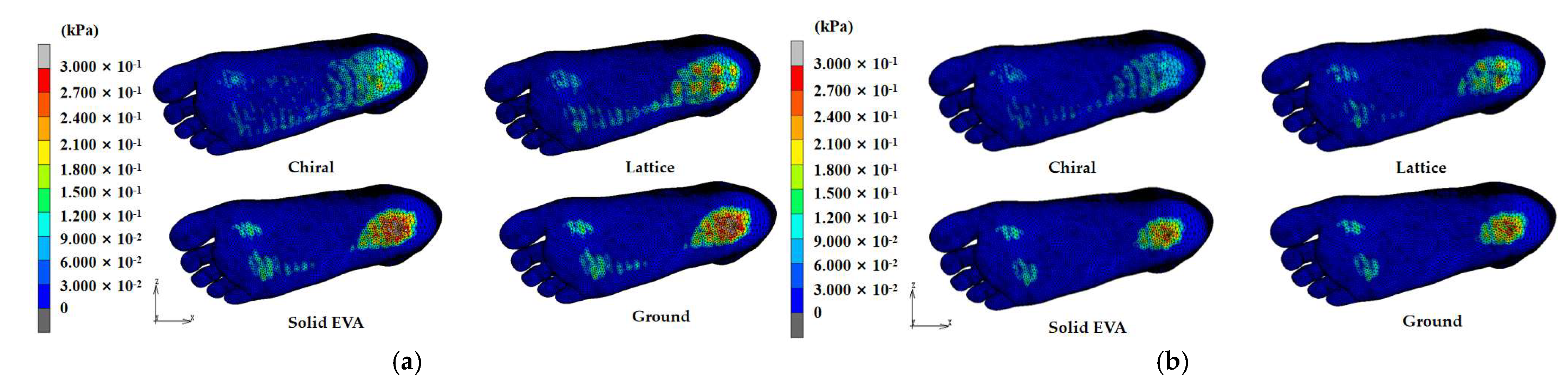
3.1. Distribution of Plantar Pressure
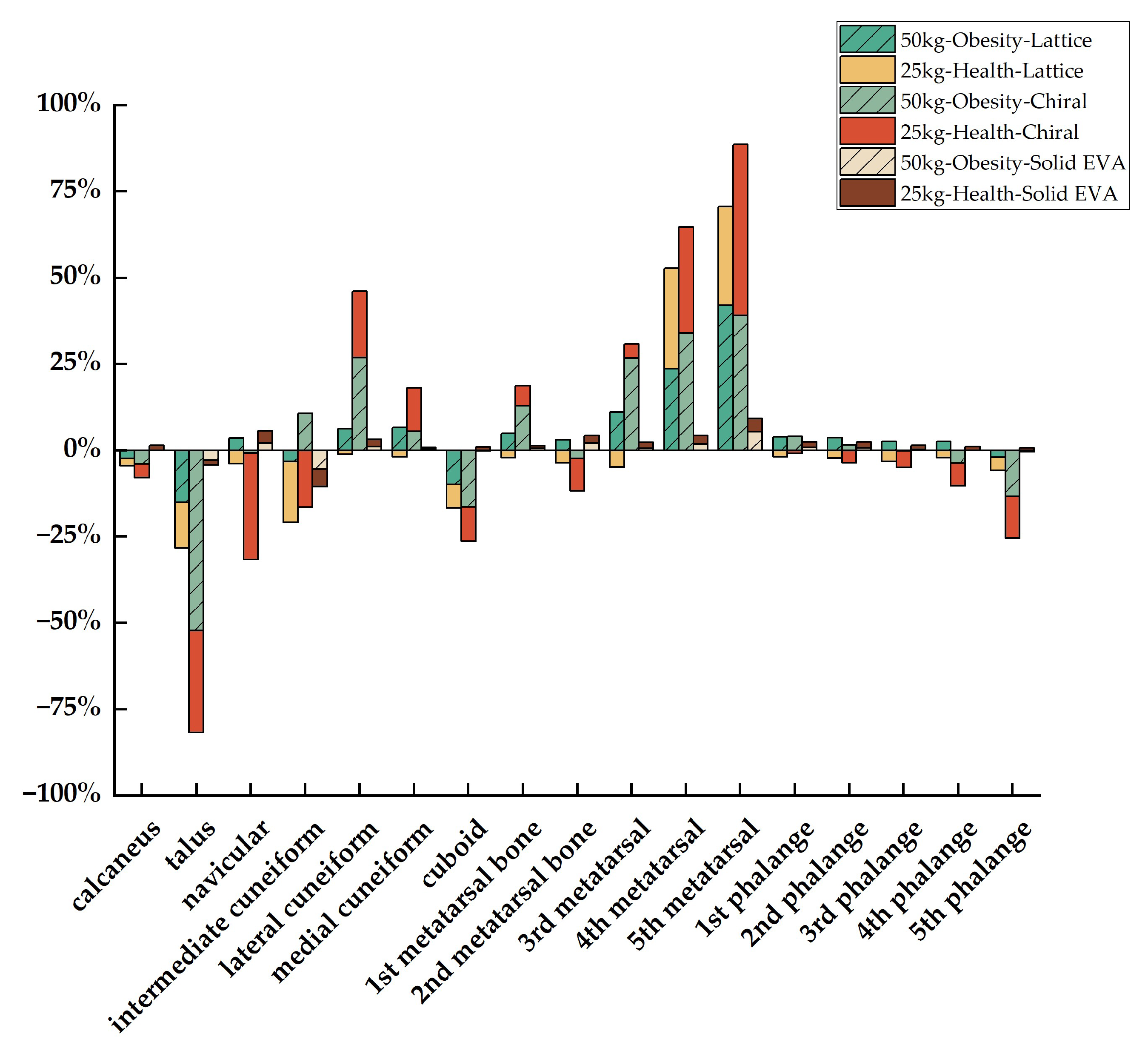
3.2. Stress Distribution of Foot Bone
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Distribution of Plantar Pressure
4.2. Comparison of Stress Distribution of Foot Bone
4.3. Comparison of Obese and Healthy Child
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pacific, R.; Martin, H.D.; Kulwa, K.; Petrucka, P. Contribution of Home and School Environment in Children’s Food Choice and Overweight/Obesity Prevalence in African Context: Evidence for Creating Enabling Healthful Food Environment. Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2020, 11, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Tang, Y.; Zou, Y. Integrating High-Intensity Interval Training into a School Setting Improve Body Composition, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Physical Activity in Children with Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Mo, P.K.H.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Cai, W.; Feng, Y.; Niu, Y. Skeletal Muscle Mass Has Stronger Association with the Risk of Hyperuricemia Than Body Fat Mass in Obese Children and Adolescents. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 792234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Otake, Y.; Nakao, S.; Kurokawa, H.; Kosugi, S.; Taniguchi, A.; Soufi, M.; Sato, Y.; Tanaka, Y. 4D-foot analysis on effect of arch support on ankle, subtalar, and talonavicular joint kinematics. J. Orthop. Sci. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Huo, H.; Lu, P.; Luan, Y.; Koga, A.; Liu, J. Analysis of plantar impact characteristics of walking in patients with flatfoot according to basic mechanical features and continuous wavelet transform. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 1058615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarapanich, N.; Wongsiri, S.; Sitthiseripratip, K. Influence of insole slope on bone joint stress, foot bone stress, and foot pressure distribution. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. (SJST) 2019, 41, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lewis, C.L.; Gill, S.V. Effects of obesity and foot arch height on gait mechanics: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, Y.-J. Effectiveness of Shock-Absorbing Insole for High-Heeled Shoes on Gait: Randomized Controlled Trials. