Bioengineering Progress in Lung Assist Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Historical Progress
2.1. Prehistory of Clinical Oxygenators
2.2. Direct-Contact Oxygenators for Clinical Usage
2.3. Rise of Membrane Oxygenators
2.4. Towards Prolonged Life Support
2.5. From ECMO to Artificial Lungs
3. Modern Technologies
3.1. Ecmo Today
3.2. Intravascular Lung Assist
3.3. Pumpless Extracorporeal Lung Assist
3.4. Total Artificial Lung
3.5. Artificial Lung Microtechnology
4. Portable Ventilators
5. In Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valapour, M.; Lehr, C.J.; Skeans, M.A.; Smith, J.M.; Uccellini, K.; Lehman, R.; Robinson, A.; Israni, A.K.; Snyder, J.J.; Kasiske, B.L. OPTN/SRTR 2017 Annual Data Report: Lung. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 404–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN); Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients (SRTR). OPTN/SRTR 2012 Anual Data Report; Department of Health and Human Services Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2014.
- Belt, A.E.; Smith, H.P.; Whipple, G.H. III. Factors concerned in the perfusion of living organs and tissues: Artificial solutions substituted for blood serum and the resulting injury to parenchyma cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1920, 52, 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- Le Gallois, C.J.J. Expériences sur le principe de la vie. Notamment sur Celui des Mouvemens du Coeur, et Sur le Siége de ce Principe; Suivies du rapport fait á la premiére classe de l’Institt sur celles relatives aux movemens du Coeur; D’Hautel: Paris, France, 1812. [Google Scholar]
- Lobell, C.E. De Conditionibus Quibus Secretiones in Glandulis Perficiuntur; Typ Elwerti: Sint-Hubertusstraat, The Netherlands, 1849. [Google Scholar]
- Shumacker, H.B., Jr. The Evolution of Cardiac Surgery; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IL, USA, 1992; 243p. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, C.F. Die Physiologischen Leistungen des Blutdrucks; S. Hirsel: Leipsig, Germany, 1865. [Google Scholar]
- von Schröder, W. Uber die Bildungstätte des Harnstoffs. Arch. Fur Exp. Pathol. Und Pharmakol. 1882, 15, 364–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Frey, M.; Gruber, M. Ein respirations-apparat fur isolierte organe. Virchows Arch. Fur Physiol. 1885, 9, 519–532. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, R.L.; Creech, O., Jr. History of the pump oxygenator. Arch. Surg. Chic. 1966, 93, 680–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, W.D.; Churchill-Davidson, H.C. A Practice of Anaesthesia, 3rd ed.; Lloyd-Luke: London, UK, 1972; pp. 691–715. [Google Scholar]
- Brodie, T.G. The perfusion of surviving organs. J. Physiol. 1903, 29, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, A.N.; Drinker, C.K. An apparatus for the perfusion of isolated organs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1915, 7, 467–483. [Google Scholar]
- Hooker, D.R. A study of the isolated kidney: The influence of pulse pressure upon renal function. Am. J. Physiol. 1910, 27, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brukhonenko, S.; Tchetchuline, S. Experiences avec la tete isolee du chien. J. Physiol. Pathol. Gen. 1929, 27, 31–79. [Google Scholar]
- Galletti, P.M. Cardiopulmonary bypass: A historical perspective. Artif. Organs 1993, 17, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjork, V.O. Brain perfusions in dogs with artificially oxygenated blood. Acta Chir. Scand. 1948, 96, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, L.C., Jr.; Gollan, F.; Gupta, V.B. The oxygenation of blood by gas dispersion. Science 1950, 111, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.J.; Gibbon, J.H.; Fineburg, C. An improved mechanical heart and lung apparatus; its use during open cardiotomy in experimental animals. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1953, 1, 1603–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbon, J.H., Jr. Application of a mechanical heart and lung apparatus to cardiac surgery. Minn. Med. 1954, 37, 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- Gravlee, G.P.; Davis, R.F.; Stammers, A.H.; Ungerleider, R.M. Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Principles and Practice, 3rd ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Melrose, D.G. Cardiovascular disease: Extracorporeal circulation. Annu. Rev. Med. 1961, 12, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoney, W.S. Evolution of Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Circulation 2009, 119, 2844–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirklin, J.W.; Donald, D.E.; Harshbarger, H.G.; Hetzel, P.S.; Patrick, R.T.; Swan, H.J.; Wood, E.H. Studies in extracorporeal circulation. I. Applicability of Gibbon-type pump-oxygenator to human intracardiac surgery: 40 cases. Ann. Surg. 1956, 144, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, R.M.; Cross, F.S.; Hirose, Y.; Jones, R.D.; Kay, E.B.; Zimmerman, H.A. Certain clinical aspects of the use of a pump-oxygenator. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1956, 162, 639–641. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, E.S.; Berne, R.M.; Hirose, Y. Evaluation of a rotating disc type oxygenator. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1956, 93, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.S.; Wong, H.R.; Shanley, T.P. (Eds.) Pediatric Critical Care Medicine: Basic Science and Clinical Evidence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 727–728. [Google Scholar]
- DeWall, R.A.; Gott, V.L.; Lillehei, C.W.; Read, R.C.; Varco, R.L.; Warden, H.E.; Ziegler, N.R. A simple, expendable, artificial oxygenator for open heart surgery. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 1956, 36, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, R. The technique and scope of open-heart surgery. Postgrad. Med. J. 1967, 43, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, R.H.; Harken, D.E. Instrumentation for cardiopulmonary bypass—past, present and future. Med. Instrum. 1976, 10, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, M.H.; Elias, D.O. Fundamentos da Circulação Extracorporeal; Alfa Rio: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.H., Jr.; Krumhaar, D.; Fonkalsrud, E.W.; Schjeide, O.A.; Maloney, J.V., Jr. Denaturation of plasma proteins as a cause of morbidity and death after intracardiac operations. Surgery 1961, 50, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Dobell, A.R.C.; Mitri, M.; Galva, R.; Sarkozy, E.; Murphy, D.R. Biologic evaluation of blood after prolonged recirculation through film and membrane oxygenators. Ann. Surg. 1965, 161, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.N.; Kuchiba, K. Blood trauma produced by pump oxygenators: A comparative study of five different units. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1969, 57, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddicoat, J.E.; Bekassy, S.M.; Beall, A.C., Jr.; Glaeser, D.H.; DeBakey, M.E. Membrane vs bubble oxygenator: Clinical comparison. Ann. Surg. 1975, 181, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.H. The development of prolonged extracorporeal circulation. In Extracorporeal Life Support; Arensman, R.M., Cornish, J.D., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Boston, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, M.W. The history of extracorporeal oxygenators. Anaesthesia 2006, 61, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.H. Extracorporeal life support: History and new directions. Semin. Perinatol. 2005, 29, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolff, W.J.; Berk, H.T. Artificial kidney: Dialyzer with great area. Acta Med. Scand. 1944, 117, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolff, W.J.; Effler, D.B.; Groves, L.K.; Peereboom, G.; Moraca, P.P. Disposable membrane oxygenator (heart-lung machine) and its use in experimental surgery. Clevel. Clin. Q. 1956, 23, 69–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbelman, C.P. Attempts to design an Artificial Heart-Lung Apparatus for the Human Adult. Acta Physiol. et Pharmacol. Neerl. 1953, 2, 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Kolff, W.J.; Baltzer, R. The artificial coil lung. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1955, 1, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Clowes, G.H.A., Jr.; Neville, W.E. The Membrane Oxygenator. Extracorporeal Circulation; Thomas: Springfield, MA, USA, 1958; pp. 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Peirce, E.C., II; Converse, E.; Peirce, G. The membrane lung: The influence of membrane characteristics and lung design on gas exchange. J. Surg. Res. 1963, 3, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, N. Production of a silicone rubber film for the membrane lung. Biomed. Eng. 1969, 4, 356–359. [Google Scholar]
