Cascade of Denoising and Mapping Neural Networks for MRI R2* Relaxometry of Iron-Loaded Liver
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Datasets
2.2. Simulation Datasets
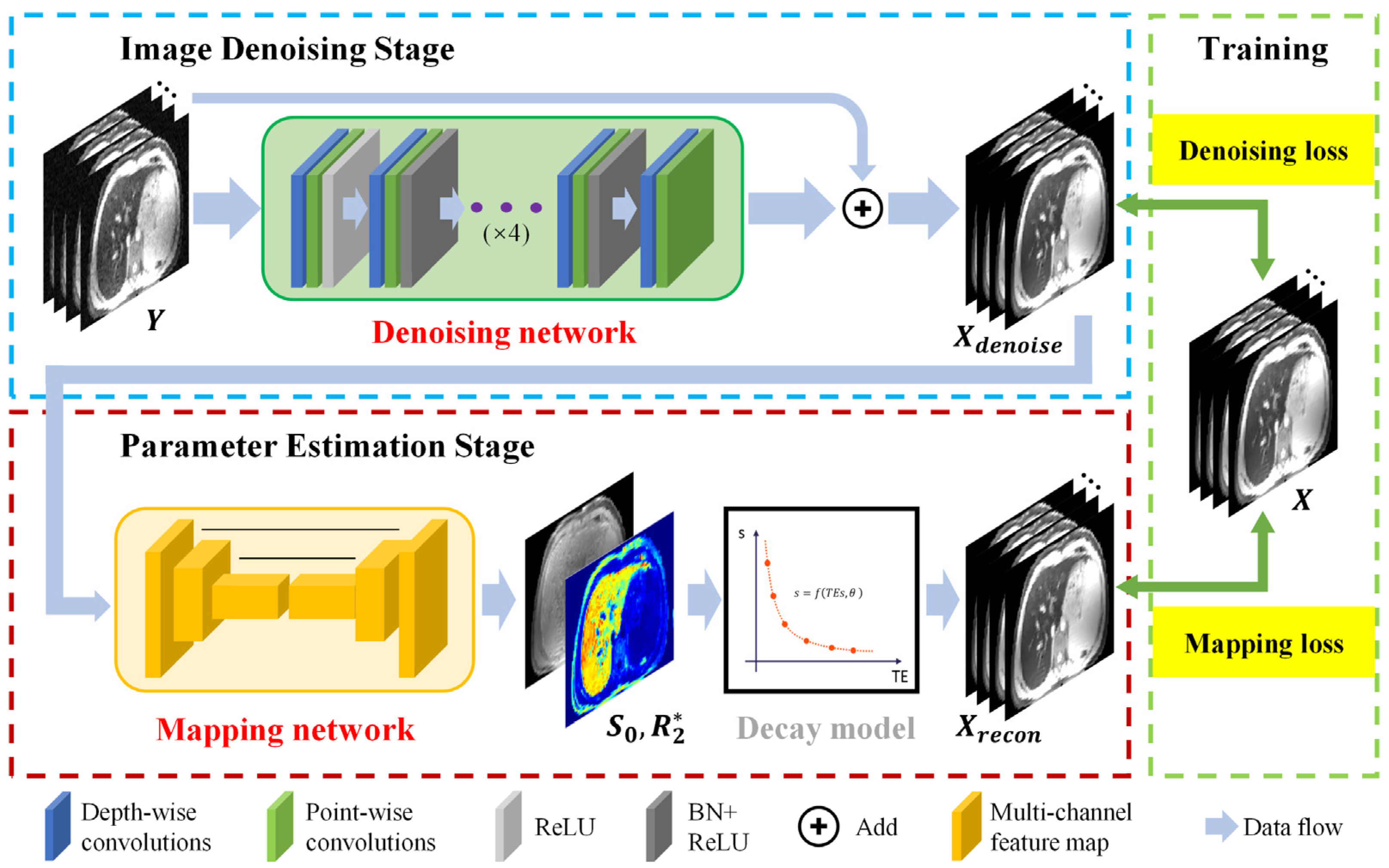
2.3. CadamNet Framework
2.4. Network Training
2.5. Evaluation Metrics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Simulated Results
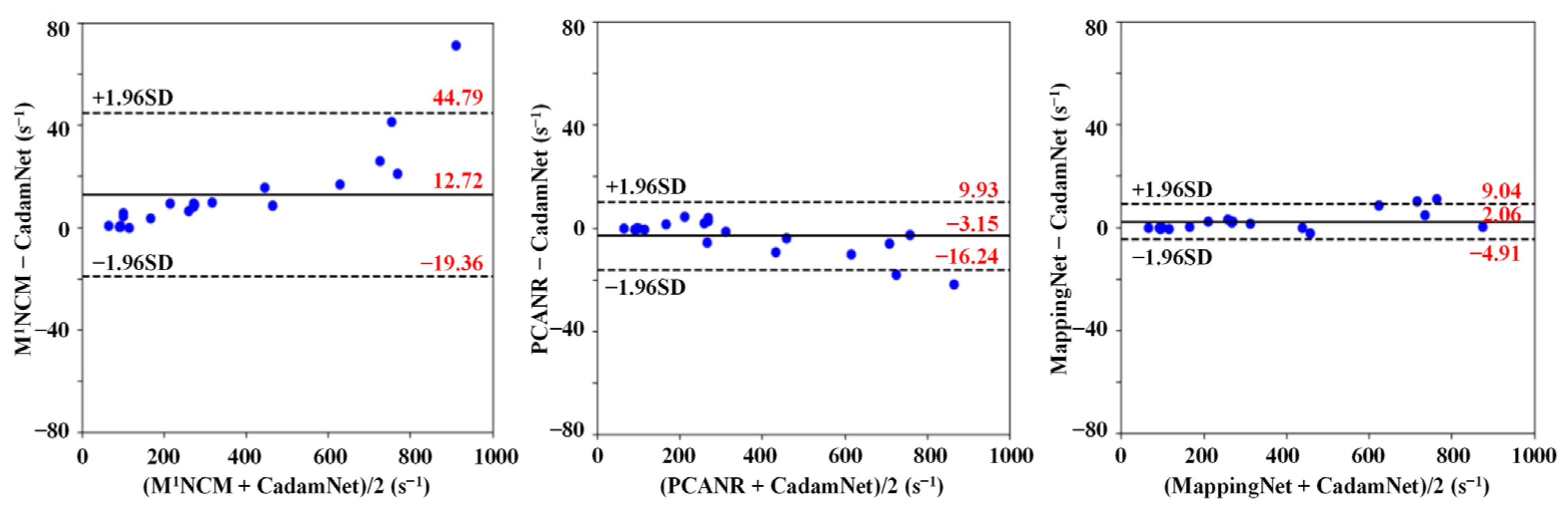
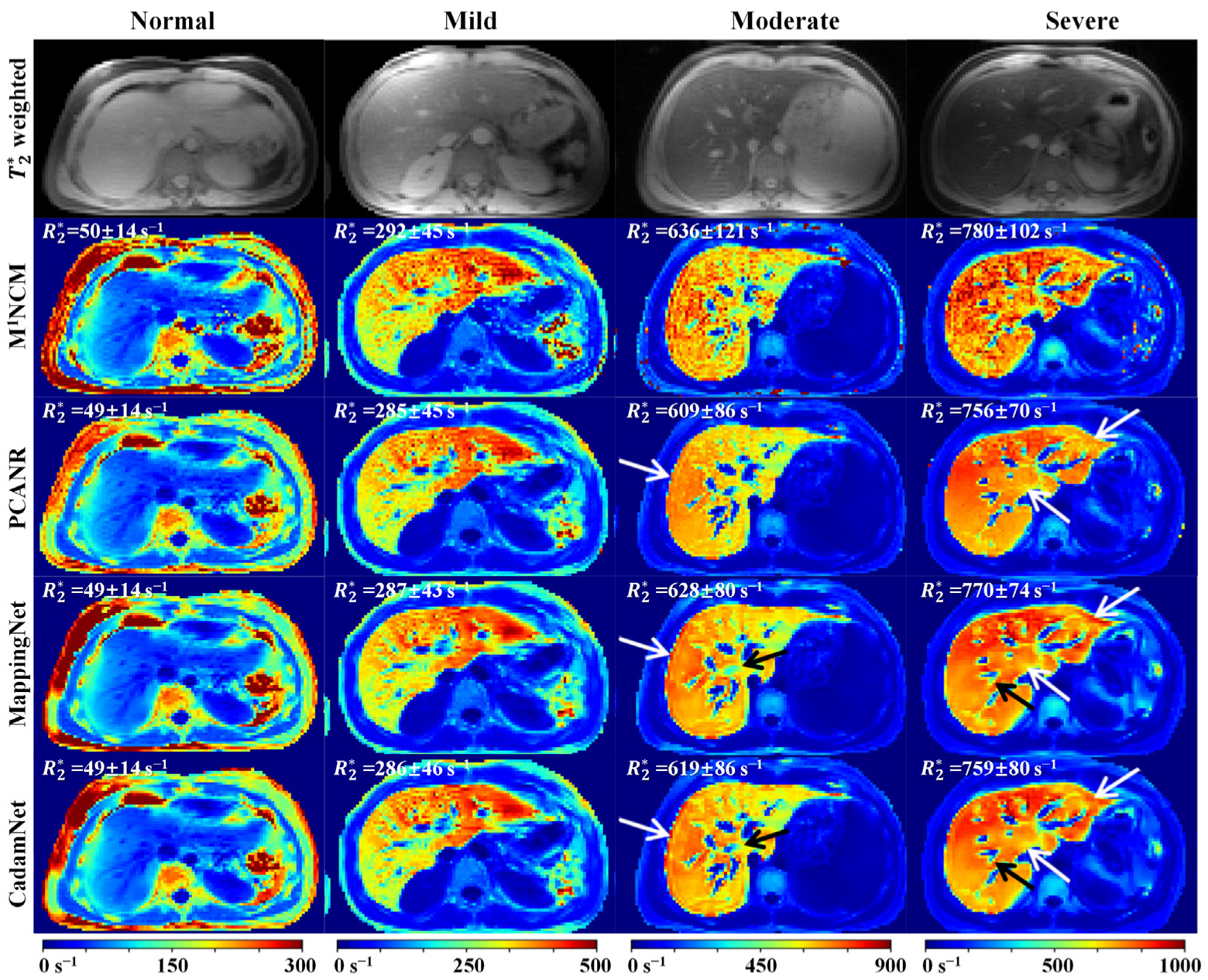
3.2. Clinical Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Labranche, R.; Gilbert, G.; Cerny, M.; Vu, K.N.; Soulières, D.; Olivié, D.; Billiard, J.S.; Yokoo, T.; Tang, A. Liver Iron Quantification with MR Imaging: A Primer for Radiologists. Radiographics 2018, 38, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev, A.; Berho, M.; Jeffers, L.J.; Milikowski, C.; Molina, E.G.; Pyrsopoulos, N.T.; Feng, Z.Z.; Reddy, K.R.; Schiff, E.R. Sampling Error and Intraobserver Variation in Liver Biopsy in Patients with Chronic HCV Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2614–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockey, D.C.; Caldwell, S.H.; Goodman, Z.D.; Nelson, R.C.; Smith, A.D. Liver Biopsy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1017–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.C.; Enriquez, C.; Ghugre, N.; Tyzka, J.M.; Carson, S.; Nelson, M.D.; Coates, T.D. MRI R2 and R2* Mapping Accurately Estimates Hepatic Iron Concentration in Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Disease Patients. Blood 2005, 106, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, J.H.; Akkerman, E.M.; Troelstra, M.A.; Nederveen, A.J.; Beuers, U.; Stoker, J. Comparison of Clinical MRI Liver Iron Content Measurements Using Signal Intensity Ratios, R2 and R2*. Abdom. Radiol. 2016, 41, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, P.; He, T.; Anderson, L.J.; Roughton, M.; Tanner, M.A.; Lam, W.W.M.; Au, W.Y.; Chu, W.C.W.; Chan, G.; Galanello, R.; et al. International Reproducibility of Single Breathhold T2* MR for Cardiac and Liver Iron Assessment among Five Thalassemia Centers. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 32, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, A.; Zmyewski, H.; Rienhoff, H.Y.; Jones, A.; Pepe, A.; Lombardi, M.; Wood, J.C. Fast Approximation to Pixelwise Relaxivity Maps: Validation in Iron Overloaded Subjects. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaikner, M.; Kremser, C.; Zoller, H.; Jaschke, W.; Steurer, M.; Viveiros, A.; Henninger, B. Evaluation of Liver Iron Overload with R2* Relaxometry with versus without Fat Suppression: Both Are Clinically Accurate but There Are Differences. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 5826–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Wood, J.; Manwani, D.; Taragin, B.; Oyeku, S.O.; Peng, Q. Hepatic Iron Quantification on 3 Tesla (3 T) Magnetic Resonance (MR): Technical Challenges and Solutions. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 628150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, C.D.; Atalar, E.; McVeigh, E.R. Signal-to-Noise Measurements in Magnitude Images from NMR Phased Arrays. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 38, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; He, T.; Gatehouse, P.D.; Li, X.; Harith Alam, M.; Pennell, D.J.; Chen, W.; Firmin, D.N. Improved MRI R2* Relaxometry of Iron-Loaded Liver with Noise Correction. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Shah, S.; Katsaggelos, A.K.; Larson, A.C. Improved R2* Measurement Accuracy with Absolute SNR Truncation and Optimal Coil Combination. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Pierre, T.G.; Clark, P.R.; Chua-anusorn, W. Single Spin-Echo Proton Transverse Relaxometry of Iron-Loaded Liver. NMR Biomed. 2004, 17, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; He, T.; Chen, W.; Feng, Q.; Feng, Y. Improved Liver R2* Mapping by Pixel-Wise Curve Fitting with Adaptive Neighborhood Regularization. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Kramer, C.M.; Salerno, M.; Weller, D.S. A Myocardial T1-Mapping Framework with Recurrent and U-Net Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020; pp. 1941–1944. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Kijowski, R.; El Fakhri, G.; Feng, L. Magnetic Resonance Parameter Mapping Using Model-guided Self-supervised Deep Learning. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 3211–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Feng, L.; Kijowski, R. MANTIS: Model-Augmented Neural Network with Incoherent k-Space Sampling for Efficient MR Parameter Mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Kijowski, R.; Feng, L.; El Fakhri, G. High-Performance Rapid MR Parameter Mapping Using Model-Based Deep Adversarial Learning. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 74, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torop, M.; Kothapalli, S.V.V.N.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Kahali, S.; Yablonskiy, D.A.; Kamilov, U.S. Deep Learning Using a Biophysical Model for Robust and Accelerated Reconstruction of Quantitative, Artifact-Free and Denoised R2* Images. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 2932–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, N.; Sidike, P.; Elkin, C.; Devabhaktuni, V. U-Net and Its Variants for Medical Image Segmentation: Theory and Applications. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.01118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antun, V.; Renna, F.; Poon, C.; Adcock, B.; Hansen, A.C. On Instabilities of Deep Learning in Image Reconstruction and the Potential Costs of AI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 30088–30095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a Gaussian Denoiser: Residual Learning of Deep CNN for Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, M.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Denoising of 3D Magnetic Resonance Images Using a Residual Encoder–Decoder Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 55, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.M. A Review of Image Denoising Algorithms, with a New One. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2005, 4, 490–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhang, J.; Carpenter, J.P.; Feng, Y.; Smith, G.C.; Pennell, D.J.; Firmin, D.N. Automated Truncation Method for Myocardial T2* Measurement in Thalassemia. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image Super-Resolution Using Deep Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, R.; Itasaka, T.; Okuda, M. Zero-Shot Hyperspectral Image Denoising With Separable Image Prior. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1416–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. ISBN 9783319245737. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, T.; Liu, X.; Zhong, S.; Chen, W.; Feng, Y. Rapid Look-up Table Method for Noise-Corrected Curve Fitting in the R2∗ Mapping of Iron Loaded Liver. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Ghodrati, V.; Nguyen, K.; Hu, P. Fast and Accurate Calculation of Myocardial T 1 and T 2 Values Using Deep Learning Bloch Equation Simulations (DeepBLESS). Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 2831–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruessmann, K.P.; Weiger, M.; Scheidegger, M.B.; Boesiger, P. SENSE: Sensitivity Encoding for Fast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griswold, M.A.; Jakob, P.M.; Heidemann, R.M.; Nittka, M.; Jellus, V.; Wang, J.; Kiefer, B.; Haase, A. Generalized Autocalibrating Partially Parallel Acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 47, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, D.; Kramer, J.H.; Reeder, S.B. Multipeak Fat-Corrected Complex R2* Relaxometry: Theory, Optimization, and Clinical Validation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henninger, B.; Alustiza, J.; Garbowski, M.; Gandon, Y. Practical Guide to Quantification of Hepatic Iron with MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches-Rocha, L.; Serpa, B.; Figueiredo, E.; Hamerschlak, N.; Baroni, R. Comparison between Multi-Echo T2* with and without Fat Saturation Pulse for Quantification of Liver Iron Overload. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, A.; Michael Tyszka, J.; Pepe, A.; Wood, J.C. Effect of Inversion Recovery Fat Suppression on Hepatic R2∗ Quantitation in Transfusional Siderosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11966–11976. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. ADMM-CSNet: A Deep Learning Approach for Image Compressive Sensing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemper, J.; Caballero, J.; Hajnal, J.V.; Price, A.N.; Rueckert, D. A Deep Cascade of Convolutional Neural Networks for Dynamic MR Image Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.; Shin, H.; Eo, T.; Kim, T.; Hwang, D. Deep Model-Based Magnetic Resonance Parameter Mapping Network (DOPAMINE) for Fast T1 Mapping Using Variable Flip Angle Method. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 70, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Karkalousos, D.; Bazin, P.L.; Coolen, B.F.; Vrenken, H.; Sonke, J.J.; Forstmann, B.U.; Poot, D.H.J.; Caan, M.W.A. A Unified Model for Reconstruction and R2* Mapping of Accelerated 7T Data Using the Quantitative Recurrent Inference Machine. Neuroimage 2022, 264, 119680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Methods | Metrics | σg = 7 (SNR = 30.95) | 9 (SNR = 24.07) | 11 (SNR = 19.71) | 13 (SNR = 16.64) | 15 (SNR = 14.46) | 17 (SNR = 12.70) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1NCM | NRMSE SSIM | 6.15 (4.00) 94.03 (7.46) | 8.49 (6.26) 91.40 (10.14) | 10.55 (7.69) 88.22 (12.32) | 12.86 (9.98) 85.34 (14.66) | 15.30 (12.14) 82.33 (16.66) | 18.03 (13.81) 78.48 (18.71) |