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Alsenoy, K.; Ryu, J.H.; Girard, O. No Effect of EVA and TPU Custom Foot Orthoses on Mechanical Asymmetries during Acute Intense Fatigue. Symmetry 2023, 15, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggoro, P.; Bawono, B.; Jamari, J.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Bayuseno, A. Advanced design and manufacturing of custom orthotics insoles based on hybrid Taguchi-response surface method. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Bader, D.L.; Moser, D.; Parker, D.J.; Forghany, S.; Nester, C.J.; Jiang, L. A Wearable Insole System to Measure Plantar Pressure and Shear for People with Diabetes. Sensors 2023, 23, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, M.S.-H.; Yick, K.-L.; Sun, Y.; Chow, L.; Ng, S.-P. 3D printed auxetic heel pads for patients with diabetic mellitus. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 146, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, R.R.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K.; Brandon, S.C.E. Effect of Simulated Mass-Tunable Auxetic Midsole on Vertical Ground Reaction Force. J. Biomech. Eng. 2022, 144, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, G.; Collet, M.; Demore, F.; Eidel, B.; Neff, P.; Madeo, A. Exploring Metamaterials’ Structures through the Relaxed Micromorphic Model: Switching an Acoustic Screen into an Acoustic Absorber. Front. Mater. 2021, 7, 589701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, V.; Gastaldi, L.; Rosso, V.; Knaflitz, M.; Tadano, S. A Wearable Magneto-Inertial System for Gait Analysis (H-Gait): Validation on Normal Weight and Overweight/Obese Young Healthy Adults. Sensors 2017, 17, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lockhart, T.E.; Yeoh, H.T. Effects of obesity on slip-induced fall risks among young male adults. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.A.O.; Santos-Pontelli, T.E.; Vilaça, K.H.; Pfrimer, K.; Colafêmina, J.F.; Carneiro, A.A.O.; Ferriolli, E. Obese elderly women exhibit low postural stability: A novel three-dimensional evaluation system. Clinics 2012, 67, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramonti, C.; Iacopi, E.; Cafalli, M.; Riitano, N.; Piaggesi, A.; Chisari, C. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: The synergistic effects on human locomotor function. Clin. Biomech. 