Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Agricultural Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. BMP and RMP Assays
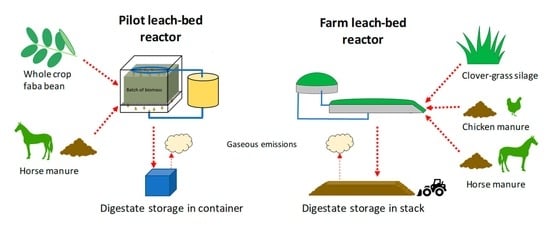
2.3. Pilot-Scale Experiments
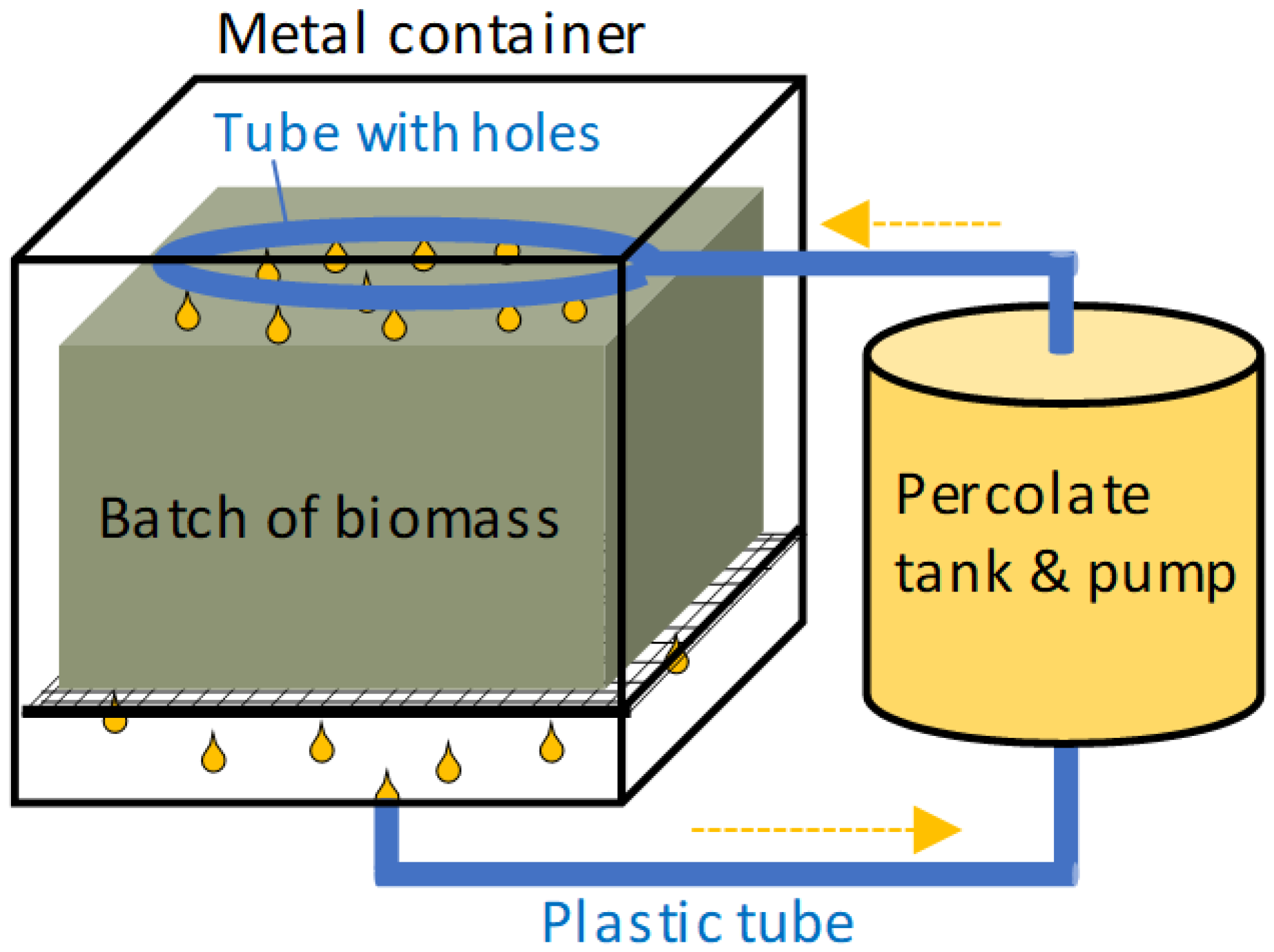
2.3.1. Pilot-Scale Reactor
2.3.2. Pilot-Scale Mass Balance Calculations
2.4. Farm-Scale Experiments
2.4.1. Monitoring Biogas Plant Operation
2.4.2. Data Collection
2.4.3. Calculation of Methane Production Potential and Biogas Production
2.4.4. Farm-Scale Mass Balance Calculations
2.5. Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pilot-Scale Experiments
3.1.1. Pilot-Scale Methane Production
3.1.2. Pilot-Scale Digestion Mass Balance
3.2. Farm-Scale Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| BMP L CH4/kgVS | VS (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| FB pilot I/FB | 272 ± 1 | 48 |
| FB pilot II/FB | 320 ± 7 | 48 |
| FB + HM pilot I and II/FB | 227 ± 28 | 51 |
| FB + HM pilot I and II/HM | 48 ± 9 | 51 |
| FB pilot I/percolation liquid | 160 ± 11 | 48 |
| FB pilot II/percolation liquid | 74 ± 22 | 48 |
| FB + HM pilot I and II/percolation liquid | 57 ± 16 | 51 |
| Farm I and II/CGS | 256 ± 15 | 67 |
| Farm I and II/HM | 93 ± 14 | 67 |
| Farm I and II/CM | 150 ± 18 | 67 |
| RMP L CH4/kgVS | ||
| FB pilot I/digestate | 174 ± 13 | 48 |
| FB pilot II/digestate | 304 ± 16 | 88 |
| FB + HM pilot I/digestate | 50 ± 6 | 55 |
| FB + HM pilot II/digestate | 242 ± 56 | 55 |
| FB pilot I/percolation liquid | 373 ± 188 | 88 |
| FB pilot II/percolation liquid | 128 ± 82 | 88 |
| FB + HM pilot I/percolation liquid | 14 ± 4 | 55 |
| FB + HM pilot II/percolation liquid | 12 ± 6 | 55 |
| Farm I/digestate | 218 ± 27 | 67 |
| Farm II/digestate | 136 ± 25 | 51 |
| Experiment | Sample | TS (%) | VS (%) | Ntot (kg/t) | NH4–N (kg/t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm I | Digestate (117 days) | 22.7 ± 0.5 | 19.8 ± 0.2 | 6.66 ± 0.01 | 0.63 ± 0.23 |
| Digestate after storage (26 days) | 36.1 ± 1.3 | 32.1 ± 1.9 | 8.78 ± 0.04 | 0.90 ± 0.28 | |
| Farm II | Digestate (185 days) | 20.1 ± 2.2 | 17.0 ± 2.0 | 6.58 ± 0.07 | 1.07 ± 0.08 |
| Digestate after storage (125 days) | 17.4 ± 2.9 | 15.1 ± 2.9 | 5.90 ± 0.08 | 0.66 ± 0.11 | |
| Percolation liquid | Sample 1 (13 March 2019) | 1.8 | 1.58 | 0.90 | |
| Sample 2 (8 July 2019) | 2.0 | 0.9 | 2.20 | 1.18 | |
| Sample 3 (14 January 2020) | 1.7 | 2.21 | 1.35 |
References
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. The Paris Agreement. Available online: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- European Commission. Available online: https://commission.europa.eu/strategy-and-policy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal_en (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- European Council. Fit for 55. Available online: https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/policies/green-deal/fit-for-55-the-eu-plan-for-a-green-transition/ (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook 2022. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/830fe099-5530-48f2-a7c1-11f35d510983/WorldEnergyOutlook2022.