Validation of Lead-DBS β-Oscillation Localization with Directional Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Clinical Assessment
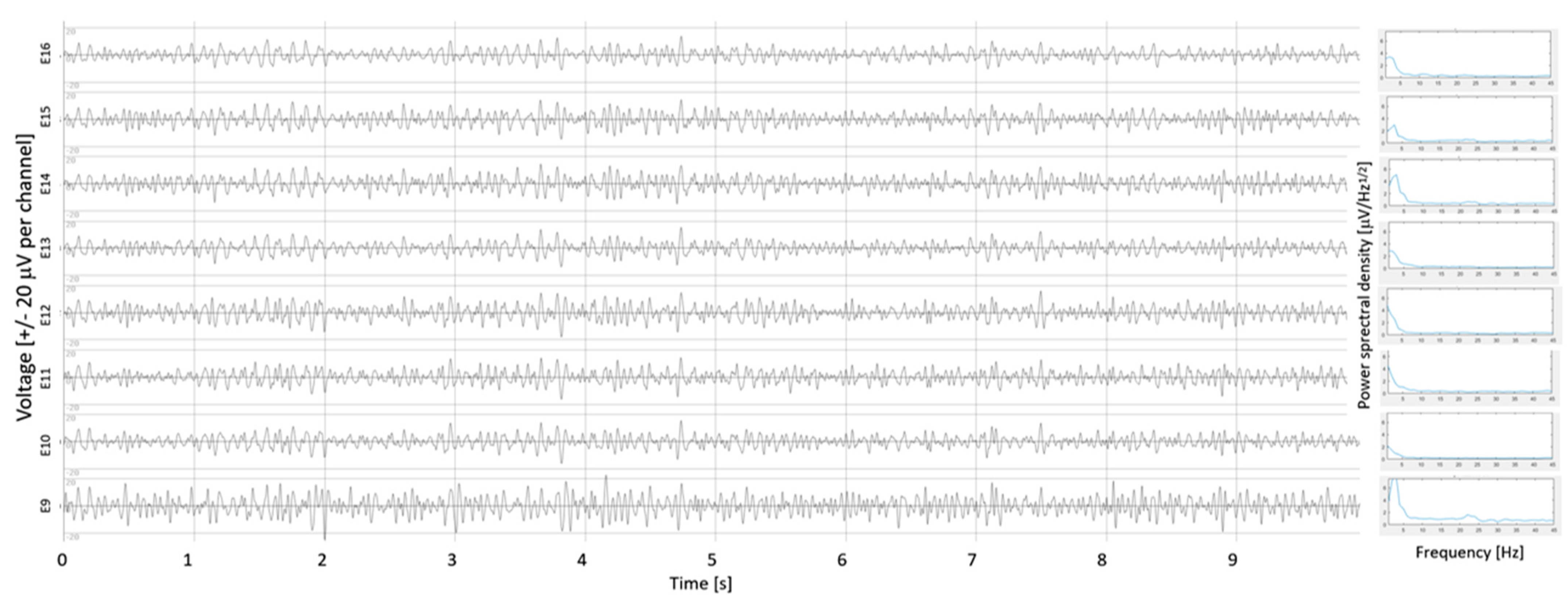
2.2. β-Oscillation Measurements
2.3. Postoperative Image Reconstruction
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
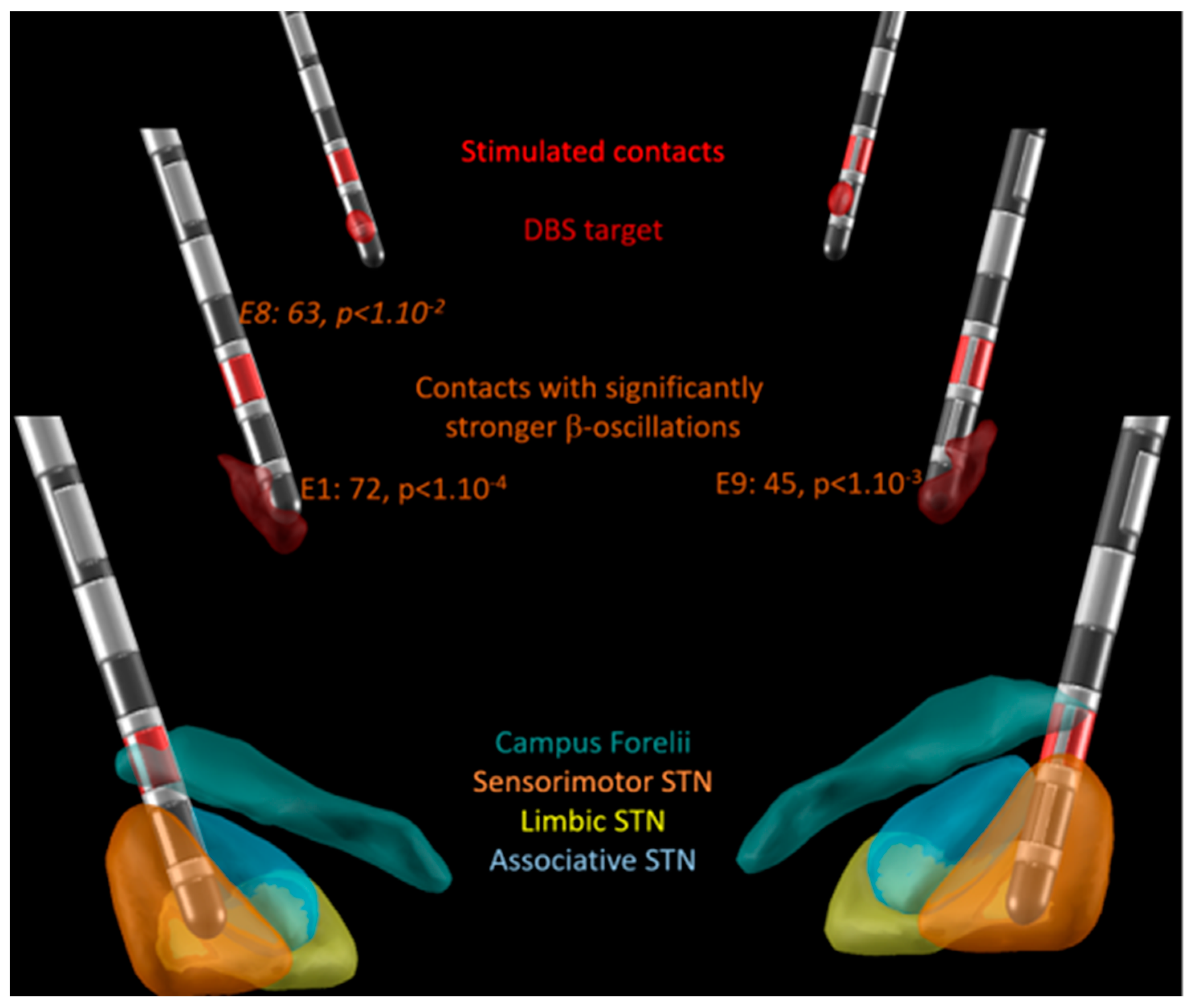
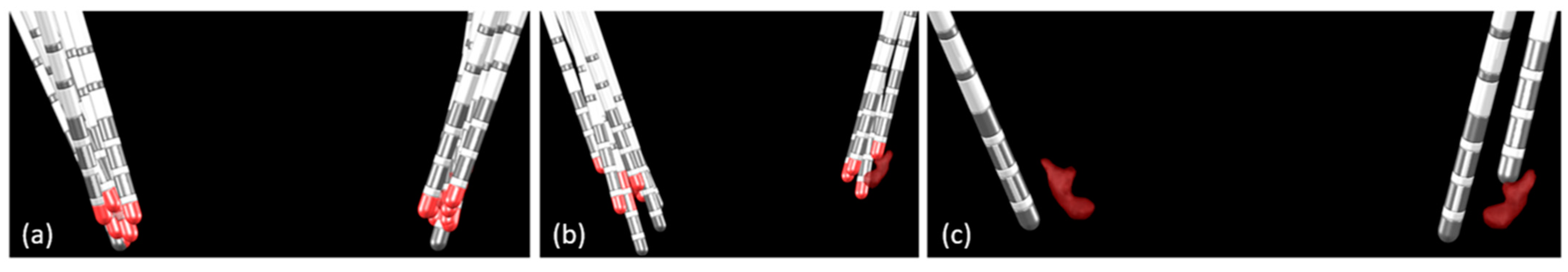
3.1. β-Oscillations
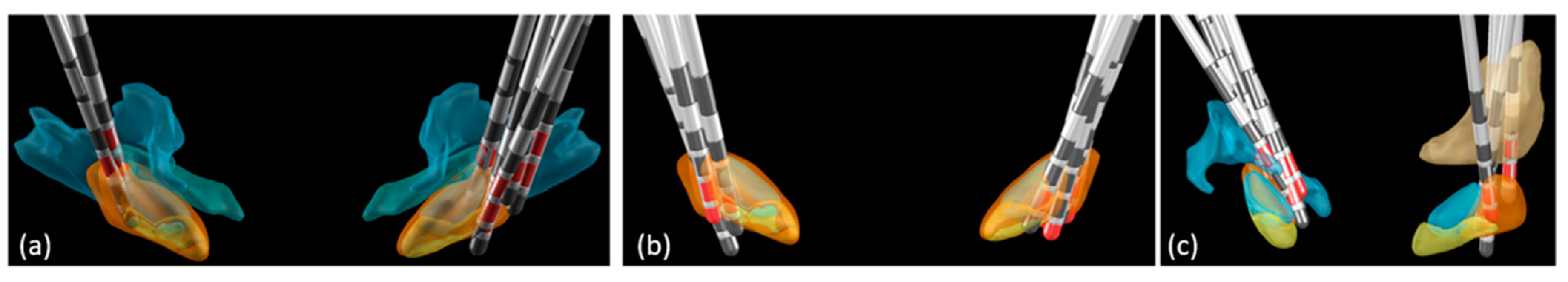
3.2. Electrode Location and Motor Outcome
4. Discussion
4.1. β-Oscillations
4.2. Electrode Location and Motor Outcomes
4.3. Considerations for DBS Surgery
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, P.; Oliviero, A.; Mazzone, P.; Insola, A.; Tonali, P.; Di Lazzaro, V. Dopamine dependency of oscillations between subthalamic nucleus and pallidum in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, R.; Ashby, P.; Hutchison, W.D.; Lang, A.E.; Lozano, A.M.; Dostrovsky, J.O. Dependence of subthalamic nucleus oscillations on movement and dopamine in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2002, 125, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.; Mazzone, P.; Oliviero, A.; Altibrandi, M.G.; Pilato, F.; Tonali, P.A.; Di Lazzaro, V. Effects of stimulation of the subthalamic area on oscillatory pallidal activity in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 188 Pt 6, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidel, A.; Spivak, A.; Grieb, B.; Bergman, H.; Israel, Z. Subthalamic span of beta oscillations predicts deep brain stimulation efficacy for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2010, 133 Pt 7, 2007–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, A.; Kuhn, A.A. Lead-DBS: A toolbox for deep brain stimulation electrode localizations and visualizations. Neuroimage 2015, 107, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewert, S.; Plettig, P.; Li, N.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Collins, D.L.; Herrington, T.M.; Kuhn, A.A.; Horn, A. Toward defining deep brain stimulation targets in MNI space: A subcortical atlas based on multimodal MRI, histology and structural connectivity. Neuroimage 2018, 170, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, A.; Kuhn, A.A.; Merkl, A.; Shih, L.; Alterman, R.; Fox, M. Probabilistic