Edge-AI Enabled Wearable Device for Non-Invasive Type 1 Diabetes Detection Using ECG Signals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
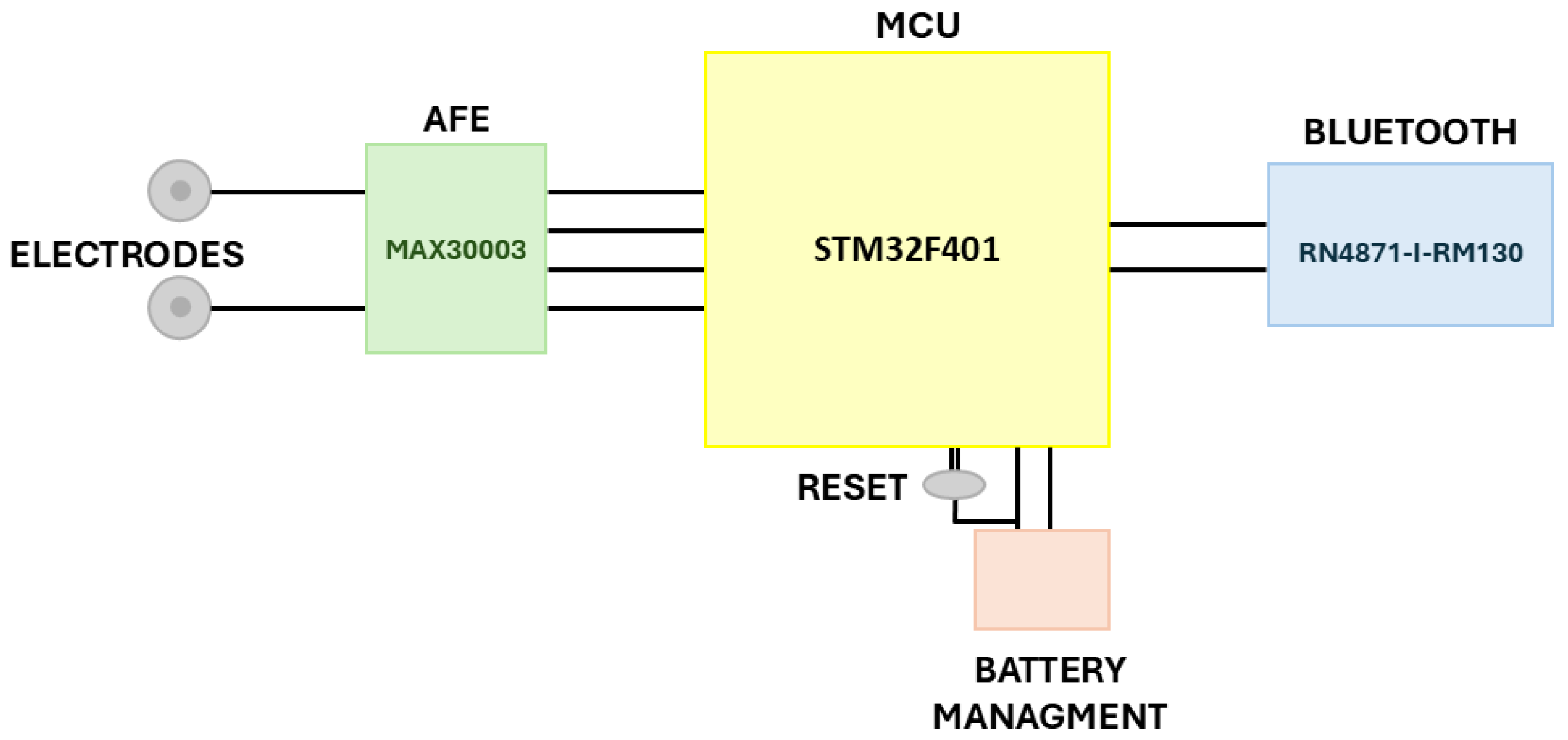
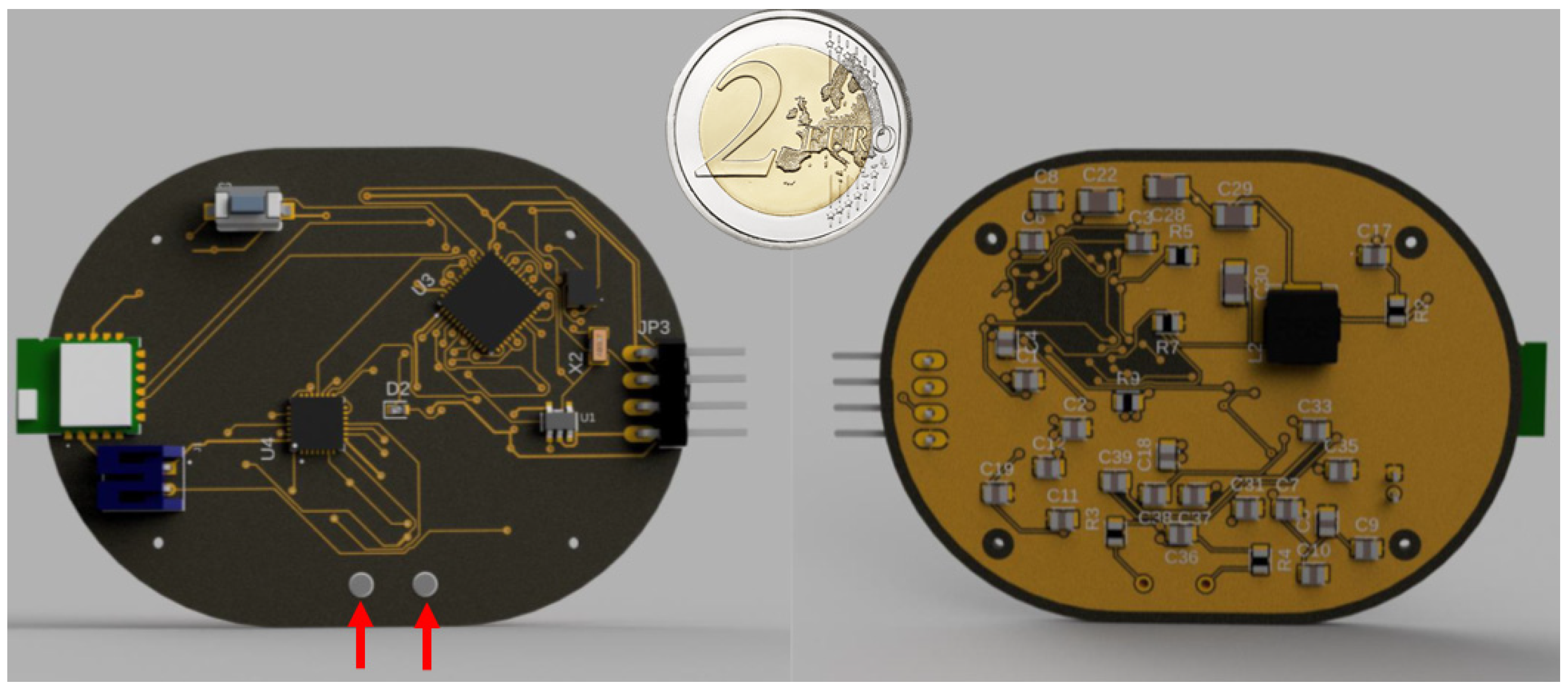
3.1. Hardware Components Selection
3.2. Proposed Method
3.2.1. Dataset
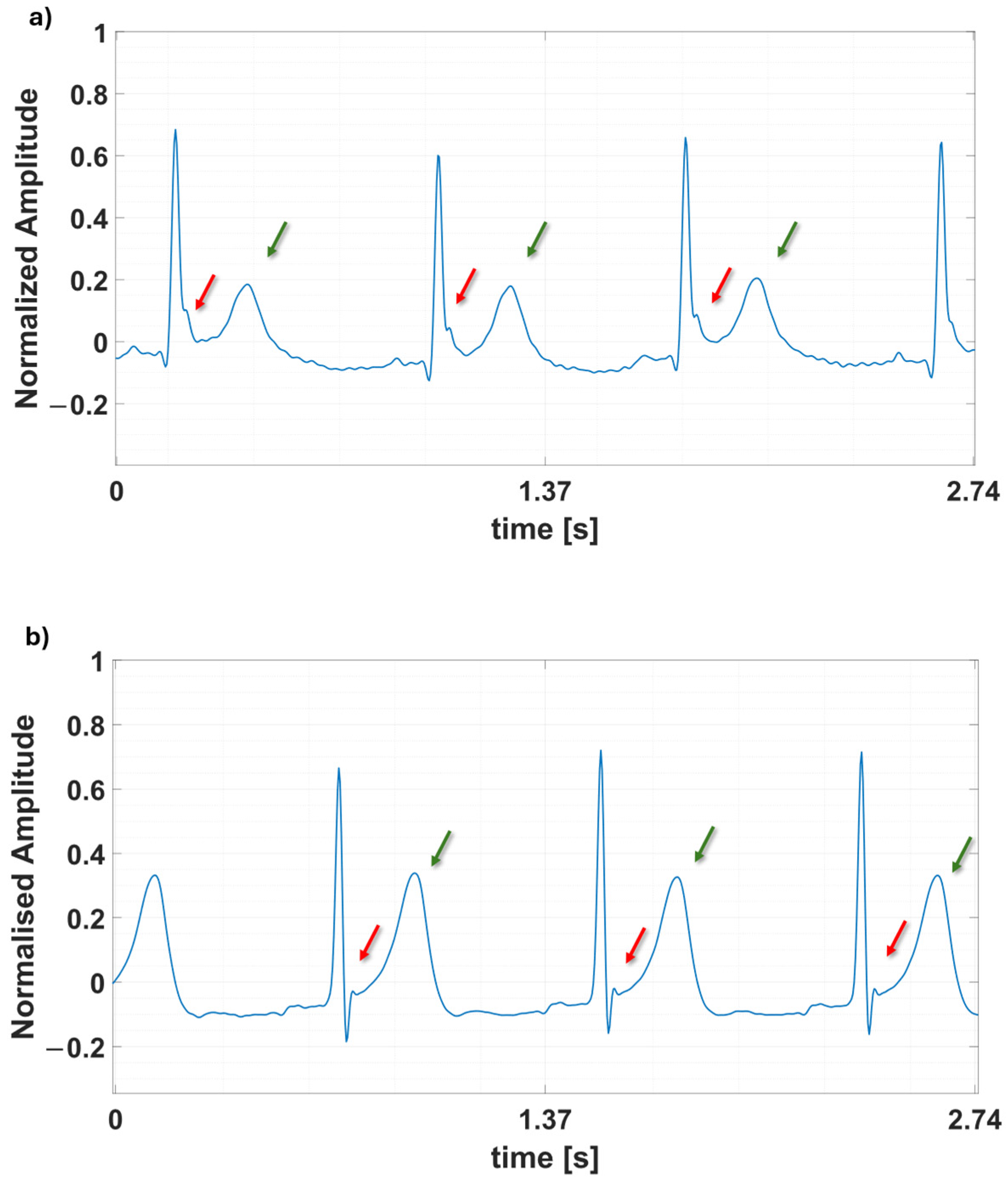
3.2.2. Preprocessing Steps
3.2.3. Neural Networks Design
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
 |
| Patient | Number of 1 min ECG Frames | Label |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | 452 | Healthy |
| 10 | 28 | Healthy |
| 11 | 274 | Healthy |
| 12 | 83 | Healthy |
| 13 | 120 | Healthy |
| 14 | 118 | Healthy |
| 15 | 3 | Healthy |
| 16 | 199 | Healthy |
| 17 | 78 | Healthy |
| 18 | 18 | Healthy |
| 19 | 19 | Healthy |
| 20 | 20 | Healthy |
| 2 | 202 | Diabetic |
| 4 | 760 | Diabetic |
| 6 | 619 | Diabetic |
| 8 | 85 | Diabetic |
| Patient | Number of 1 min ECG Frames | Label |
| 1 | 110 | Healthy |
| 2 | 152 | Healthy |
| 3 | 116 | Healthy |
| 4 | 77 | Healthy |
| 5 | 93 | Healthy |
| 8 | 144 | Healthy |
| 9 | 93 | Healthy |
| 1 | 396 | Diabetic |
| 3 | 62 | Diabetic |
| 5 | 27 | Diabetic |
| 7 | 349 | Diabetic |
| 9 | 162 | Diabetic |
References
- Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- What Is Diabetes?—NIDDK, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Laha, S.; Rajput, A.; Laha, S.S.; Jadhav, R. A Concise and Systematic Review on Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring for Potential Diabetes Management. Biosensors 2022, 12, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, G.; Balder, A.; Zagarins, S. Telehealth Program for Type 2 Diabetes: Usability, Satisfaction, and Clinical Usefulness in