2022, 100, 105759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirgamanathan, B.; Silva, P.; Fernandez, J. Does obesity affect the biomechanics of the foot? A preliminary computational and experimental study. In Proceedings of the 2017 Moratuwa Engineering Research Conference (MERCon), Moratuwa, Sri Lanka, 29–31 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirgamanathan, B.; Silva, P.; Fernandez, J. Implication of obesity on motion, posture and internal stress of the foot: An experimental and finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 22, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, M.; Arshi, A.; Salehi, M.; Akrami, M.; Naemi, R. Associations between changes in loading pattern, deformity, and internal stresses at the foot with hammer toe during walking; a finite element approach. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yue, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, X.; Hao, Y.; Lu, Y. Analysis of transient response of the human foot based on the finite element method. Technol. Health Care 2022, 30, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, A.; Luboz, V.; Bucki, M.; Vuillerme, N.; Payan, Y. Conception and evaluation of a 3D musculoskeletal finite element foot model. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 18 (Suppl. 1), 2024–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaragavan, E.; Gopal, T.V. Biomechanical Modeling of Human Foot using Finite Element Methods. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Lin, J.; Xu, X.; Ma, Z.; Tang, L.; Sun, C.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L. Design and 3D printing of adjustable modulus porous structures for customized diabetic foot insoles. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2019, 2, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, T.; Pang, H.; Meng, X.; Zhou, F. Study on Design and Additive Manufacturing of Customized Bionic Sports Sole for the Elderly. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 69830–69838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhou, S.-Y.; Hsu, C.-C.; Yeh, J.-C. The Dynamic Impact Response of 3D-Printed Polymeric Sandwich Structures with Lattice Cores: Numerical and Experimental Investigation. Polymers 2021, 13, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Leong, K.; Gu, Y. Construction and finite element analysis of a coupled finite element model of foot and barefoot running footwear. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part P J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2019, 233, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Tessier, D.; Zhao, Y.F. Design of Shoe Soles Using Lattice Structures Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the Design Society: International Conference on Engineering Design, Bordeaux, France, 24–28 July 2023; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Dong, G.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Q. Data-Driven Design of Customized Porous Lattice Sole Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2021, 53, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malisoux, L.; Gette, P.; Backes, A.; Delattre, N.; Cabri, J.; Theisen, D. Relevance of Frequency-Domain Analyses to Relate Shoe Cushioning, Ground Impact Forces and Running Injury Risk: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Trial with 800+ Recreational Runners. Front. Sports Act. Living 2021, 3, 744658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almesmari, A.; Sheikh-Ahmad, J.; Jarrar, F.; Bojanampati, S. Optimizing the specific mechanical properties of lattice structures fabricated by material extrusion additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 1821–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D575-91; Standard Test Methods for Rubber Properties in Compression. ASTM Committee: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- Balaji, V.; Rajesh, D.; Nachippan, N.M.; Maridurai, T.; Sathish, T.; Balakrishnan, E. Finite element analysis of a human foot. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 4265–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
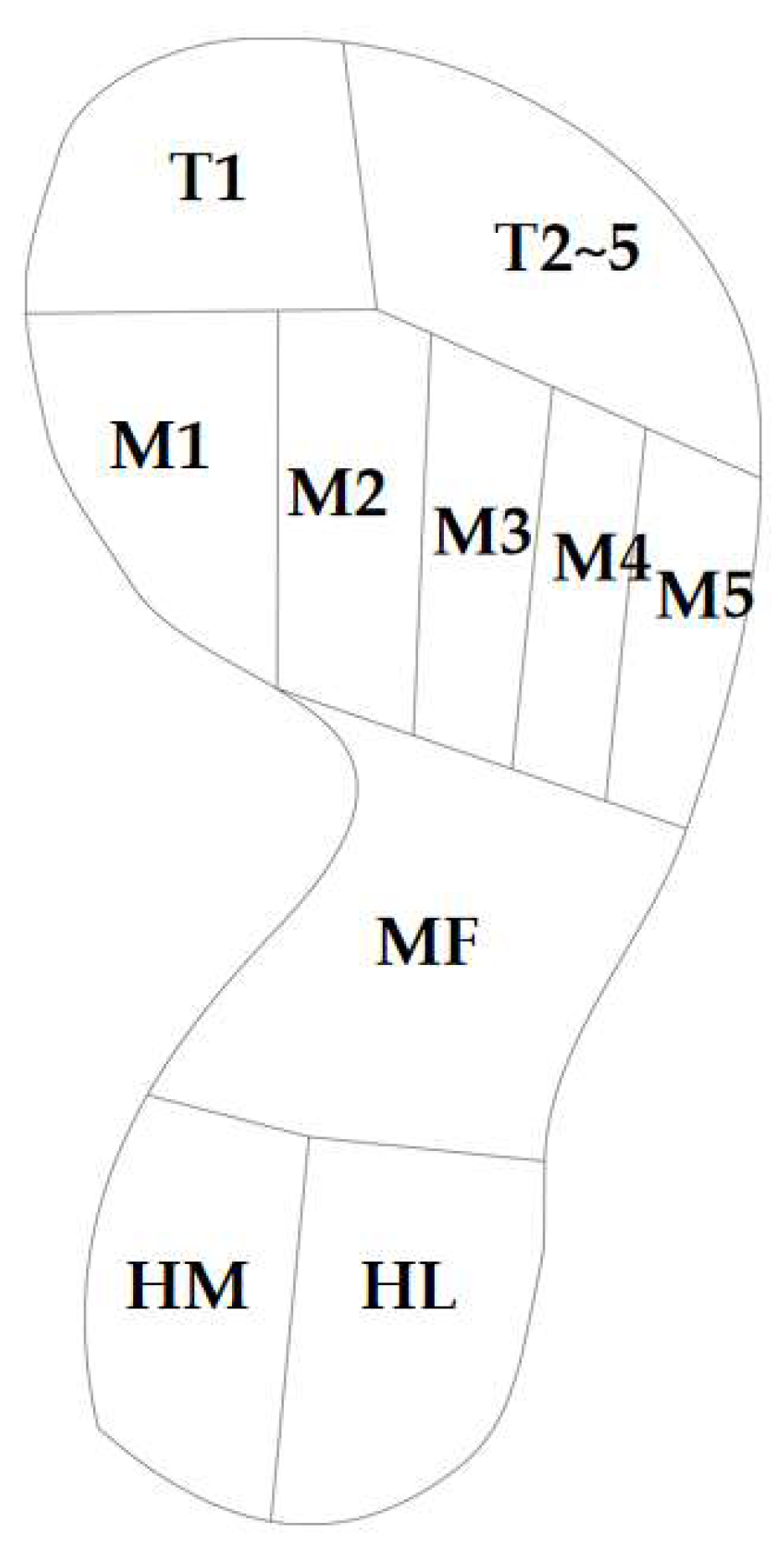
- Lian, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Li, J. An Improved Plantar Regional Division Algorithm for Aided Diagnosis of Early Diabetic Foot. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 2057006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RSanchis-Sanchis, R.; Blasco-Lafarga, C.; Encarnación-Martínez, A.; Pérez-Soriano, P. Changes in plantar pressure and spatiotemporal parameters during gait in older adults after two different training programs. Gait Posture 2020, 77, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Ning, B. Gait Recognition Based on the Plantar Pressure Data of Ice and Snow Athletes. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2982894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselbacher, M.; Mader, K.; Werner, M.; Nogler, M. Effect of Ski Mountaineering Track on Foot Sole Loading Pattern. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2014, 25, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
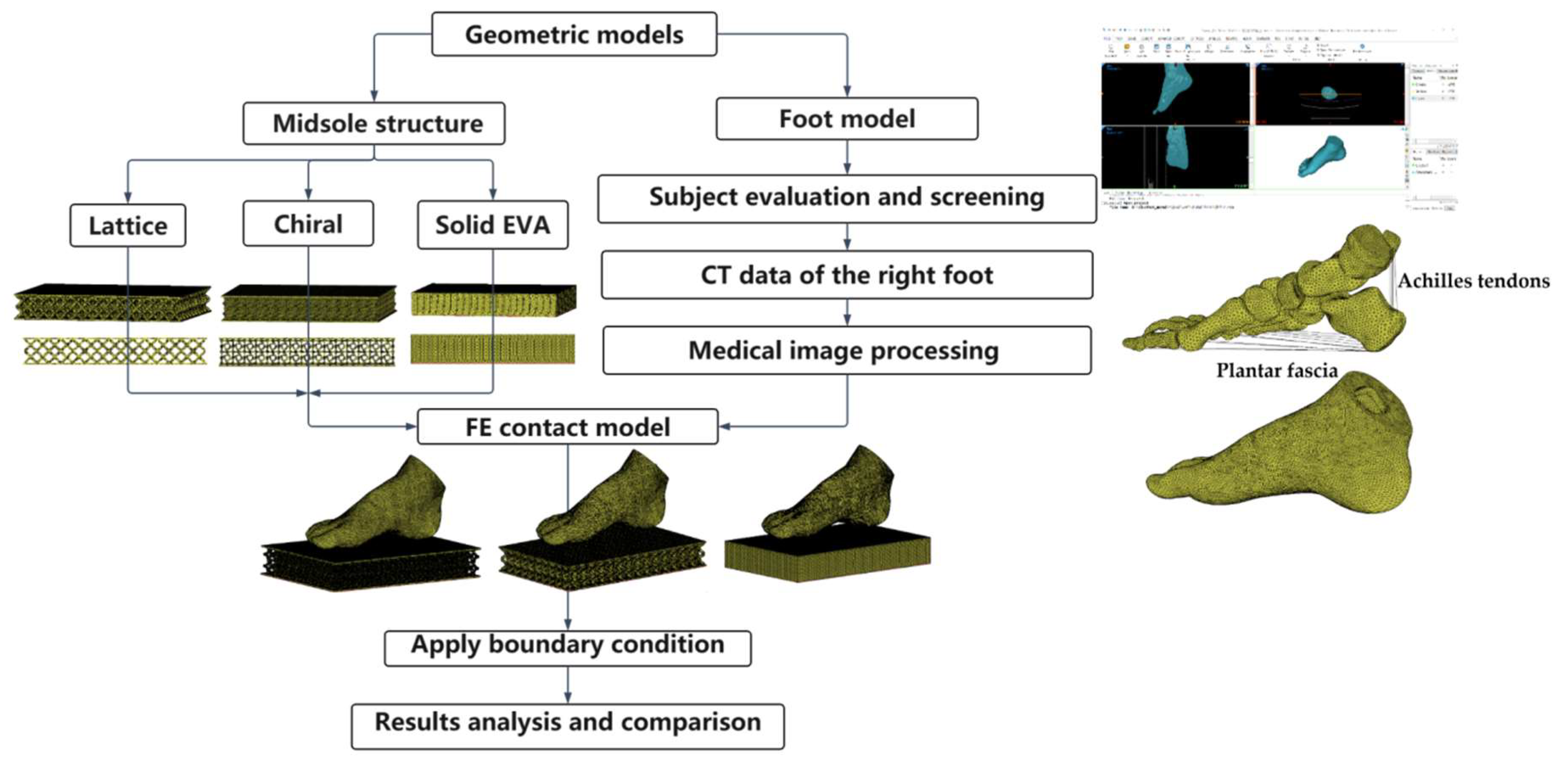




| Part | Element Type | Meshing Size (mm) | Element Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone | 3D Tetrahedral | 1.5 | 107,545 |
| Soft tissue | 3D Tetrahedral | 1.5 | 478,783 |
| Plantar fascia | Line element | 2 | 10 |
| Achilles tendons | Line element | 2 | 4 |
| Component | Material Type | E (MPa) | ν |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soft tissue | Linear elasticity | 0.45 | 0.49 |
| Bone | Linear elasticity | 7300 | 0.3 |
| Lattice/Chiral | Linear elasticity | 8.9 | 0.33 |
| Achilles tendon | Linear elasticity | 816 | 0.3 |
| Plantar fascia | Linear elasticity | 3.5 | 0.4 |
| Ground | Linear elasticity | 210,000 | 0.3 |
| Solid EVA | Foam | μ1 = 2.13, μ2 = −1.012, α1 = 11.95, α2 = −6.06, β1 = 0, β2 = 0 | |
| Pr of MPP/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 kg Obese Child | 25 kg Healthy Child | |||||
| Lattice | Chiral | Solid EVA | Lattice | Chiral | Solid EVA | |
| HF | 43.73% | 54.55% | 13.49% | 50.53% | 57.87% | 32.03% |
| T1 | 59.10% | 64.54% | 52.48% | 56.89% | 72.13% | 67.21% |
| T2~5 | 55.55% | 36.25% | 17.83% | 50.06% | 41.72% | 21.28% |
| M1 | 26.50% | 38.69% | −2.73% | 29.42% | 33.99% | 19.97% |
| M2 | 12.10% | 44.24% | 29.14% | 7.10% | 57.62% | 25.15% |
| M3 | 29.27% | 72.70% | 0.14% | 44.44% | 78.94% | 8.68% |
| M4 | −7.16% | 34.25% | −37.41% | −15.97% | 28.25% | −27.88% |
| M5 | 62.27% | −196.41% | 42.62% | 57.06% | −171.03% | −7.61% |
| MF | −109.58% | −172.98% | 46.81% | −99.18% | −369.73% | 8.04% |
| HM | 24.04% | 64.24% | 4.07% | 37.12% | 56.08% | 21.66% |
| HL | 36.88% | 54.03% | −4.17% | 35.14% | 56.96% | −2.63% |
| Mean Plantar Pressure/kPa | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 kg Obese Child | 25 kg Healthy Child | |||||||
| Lattice | Chiral | Solid EVA | Ground | Lattice | Chiral | Solid EVA | Ground | |
| HF | 50.07 | 40.44 | 76.97 | 88.97 | 22.58 | 19.23 | 31.02 | 45.64 |
| T1 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.49 | 1.02 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.61 |
| T2~5 | 0.51 | 0.73 | 0.94 | 1.14 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.46 | 0.59 |
| M1 | 42.73 | 35.64 | 59.71 | 58.13 | 34.44 | 32.21 | 39.06 | 48.80 |
| M2 | 14.86 | 9.42 | 11.98 | 16.90 | 12.24 | 5.59 | 9.87 | 13.18 |
| M3 | 36.48 | 14.08 | 51.50 | 51.58 | 22.12 | 8.38 | 36.35 | 39.81 |
| M4 | 38.78 | 23.80 | 49.73 | 36.19 | 20.97 | 12.98 | 23.13 | 18.09 |
| M5 | 2.29 | 17.99 | 3.48 | 6.07 | 1.11 | 6.99 | 2.78 | 2.58 |
| MF | 11.66 | 15.19 | 2.96 | 5.56 | 2.30 | 5.42 | 1.06 | 1.15 |
| HM | 116.34 | 54.77 | 146.91 | 153.15 | 50.10 | 35.00 | 62.42 | 79.68 |
| HL | 108.74 | 79.19 | 179.47 | 172.28 | 61.29 | 40.67 | 96.98 | 94.49 |
| Maximum Von Mises Stress/kPa | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 kg Obese Child | 25 kg Healthy Child | |||||||
| Lattice | Chiral | Solid EVA | Ground | Lattice | Chiral | Solid EVA | Ground | |
| Calcaneus | 5788 | 5885 | 5656 | 5656 | 3018 | 3068 | 2912 | 2956 |
| Talus | 2512 | 3322 | 2246 | 2183 | 1259 | 1441 | 1127 | 1112 |
| Navicular | 1043 | 1089 | 1059 | 1081 | 559 | 704 | 518 | 538 |
| Intermediate cuneiform | 867 | 750 | 886 | 840 | 532 | 526 | 475 | 452 |
| Lateral cuneiform | 537 | 419 | 567 | 573 | 290 | 232 | 281 | 287 |
| Medial cuneiform | 367 | 371 | 391 | 393 | 285 | 245 | 279 | 280 |
| Cuboid | 879 | 931 | 801 | 800 | 430 | 443 | 399 | 403 |
| 1st metatarsal bone | 343 | 314 | 359 | 361 | 254 | 235 | 247 | 249 |
| 2nd metatarsal bone | 1030 | 1087 | 1040 | 1062 | 518 | 547 | 489 | 500 |
| 3rd metatarsal | 974 | 801 | 1088 | 1095 | 582 | 533 | 546 | 555 |
| 4th metatarsal | 423 | 365 | 544 | 554 | 266 | 260 | 366 | 375 |
| 5th metatarsal | 169 | 178 | 276 | 292 | 170 | 120 | 229 | 238 |
| 1st phalange | 604 | 603 | 623 | 628 | 385 | 381 | 372 | 378 |
| 2nd phalange | 1369 | 1399 | 1410 | 1421 | 856 | 868 | 824 | 838 |
| 3rd phalange | 1454 | 1493 | 1489 | 1492 | 898 | 913 | 859 | 870 |
| 4th phalange | 1633 | 1738 | 1676 | 1676 | 991 | 1035 | 960 | 971 |
| 5th phalange | 894 | 994 | 880 | 877 | 533 | 575 | 509 | 513 |
| Pr of MVSS/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 kg Obese Child | 25 kg Healthy Child | |||||
| Lattice | Chiral | Solid EVA | Lattice | Chiral | Solid EVA | |
| Calcaneus | −2.33% | −4.05% | 0.00% | −2.10% | −3.79% | 1.49% |