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Winquist, E.; Rikkonen, P.; Pyysiäinen, J.; Varho, V. Is biogas an energy or a sustainability product?—Business opportunities in the Finnish biogas branch. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttinen, S.; Luostarinen, S.; Winquist, E.; Timonen, K. Rural Biogas: Feasibility and Role in Finnish Energy System, BEST Suitable Bioenergy Solutions for Tomorrow; Research Report no 1.1.3-4; Cluster for Energy and Environment: Helsinki, Finland, 2015; Available online: www.bestfinalreport.fi (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Koppelmäki, K.; Parviainen, T.; Virkkunen, E.; Winquist, E.; Schulte, R.P.O.; Helenius, J. Ecological intensification by integrating biogas production into nutrient cycling: Modeling the case of Agroecological Symbiosis. Agric. Syst. 2019, 170, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Stinner, W.; Deuker, A.; Leithold, G. Effects of different manuring systems with and without biogas digestion on nitrogen cycle and crop yield in mixed organic dairy farming systems. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2008, 82, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Müller, T. Effects of anaerobic digestion on digestate nutrient availability and crop growth: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmeier, T.; Blumenstein, B.; Möller, D. Farm biogas production in organic agriculture: System implications. Agric. Syst. 2015, 139, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinner, W.; Möller, K.; Leithold, G. Effects of biogas digestion of clover/grass-leys, cover crops and crop residues on nitrogen cycle and crop yield in organic stockless farming systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2008, 29, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppelmäki, K.; Lamminen, M.; Helenius, J.; Schulte, R.P.O. Smart integration of food and bioenergy production delivers on multiple ecosystem services. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, Å.; Jarvis, Å.; Stenberg, B.; Mathisen, B.; Svensson, B. Anaerobic digestion of alfalfa silage with recirculation of process liquid. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, D.P.; Fujiwara, F.; Tho, B.L.; Toan, P.P.S.; Minh, G.H. A review of anaerobic digestion systems for biodegradable waste: Configurations, operating parameters, and current trends. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jha, A.K.; Li, J.; Nies, L.; Zhang, L. Research advances in dry anaerobic digestion process of solid organic wastes. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 14242–14253. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, O.P.; Visvanathan, C. Bio-energy recovery from high-solid organic substrates by dry anaerobic bio-conversion processes: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdara, A.; Sürmelia, R.Ö.; Çallia, B. Anaerobic digestion of chicken manure by a leach-bed process coupled with side-stream membrane ammonia separation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumenti, A.; da Borso, F.; Limina, S. Dry anaerobic digestion of cow manure and agricultural products in a full-scale plant: Efficiency and comparison with wet fermentation. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riya, S.; Meng, L.; Wang, Y.; Lee, C.G.; Zhou, S.; Toyota, K.; Hosomi, M. Dry Anaerobic Digestion for Agricultural Waste Recycling. In Biogas—Recent Advances and Integrated Approaches; Abomohra, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/71149 (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Demirer, G.N.; Chen, S. Anaerobic biogasification of undiluted dairy manure in leaching bed reactors. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitenbeck, G.A.; Schellinger, D. Calculating the Reduction in Material Mass And Volume during Composting. Compost Sci. Util. 2004, 12, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnish Meteorological Institute. Temperature Data for Jokioinen Ilmala. Available online: https://en.ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/download-observations (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- SFS 3008; Veden, Lietteen ja Sedimentin Kuiva-Aineen ja Hehkutusjäännöksen Määritys: Standardi (In Finnish, A Standard for Determination of Dry Matter and Volatile Solids for Water, Slurry and Sediment). Finnish Standards Association (SFS): Helsinki, Finland, 1990.
- Vahlberg, C.; Nordell, E.; Wiberg, L.; Schnürer, A. Method for Correction of VFA Loss in Determination of Dry Matter in Biomass. SGC Rapport, 2013, p. 273. Available online: http://www.sgc.se/ckfinder/userfiles/files/SGC273.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Tampio, E.; Ervasti, S.; Paavola, T.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.; Rintala, J. Anaerobic digestion of autoclaved and untreated food waste. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCullough, H. The determination of ammonia in whole blood by a direct colorimetric method. Clin. Chim. Acta 1967, 17, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC 984.13-1994; Protein (Crude) in Animal Feed and Pet Food. Association of Official Agricultural Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- EN 13040: 2008; Soil Improvers and Growing media—Sample Preparation for Chemical and Physical Tests, Determination of Dry Matter Content, Moisture Content and Laboratory Compacted Bulk Density. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2008.
- EN 15935: 2012-11; Sludge, Treated Biowaste, Soil and Waste—Determination of Loss on Ignition. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2012.
- EF2018; In-House Method EF 2018, IC-Technique. Eurofins Environment Testing Finland Ltd.: Helsinki, Finland, 2018. Available online: https://www.finas.fi/Documents/T039_M50_2023.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- EN 13654-1; Soil Improvers and Growing Media. Determination of Nitrogen. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2001.
- EN 13342:2000; Characterization of Sludges—Determination of Kjeldahl Nitrogen. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2000.