an Urban Community Health Center. Telemed. E-Health 2015, 21, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanelli, S.; Ammi, M.; Hallab, M.; El Yacoubi, M.A. Diabetes Detection and Management through Photoplethysmographic and Electrocardiographic Signals Analysis: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreozzi, E.; Sabbadini, R.; Centracchio, J.; Bifulco, P.; Irace, A.; Breglio, G.; Riccio, M. Multimodal Finger Pulse Wave Sensing: Comparison of Forcecardiography and Photoplethysmography Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piet, A.; Jablonski, L.; Daniel Onwuchekwa, J.I.; Unkel, S.; Weber, C.; Grzegorzek, M.; Ehlers, J.P.; Gaus, O.; Neumann, T. Non-Invasive Wearable Devices for Monitoring Vital Signs in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gragnaniello, M.; Borghese, A.; Marrazzo, V.R.; Maresca, L.; Breglio, G.; Irace, A.; Riccio, M. Real-Time Myocardial Infarction Detection Approaches with a Microcontroller-Based Edge-AI Device. Sensors 2024, 24, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gragnaniello, M.; Balbi, F.; Martellotta, G.; Borghese, A.; Marrazzo, V.R.; Maresca, L.; Breglio, G.; Irace, A.; Riccio, M. Edge-AI on Wearable Devices: Myocardial Infarction Detection with Spectrogram and 1D-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 22nd Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference, MELECON 2024, Porto, Portugal, 25–27 June 2024; pp. 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragnaniello, M.; Borghese, A.; Marrazzo, V.R.; Breglio, G.; Irace, A.; Riccio, M. A Microcontroller-Based System for Human-Emotion Recognition with Edge-AI and Infrared Thermography. Lect. Notes Electr. Eng. 2024, 1110, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksen, J.L.; Graff, C.; Ellervik, C.; Jensen, J.S.; Andersen, H.U.; Rossing, P.; Kanters, J.K.; Jensen, M.T. Type 1 diabetes is associated with T-wave morphology changes. The Thousand & 1 Study. J. Electrocardiol. 2018, 51, S72–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The ECG in Diabetes Mellitus. Available online: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/epub/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.897496 (accessed on 4 October 2024).
- Kittnar, O. Electrocardiographic changes in diabetes mellitus. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, S559–S566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andellini, M.; Castaldo, R.; Cisuelo, O.; Franzese, M.; Haleem, M.S.; Ritrovato, M.; Pecchia, L.; Schiaffini, R. Are the variations in ECG morphology associated to different blood glucose levels? implications for non-invasive glucose monitoring for T1D paediatric patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 212, 111708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andellini, M.; Haleem, S.; Angelini, M.; Ritrovato, M.; Schiaffini, R.; Iadanza, E.; Pecchia, L. Artificial intelligence for non-invasive glycaemic-events detection via ECG in a paediatric population: Study protocol. Health Technol. 2023, 13, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Verma, A.; Verma, A.K. Non-invasive and Automatic Identification of Diabetes Using ECG Signals. Int. J. Electr. Electron. Res. 2023, 11, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Verma, A.; Verma, A.K.; Bajaj, V. Tunable Q-factor wavelet transform based identification of diabetic patients using ECG signals. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 2024. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.; Bajaj, V. A Robust Framework for Automated Screening of Diabetic Patient Using ECG Signals. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 24222–24229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, R.; Karimian, N.; Park, Y. Hyperglycemia Identification Using ECG in Deep Learning Era. Sensors 2021, 21, 6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisuelo, O.; Haleem, M.S.; Hattersley, J.; Pecchia, L. Spectrogram-Driven Convolutional Neural Network for Real-Time Non-invasive Hyperglycaemia Detection in Paediatric Type-1 Diabetes via Wearable Sensors. In MEDICON’23 and CMBEBIH’23; Badnjević, A., Gurbeta Pokvić, L., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, O.; Talo, M.; Ay, B.; Baloglu, U.B.; Aydin, G.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of diabetic subject using pre-trained 2D-CNN models with frequency spectrum images extracted from heart rate signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 113, 103387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NUCLEO-F401RE-STM32 Nucleo-64 Development Board with STM32F401RE MCU, Supports Arduino and ST Morpho Connectivity—STMicroelectronics. Available online: https://www.st.com/en/evaluation-tools/nucleo-f401re.html (accessed on 23 December 2023).
- Arm Cortex-M4—Microcontrollers—STMicroelectronics. Available online: https://www.st.com/content/st_com/en/arm-32-bit-microcontrollers/arm-cortex-m4.html (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- STM32F4—ARM Cortex-M4 High-Performance MCUs—STMicroelectronics. Available online: https://www.st.com/en/microcontrollers-microprocessors/stm32f4-series.html (accessed on 4 October 2024).
- MAX30003 Datasheet and Product Info|Analog Devices. Available online: https://www.analog.com/en/products/max30003.html#product-overview (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- ad8232.pdf. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ad8232.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- RN4870_71_Bluetooth_Low_Energy_Module_DS50002489-3002868.pdf. Available online: https://www.mouser.it/datasheet/2/268/RN4870_71_Bluetooth_Low_Energy_Module_DS50002489-3002868.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2024).
- Dubosson, F.; Ranvier, J.-E.; Bromuri, S.; Calbimonte, J.-P.; Ruiz, J.; Schumacher, M. The open D1NAMO dataset: A multi-modal dataset for research on non-invasive type 1 diabetes management. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2018, 13, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D1NAMO ECG Glucose Data. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sarabhian/d1namo-ecg-glucose-data (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Zephyr BioHarness—Zephyr—Catalogo PDF|Documentazione tecnica|Brochure. Available online: https://pdf.medicalexpo.it/pdf-en/zephyr/zephyr-bioharness/83995-97427.html#open684688 (accessed on 4 October 2024).
- Edge Impulse. Available online: https://edgeimpulse.com/ (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Pradhan, B.K.; Neelappu, B.C.; Sivaraman, J.; Kim, D.; Pal, K. A Review on the Applications of Time-Frequency Methods in ECG Analysis. J. Healthc. Eng. 2023, 2023, 3145483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyout, A.; Alquran, H.; Mustafa, W.A.; Alqudah, A.M. Advanced Time-Frequency Methods for ECG Waves Recognition. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, P.; Zoph, B.; Le, Q.V. Searching for Activation Functions. Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=SkBYYyZRZ (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- EON Compiler|Edge Impulse Documentation. Available online: https://docs.edgeimpulse.com/docs/edge-impulse-studio/deployment/eon-compiler (accessed on 4 October 2024).
- ST Edge AI Developer Cloud, STMicroelectronics—STM32 AI. Available online: https://stm32ai.st.com/st-edge-ai-developer-cloud/ (accessed on 4 October 2024).



| Article | Method | Signal | Results | Suitable for Wearable Device? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | Medium Tree Classifier | ECG | Acc = 87.19% | It is possible, but real-time performance was not evaluated. |
| [17] | TQWT and SVM Classifier | ECG | Acc = 91.50% | Although TQWT is more flexible for signal analysis, it requires higher computational complexity and resources, making it unsuitable for low-resource MCUs. |
| [18] | ITD and Fine Decision Classifier | ECG | Acc = 86.90% | It is possible, but the ITD algorithm requires optimization to work within the computational constraints of an MCU. |
| [19] | Deep Learning Classifier | ECG | AUC = 94.53% | Not suitable for an MCU with limited memory due to the deep NN, and the noise-sensitive feature extraction may cause errors in real-time. |
| [20] | Spectrogram and 2D-CNN | ECG | Acc = 96.90% | Despite its significant results, this technique demands excessive computational and memory resources. |
| [21] | Spectrogram and Pre-Trained Deep Models | HR | Acc = 97.20% | Pre-trained networks require an excessive number of parameters, as they are not designed to operate with limited resources. |
| Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| AUC | 0.90 |
| Weighted average precision | 0.91 |
| Weighted average recall | 0.90 |
| Weighted average F1 score | 0.90 |
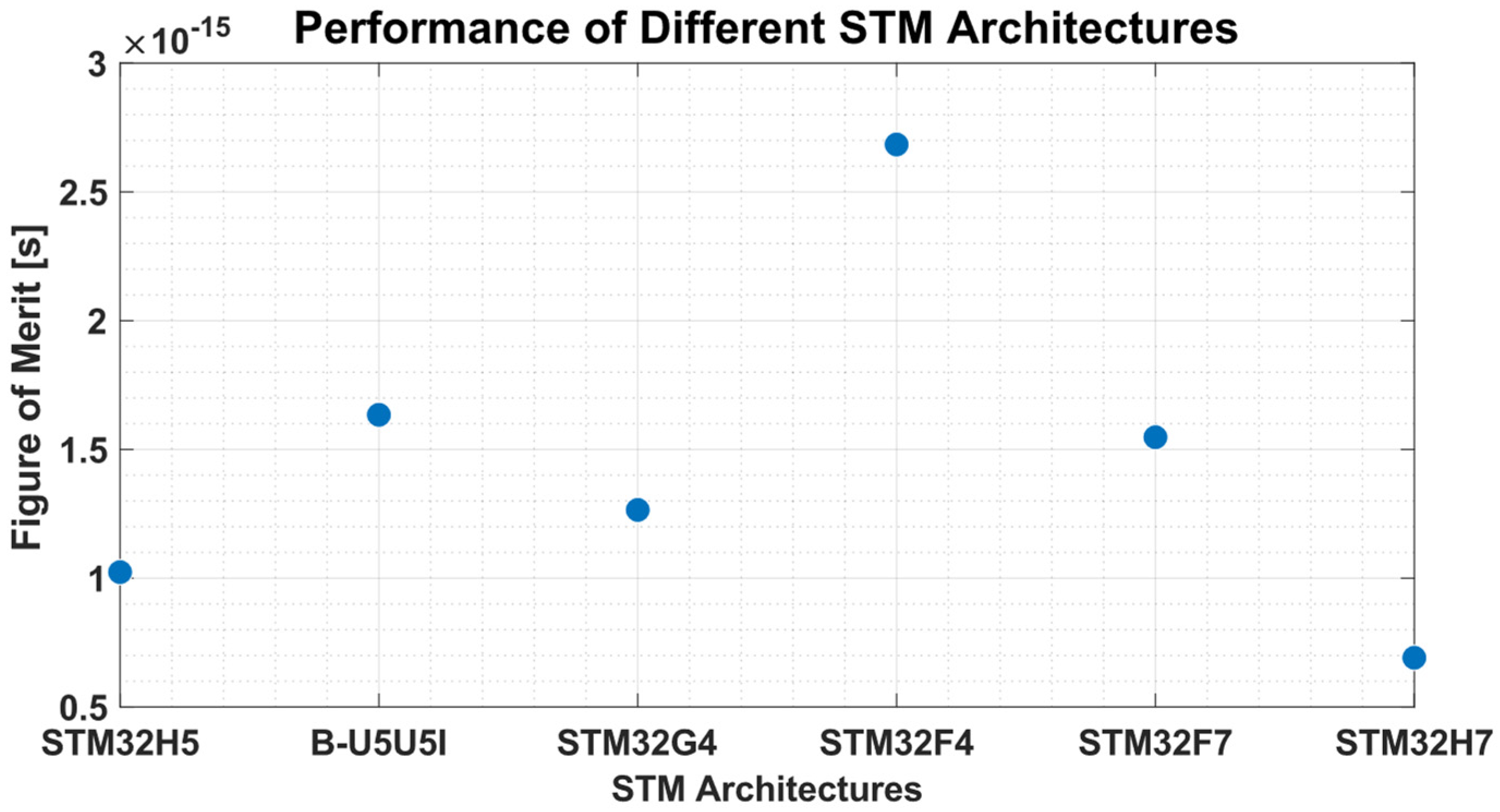
| Method | Clock Frequency (MHz) | Inference Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| STM32H5 | 250 | 15.63 |
| B-U5U5I | 160 | 23.90 |
| STM32G4 | 170 | 27.35 |
| STM32F4 | 84 | 52.80 |
| STM32F7 | 216 | 13.85 |
| STM32H7 | 480 | 6.28 |
| Method | Memory Footprint Obtained |
|---|---|
| EON Compiler | RAM = 33.2 kB FLASH = 352.2 kB |
| ST Edge AI Developer Cloud | RAM = 23 kB FLASH = 347 kB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gragnaniello, M.; Marrazzo, V.R.; Borghese, A.; Maresca, L.; Breglio, G.; Riccio, M. Edge-AI Enabled Wearable Device for Non-Invasive Type 1 Diabetes Detection Using ECG Signals. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010004
Gragnaniello M, Marrazzo VR, Borghese A, Maresca L, Breglio G, Riccio M. Edge-AI Enabled Wearable Device for Non-Invasive Type 1 Diabetes Detection Using ECG Signals. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleGragnaniello, Maria, Vincenzo Romano Marrazzo, Alessandro Borghese, Luca Maresca, Giovanni Breglio, and Michele Riccio. 2025. "Edge-AI Enabled Wearable Device for Non-Invasive Type 1 Diabetes Detection Using ECG Signals" Bioengineering 12, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010004
APA StyleGragnaniello, M., Marrazzo, V. R., Borghese, A., Maresca, L., Breglio, G., & Riccio, M. (2025). Edge-AI Enabled Wearable Device for Non-Invasive Type 1 Diabetes Detection Using ECG Signals. Bioengineering, 12(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010004











