Non-Invasive Localization of Epileptogenic Zone in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy Based on Time–Frequency Analysis and VGG Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
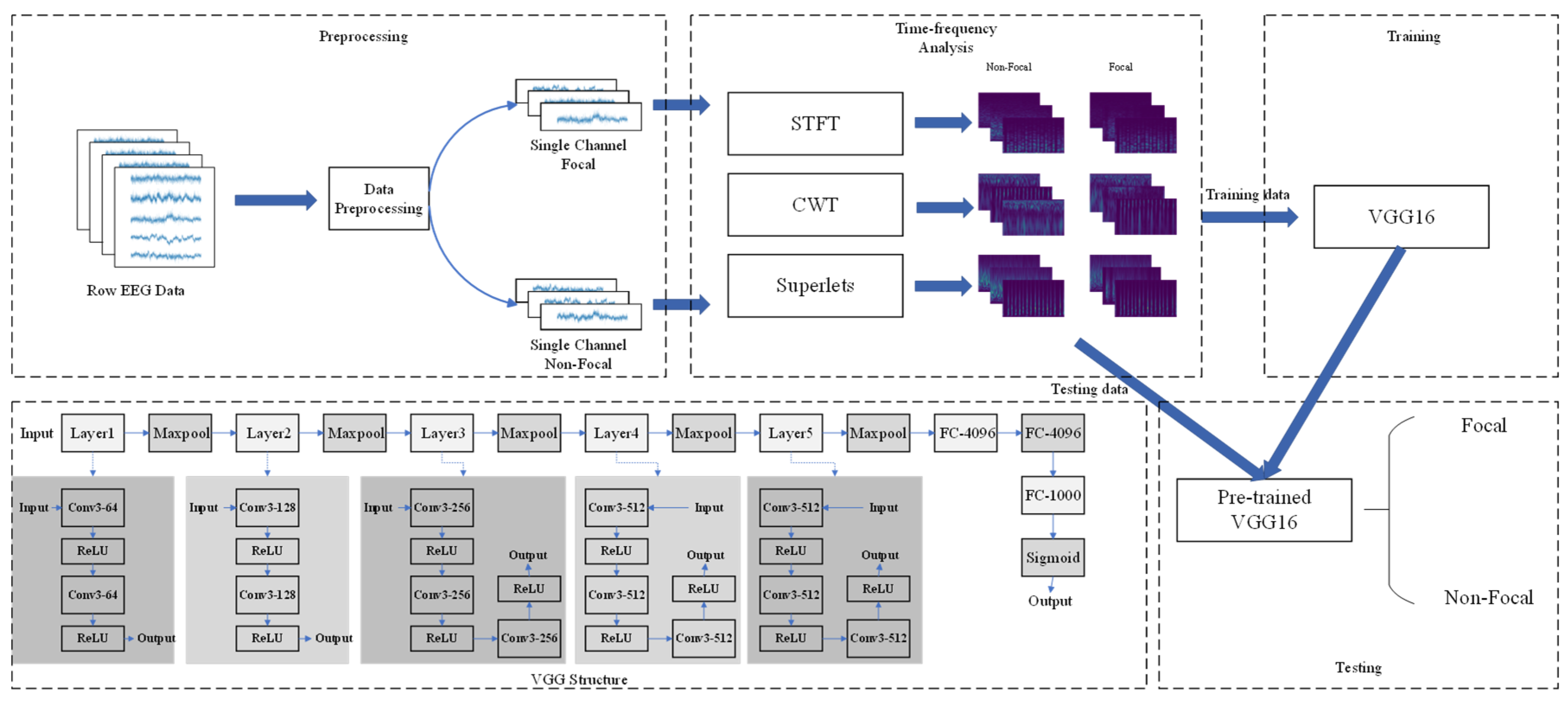
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Description
2.2. EEG Source Imaging
2.3. Short-Time Fourier Transform
2.4. Continuous Wavelet Transform
2.5. Superlets Transform
2.6. VGG Convolutional Neural Network
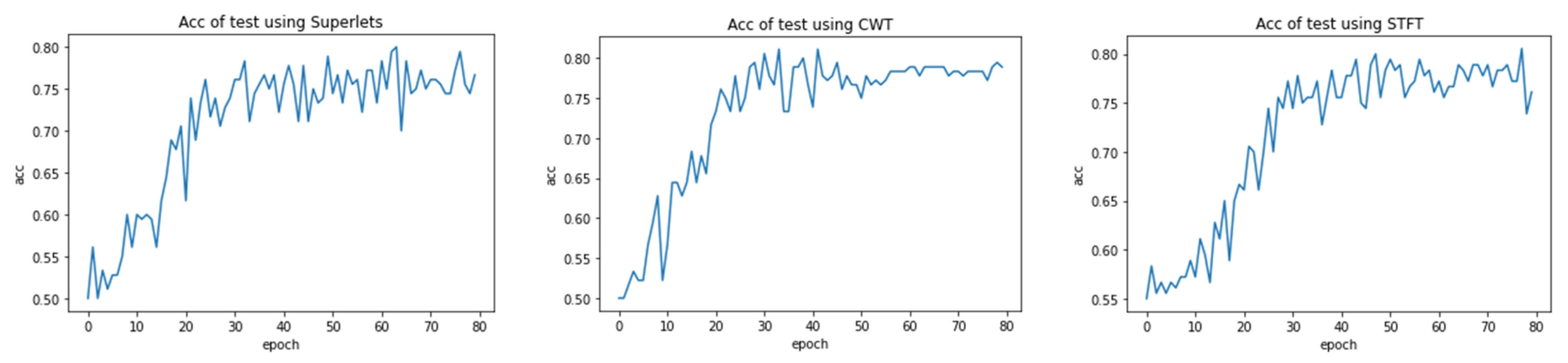
3. Results
4. Discussion
- (1)
- Excellent model performance and relatively high classification accuracy.
- (2)
- Using non-invasive methods to locate the epileptogenic zone.
- (3)
- There are a large number of datasets with diverse categories.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, R.S.; van Emde Boas, W.; Blume, W.; Elger, C.; Genton, P.; Lee, P.; Engel, J., Jr. Epileptic Seizures and Epilepsy: Definitions Proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 2005, 46, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafstrom, C.E.; Carmant, L. Seizures and Epilepsy: An Overview for Neuroscientists. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, X.; Song, M.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, L. The Burden of Epilepsy in the People’s Republic of China from 1990 to 2019: Epidemiological Trends and Comparison with the Global Burden of Epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1303531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Liu, S.; Qin, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, X. Drug-Resistant Epilepsy and Surgery. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Stavem, K. Long-Term Seizure Outcome of Surgery versus No Surgery for Drug-Resistant Partial Epilepsy: A Review of Controlled Studies. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemmar, A.; Nelson, B.J.; Neimat, J.S. Laser Thermal Therapy for Epilepsy Surgery: Current Standing and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Yang, X.; Xu, X.; Ren, L.; Yu, T.; Zhou, W.; Shao, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; et al. Expert Consensus on Clinical Applications of High-Frequency Oscillations in Epilepsy. Acta Epileptol. 2020, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brázdil, M.; Halámek, J.; Jurák, P.; Daniel, P.; Kuba, R.; Chrastina, J.; Novák, Z.; Rektor, I. Interictal High-Frequency Oscillations Indicate Seizure Onset Zone in Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Epilepsy Res. 2010, 90, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstl, J.V.E.; Kiseleva, A.; Imbach, L.; Sarnthein, J.; Fedele, T. High Frequency Oscillations in Relation to Interictal Spikes in Predicting Postsurgical Seizure Freedom. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirodi, M.; Tamilia, E.; Grant, P.E.; Madsen, J.R.; Stufflebeam, S.M.; Pearl, P.L.; Papadelis, C. Noninvasive Localization of High-Frequency Oscillations in Children with Epilepsy: Validation against Intracranial Gold-Standard. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23 July 2019; pp. 1555–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Frauscher, B.; Bartolomei, F.; Kobayashi, K.; Cimbalnik, J.; van ‘t Klooster, M.A.; Rampp, S.; Otsubo, H.; Höller, Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Asano, E.; et al. High-Frequency Oscillations: The State of Clinical Research. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliske, S.V.; Irwin, Z.T.; Chestek, C.; Hegeman, G.L.; Brinkmann, B.; Sagher, O.; Garton, H.J.L.; Worrell, G.A.; Stacey, W.C. Variability in the Location of High Frequency Oscillations during Prolonged Intracranial EEG Recordings. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guragain, H.; Cimbalnik, J.; Stead, M.; Groppe, D.M.; Berry, B.M.; Kremen, V.; Kenney-Jung, D.; Britton, J.; Worrell, G.A.; Brinkmann, B.H. Spatial Variation in High-Frequency Oscillation Rates and Amplitudes in Intracranial EEG. Neurology 2018, 90, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweiphenning, W.; van ’t Klooster, M.A.; van Klink, N.E.C.; Leijten, F.S.S.; Ferrier, C.H.; Gebbink, T.; Huiskamp, G.; van Zandvoort, M.J.E.; van Schooneveld, M.M.J.; Bourez, M.; et al. Intraoperative Electrocorticography Using High-Frequency Oscillations or Spikes to Tailor Epilepsy Surgery in the Netherlands (the HFO Trial): A Randomised, Single-Blind, Adaptive Non-Inferiority Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Dong, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Recent Advances in the Noninvasive Detection of High-Frequency Oscillations in the Human Brain. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 32, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspita, J.W.; Gunadharma, S.; Indratno, S.W.; Soewono, E. Bayesian Approach to Identify Spike and Sharp Waves in EEG Data of Epilepsy Patients. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 35, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Inati, S.; Zaghloul, K.; Sarma, S. Fragility in Epileptic Networks: The Epileptogenic Zone. In Proceedings of the 2017 American Control Conference (ACC), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 May 2017; pp. 2817–2822. [Google Scholar]