- Bodell, B.R.; Head, J.M.; Head, L.R.; Formolo, A.J.; Head, J.R. A capillary membrane oxygenator. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1963, 46, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramson, M.L.; Osborn, J.J.; Main, F.B.; O’Brien, M.F.; Wright, J.S.; Gerbode, F. A new disposable membrane oxygenator with integral heat exchange. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1965, 50, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobow, T.; Bowman, R.L. Construction and evaluation of an alveolar membrane artificial heart-lung. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs. 1963, 9, 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Drinker, P.A. Progress in membrane oxygenator designs. Anesthesiology 1972, 37, 242–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.D.; O’Brien, T.G.; Murray, J.J.; Dontigny, L.; Bramson, M.L.; Osborn, J.J.; Gerbode, F. Prolonged extracorporeal oxygenation for acute post-traumatic respiratory failure (shock–lung syndrome). Use of the Bramson membrane lung. N. Engl. J. Med. 1972, 286, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, W.; Trudell, L.A.; Friedman, L.I.; Kakvan, M.; Richardson, P.D.; Karlson, K.; Galletti, P.M. Laboratory and clinical experience with a microporous membrane oxygenator. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1974, 20, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, R.H.; Fong, S.W.; Woldanski, C.; Hung, E.; Styler, D.; MacArthur, C. Hematologic responses to prolonged extracorporeal circulation (ECC) with microporous membrane devices. ASAIO J. 1975, 21, 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, J.D.; Iatridis, A.; O’Keefe, R.; Kitrilakis, S. Technique for achieving high gas exchange rates in membrane oxygenation. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1974, 20, 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Zapol, W.M.; Snider, M.T.; Schneider, R.C. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute respiratory failure. Anesthesiology 1977, 46, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drinker, P.A.; Lehr, J.L. Engineering aspects of ECMO technology. Artif. Organs 1978, 2, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, R.J. The transition from the bubble oxygenator to the microporous membrane oxygenator. Perfusion 2003, 18, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbecker, R. The membrane lung—A quiet revolution. Am. J. Cardiol. 1976, 37, 1117–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhees, M.E.; Brian, B.F., III. Blood-gas exchange devices. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 1996, 34, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.H.; Fong, S.W.; Burns, N.E.; Gazzaniga, A.B. Prolonged partial venoarterial bypass: Physiologic, biochemical, and hematologic responses. Ann. Surg. 1974, 180, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, S.W.; Burns, N.E.; Williams, G.; Woldanski, C.; Gazzaniga, A.B.; Bartlett, R.H. Changes in coagulation and platelet function during prolonged extracorporeal circulation (ECC) in sheep and man. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1974, 20, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Zapol, W.M.; Snider, M.T.; Hill, J.D.; Fallat, R.J.; Bartlett, R.H.; Edmunds, L.H.; Morris, A.H.; Peirce, E.C.; Thomas, A.N.; Proctor, H.J.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in severe acute respiratory failure. A randomized prospective study. JAMA 1979, 242, 2193–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.H.; Roloff, D.W.; Cornell, R.G.; Andrews, A.F.; Dillon, P.W.; Zwischenberger, J.B. Extracorporeal circulation in neonatal respiratory failure: A prospective randomized study. Pediatrics 1985, 76, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobow, T.; Borelli, M.; Spatola, R. Artificial lung (oxygenators). Artif. Organs 1986, 10, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelems, J.M.; Rebuck, A.S.; Cooper, J.D.; Goldberg, M.; Halloran, P.F.; Vellend, H. Human lung transplantation. CHEST J. 1980, 78, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylor, J.D.S. Membrane oxygenators: Current developments in design and application. J. Biomed. Eng. 1988, 10, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapol, W.M.; Kolobow, T. Extracorporeal membrane lung gas exchange. In The Lungs; Scientific Foundations; Crystal, R.G., West, J.B., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 2197–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Servas, F.M.; Diettrich, L.J.; Jones, K.; Whittaker, D.; Curtis, R. High efficiency membrane oxygenator. ASAIO J. 1983, 29, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Bergdahl, M.E.; Bergdahl, L.A. A Comparison of Flat-Sheet and Hollow-Fiber Membrane Oxygenators: The Shiley M-2000 vs. the Bentley BOS-CM 40. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 1989, 16, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, F.J.; Fuller, L.E.; Irmiter, R.J. Oxygenator Having an Improved Heat Exchanger. U.S. Patent US 4,645,645, 24 February 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, T.; Suma, K.; Tanishita, K.; Fukazawa, H.; Kanno, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Takahashi, A. Development and clinical evaluation of hollow fiber membrane oxygenator. ASAIO J. 1981, 27, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, L.I.; Richardson, P.D.; Galletti, P.M. Observations of acute thrombogenesis in membrane oxygenators. ASAIO J. 1971, 17, 369–375. [Google Scholar]