conversion of neurosurgical DBS electrode coordinates into MNI space. Neuroimage 2017, 150, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, A.; Neumann, W.J.; Degen, K.; Schneider, G.H.; Kuhn, A.A. Toward an electrophysiological “sweet spot” for deep brain stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 3377–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Awadhi, A.; Tyrand, R.; Horn, A.; Kibleur, A.; Vincentini, J.; Zacharia, A.; Burkhard, P.R.; Momjian, S.; Boex, C. Electrophysiological confrontation of Lead-DBS-based electrode localizations in patients with Parkinson’s disease undergoing deep brain stimulation. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 34, 102971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacki, A.; Nguyen, T.A.; Tinkhauser, G.; Petermann, K.; Debove, I.; Wiest, R.; Pollo, C. Accuracy of different three-dimensional subcortical human brain atlases for DBS -lead localisation. Neuroimag. Clin. 2018, 20, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, C.; Foffani, G.; Dileone, M.; Catalan-Alonso, M.J.; Gonzalez-Hidalgo, M.; Barcia, J.A.; Alonso-Frech, F. Directional local field potential recordings for symptom-specific optimization of deep brain stimulation. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boex, C.; Tyrand, R.; Horvath, J.; Fleury, V.; Sadri, S.; Corniola, M.; Burkhard, P.R.; Momjian, S. What Is the Best Electrophysiologic Marker of the Outcome of Subthalamic Nucleus Stimulation in Parkinson Disease? World Neurosurg. 2018, 120, e1217–e1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleopra, R.; Rinaldo, S.; Devigili, G.; Lettieri, C.; Mondani, M.; D’Auria, S.; Piacentino, M.; Pilleri, M. Brain impedance variation of directional leads implanted in subthalamic nuclei of Parkinsonian patients. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönecker, T.; Kupsch, A.; Kühn, A.A.; Schneider, G.-H.; Hoffmann, K.T. Automated optimization of subcortical cerebral MR imaging-atlas coregistration for improved postoperative electrode localization in deep brain stimulation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avants, B.B.; Epstein, C.L.; Grossman, M.; Gee, J.C. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: Evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonov, V.; Evans, A.C.; Botteron, K.; Almli, C.R.; McKinstry, R.C.; Collins, D.L.; Brain Development Cooperative, G. Unbiased average age-appropriate atlases for pediatric studies. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 2005, 26, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Tononi, G.; Reeke, G.N., Jr.; Sporns, O.; Edelman, G.M. Value-dependent selection in the brain: Simulation in a synthetic neural model. Neuroscience 1994, 59, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husch, A.; Petersen, M.V.; Gemmar, P.; Goncalves, J.; Hertel, F. PaCER—A fully automated method for electrode trajectory and contact reconstruction in deep brain stimulation. Neuroimag. Clin. 2018, 17, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembek, T.A.; Hellerbach, A.; Jergas, H.; Eichner, M.; Wirths, J.; Dafsari, H.S.; Barbe, M.T.; Hunsche, S.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Treuer, H. DiODe v2: Unambiguous and Fully-Automated Detection of Directional DBS Lead Orientation. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallet, N.; Pogosyan, A.; Marton, L.F.; Bolam, J.P.; Brown, P.; Magill, P.J. Parkinsonian beta oscillations in the external globus pallidus and their relationship with subthalamic nucleus activity. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14245–14258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulberti, A.; Hamel, W.; Buhmann, C.; Boelmans, K.; Zittel, S.; Gerloff, C.; Westphal, M.; Engel, A.K.; Schneider, T.R.; Moll, C.K. Subthalamic deep brain stimulation improves auditory sensory gating deficit in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, H.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Jbabdi, S.; Georgiev, D.; Mahlknecht, P.; Hyam, J.; Foltynie, T.; Limousin, P.; De Vita, E.; Jahanshahi, M.; et al. Subthalamic deep brain stimulation sweet spots and hyperdirect cortical connectivity in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage 2017, 158, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maks, C.B.; Butson, C.R.; Walter, B.L.; Vitek, J.L.; McIntyre, C.C. Deep brain stimulation activation volumes and their association with neurophysiological mapping and therapeutic outcomes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, G.J.B.; Boutet, A.; Joel, S.E.; Germann, J.; Gwun, D.; Neudorfer, C.; Gramer, R.M.; Algarni, M.; Paramanandam, V.; Prasad, S.; et al. Probabilistic Mapping of Deep Brain Stimulation: Insights from 15 Years of Therapy. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, D.; Guridi, J.; Toledo, J.B.; Alegre, M.; Obeso, J.A.; Rodriguez-Oroz, M.C. Stimulation sites in the subthalamic nucleus and clinical improvement in Parkinson’s disease: A new approach for active contact localization. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, S.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Jing, J.; Su, M.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Role of the Cortico-Subthalamic Hyperdirect Pathway in Deep Brain Stimulation for the Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. World Neurosurg. 2018, 114, e1079–e1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, J.; Boogers, A.; Van Bogaert, T.; Dembek, T.A.; Gransier, R.; Wouters, J.; Vandenberghe, W.; De Vloo, P.; Nuttin, B.; Mc Laughlin, M. Towards biomarker-based optimization of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease patients. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1091781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avecillas-Chasin, J.M.; Hurwitz, T.A.; Bogod, N.M.; Honey, C.R. An Analysis of Clinical Outcome and Tractography following Bilateral Anterior Capsulotomy for Depression. Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2019, 97, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, K.; Mori, S.; Troncoso, J.C.; Lenz, F.A. Mapping tracts in the human subthalamic area by 11.7T ex vivo diffusion tensor imaging. Brain Struct. Funct. 2020, 225, 1293–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Pogosyan, A.; Zrinzo, L.U.; Tisch, S.; Limousin, P.; Ashkan, K.; Yousry, T.; Hariz, M.I.; Brown, P. Intra-operative recordings of local field potentials can help localize the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease surgery. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 198, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehnemouyi, Y.M.; Wilkins, K.B.; Anidi, C.M.; Anderson, R.W.; Afzal, M.F.; Bronte-Stewart, H.M. Modulation of beta bursts in subthalamic sensorimotor circuits predicts improvement in bradykinesia. Brain 2021, 144, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, A.A.; Kupsch, A.; Schneider, G.H.; Brown, P. Reduction in subthalamic 8-35 Hz oscillatory activity correlates with clinical improvement in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 1956–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, W.J.; Degen, K.; Schneider, G.H.; Brucke, C.; Huebl, J.; Brown, P.; Kuhn, A.A. Subthalamic synchronized oscillatory activity correlates with motor impairment in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1748–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houeto, J.L.; Welter, M.L.; Bejjani, P.B.; Tezenas du Montcel, S.; Bonnet, A.M.; Mesnage, V.; Navarro, S.; Pidoux, B.; Dormont, D.; Cornu, P.; et al. Subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson disease: Intraoperative predictive factors. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boëx, C.; Awadhi, A.A.; Tyrand, R.; Corniola, M.V.; Kibleur, A.; Fleury, V.; Burkhard, P.R.; Momjian, S. Validation of Lead-DBS β-Oscillation Localization with Directional Electrodes. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080898
Boëx C, Awadhi AA, Tyrand R, Corniola MV, Kibleur A, Fleury V, Burkhard PR, Momjian S. Validation of Lead-DBS β-Oscillation Localization with Directional Electrodes. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(8):898. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080898
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoëx, Colette, Abdullah Al Awadhi, Rémi Tyrand, Marco V. Corniola, Astrid Kibleur, Vanessa Fleury, Pierre R. Burkhard, and Shahan Momjian. 2023. "Validation of Lead-DBS β-Oscillation Localization with Directional Electrodes" Bioengineering 10, no. 8: 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080898
APA StyleBoëx, C., Awadhi, A. A., Tyrand, R., Corniola, M. V., Kibleur, A., Fleury, V., Burkhard, P. R., & Momjian, S. (2023). Validation of Lead-DBS β-Oscillation Localization with Directional Electrodes. Bioengineering, 10(8), 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080898