- Itakura, T.; Tanaka, T. Epileptic Focus Localization Based on Bivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition and Entropy. In Proceedings of the 2017 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–15 December 2017; pp. 1426–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Al Ghayab, H.R.; Li, Y.; Siuly, S.; Abdulla, S. Epileptic EEG Signal Classification Using Optimum Allocation Based Power Spectral Density Estimation. IET Signal Process. 2018, 12, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Pachori, R.B.; Acharya, U.R. An Integrated Index for the Identification of Focal Electroencephalogram Signals Using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Entropy Measures. Entropy 2015, 17, 5218–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, H.; Bayoumi, M. Deep Learning Approach for Epileptic Focus Localization. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 14, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.B.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H. Discrimination and Classification of Focal and Non-Focal EEG Signals Using Entropy-Based Features in the EMD-DWT Domain. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 29, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, Q.; Tanaka, T.; Cao, J.; Kong, W.; Sugano, H.; Yoshida, N. Detection of Epileptic Foci Based on Interictal iEEG by Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Shanghai, China, 19–21 November 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, E.; Juhász, C.; Shah, A.; Muzik, O.; Chugani, D.C.; Shah, J.; Sood, S.; Chugani, H.T. Origin and Propagation of Epileptic Spasms Delineated on Electrocorticography. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, G.; Müller, P.M.; Holtkamp, M.; Meisel, C. Prediction of Epilepsy Surgery Outcome Using Foramen Ovale EEG—A Machine Learning Approach. Epilepsy Res. 2023, 191, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, F.; Tyvaert, L.; Nguyen, D.K.; LeVan, P.; Bouthillier, A.; Kobayashi, E.; Tampieri, D.; Dubeau, F.; Gotman, J. EEG-fMRI:Adding to Standard Evaluations of Patients with Nonlesional Frontal Lobe Epilepsy. Neurology 2009, 73, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarrese, M.A.G.; Loppini, A.; Fabbri, L.; Tamilia, E.; Perry, M.S.; Madsen, J.R.; Bolton, J.; Stone, S.S.D.; Pearl, P.L.; Filippi, S.; et al. Spike Propagation Mapping Reveals Effective Connectivity and Predicts Surgical Outcome in Epilepsy. Brain 2023, 146, 3898–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, I.Z.; Bulacio, J.C.; Mosher, J.C.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Alexopoulos, A.V.; Najm, I.M.; So, N.K. Ripple Classification Helps to Localize the Seizure-Onset Zone in Neocortical Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilia, E.; Matarrese, M.A.G.; Ntolkeras, G.; Grant, P.E.; Madsen, J.R.; Stufflebeam, S.M.; Pearl, P.L.; Papadelis, C. Noninvasive Mapping of Ripple Onset Predicts Outcome in Epilepsy Surgery. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Q.; Tanaka, T.; Cao, J. Localization of Epileptic Foci by Using Convolutional Neural Network Based on iEEG. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations; MacIntyre, J., Maglogiannis, I., Iliadis, L., Pimenidis, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, M.; Sui, L.; Zhao, X.; Tanaka, T.; Cao, J. Convolution Neural Network Recognition of Epileptic Foci Based on Composite Signal Processing of Electroencephalograph Data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 192, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wilke, C.; Brinkmann, B.; Worrell, G.A.; He, B. Dynamic Imaging of Ictal Oscillations Using Non-Invasive High-Resolution EEG. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 1908–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.M.; Brunet, D. EEG Source Imaging: A Practical Review of the Analysis Steps. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Broek, S.P.; Reinders, F.; Donderwinkel, M.; Peters, M.J. Volume Conduction Effects in EEG and MEG. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 106, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, J.G.; Peled, N.; Mamashli, F.; Ahveninen, J.; Hämäläinen, M.S. Spatial Fidelity of MEG/EEG Source Estimates: A General Evaluation Approach. NeuroImage 2021, 224, 117430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadat-Nejad, Y.; Beheshti, S. Efficient High Resolution sLORETA in Brain Source Localization. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 016013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R. Standardized Low-Resolution Brain Electromagnetic Tomography (sLORETA): Technical Details. METHODS Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 24, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kıymık, M.K.; Güler, İ.; Dizibüyük, A.; Akın, M. Comparison of STFT and Wavelet Transform Methods in Determining Epileptic Seizure Activity in EEG Signals for Real-Time Application. Comput. Biol. Med. 2005, 35, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bünau, P.; Meinecke, F.C.; Scholler, S.; Müller, K.-R. Finding Stationary Brain Sources in EEG Data. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 2810–2813. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Q.; Tanaka, T.; Cao, J. Hybrid Convolutional Neural Network for Localization of Epileptic Focus Based on iEEG. Neural Plast. 2021, 2021, 6644365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhif, M.; Ben Abbes, A.; Farah, I.R.; Martínez, B.; Sang, Y. Wavelet Transform Application for/in Non-Stationary Time-Series Analysis: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabby, M.K.M.; Islam, A.K.M.K.; Belkasim, S.; Bikdash, M.U. Wavelet Transform-Based Feature Extraction Approach for Epileptic Seizure Classification. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Southeast Conference; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, C. Fourier and Wavelet Analyses of Normal and Epileptic Electroencephalogram (EEG). In Proceedings of the First International IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, Capri Island, Italy, 20–22 March 2003; pp. 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Samdin, S.B.; Minhad, K.N. Window-Based Time-Frequency Methods for Analyzing Epileptic EEG Signals. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 7–9 December 2022; pp. 292–297. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Huynh, C.; Fitzgerald, Z.; Cajigas, I.; Brusko, D.; Jagid, J.; Claudio, A.O.; Kanner, A.M.; Hopp, J.; Chen, S.; et al. Neural Fragility as an EEG Marker of the Seizure Onset Zone. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-W.; Lee, M.-H.; Kuroda, N.; Sakakura, K.; O’Hara, N.; Juhasz, C.; Asano, E. Multi-Scale Deep Learning of Clinically Acquired Multi-Modal MRI Improves the Localization of Seizure Onset Zone in Children With Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 5529–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.M.; von Paternos, A.J.; Santaniello, S. A Novel HFO-Based Method for Unsupervised Localization of the Seizure Onset Zone in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 1054–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Vorderwülbecke, B.J.; Baroumand, A.G.; Spinelli, L.; Seeck, M.; van Mierlo, P.; Vulliémoz, S. Automated Interictal Source Localisation Based on High-Density EEG. Seizure-Eur. J. Epilepsy 2021, 92, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi Sebastiano, D.; Tassi, L.; Duran, D.; Visani, E.; Gozzo, F.; Cardinale, F.; Nobili, L.; Del Sole, A.; Rubino, A.; Dotta, S.; et al. Identifying the Epileptogenic Zone by Four Non-Invasive Imaging Techniques versus Stereo-EEG in MRI-Negative Pre-Surgery Epilepsy Patients. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, S.S.; Parhi, K.K. Seizure Onset Zone Identification From iEEG: A Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 62535–62547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, L.; Tamilia, E.; Perry, M.S.; Madsen, J.R.; Bolton, J.; Stone, S.S.D.; Stufflebeam, S.M.; Pearl, P.L.; Papadelis, C. Non-Invasive Mapping of Epileptogenic Networks Predicts Surgical Outcome. Brain 2023, 146, 1916–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Önal, Ç.; Otsubo, H.; Araki, T.; Chitoku, S.; Ochi, A.; Weiss, S.; Logan, W.; Elliott, I.; Snead, O.C.; Rutka, J.T. Complications of Invasive Subdural Grid Monitoring in Children with Epilepsy. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Kokkinos, V.; Ye, S.; Urban, A.; Bagić, A.; Richardson, M.; He, B. Interictal SEEG Resting-State Connectivity Localizes the Seizure Onset Zone and Predicts Seizure Outcome. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| # | Sex | Age at Surgery | Age Epilepsy Onset | Etiology | Engel Grading | Num. of EZ | Num. of Seizures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 31 | 27 | Unknow | Engel I | 5 | 1 |
| 2 | M | 23 | 3 | FCD | Engel I | 14 | 2 |
| 3 | F | 12 | 11 | Unknow | Engel I | 11 | 4 |
| 4 | M | 28 | 20 | Unknow | Engel I | 13 | 4 |
| 5 | F | 8 | 7 | Unknow | Engel I | 10 | 2 |
| 6 | F | 28 | 12 | Unknow | Engel I | 12 | 3 |
| 7 | M | 36 | 18 | Unknow | Engel I | 12 | 2 |
| 8 | M | 23 | 16 | Unknow | Engel I | 11 | 2 |
| 9 | M | 15 | 3 | FCD | Engel I | 18 | 4 |
| 10 | M | 30 | 25 | Unknow | Engel I | 10 | 2 |
| 11 | F | 26 | 6 | Unknow | Engel I | 11 | 3 |
| 12 | M | 22 | 7 | Unknow | Engel I | 9 | 3 |
| 13 | F | 16 | 13 | Unknow | Engel I | 7 | 2 |
| 14 | M | 12 | 7 | Unknow | Engel I | 10 | 1 |
| 15 | M | 22 | 20 | FCD | Engel I | 5 | 2 |
| 16 | F | 35 | 16 | Unknow | Engel I | 15 | 4 |
| 17 | M | 28 | 4 | Unknow | Engel I | 10 | 1 |
| 18 | F | 31 | 5 | FCD | Engel I | 6 | 3 |
| 19 | F | 26 | 7 | Unknow | Engel I | 6 | 3 |
| 20 | M | 37 | 35 | FCD | Engel I | 15 | 2 |
| 21 | F | 20 | 18 | Unknow | Engel I | 25 | 2 |
| 22 | M | 18 | 10 | FCD | Engel I | 10 | 2 |
| 23 | F | 31 | 21 | Tuberous sclerosis | Engel I | 11 | 3 |
| 24 | M | 26 | 1 | Unknow | Engel I | 28 | 2 |
| 25 | M | 22 | 9 | Unknow | Engel I | 5 | 1 |
| Time–Frequency Spectrum | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | N-Precision | N-Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STFT | 80.2% | 80.1% | 80.7% | 80.7% | 79.6% |
| CWT | 81.7% | 82.1% | 81.4% | 81.8% | 81.7% |
| superlets | 83.1% | 83.0% | 83.3% | 83.4% | 82.8% |
| Author (Year) | Data | Extraction Methods | Classifier | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adam Li et al. (2022) [45] | iEEG | neural fragility of the iEEG network | / | 76% |
| Jeong-Won et al. (2022) [46] | iEEG | multi-model MRI features | msResNet | 75% |
| Paige M.Murphy et al. (2017) [47] | iEEG | HFO | / | 70% |
| Bernd et al. (2021) [48] | HD-EEG | spike detection and clustering | / | 55–71% |
| Davide et al. (2020) [49] | PET, MEG, EEG-fMRI, HR-EEG | / | / | 80% |
| Ours | Scalp EEG | STFT | VGG-16 | 80.20% |
| CWT | 81.70% | |||
| superlets | 83.10% |
| Deep Learning | Time–Frequency Feature | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | N-Precision | N-Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SqueezeNet | STFT | 79.1% | 78.1% | 79.7% | 80.2% | 78.4% |
| CWT | 79.8% | 81.1% | 79.2% | 80.2% | 80.3% | |
| Superlets | 80.3% | 81.4% | 82.2% | 81.8% | 81.1% | |
| ResNet | STFT | 79.3% | 78.2% | 79.5% | 79.8% | 78.8% |
| CWT | 79.9% | 80.8% | 80.0% | 80.4% | 80.1% | |
| Superlets | 80.6% | 81.1% | 81.8% | 81.6% | 80.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Non-Invasive Localization of Epileptogenic Zone in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy Based on Time–Frequency Analysis and VGG Convolutional Neural Network. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050443
Liu Y, Wang Y, Wang T. Non-Invasive Localization of Epileptogenic Zone in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy Based on Time–Frequency Analysis and VGG Convolutional Neural Network. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(5):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050443
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yaqing, Yalin Wang, and Tiancheng Wang. 2025. "Non-Invasive Localization of Epileptogenic Zone in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy Based on Time–Frequency Analysis and VGG Convolutional Neural Network" Bioengineering 12, no. 5: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050443
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wang, Y., & Wang, T. (2025). Non-Invasive Localization of Epileptogenic Zone in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy Based on Time–Frequency Analysis and VGG Convolutional Neural Network. Bioengineering, 12(5), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050443