| Talus | −15.07% | −52.18% | −2.89% | −13.22% | −29.59% | −1.35% |
| Navicular | 3.52% | −0.74% | 2.04% | −3.90% | −30.86% | 3.72% |
| Intermediate cuneiform | −3.21% | 10.71% | −5.48% | −17.70% | −16.37% | −5.09% |
| Lateral cuneiform | 6.28% | 26.88% | 1.05% | −1.05% | 19.16% | 2.09% |
| Medial cuneiform | 6.62% | 5.60% | 0.51% | −1.79% | 12.50% | 0.36% |
| Cuboid | −9.88% | −16.38% | −0.13% | −6.70% | −9.93% | 0.99% |
| 1st metatarsal bone | 4.99% | 13.02% | 0.55% | −2.01% | 5.62% | 0.80% |
| 2nd metatarsal bone | 3.01% | −2.35% | 2.07% | −3.60% | −9.40% | 2.20% |
| 3rd metatarsal | 11.05% | 26.85% | 0.64% | −4.86% | 3.96% | 1.62% |
| 4th metatarsal | 23.65% | 34.12% | 1.81% | 29.07% | 30.67% | 2.40% |
| 5th metatarsal | 42.12% | 39.04% | 5.48% | 28.57% | 49.58% | 3.78% |
| 1st phalange | 3.82% | 3.98% | 0.80% | −1.85% | −0.79% | 1.59% |
| 2nd phalange | 3.66% | 1.55% | 0.77% | −2.15% | −3.58% | 1.67% |
| 3rd phalange | 2.55% | −0.07% | 0.20% | −3.22% | −4.94% | 1.26% |
| 4th phalange | 2.57% | −3.70% | 0.00% | −2.06% | −6.59% | 1.13% |
| 5th phalange | −1.94% | −13.34% | −0.34% | −3.90% | −12.09% | 0.78% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.; Niu, W.; Yick, K.-L.; Gu, B.; Sun, Y. Numerical Simulation of the Effect of Different Footwear Midsole Structures on Plantar Pressure Distribution and Bone Stress in Obese and Healthy Children. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111306
Zhou Q, Niu W, Yick K-L, Gu B, Sun Y. Numerical Simulation of the Effect of Different Footwear Midsole Structures on Plantar Pressure Distribution and Bone Stress in Obese and Healthy Children. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(11):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111306
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qixuan, Wenxin Niu, Kit-Lun Yick, Bingfei Gu, and Yue Sun. 2023. "Numerical Simulation of the Effect of Different Footwear Midsole Structures on Plantar Pressure Distribution and Bone Stress in Obese and Healthy Children" Bioengineering 10, no. 11: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111306
APA StyleZhou, Q., Niu, W., Yick, K.-L., Gu, B., & Sun, Y. (2023). Numerical Simulation of the Effect of Different Footwear Midsole Structures on Plantar Pressure Distribution and Bone Stress in Obese and Healthy Children. Bioengineering, 10(11), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111306