- Mockros, L.F.; Leonard, R. Compact cross-flow tubular oxygenators. ASAIO J. 1985, 31, 628–633. [Google Scholar]
- Colton, C.K. Fundamentals of gas transport in blood. In Artificial Lungs for Acute Respiratory Failure Theory and Practice; Zapol, W.M., Qvist, J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 3–41. [Google Scholar]
- Spratt, E.H.; Melrose, D.; Bellhouse, B.; Badolato, A.; Thompson, R. Evaluation of a membrane oxygenator for clinical cardiopulmonary bypass. ASAIO J. 1981, 27, 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington, K.L.; Ralph, M.E.; Bellhouse, B.J.; Gardaz, J.P.; Sykes, M.K. Oxygen and CO2 transfer of a polypropylene dimpled membrane lung with variable secondary flows. J. Biomed. Eng. 1985, 7, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, W.S. The development of the modern oxygenator. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 76, S2216–S2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottaghy, K.; Oedekoven, B.; Starmans, H.; Müller, B.; Kashefi, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Böhm, S. Technical aspects of plasma leakage prevention in microporous capillary membrane oxygenators. ASAIO J. 1989, 35, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.P.; Shanley, C.J.; Merz, S.I.; Bartlett, R.H. Plasma leakage through microporous membranes: Role of phospholipids. ASAIO J. 1992, 38, M399–M405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peek, G.J.; Killer, H.M.; Reeves, R.; Sosnowski, A.W.; Firmin, R.K. Early experience with a polymethyl pentene oxygenator for adult extracorporeal life support. ASAIO J. 2002, 48, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobow, T.; Gattinoni, L.; Tomlinson, T.A.; Pierce, J.E. Control of breathing using an extracorporeal membrane lung. Anesthesiology 1977, 46, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolobow, T.; Gattinoni, L.; Tomlinson, T.; Pierce, J.E. An alternative to breathing. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1978, 75, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Pesenti, A.; Mascheroni, D.; Marcolin, R.; Fumagalli, R.; Rossi, F.; Lapichino, G.; Romagnoli, G.; Uziel, L.; Agostoni, A.; et al. Low frequency positive pressure ventilation with extracorporeal CO2 removal in severe acute respiratory failure. JAMA 1986, 256, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, F.; Belghith, M.; Mira, J.P.; Lanore, J.J.; Vaxelaire, J.F.; Santucci, J.D.A.; Dhainaut, J.F. Extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal and low frequency positive pressure ventilation: Improvement in arterial oxygenation with reduction of risk of pulmonary barotrauma in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Chest J. 1993, 104, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, A.H.; Wallace, C.J.; Menlove, R.L.; Clemmer, T.P.; Orme, J.F., Jr.; Weaver, L.K. Randomized clinical trial of pressure controlled inverse ratio ventilation and extracorporeal CO2 removal for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.H.; Andrews, A.F.; Toomasian, J.M.; Haiduc, N.J.; Gazzaniga, A.B. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for newborn respiratory failure: Forty-five cases. Surgery 1982, 92, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, R.H.; Gazzaniga, A.B.; Toomasian, J.M.; Coran, A.G.; Roloff, D.; Rucker, R.; Corwin, A.G. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in neonatal respiratory failure. 100 cases. Ann. Surg. 1986, 204, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, P.P.; Crone, R.K.; Vacanti, J.P.; Ware, J.H.; Lillehei, C.W.; Parad, R.B.; Epstein, M.F. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and conventional medical therapy in neonates with persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: A prospective randomized study. Pediatrics 1989, 84, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toomasian, J.M.; Snedecor, S.M.; Cornell, R.G.; Cilley, R.E.; Bartlett, R.H. National experience with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for newborn respiratory failure: Data from 715 cases. ASAIO J. 1988, 34, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, J.A. Oxygenator anatomy and function. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 1997, 11, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, S.E.; Ankney, N.; Cochran, J.B.; Highland, K.B. Critical care challenges in the adult ECMO patient. Dimens. Crit. Care Nurs. 2005, 24, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.G. Changing criteria for the artificial lung: Historic controls on the technology of ECMO. ASAIO J. 1994, 40, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosse, E.; Moen, O.; Johnson, E.; Semb, G.; Brockmeier, V.; Mollnes, T.E.; Fagerhol, M.K.; Venge, P. Reduced complement and granulocyte activation with heparin-coated cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1994, 58, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, O.; Fosse, E.; Dregelid, E.; Brockmeier, V.; Andersson, C.; Høgåsen, K.; Venge, P.; Mollnes, T.E.; Kierulf, P. Centrifugal pump and heparin coating improves cardiopulmonary bypass biocompatibility. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1996, 62, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, O.; Fosse, E.; Bråten, J.; Andersson, C.; Høgåsen, K.; Mollnes, T.E.; Venge, P.; Kierulf, P. Differences in blood activation related to roller/centrifugal pumps and heparin coated/uncoated surfaces in a cardiopulmonary bypass model circuit. Perfusion 1996, 11, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbin, E.; Roberts, N.; Harvey, C.; Machin, D.; Killer, H.; Peek, G.J. Poly-methyl pentene oxygenators have improved gas exchange capability and reduced transfusion requirements in adult extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. ASAIO J. 2005, 51, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, D.S.; Ing, R.; Cheifetz, I.M.; Walczak, R.; Craig, D.; Schulman, S. Hemolytic characteristics of three commercially available centrifugal blood pumps. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 6, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshbin, E.; Westrope, C.; Pooboni, S.; Machin, D.; Killer, H.; Peek, G.J. Performance of polymethyl pentene oxygenators for neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A comparison with silicone membrane oxygenators. Perfusion 2005, 20, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodin, M.S.; Thor, E.J.; Haworth, W.S. Use of computational fluid dynamics in the design of the Avecor Affinity oxygenator. Perfusion 1994, 9, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, N.; Nakamura, M.; Sakai, K.; Kuwana, K.; Tahara, K. Theoretical and experimental evaluation for blood pressure drop and oxygen transfer rate in outside blood flow membrane oxygenator. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1999, 32, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, M.J.; Wilhelm, C.R.; Gage, K.L.; Fabrizio, M.C.; Wagner, W.R. Modeling flow effects on thrombotic deposition in a membrane oxygenator. Artif. Organs 2000, 24, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLaren, G.; Combes, A.; Bartlett, R.H. Contemporary extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for adult respiratory failure: Life support in the new era. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.H. Exciting new ECMO technology awaits compelling scientific evidence for widespread use in adults with respiratory failure. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, R.H.; Gattinoni, L. Current status of extracorporeal life support (ECMO) for cardiopulmonary failure. Minerva Anestesiol. 2010, 76, 534–540. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Guzman, E.; Hoopes, C.W.; Zwischenberger, J.B. The evolution of extracorporeal life support as a bridge to lung transplantation. ASAIO J. 2013, 59, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.T.; Zwischenberger, J.B. Artificial Lung and Novel Devices for Respiratory Support. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 25, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Niu, S.; Bianchi, G.; Wei, X.; Garimella, N.; Griffith, B.P.; Wu, Z.J. Biocompatibility Assessment of a Long-Term Wearable Artificial Pump-Lung in Sheep. Artif. Organs 2013, 37, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaslef, S.N. Implantable artificial lungs: Fantasy or feasibility. Eurekah Biosci. 2005, 1, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen, J.D.; Berry, G. Conceptual and design features of a practical, clinically effective intravenous mechanical blood oxygen/carbon dioxide exchange device (IVOX). Int. J. Artif. Organs 1989, 12, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwischenberger, J.B.