Deep Learning-Based Automated Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation of the Lumbar Structure and Its Adjacent Structures at the L4/5 Level
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Image Annotation and Preprocessing
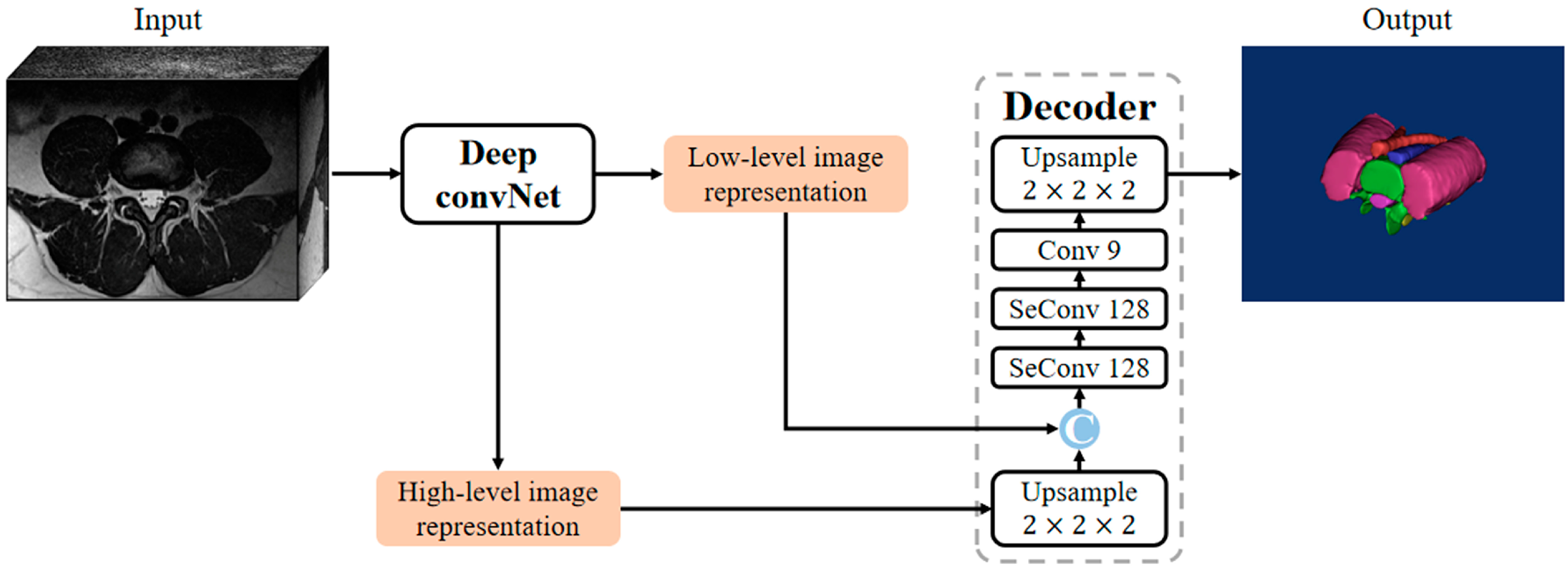
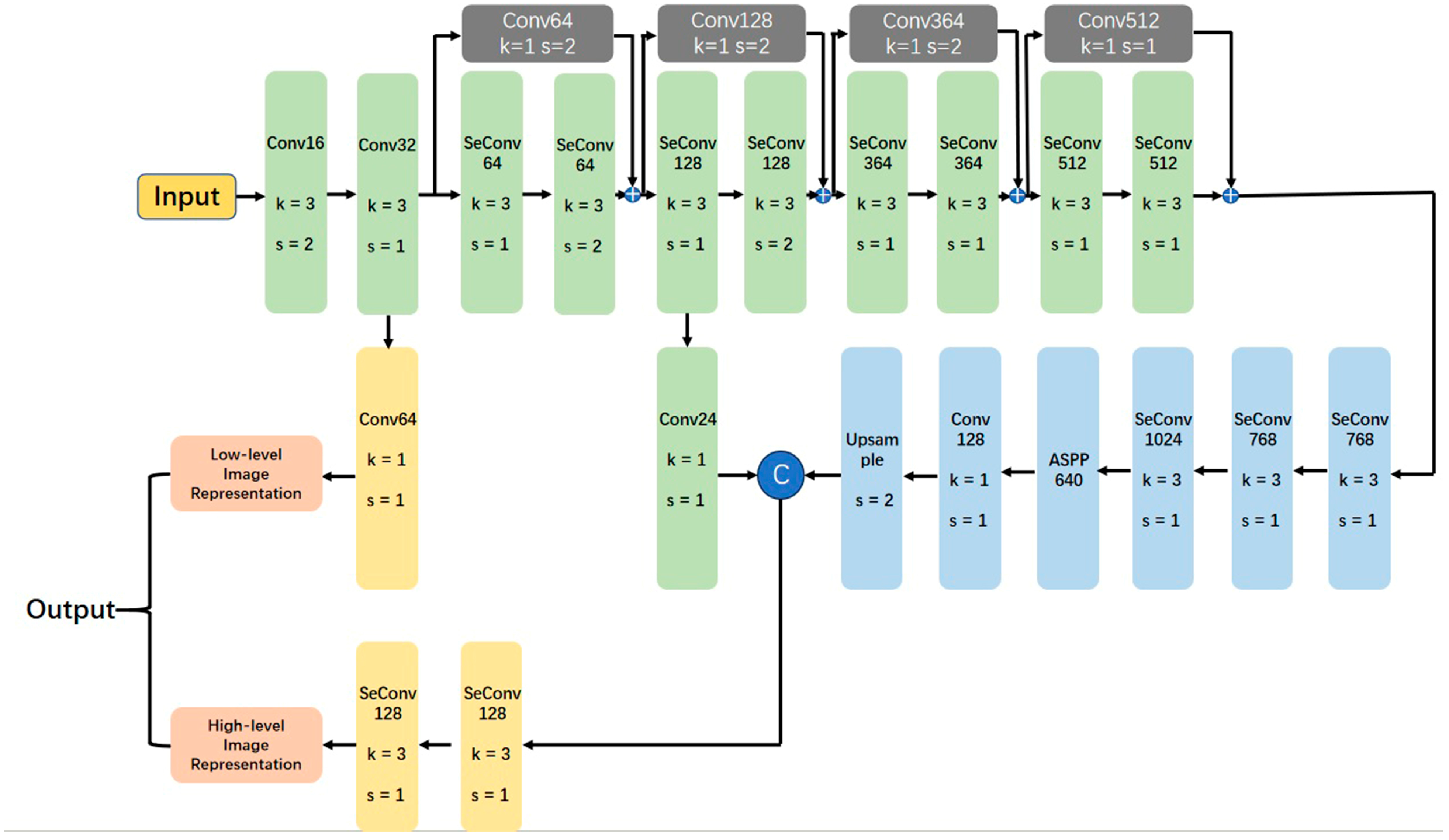
2.3. Model Architecture
2.4. Experimental Configurations
2.5. Examination of Model Performance and Morphometric Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
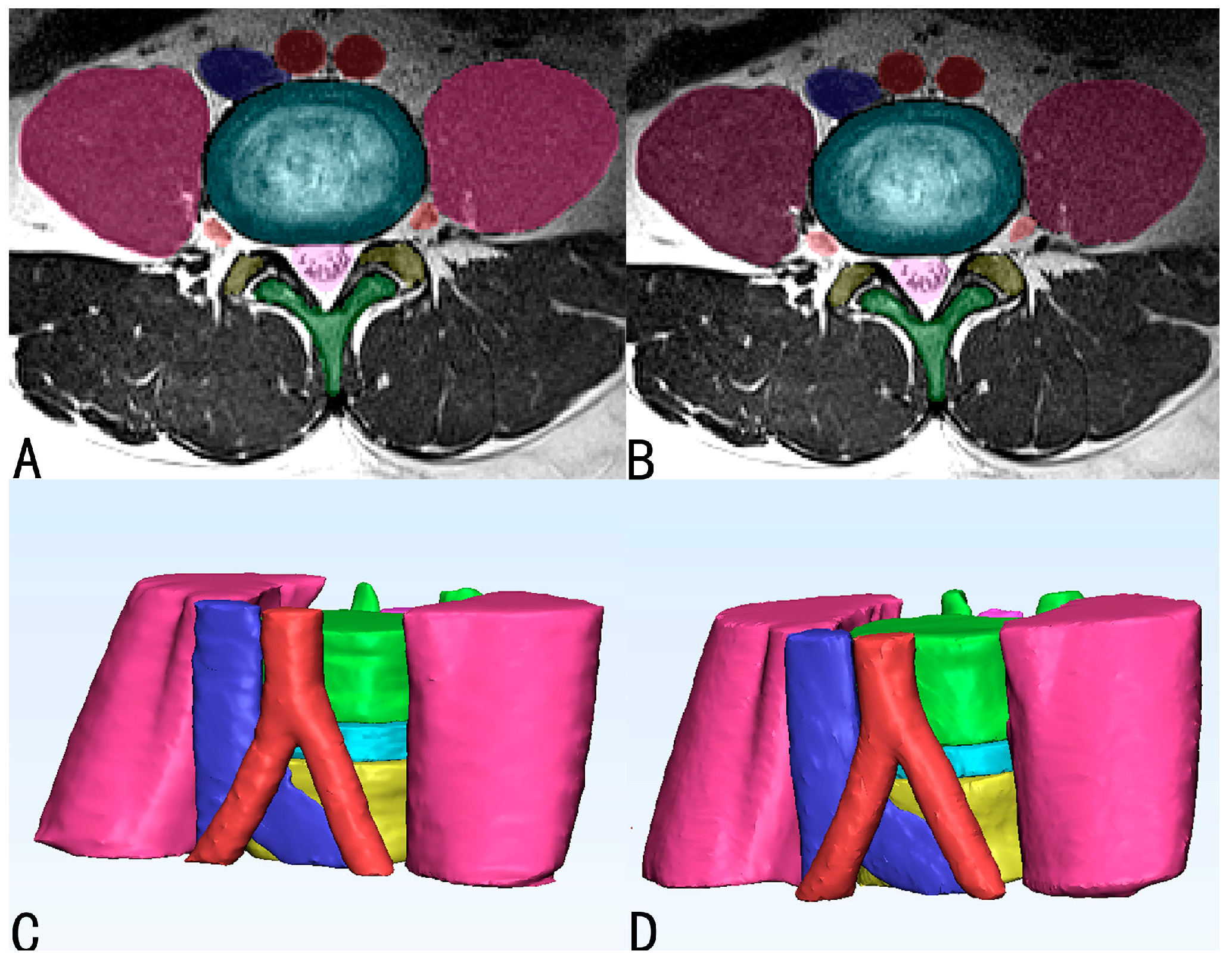
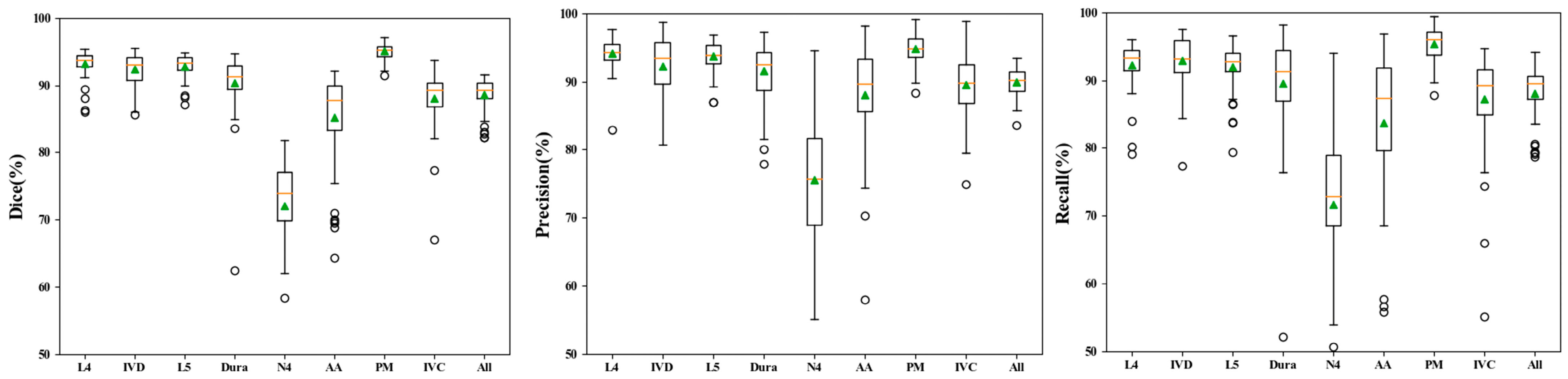
3.1. Performance of Automatic Segmentation
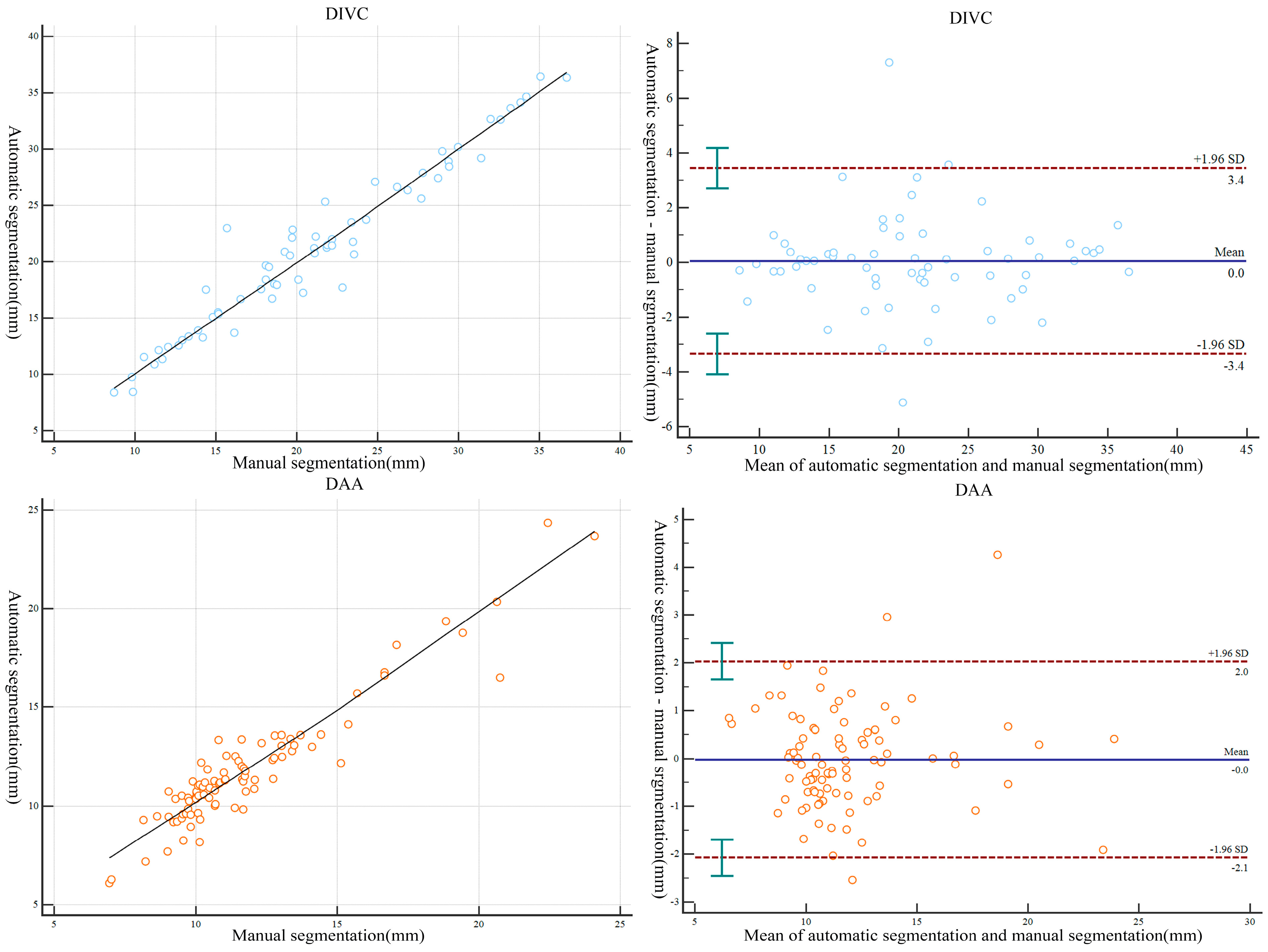
3.2. Morphometric Correlation of Parameters and Difference between Manually and Automatically Segmented Images
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, R.; van Tulder, M.; Öberg, B.; Costa, L.M.; Woolf, A.; Schoene, M.; Croft, P.; Lancet Low Back Pain Series Working Group. Low back pain: A call for action. Lancet 2018, 391, 2384–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrills, P.; Nowesenitz, G.; Barnard, A. Prevalence and Characteristics of Discogenic Pain in Tertiary Practice: 223 Consecutive Cases Utilizing Lumbar Discography. Pain Med. 2015, 16, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Barzouhi, A.; Vleggeert-Lankamp, C.L.; Lycklama à Nijeholt, G.J.; Van der Kallen, B.F.; van den Hout, W.B.; Jacobs, W.C.; Koes, B.W.; Peul, W.C.; Leiden-The Hague Spine Intervention Prognostic Study Group. Magnetic resonance imaging in follow-up assessment of sciatica. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasch, R.; Truthmann, J.; Hancock, M.J.; Maher, C.G.D.; Otto, M.; Nell, C.; Reichwein, N.; Bülow, R.M.; Chenot, J.