| PCANR | NRMSE SSIM | 5.91 (2.19) 94.55 (4.63) | 7.00 (2.44) 92.68 (5.85) | 7.82 (2.60) 91.12 (6.73) | 8.69 (2.91) 89.18 (8.07) | 9.49 (2.96) 87.81 (8.49) | 10.24 (3.09) 85.91 (9.57) |
| MappingNet | NRMSE SSIM | 4.06 (1.73) 97.40 (3.19) | 4.87 (2.00) 96.35 (3.47) | 5.71 (2.21) 95.50 (3.97) | 6.35 (2.36) 94.63 (4.28) | 6.96 (2.56) 93.53 (5.21) | 8.50 (2.49) 92.40 (5.96) |
| CadamNet | NRMSE SSIM | 3.96 (1.66) 97.60 (2.33) | 4.73 (1.87) 96.64 (3.16) | 5.34 (2.02) 96.05 (3.29) | 6.00 (2.21) 95.00 (3.86) | 6.69 (2.39) 94.03 (4.82) | 7.25 (2.50) 93.09 (5.30) |
| MappingNet-m | NRMSE SSIM | 4.20 (1.88) 97.26 (2.78) | 4.93 (2.04) 96.29 (3.61) | 5.60 (2.23) 95.49 (4.05) | 6.25 (2.31) 94.60 (4.50) | 6.97 (2.50) 93.46 (5.31) | 7.57 (2.73) 92.19 (6.33) |
| CadamNet-m | NRMSE SSIM | 4.06 (1.76) 97.48 (2.41) | 4.77 (1.98) 96.55 (3.23) | 5.43 (2.11) 95.79 (3.66) | 6.05 (2.20) 95.02 (3.96) | 6.68 (2.36) 94.05 (4.64) | 7.22 (2.51) 93.00 (5.34) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Q.; Wang, C.; Lian, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Feng, Q.; Feng, Y. Cascade of Denoising and Mapping Neural Networks for MRI R2* Relaxometry of Iron-Loaded Liver. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020209
Lu Q, Wang C, Lian Z, Zhang X, Yang W, Feng Q, Feng Y. Cascade of Denoising and Mapping Neural Networks for MRI R2* Relaxometry of Iron-Loaded Liver. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(2):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020209
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Qiqi, Changqing Wang, Zifeng Lian, Xinyuan Zhang, Wei Yang, Qianjin Feng, and Yanqiu Feng. 2023. "Cascade of Denoising and Mapping Neural Networks for MRI R2* Relaxometry of Iron-Loaded Liver" Bioengineering 10, no. 2: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020209
APA StyleLu, Q., Wang, C., Lian, Z., Zhang, X., Yang, W., Feng, Q., & Feng, Y. (2023). Cascade of Denoising and Mapping Neural Networks for MRI R2* Relaxometry of Iron-Loaded Liver. Bioengineering, 10(2), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020209