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tao, W.; Bush, P.E.; Cox, C.S.; Traber, D.L. IVOX with gradual permissive hypercapnia: A new management technique for respiratory failure. J. Surg. Res. 1994, 57, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwischenberger, J.B.; Tao, W.; Niranjan, S.; Clark, J.W.; Bidani, A. Intravascular membrane oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal with IVOX: Can improved design and permissive hypercapnia achieve adequate respiratory support during severe respiratory failure? Artif. Organs 1994, 18, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwischenberger, J.B.; Tao, W.; Bidani, A. Intravascular membrane oxygenator and carbon dioxide removal devices: A review of performance and improvements. ASAIO J. 1999, 45, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaslef, S.N.; Mockros, L.F.; Anderson, R.W. Development of an intravascular lung assist device. ASAIO Trans. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1988, 35, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarewicz, A.J.; Mockros, L.F.; Anderson, R.W. A dynamic intravascular artificial lung. ASAIO J. 1994, 40, M747–M750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattler, B.G.; Lund, L.W.; Golob, J.; Russian, H.; Lann, M.F.; Merrill, T.L. A respiratory gas exchange catheter: In vitro and in vivo tests in large animals. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2002, 124, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eash, H.J.; Frankowski, B.J.; Hattler, B.G.; Federspiel, W.J. Evaluation of local gas exchange in a pulsating respiratory support catheter. ASAIO J. 2005, 51, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mihelc, K.M.; Frankowski, B.J.; Lieber, S.C.; Moore, N.D.; Hattler, B.G.; Federspiel, W.J. Evaluation of a respiratory assist catheter that uses an impeller within a hollow fiber membrane bundle. ASAIO J. 2009, 55, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, D.; Boffini, M.; Del Sorbo, L.; El Qarra, S.; Comoglio, C.; Ribezzo, M. The Use of CO2 Removal Devices in Patients Awaiting Lung Transplantation: An Initial Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camboni, D.; Philipp, A.; Arlt, M.; Pfeiffer, M.; Hilker, M.; Schmid, C. First experience with a paracorporeal artificial lung in humans. ASAIO J. 2009, 55, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegger, D.; Revelly, J.P.; Horisberger, J.; Mallabiabarrena, I.; Seigneul, I.; Jachertz, M.; Von Segesser, L.K. Ex vivo evaluation of a new extracorporeal lung assist device: NovaLung membrane oxygenator. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2005, 28, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Simon, A.R.; Welte, T.; Hoeper, M.M.; Meyer, A.; Tessmann, R. Bridge to lung transplantation with the novel pumpless interventional lung assist device NovaLung. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006, 131, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, S.; Hoeper, M.M.; Tomaszek, S.; Simon, A.; Gottlieb, J.; Welte, T. Bridge to lung transplantation with the extracorporeal membrane ventilator Novalung in the veno-venous mode: The initial Hannover experience. ASAIO J. 2007, 53, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosik, W.; Egan, J.J.; Wood, A.E. The Novalung interventional lung assist as bridge to lung transplantation for self-ventilating patients–initial experience. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 13, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.A.; Hartwig, M.; Lin, S.; Davis, R.D. Bridging to Lung Transplant: What Method and for Whom? Curr. Respir. Care Rep. 2013, 2, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopp, R.; Bensberg, R.; Wardeh, M.; Rossaint, R.; Kuhlen, R.; Henzler, D. Pumpless arterio-venous extracorporeal lung assist compared with veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during experimental lung injury. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 108, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ried, M.; Bein, T.; Philipp, A.; Mueller, T.; Graf, B.; Schmid, C. Extracorporeal lung support in trauma patients with severe chest injury and acute lung failure: A 10-year institutional experience. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matheis, G. New technologies for respiratory assist. Perfusion 2003, 18, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwischenberger, J.B.; Alpard, S.K. Artificial lungs: A new inspiration. Perfusion 2002, 17, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwischenberger, J.B.; Anderson, C.M.; Cook, K.E.; Lick, S.D.; Mockros, L.F.; Bartlett, R.H. Development of an implantable artificial lung: Challenges and progress. ASAIO J. 2001, 47, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lick, S.D.; Zwischenberger, J.B.; Wang, D.; Deyo, D.J.; Alpard, S.K.; Chambers, S.D. Improved right heart function with a compliant inflow artificial lung in series with the pulmonary circulation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2001, 72, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, R.R.; Wang, D.; Zwischenberger, J.B.; Clark, J.W., Jr. Hemodynamic analysis and design of a paracorporeal artificial lung device. Cardiovasc. Eng. 2006, 6, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; McGillicuddy, J.W.; Griffith, G.W.; Cosnowski, A.M.; Chambers, S.D.; Hirschl, R.B. Effect of artificial lung compliance on in vivo pulmonary system hemodynamics. ASAIO J. 2006, 52, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Hall, C.M.; Lafayette, N.G.; Pohlmann, J.R.; Padiyar, N.; Toomasian, J.M. Thirty-day in-parallel artificial lung testing in sheep. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 84, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, B.; Reoma, J.L.; Camboni, D.; Pohlmann, J.R.; Albert, J.M.; Kawatra, A. In-parallel artificial lung attachment at high flows in normal and pulmonary hypertension models. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 90, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schewe, R.E.; Khanafer, K.M.; Arab, A.; Mitchell, J.A.; Skoog, D.J.; Cook, K.E. Design and In Vitro Assessment of an Improved, Low-Resistance Compliant Thoracic Artificial Lung. ASAIO J. 2012, 58, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scipione, C.N.; Schewe, R.E.; Koch, K.L.; Shaffer, A.W.; Iyengar, A.; Cook, K.E. Use of a low-resistance compliant thoracic artificial lung in the pulmonary artery to pulmonary artery configuration. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 145, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naito, N.; Ukita, R.; Cook, K.E. The effects of Zwitterionic polymer coatings and nitric oxide on artificial lungs. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Med. Biol. Eng. 2018, 56, S151. [Google Scholar]
- Amoako, K.A.; Montoyan, P.J.; Major, T.C.; Suhaib, A.B.; Handa, H.; Brant, D.O.; Meyerhoff, M.E.; Bartlett, R.H.; Cook, K.E. Fabrication and in vivo thrombogenicity testing of nitric oxide generating artificial lungs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2013, 101, 3511–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- High, K.M.; Snider, M.T.; Panol, G.R.; Richard, R.B.; Gray, D.N. Polysulfone coating for hollow fiber artificial lungs operated at hypobaric and hyperbaric pressures. ASAIO J. 1996, 42, M442–M445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, N.; Ukita, R.; Wilbs, J.; Wu, K.; Lin, X.; Carleton, N.M.; Roberts, K.; Jiang, S.; Heinis, C.; Cook, K.E. Combination of polycarboxybetaine coating and factor XII inhibitor reduces clot formation while preserving normal tissue coagulation during extracorporeal life suppor. Biomaterials 2021, 272, 120778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, A.; Demarest, C.T.; Do-Nguyen, C.C.; Ukita, R.; Skoog, D.J.; Carleton, N.M.; Amoako, K.A.; Montoya, P.J.; Cook, K.E. 72-Hour in vivo evaluation of nitric oxide generating artificial lung gas exchange fibers in sheep. Acta Biomater. 2019, 90, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukita, R.; Wu, K.; Lin, X.; Carleton, N.M.; Naito, N.; Lai, A.; Do-Nguyen, C.C.; Demarest, C.T.; Jiang, S.; Cook, K.E. Zwitterionic poly-carboxybetaine coating reduces artificial lung thrombosis in sheep and rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilbs, J.; Kong, X.D.; Middendorp, S.J.; Prince, R.; Cooke, A.; Demarest, C.T.; Abdelhafez, M.M.; Roberts, K.; Umei, N.; Gonschorek, P.; et al. Cyclic peptide FXII inhibitor provides safe anticoagulation in a thrombosis model and in artificial lungs. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Khanafer, K.M.; Bartlett, R.H.; Hirschl, R.B.; Bull, J.L. An investigation of pulsatile flow past two cylinders as a model of blood flow in an artificial lung. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qamar, A.; Seda, R.; Bull, J.L. Pulsatile flow past an oscillating cylinder. Phys. Fluids 2011, 23, 041903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qamar, A.; Bull, J.L. Transport and flow characteristics of an oscillating cylindrical fiber for total artificial lung application. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 20, 1195–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, A.; Samtaney, R.; Bull, J.L. Pulsatility role in cylinder flow dynamics at low Reynolds number. Phys. Fluids. 2012, 20, 081701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.M.; Cook, K.; Marafie, A. The role of porous media in modeling fluid flow within hollow fiber membranes of the total artificial lung. J. Porous Media 2012, 15, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huh, D.; Matthews, B.D.; Mammoto, A.; Montoya-Zavala, M.; Hsin, H.Y.; Ingber, D.E. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science 2010, 328, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.K.; Kung, H.H.; Mockros, L.F. Microchannel technologies for artificial lungs: (1) theory. ASAIO J. 2008, 54, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahto, S.K.; Tenenbaum-Katan, J.; Sznitman, J. Respiratory Physiology on a Chip. Scientifica 2012, 364054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgess, K.A.; Hu, H.H.; Wagner, W.R.; Federspiel, W.J. Towards microfabricated biohybrid artificial lung modules for chronic respiratory support. Biomed. Microdev. 2009, 11, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoganson, D.M.; Anderson, J.L.; Weinberg, E.F.; Swart, E.J.; Orrick, B.K.; Borenstein, J.T.; Vacanti, J.P. Branched vascular network architecture: A new approach to lung assist device technology. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 140, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoganson, D.M.; Pryor, H.I., II; Bassett, E.K.; Spool, I.D.; Vacanti, J.P. Lung assist device technology with physiologic blood flow developed on a tissue engineered scaffold platform. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniazeva, T.; Hsiao, J.C.; Charest, J.L.; Borenstein, J.T. A microfluidic respiratory assist device with high gas permeance for artificial lung applications. Biomed. Microdev. 2011, 13, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Rochow, N.; Chan, E.; Manan, A.; Fusch, C.; Nagpal, D. Lung assist device: Development of microfluidic oxygenators for preterm infants with respiratory failure. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potkay, J.A.; Magnetta, M.; Vinson, A.; Cmolik, B. Bioinspired, effcient, artificial lung employing air as the ventilating gas. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2901–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukita, R.; Potkay, J.A.; Khanafe, R.K.; Cook, K.E. Advancing Front Oxygen Transfer Model for the Design of Microchannel Artificial Lungs. ASAIO J. 2020, 66, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Máca, J.; Jor, O.; Holub, M.; Sklienka, P.; Burša, F.; Burda, M.; Janout, V.; Ševčík, P. Past and present ARDS mortality rates: A systematic review. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pierson, D.J. Complications associated with mechanical ventilation. Crit. Care Clin. 1990, 6, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powelson, S.K. Design and Prototyping of a Low-Cost Portable Mechanical Ventilator; Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Department of Mechanical Engineering: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Darwood, A.; McCanny, J.; Kwasnicki, R.; Martin, B.; Jones, P. The design and evaluation of a novel low-cost portable ventilator. Anaesthesia 2019, 74, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.Y.; Lin, H.; Kuo, H.T.; Wu, C.L.; Wu, W.J.; Chen, C.H.; Liao, Y.T. Design and study of a portable high-frequency ventilator for clinical applications. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
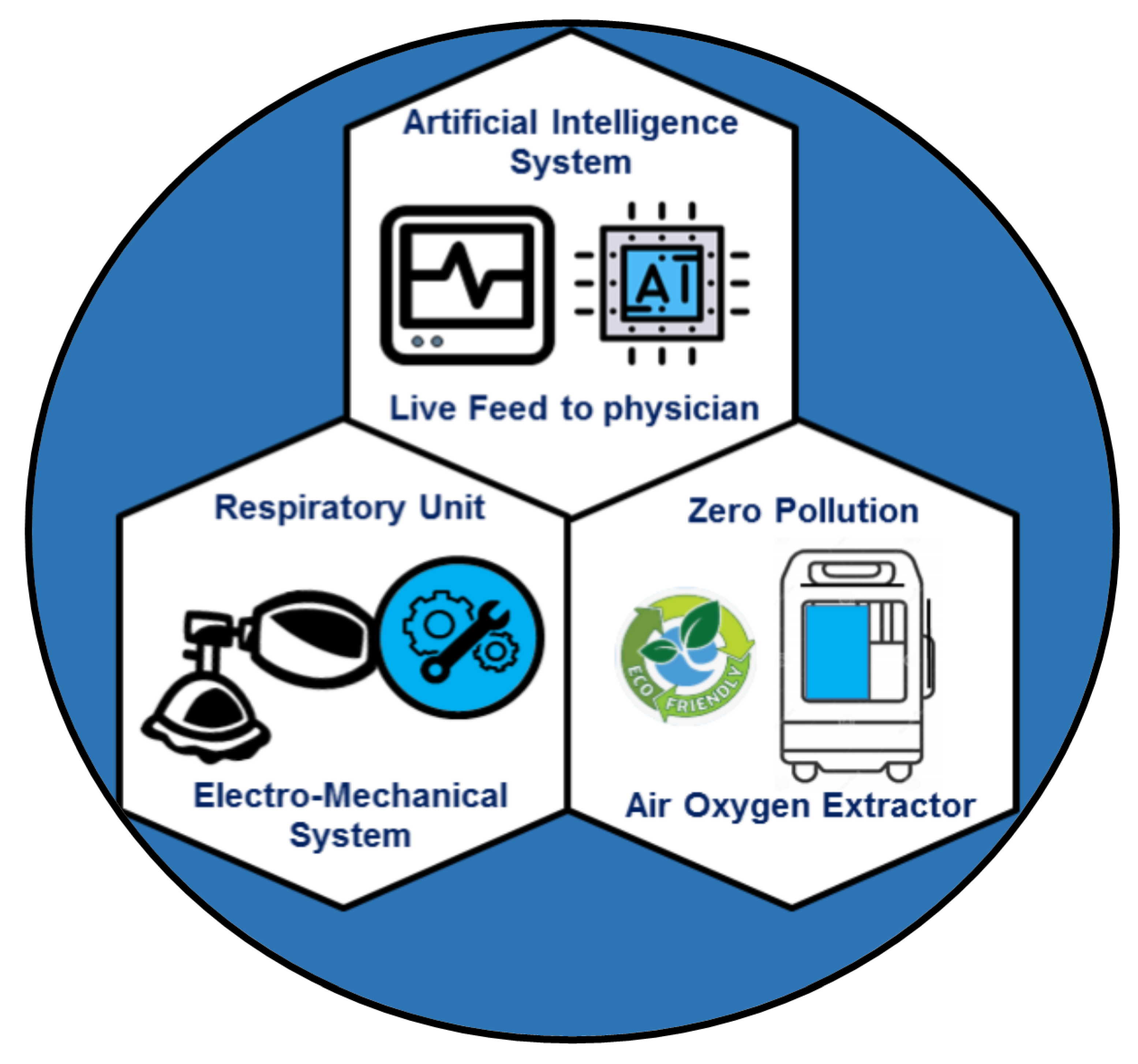
- Qamar, A.; Syed, A. Smart Bag-Pack Ventilator for Breathing Support: AI Powered, Self-Reliant and Portable. Provisional Patent 63/071,590, 28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Syed, A.; Kerdi, S.; Qamar, A. Bioengineering Progress in Lung Assist Devices. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8070089
Syed A, Kerdi S, Qamar A. Bioengineering Progress in Lung Assist Devices. Bioengineering. 2021; 8(7):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8070089
Chicago/Turabian StyleSyed, Ahad, Sarah Kerdi, and Adnan Qamar. 2021. "Bioengineering Progress in Lung Assist Devices" Bioengineering 8, no. 7: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8070089
APA StyleSyed, A., Kerdi, S., & Qamar, A. (2021). Bioengineering Progress in Lung Assist Devices. Bioengineering, 8(7), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8070089





