Platelet-Rich Plasma Lysate-Incorporating Gelatin Hydrogel as a Scaffold for Bone Reconstruction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rat MSC Expansion and Differentiation Assay
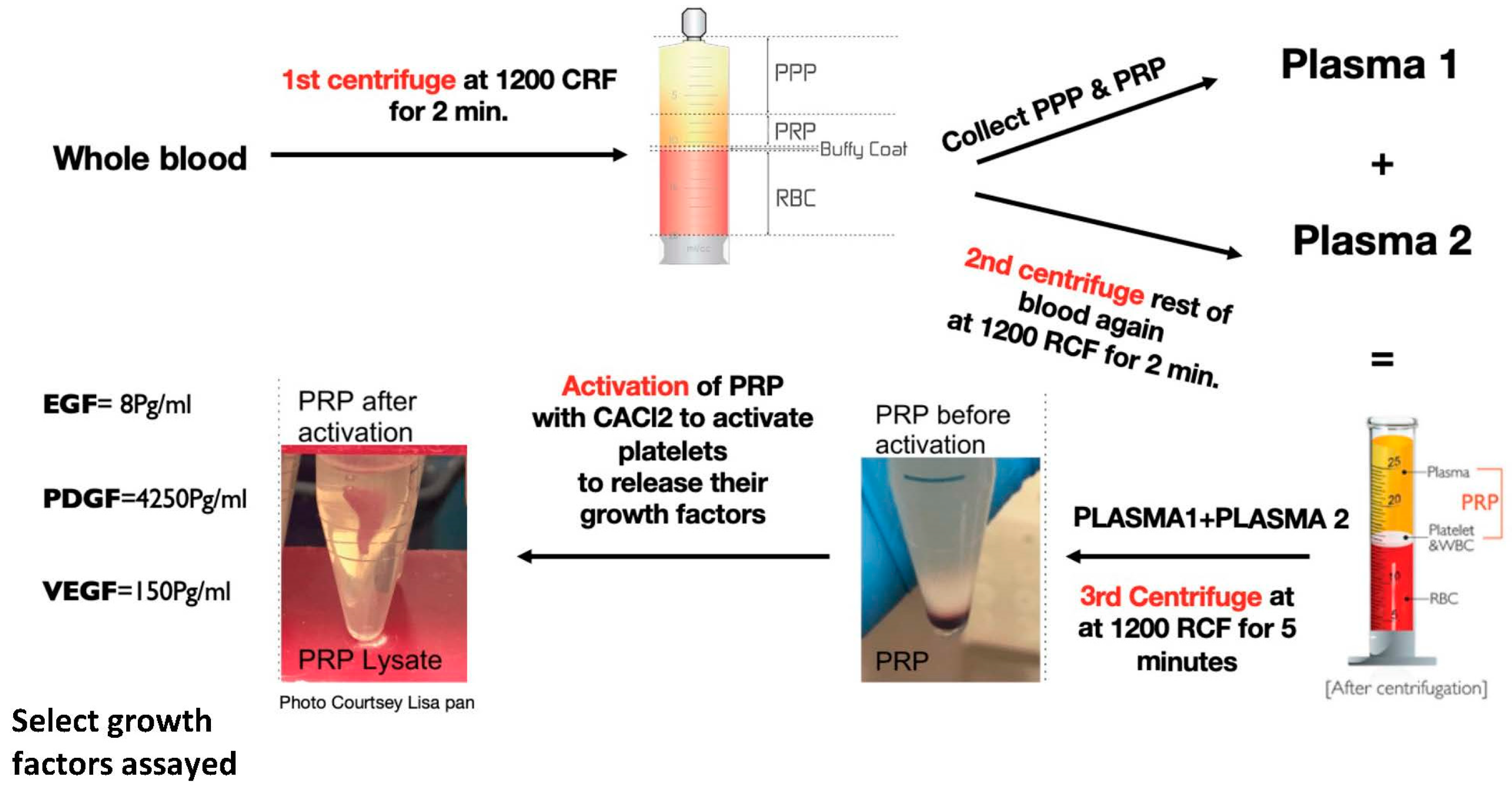
2.2. PRP Lysate Preparation
2.3. PRP Standardization and Growth Factors Quantification
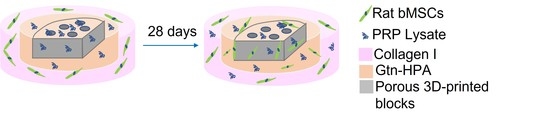
2.4. Gtn–HPA Gel Formation
3. Experimental Protocols
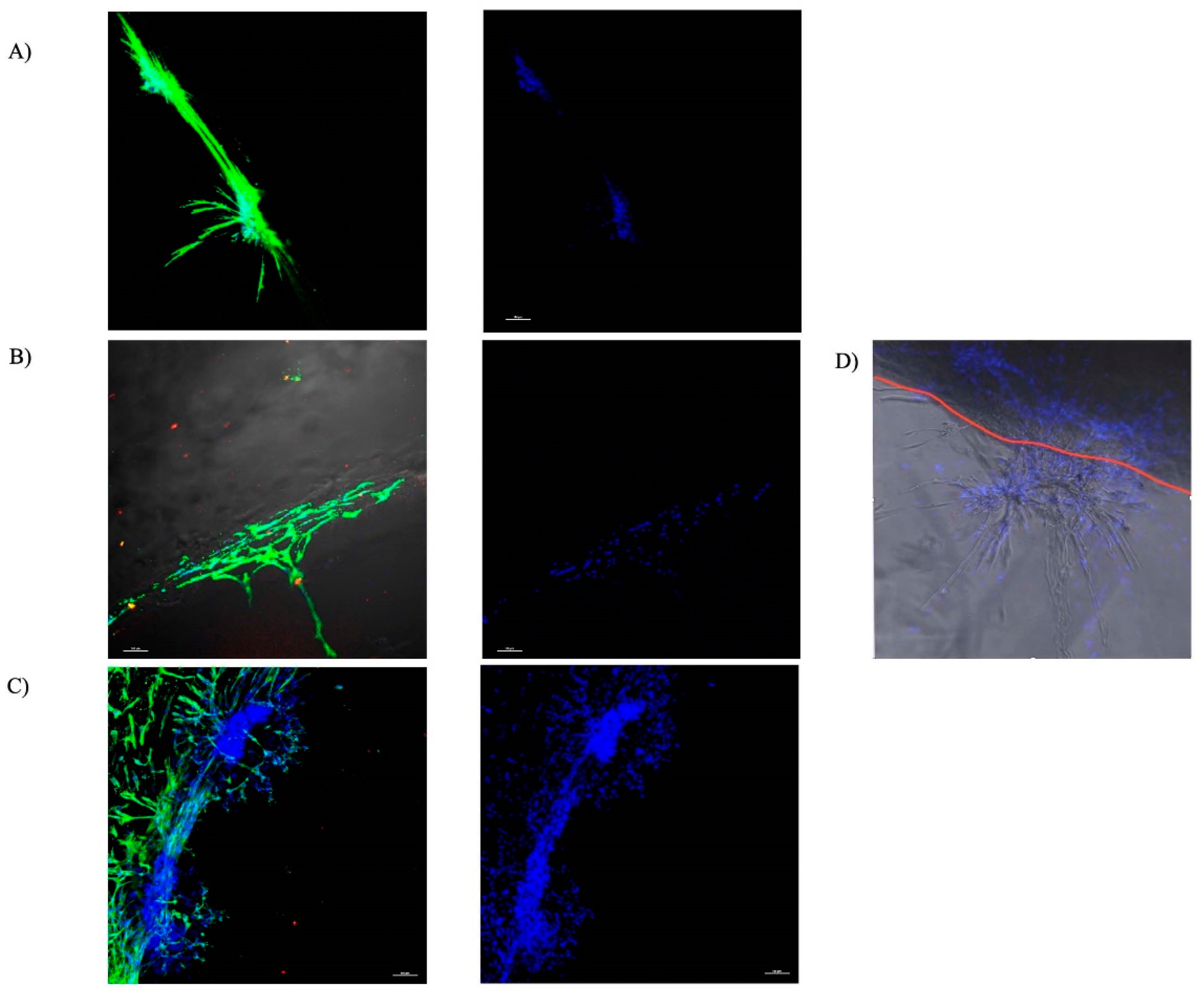
3.1. Core-Ring 3D Assembly Migration Assay (n = 6) [32]
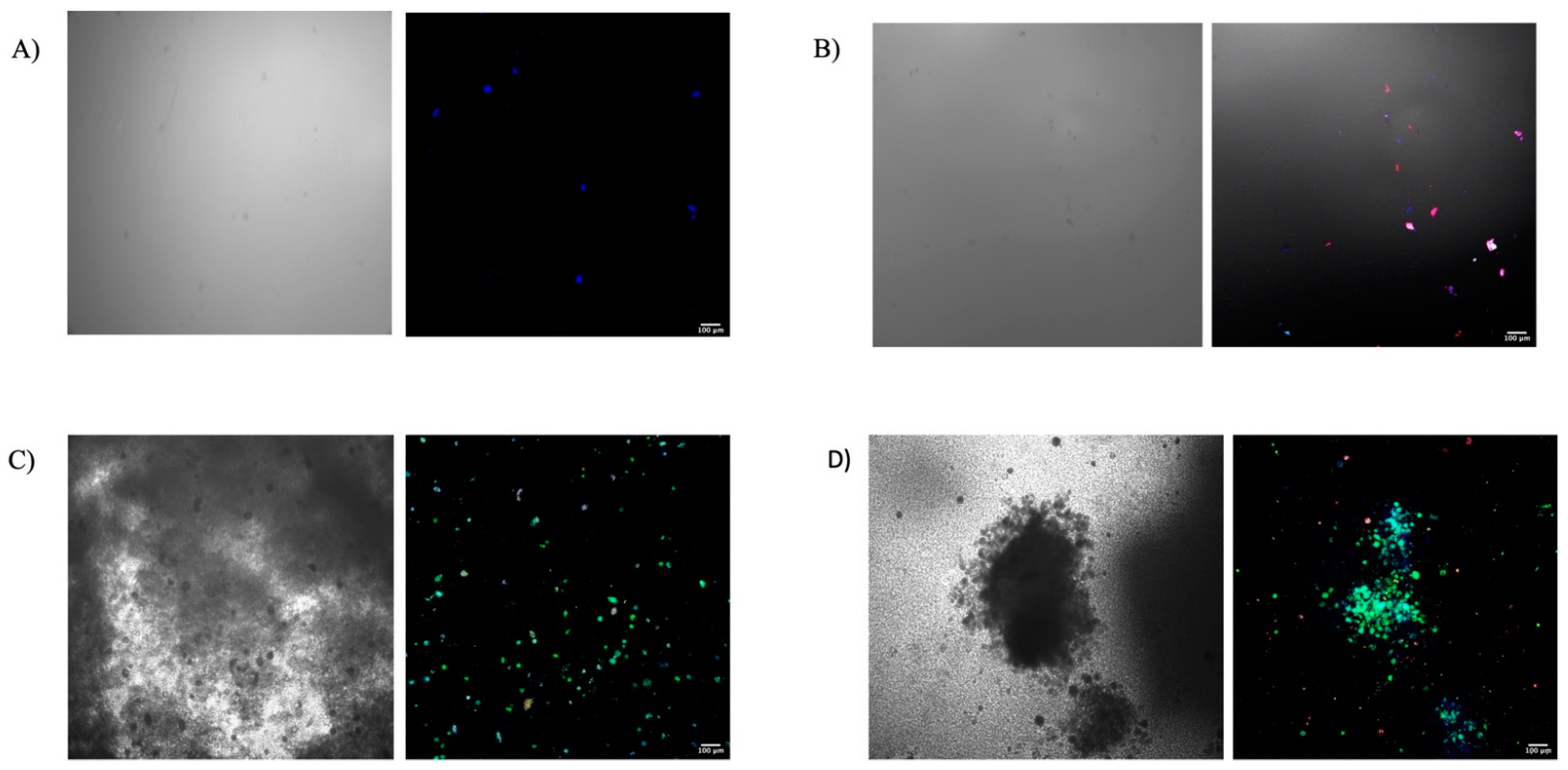
3.2. Assessing Cell Osteogenic Differentiation in PRP-Lysate-Infused Cell-Seeded Hydrogel
3.3. The Release Profile of PDGF-BB from Gels Incorporating PRP Lysate and Recombinant PDGF-BB
- (1)
- 2% Gtn–HPA blank hydrogel;
- (2)
- PRP lysate preparation I incorporated into Gtn–HPA;
- (3)
- PRP lysate preparation II incorporated into Gtn–HPA;
- (4)
- Recombinant rat PDGF-BB (50 ng/mL) incorporated into Gtn–HPA.
4. Results
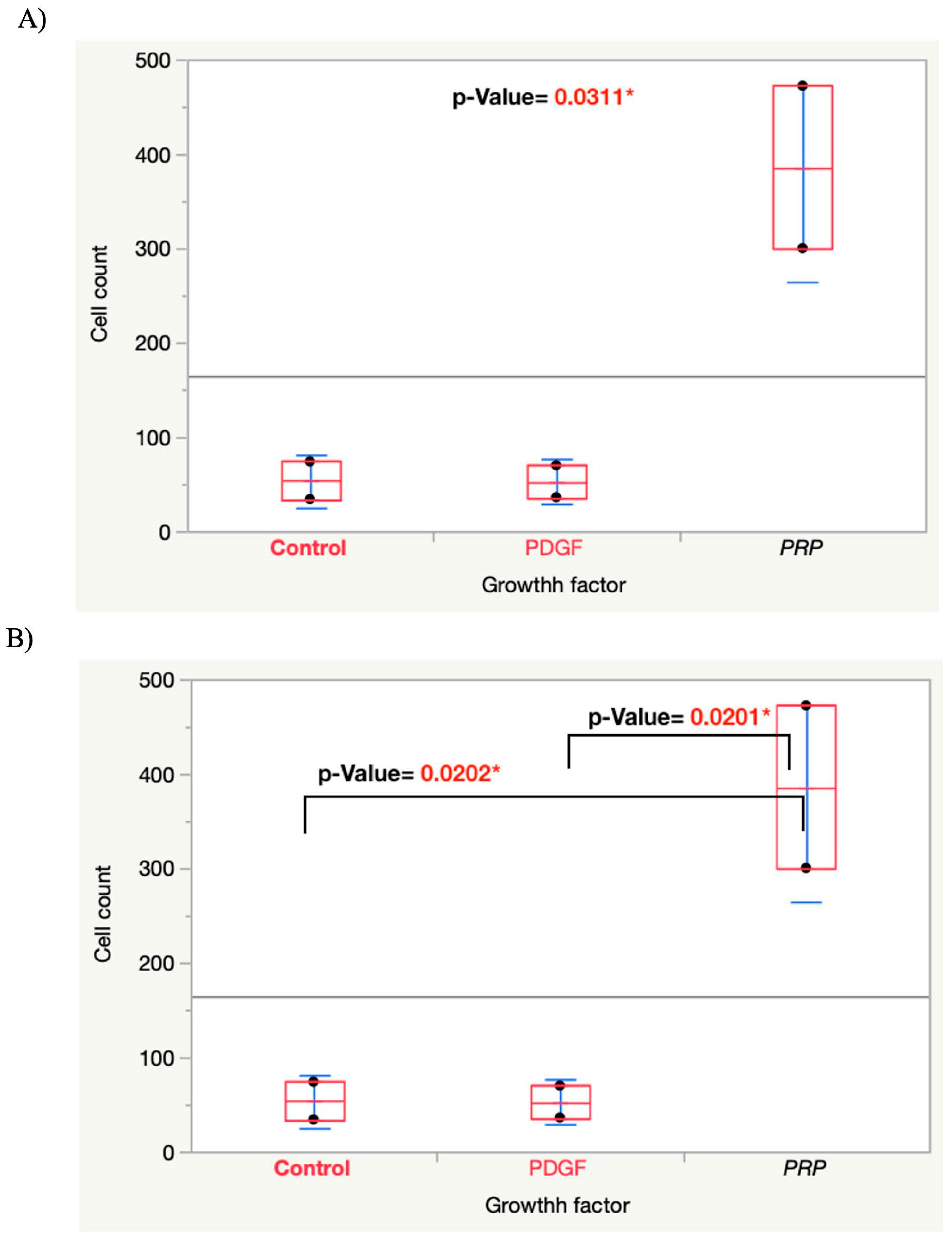
4.1. Cell Migration into the Gtn–HPA Hydrogel
4.2. Osteogenic Differentiation of MSCs in the Gtn–HPA Hydrogel
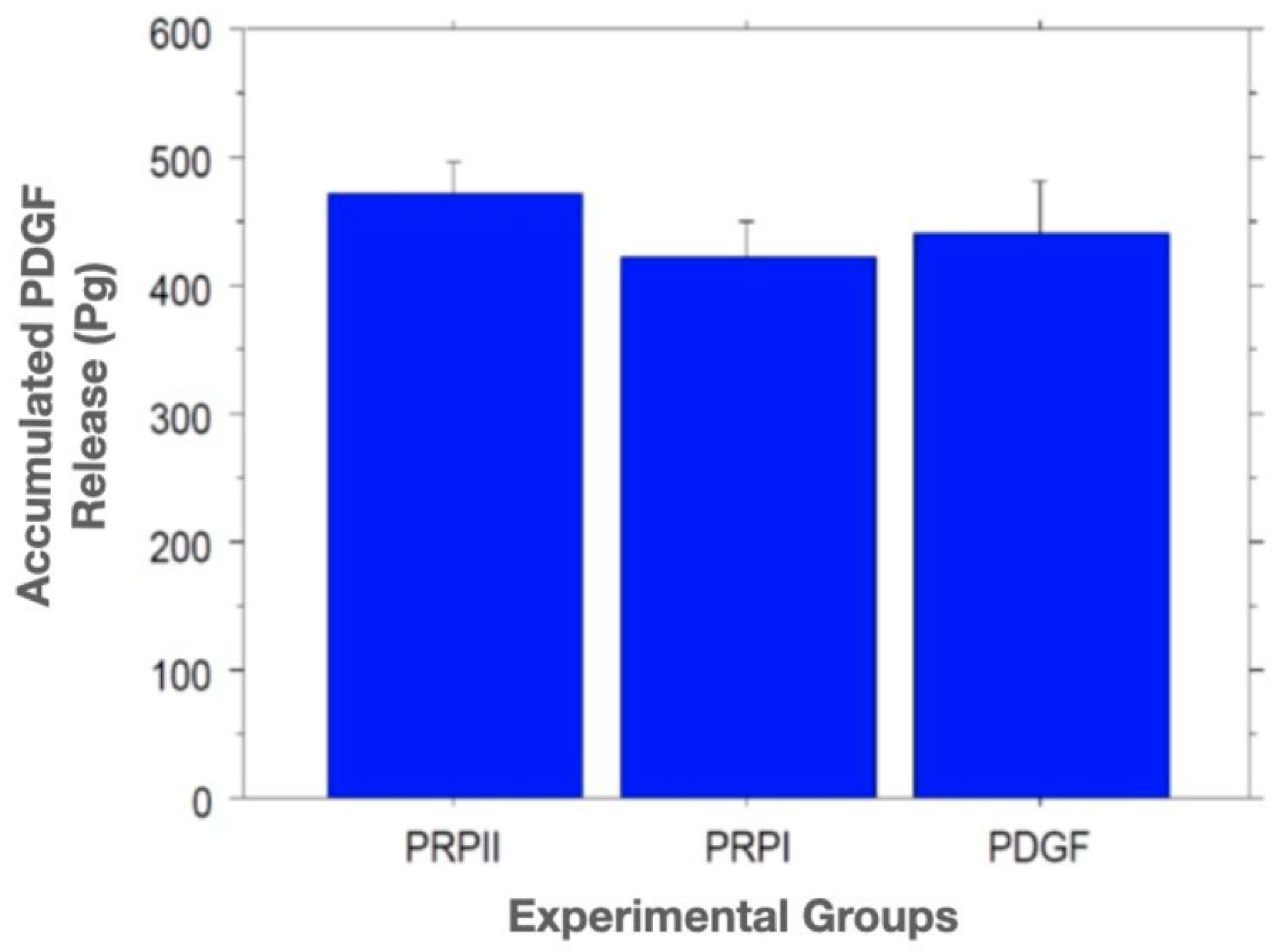
4.3. ELISA Release Assay
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Contribution to the Field Statement
References
- Araújo, M.G.; Silva, C.O.; Souza, A.B.; Sukekava, F. Socket healing with and without immediate implant placement. Periodontology 2000 2019, 79, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, D.; Martin, W.; Belser, U.C. Optimizing esthetics for implant restorations in the anterior maxilla: Anatomic and surgical considerations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2004, 2, 43–61. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, M.G.; Silva, C.O.; Misawa, M.; Sukekava, F. Alveolar socket healing: What can we learn? Periodontology 2000 2015, 68, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiapasco, M.; Casentini, P. Horizontal bone-augmentation procedures in implant dentistry: Prosthetically guided regeneration. Periodontology 2000 2018, 77, 213–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, I.A.; Montero, E.; Monje, A.; Sanz-Sanchez, I. Effectiveness of vertical ridge augmentation interventions. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, I.A.; Monje, A.; Lozada, J.; Wang, H.-L. Principles for Vertical Ridge Augmentation in the Atrophic Posterior Mandible: A Technical Review. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2017, 37, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simion, M.; Nevins, M.; Rocchietta, I.; Fontana, F.; Maschera, E.; Schupbach, P.; Kim, D.M. Vertical ridge augmentation using an equine block infused with recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB: A histologic study in a canine model. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2009, 29, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Pilipchuk, S.P.; Plonka, A.B.; Monje, A.; Taut, A.D.; Lanis, A.; Kang, B.; Giannobile, W.V. Tissue engineering for bone regeneration and osseointegration in the oral cavity. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Kluzek, M.; Iuster, N.; Shimoni, E.; Kampf, N.; Goldberg, R.; Klein, J. Cartilage-inspired, lipid-based boundary-lubricated hydrogels. Science 2020, 370, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaie, A.; Owston, H.; Jones, E. Use of platelet lysate for bone regeneration—Are we ready for clinical translation? World J. Stem Cells 2016, 8, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meftahpour, V.; Malekghasemi, S.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Aghebati-Maleki, A.; Pourakbari, R.; Fotouhi, A. Platelet lysate: A promising candidate in regenerative medicine. Regen. Med. 2021, 16, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbertie, J.M.; Schaer, T.P.; Schubert, A.G.; Jacob, M.E.; Menegatti, S.; Ashton Lavoie, R.; Schnabel, L.V. Platelet-rich plasma lysate displays antibiofilm properties and restores antimicrobial activity against synovial fluid biofilms in vitro. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pötter, N.; Westbrock, F.; Grad, S.; Alini, M.; Stoddart, M.J.; Schmal, H.; Kubosch, D.; Salzmann, G.; Kubosch, E.J. Evaluation of the influence of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet lysate (PL) and mechanical loading on chondrogenesis in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbertie, J.M.; Long, J.M.; Schubert, A.G.; Berglund, A.K.; Schaer, T.; Schnabel, L.V. Pooled Platelet-Rich Plasma Lysate Therapy Increases Synoviocyte Proliferation and Hyaluronic Acid Production While Protecting Chondrocytes from Synoviocyte-Derived Inflammatory Mediators. Front. Veter. Sci. 2018, 5, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E. Platelet-rich plasma: Evidence to support its use. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14877–14887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, M.; Gao, H.; Hu, B.; Tan, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.M. Investigation of mechanism of bone regeneration in a porous biodegradable calcium phosphate (CaP) scaffold by a combination of a multi-scale agent-based model and experimental optimization/validation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14877–14887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asa’Ad, F.; Pagni, G.; Pilipchuk, S.P.; Gianni’, A.; Giannobile, W.; Rasperini, G. 3D-Printed Scaffolds and Biomaterials: Review of Alveolar Bone Augmentation and Periodontal Regeneration Applications. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 1239842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, A.; Cheok, C.; Teoh, S.H.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Buser, D.; Bosshardt, D.D. Lateral ridge augmentation using a PCL-TCP scaffold in a clinically relevant but challenging micropig model. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buwalda, S.J.; Boere, K.W.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Feijen, J.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels in a historical perspective: From simple networks to smart materials. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Kwon, I.K.; Park, K. Hydrogels for delivery of bioactive agents: A historical perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 65, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buwalda, S.J.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels for Therapeutic Delivery: Current Developments and Future Directions. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.S.; Du, C.; Toh, W.S.; Wan, A.C.; Gao, S.J.; Kurisawa, M. Modulation of chondrocyte functions and stiffness-dependent cartilage repair using an injectable enzymatically crosslinked hydrogel with tunable mechanical properties. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, S.; Hirose, K.; Taguchi, K.; Ogushi, Y.; Kawakami, K. An injectable, in situ enzymatically gellable, gelatin derivative for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3371–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-S.; Chung, J.E.; Chan, P.P.-Y.; Kurisawa, M. Injectable biodegradable hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties for the stimulation of neurogenesic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in 3D culture. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Xu, L.; Sun, Y.; Wu, T.; Wang, K.; Li, G. An improved protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone marrow. J. Orthop. Translat. 2015, 3, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshihri, A.; Niu, W.; Kämmerer, P.W.; Al-Askar, M.; Yamashita, A.; Kurisawa, M.; Spector, M. The effects of shock wave stimulation of mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, and differentiation in an injectable gelatin matrix for osteogenic regeneration. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textor, J.A.; Tablin, F. Activation of equine platelet-rich plasma: Comparison of methods and characterization of equine autologous thrombin. Vet. Surg. 2012, 41, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.S.; Du, C.; Chung, J.E.; Kurisawa, M. Enzymatically cross-linked gelatin-phenol hydrogels with a broader stiffness range for osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1826–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.S.; Boulaire, J.; Chan, P.P.; Chung, J.E.; Kurisawa, M. The role of stiffness of gelatin-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid hydrogels formed by enzyme-mediated crosslinking on the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cell. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8608–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.C.; Toh, W.S.; Wang, L.-S.; Kurisawa, M.; Spector, M. The effect of injectable gelatin-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid hydrogel matrices on the proliferation, migration, differentiation and oxidative stress resistance of adult neural stem cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3446–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Lim, T.; