Predicting Health-Related Quality of Life Using Social Determinants of Health: A Machine Learning Approach with the All of Us Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Population
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. SDOH Features
2.6. Health-Related Quality of Life
2.7. Algorithm Selection and Performance Measures
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Performance of ML Algorithms to Predict Health-Related Quality of Life
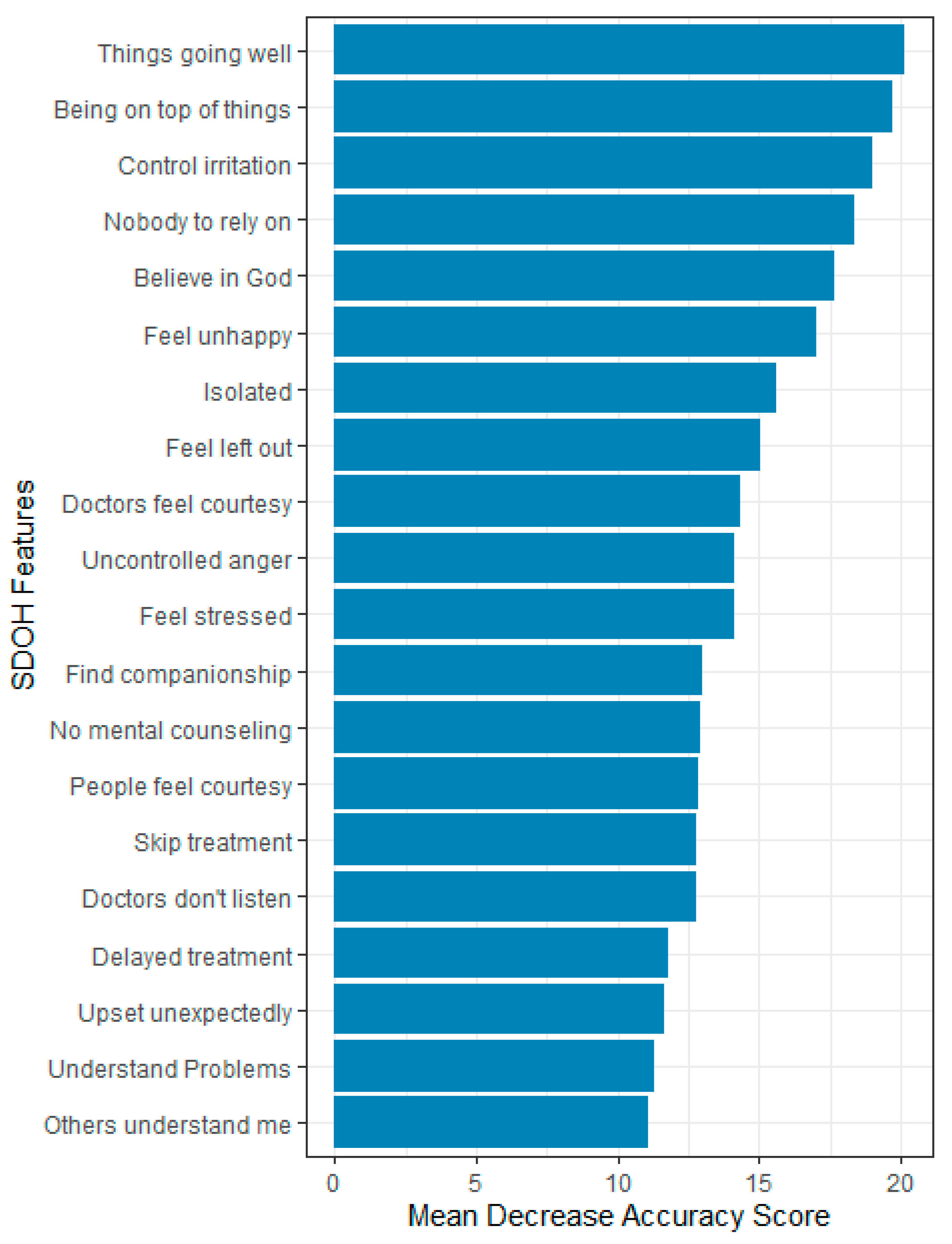
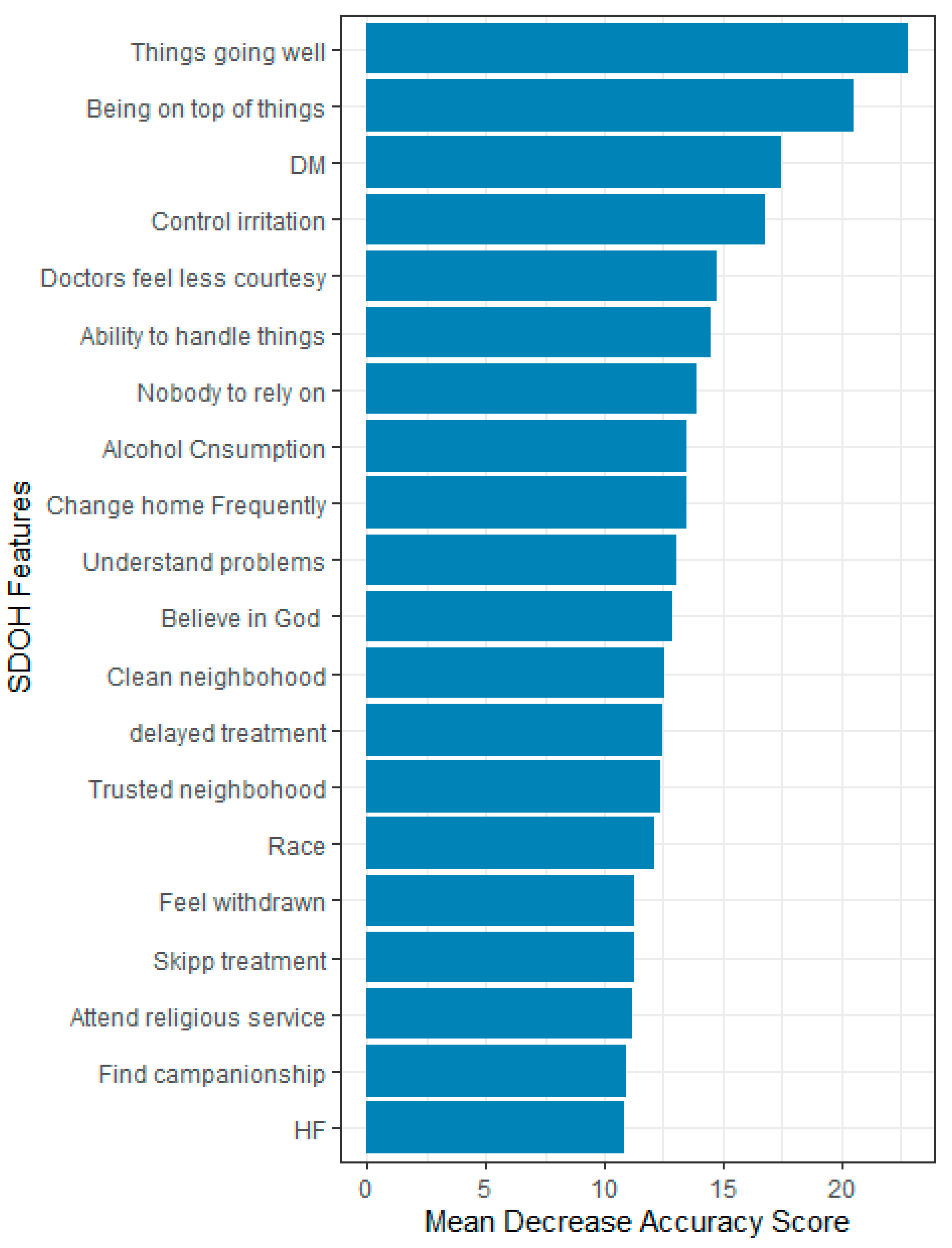
3.3. Feature Importance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abegaz, T.M.; Ali, A.A. Health-Related Quality of Life and Healthcare Events in Patients with Monotherapy of Anti-Diabetes Medications. Healthcare 2023, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meraya, A.M.; Alwhaibi, M. Health related quality of life and healthcare utilization among adults with diabetes and kidney and eye complications in the United States. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Social Determinants of Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/social-determinants-of-health#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Braveman, P.; Gottlieb, L. The social determinants of health: It’s time to consider the causes of the causes. Public Health Rep. 2014, 129, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, C.M.; Gennuso, K.P.; Swain, G.R.; Catlin, B.B. County health rankings: Relationships between determinant factors and health outcomes. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 50, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, J.; Oliveira, L.C.; Highfield, L.; Hwang, K.O.; Giancardo, L.; Bernstam, E.V. Predicting health-related social needs in Medicaid and Medicare populations using machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavnani, S.K.; Zhang, W.; Bao, D.; Raji, M.; Ajewole, V.; Hunter, R.; Kuo, Y.-F.; Schmidt, S.; Pappadis, M.R.; Bokov, A. Subtyping Social Determinants of Health in All of Us: Opportunities and Challenges in Integrating Multiple Datatypes for Precision Medicine. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conversano, C.; Rotondo, A.; Lensi, E.; Della Vista, O.; Arpone, F.; Reda, M.A. Optimism and its impact on mental and physical well-being. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2010, 6, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.O.; James, P.; Zevon, E.S.; Kim, E.S.; Trudel-Fitzgerald, C.; Spiro, A., III; Grodstein, F.; Kubzansky, L.D. Optimism is associated with exceptional longevity in 2 epidemiologic cohorts of men and women. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18357–18362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivits, J.; Erpelding, M.-L.; Guillemin, F. Social determinants of health-related quality of life. Rev. D’epidemiologie Et De Sante Publique 2013, 61, S189–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohls, J.K.; König, H.-H.; Quirke, E.; Hajek, A. Anxiety, depression and quality of life—A systematic review of evidence from longitudinal observational studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baernholdt, M.; Hinton, I.; Yan, G.; Rose, K.; Mattos, M. Factors associated with quality of life in older adults in the United States. Qual. Life Res. 2012, 21, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Rab, S. Significance of machine learning in healthcare: Features, pillars and applications. Int. J. Intell. Netw. 2022, 3, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, K.; Lee, S.; Baek, Y. Machine-learning model predicting quality of life using multifaceted lifestyles in middle-aged South Korean adults: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.-W.; Hsieh, Y.-W.; Lee, T.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Wu, C.-Y. Machine learning predicts clinically significant health related quality of life improvement after sensorimotor rehabilitation interventions in chronic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, T.D.; Nataraj, C.; Wu, C. A machine learning approach to predict quality of life changes in patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2023, 10, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karri, R.; Chen, Y.-P.P.; Drummond, K.J. Using machine learning to predict health-related quality of life outcomes in patients with low grade glioma, meningioma, and acoustic neuroma. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaudoin, M.; Hudon, A.; Giguère, C.-E.; Potvin, S.; Dumais, A. Prediction of quality of life in schizophrenia using machine learning models on data from Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) schizophrenia trial. Schizophrenia 2022, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turecamo, S.E.; Xu, M.; Dixon, D.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Mumma, M.T.; Joo, J.; Gupta, D.K.; Lipworth, L.; Roger, V.L. Association of rurality with risk of heart failure. JAMA Cardiol. 2023, 8, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segar, M.W.; Hall, J.L.; Jhund, P.S.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Morris, A.A.; Kao, D.; Fonarow, G.C.; Hernandez, R.; Ibrahim, N.E.; Rutan, C. Machine learning–based models incorporating social determinants of health vs traditional models for predicting in-hospital mortality in patients with heart failure. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, S.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Shiba, K.; Chien, Y.-S.; Mita, C.; Kawachi, I.; Daoud, A. A scoping review on the use of machine learning in research on social determinants of health: Trends and research prospects. SSM-Popul. Health 2021, 15, 100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, A.H.; Sulieman, L.; Schlueter, D.J.; Halvorson, A.; Qian, J.; Ratsimbazafy, F.; Loperena, R.; Mayo, K.; Basford, M.; Deflaux, N.; et al. The All of Us Research Program: Data quality, utility, and diversity. Patterns 2022, 3, 100570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Health. The All of Us Research Program. Available online: https://allofus.nih.gov/get-involved/participation (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Bick, A.G.; Metcalf, G.A.; Mayo, K.R.; Lichtenstein, L.; Rura, S.; Carroll, R.J. Genomic data in the All of Us Research Program. Nature 2024, 627, 340–346. [Google Scholar]
- The Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Healthy People 20230. Social Determinants of Health. Available online: https://health.gov/healthypeople/priority-areas/social-determinants-health (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- The All of Us Research Program National Institutes of Health (NIH). Available online: https://allofus.nih.gov/ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Tesfaye, S.; Cronin, R.M.; Lopez-Class, M.; Chen, Q.; Foster, C.S.; Gu, C.A.; Guide, A.; Hiatt, R.A.; Johnson, A.S.; Joseph, C.L. Measuring social determinants of health in the All of Us Research Program. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunardon, N.; Menardi, G.; Torelli, N. ROSE: Random Over-Sampling Examples; ROSE-Package, Version 00-3, License GPL-2, CRAN; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, M.; Reynolds, E.; Andersson, H.B.; Nallamothu, B.K. Tree-based analysis: A practical approach to create clinical decision-making tools. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 12, e004879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Guo, X.; Yu, H. Variable selection using Mean Decrease Accuracy and Mean Decrease Gini based on Random Forest. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), Beijing, China, 26–28 August 2016; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Rehmsmeier, M. The precision-recall plot is more informative than the ROC plot when evaluating binary classifiers on imbalanced datasets. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menefee, D.S.; Ledoux, T.; Johnston, C.A. The importance of emotional regulation in mental health. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2022, 16, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghöfer, A.; Martin, L.; Hense, S.; Weinmann, S.; Roll, S. Quality of life in patients with severe mental illness: A cross-sectional survey in an integrated outpatient health care model. Qual. Life Res. 2020, 29, 2073–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estancial Fernandes, C.S.; Lima, M.G.; Barros, M.B.d.A. Emotional problems and health-related quality of life: Population-based study. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 3037–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Marzo, J.; Del Castillo, J.G. Relationship between quality of life, emotional symptomology and perceived emotional intelligence in a sample of burn victims. Burns 2024, 50, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guendelman, S.; Medeiros, S.; Rampes, H. Mindfulness and emotion regulation: Insights from neurobiological, psychological, and clinical studies. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhodolsky, D.G.; Golub, A.; Stone, E.C.; Orban, L. Dismantling anger control training for children: A randomized pilot study of social problem-solving versus social skills training components. Behav. Ther. 2005, 36, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Shirotsuki, K.; Sugaya, N. Cognitive–behavioral therapy for management of mental health and stress-related disorders: Recent advances in techniques and technologies. BioPsychoSocial Med. 2021, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, S.P.; Kuckel, D.P.; Huecker, M.R. Cognitive Behavior Therapy. [Updated 2023 May 23]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470241/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Borges, C.C.; Dos Santos, P.R.; Alves, P.M.; Borges, R.C.M.; Lucchetti, G.; Barbosa, M.A.; Porto, C.C.; Fernandes, M.R. Association between spirituality/religiousness and quality of life among healthy adults: A systematic review. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, N.S.d.; Fleck, M.P.d.A. Evaluation of quality of life and importance given to spirituality/religiousness/personal beliefs (SRPB) in adults with and without chronic health conditions. Arch. Clin. Psychiatry (São Paulo) 2011, 38, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinha, F.T.; Banhara, F.L.; Bom, G.C.; Kostrisch, L.M.V.; Prado, P.C.; Trettene, A.d.S. Correlation between religiosity, spirituality and quality of life in adolescents with and without cleft lip and palate. Rev. Lat.-Am. De Enferm. 2018, 26, e3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapes, B.M.; Foster, C.S.; Kusnoor, S.V.; Epelbaum, M.I.; AuYoung, M.; Jenkins, G.; Lopez-Class, M.; Richardson-Heron, D.; Elmi, A.; Surkan, K. Diversity and inclusion for the All of Us research program: A scoping review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczkodaj, W.W.; Kakiashvili, T.; Szymańska, A.; Montero-Marin, J.; Araya, R.; Garcia-Campayo, J.; Rutkowski, K.; Strzałka, D. How to reduce the number of rating scale items without predictability loss? Scientometrics 2017, 111, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
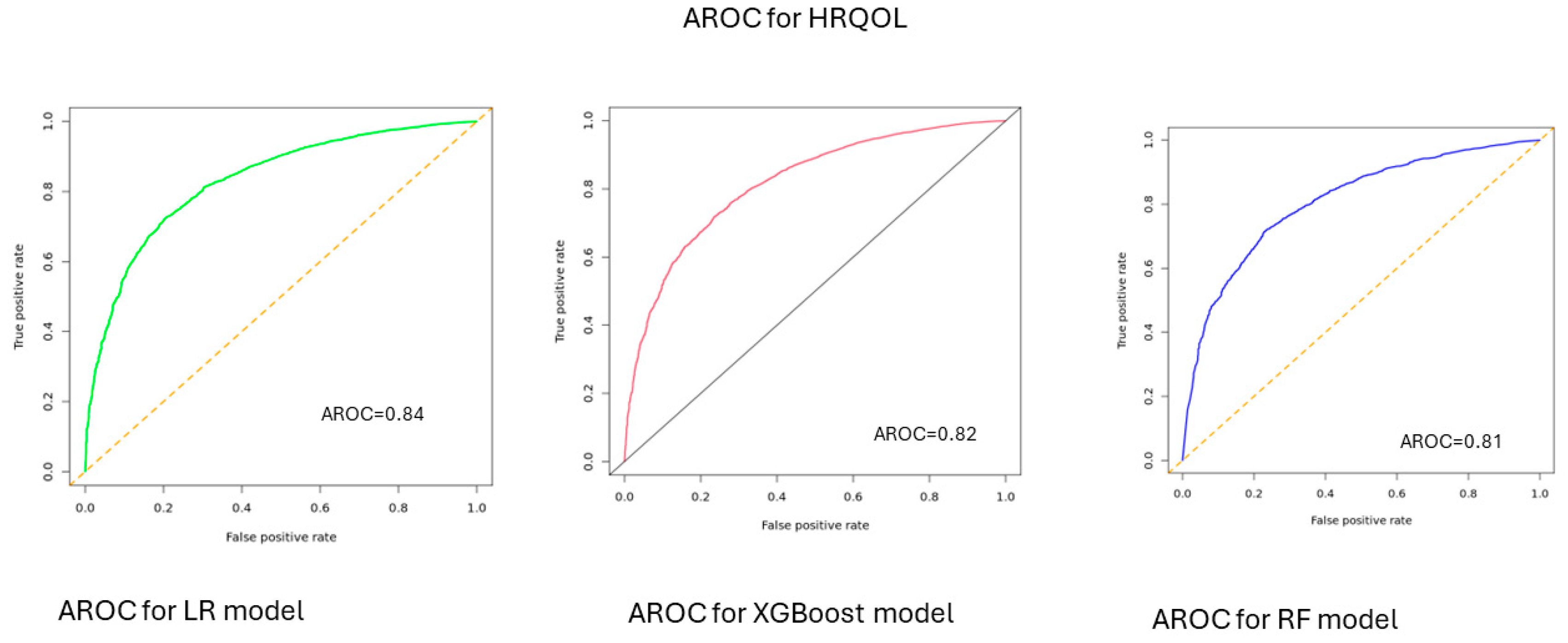



| HRQOL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | AUC-ROC | Sensitivity | Precision | F-1 | Accuracy |
| LR | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 77 [0.76–0.78] |
| XGBoost | 0.82 | 0.78 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.73 [0.72–0.74] |
| RF | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.74 [0.73–0.75] |
| Physical Health | |||||
| Models | AUC-ROC | Sensitivity | Specificity | F-1 | Accuracy |
| LR | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 0.71 [0.70–0.72] |
| XGBoost | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.70 [0.68–0.72] |
| RF | 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.60 | 0.68 | 0.70 [0.68–0.71] |
| Mental Health | |||||
| Models | AUC-ROC | Sensitivity | Specificity | F-1 | Accuracy |
| LR | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.77 [0.76–0.78] |
| XGBoost | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.74 [0.73–0.75] |
| RF | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.72 [0.71–0.73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abegaz, T.M.; Ahmed, M.; Ali, A.A.; Bhagavathula, A.S. Predicting Health-Related Quality of Life Using Social Determinants of Health: A Machine Learning Approach with the All of Us Cohort. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020166
Abegaz TM, Ahmed M, Ali AA, Bhagavathula AS. Predicting Health-Related Quality of Life Using Social Determinants of Health: A Machine Learning Approach with the All of Us Cohort. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(2):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020166
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbegaz, Tadesse M., Muktar Ahmed, Askal Ayalew Ali, and Akshaya Srikanth Bhagavathula. 2025. "Predicting Health-Related Quality of Life Using Social Determinants of Health: A Machine Learning Approach with the All of Us Cohort" Bioengineering 12, no. 2: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020166
APA StyleAbegaz, T. M., Ahmed, M., Ali, A. A., & Bhagavathula, A. S. (2025). Predicting Health-Related Quality of Life Using Social Determinants of Health: A Machine Learning Approach with the All of Us Cohort. Bioengineering, 12(2), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020166