-F.; Hofer, A.; et al. Association of Lumbar MRI Findings with Current and Future Back Pain in a Population-based Cohort Study. Spine 2022, 47, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinares, D.M.; Davis, T.T.; Fung, D.A. Retroperitoneal oblique corridor to the L2-S1 intervertebral discs: An MRI study. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 24, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillo-Olvera, J.; Lin, G.-X.; Jo, H.-J.; Kim, J.-S. Complications on minimally invasive oblique lumbar interbody fusion at L2–L5 levels: A review of the literature and surgical strategies. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, L.G.; Bodnar, A.; Battié, M.C. A comparison of two methods to evaluate a narrow spinal canal: Routine magnetic resonance imaging versus three-dimensional reconstruction. Spine J. 2016, 16, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Fang, S.-B.; Li, C.-S.; Yin, B.; Wang, L.; Wan, S.-Y.; Xie, J.-K.; Ding, Q.; Tang, L.; Zhong, S.-Z. Digital Three-Dimensional Model of Lumbar Region 4-5 and its Adjacent Structures Based on a Virtual Chinese Human. Orthop. Surg. 2013, 5, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpone, V.M.; Hirsch, J.A.; Gilligan, C.J.; Chandra, R.V. Computed tomography guidance for spinal intervention: Basics of technique, pearls, and avoiding pitfalls. Pain Physician 2013, 16, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, S.S.; Lee, S.-H.; Liu, W.C.; Erken, H.Y. A novel preoperative trajectory evaluation method for L5-S1 transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Spine J. 2018, 18, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Colak, C.; Chundru, K.K.; Gaj, S.; Nanavati, A.; Jones, M.H.; Winalski, C.S.; Subhas, N.; Li, X. Automated knee cartilage segmentation for heterogeneous clinical MRI using generative adversarial networks with transfer learning. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 2620–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalvit Carvalho da Silva, R.; Jenkyn, T.R.; Carranza, V.A. Development of a Convolutional Neural Network Based Skull Segmentation in MRI Using Standard Tesselation Language Models. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.; Pang, C.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, M.; Yang, W.; Lu, H.; Feng, Q. SpineParseNet: Spine Parsing for Volumetric MR Image by a Two-Stage Segmentation Framework With Semantic Image Representation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Tao, X.; Pang, S.; Su, Z.; Lu, H.; Li, S.; Feng, Q.; Chen, B. Multiple Axial Spine Indices Estimation via Dense Enhancing Network With Cross-Space Distance-Preserving Regularization. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 3248–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessmann, N.; van Ginneken, B.; de Jong, P.A.; Išgum, I. Iterative fully convolutional neural networks for automatic vertebra segmentation and identification. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, R.; Zeng, G.; Zheng, G. Fully automatic segmentation of lumbar vertebrae from CT images using cascaded 3D fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 893–897. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.; Pal, C.; Acharyya, A.; Chakrabarti, A.; Basu, S. Deep neural network for automated simultaneous intervertebral disc (IVDs) identification and segmentation of multi-modal MR images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 205, 106074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, S.; Lin, L.; Yuan, Z.; Pang, S.; Feng, Q.; Chen, T.; Lu, H. Three-dimensional reconstruction of Kambin’s triangle based on automated magnetic resonance image segmentation. J. Orthop. Res. 2022, 40, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, K.H.; Warfield, S.K.; Bharatha, A.; Tempany, C.M.; Kaus, M.R.; Haker, S.J.; Wells, W.M.; Jolesz, F.A.; Kikinis, R. Statistical validation of image segmentation quality based on a spatial overlap index. Acad. Radiol. 2004, 11, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Pang, C.; Su, Z.; Lin, L.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, H.; Feng, Q. DGMSNet: Spine segmentation for MR image by a detection-guided mixed-supervised segmentation network. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 75, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dourthe, B.; Shaikh, N.; Pai, S.A.; Fels, S.; Brown, S.H.M.; Wilson, D.R.; Street, J.; Oxland, T.R. Automated Segmentation of Spinal Muscles From Upright Open MRI Using a Multiscale Pyramid 2D Convolutional Neural Network. Spine 2022, 47, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golla, A.-K.; Bauer, D.F.; Schmidt, R.; Russ, T.; Norenberg, D.; Chung, K.; Tonnes, C.; Schad, L.R.; Zoellner, F.G. Convolutional Neural Network Ensemble Segmentation With Ratio-Based Sampling for the Arteries and Veins in Abdominal CT Scans. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; MA, X.; Xia, X.; Lyv, F.; Jiang, J. Anatomical assessment of the risk of sympathetic nerve injury in oblique lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Chin. J. Orthop. 2017, 12, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, C. Preoperative Simulation of the Trajectory for L5/S1 Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Discectomy: A Novel Approach for Decision-Making. World Neurosurg. 2021, 145, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Sequence and Parameters | L4/L5 Level Dataset |
|---|---|
| T2-3D-space | |
| Men II | 27 (54) |
| Women II | 23 (46) |
| Age III | 34.70 (23, 63) |
| Male Participants III | 32.37 (25, 46) |
| Female Participants III | 37.43 (23, 63) |
| Body Mass Index(kg/m2) IV | 23.79 (20.68, 26.90) |
| Datasets | L4 | IVD | L5 | Dura | N4 | AA | PM | IVC | All | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | Training | 0.951 | 0.955 | 0.951 | 0.935 | 0.805 | 0.921 | 0.976 | 0.930 | 0.928 |
| Validation | 0.926 | 0.921 | 0.925 | 0.895 | 0.700 | 0.860 | 0.951 | 0.878 | 0.882 | |
| Test | 0.931 | 0.924 | 0.928 | 0.903 | 0.721 | 0.852 | 0.950 | 0.880 | 0.886 | |
| Precision | Training | 0.956 | 0.954 | 0.955 | 0.940 | 0.810 | 0.924 | 0.974 | 0.930 | 0.930 |
| Validation | 0.938 | 0.925 | 0.930 | 0.910 | 0.731 | 0.894 | 0.952 | 0.904 | 0.898 | |
| Test | 0.941 | 0.923 | 0.937 | 0.915 | 0.756 | 0.881 | 0.948 | 0.895 | 0.899 | |
| Recall | Training | 0.947 | 0.956 | 0.945 | 0.934 | 0.818 | 0.921 | 0.979 | 0.934 | 0.929 |
| Validation | 0.916 | 0.920 | 0.921 | 0.886 | 0.703 | 0.835 | 0.951 | 0.862 | 0.874 | |
| Test | 0.923 | 0.928 | 0.920 | 0.896 | 0.717 | 0.837 | 0.953 | 0.872 | 0.881 |
| Level | Morphometric Parameters | 3D Model of Automatic Segmentation | 3D Model of Manual Segmentation | Mean Absolute Error | R Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC | 9.214 ± 4.897 (0.000–17.970) | 9.077 ± 5.038 (0.000–21.80) | 0.866 ± 0.706 (0.000, 3.830) | 0.975 | 0.259 | |
| DAA | 11.852 ± 3.150 (6.100–24.350) | 11.828 ± 3.193 (6.950–24.10) | 0.779 ± 0.697 (0.010, 4.260) | 0.945 | 0.504 | |
| DIVC | 21.081 ± 7.257 (8.420–36.430) | 21.039 ± 7.217 (8.710–36.680) | 1.121 ± 1.312 (0.050, 7.300) | 0.971 | 0.947 | |
| PI | 1.929 ± 1.504 (0.000–5.820) | 1.852 ± 1.382 (0.000–5.950) | 0.489 ± 0.462 (0.000, 2.060) | 0.895 | 0.241 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Su, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, T.; Cui, Z.; Li, S.; Pang, S.; Lu, H. Deep Learning-Based Automated Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation of the Lumbar Structure and Its Adjacent Structures at the L4/5 Level. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080963
Wang M, Su Z, Liu Z, Chen T, Cui Z, Li S, Pang S, Lu H. Deep Learning-Based Automated Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation of the Lumbar Structure and Its Adjacent Structures at the L4/5 Level. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(8):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080963
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Min, Zhihai Su, Zheng Liu, Tao Chen, Zhifei Cui, Shaolin Li, Shumao Pang, and Hai Lu. 2023. "Deep Learning-Based Automated Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation of the Lumbar Structure and Its Adjacent Structures at the L4/5 Level" Bioengineering 10, no. 8: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080963
APA StyleWang, M., Su, Z., Liu, Z., Chen, T., Cui, Z., Li, S., Pang, S., & Lu, H. (2023). Deep Learning-Based Automated Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation of the Lumbar Structure and Its Adjacent Structures at the L4/5 Level. Bioengineering, 10(8), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080963