- Maritza, M.C.; Zohrab, S.; Hanson, A.; Smith, G.; Funk, P.; Yu, H.; Longworth, J. Anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste and agricultural waste and the effect of co-digestion with dairy cow manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8288–8293. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtomäki, A.; Huttunen, T.; Lehtinen, T.M.; Rintala, J.A. Anaerobic digestion of grass silage in batch leach bed processes for methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3267–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, S.; Torrijos, M.; Debord, R.; Esposito, G.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Steyer, J.P.; Escudié, R. Mesophilic anaerobic digestion of several types of spent livestock bedding in a batch leach-bed reactor: Substrate characterization and process performance. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakarinen, A.; Maijala, P.; Jaakkola, S.; Stoddard, F.L.; Kymäläinen, M.; Viikari, L. Evaluation of preservation methods for improving biogas production and enzymatic conversion yields of annual crops. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2011, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersson, A.; Thomsen, M.; Hauggaardnielsen, H.; Thomsen, A. Potential bioethanol and biogas production using lignocellulosic biomass from winter rye, oilseed rape and faba bean. Biomass Bioenergy 2007, 31, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thamsiriroj, T.; Nizami, A.S.; Murphy, J.D. Why does mono-digestion of grass silage fail in long term operation? Appl. Energy 2012, 95, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueurce, A.; Tomas, N.; Le Roux, S.; Martinez, J.; Peu, P. Biotic and abiotic roles of leachate recirculation in batch mode solid-state anaerobic digestion of cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadin, Å.; Eriksson, O. Horse manure as feedstock for anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Castillo, R.; Llabrés-Luengo, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Temperature effect on anaerobic digestion of bedding straw in a one phase system at different inoculum concentration. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1995, 54, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Schultz, R.; Müller, T. Substrate inputs, nutrient flows and nitrogen loss of two centralized biogas plants in southern Germany. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 87, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.A.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Restrepo, A.P.; de la Fuente, C.; Paredes, C.; Moral, R.; Bernal, M.P. Co-composting of the solid fraction of anaerobic digestates, to obtain added-value materials for use in agriculture. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 43, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Raw Material | VSsubstrate:VSinoculum |
|---|---|
| FB pilot I and II | 0.5 |
| FB pilot III | 0.75 |
| HM pilot | 0.75 |
| HM | 0.5 |
| CM | 0.5 |
| Pilot percolation liquid | 0.3 and 0.75 |
| Pilot digestate RMP | 0.5 |
| Farm-scale digestate RMP | 0.5 and 2.0 |
| Pilot percolation liquid RMP | 0.1 and 0.5 |
| Feed | FB Pilot I | FB Pilot II | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kgFM 1 | kgTS 2 | kgVS 3 | kgFM | kgTS | kgVS | |
| Fava beans | 260 | 66 | 63 | 230 | 49 | 41 |
| Percolate | 150 | 11 | 9 | 150 | 5 | 3 |
| FB + HM pilot I | FB + HM pilot II | |||||
| Fava beans | 230 | 65 | 58 | 230 | 65 | 58 |
| Horse manure | 51 | 16 | 15 | 52 | 16 | 15 |
| Percolate | 140 | 2 | 1 | 150 | 2 | 1 |
| Feed | Farm I | Farm II | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tFM 1 | tTS 2 | tVS 3 | tFM | tTS | tVS | |
| CGS | 360 | 104 | 96 | 353 | 119 | 111 |
| CM | 18 | 19 | 17 | 22.5 | 3 | 3 |
| HM | 56 | 7 | 5 | 7.5 | 15 | 6 |
| Sum | 434 | 130 | 118 | 383 | 137 | 120 |
| TS (%) | VS (%) | Ntot (kg/t) | NH4–N (kg/t) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid raw material (FB + HM) | 28.91 | 25.94 | 5.87 | 0.54 |
| Digestate | 18.08 | 15.70 | 6.16 | 1.40 |
| Digestate after storage (35 d) | 16.71 | 14.41 | 5.51 | 0.96 |
| Percolate start | 1.82 | 0.69 | 1.28 | 1.12 |
| Percolate end | 1.90 | 0.52 | 2.20 | 1.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pyykkönen, V.; Winquist, E.; Seppänen, A.-M.; Vainio, M.; Virkkunen, E.; Koppelmäki, K.; Rasi, S. Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Agricultural Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactors. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10040433
Pyykkönen V, Winquist E, Seppänen A-M, Vainio M, Virkkunen E, Koppelmäki K, Rasi S. Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Agricultural Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactors. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(4):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10040433
Chicago/Turabian StylePyykkönen, Ville, Erika Winquist, Ari-Matti Seppänen, Markku Vainio, Elina Virkkunen, Kari Koppelmäki, and Saija Rasi. 2023. "Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Agricultural Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactors" Bioengineering 10, no. 4: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10040433
APA StylePyykkönen, V., Winquist, E., Seppänen, A.-M., Vainio, M., Virkkunen, E., Koppelmäki, K., & Rasi, S. (2023). Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Agricultural Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactors. Bioengineering, 10(4), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10040433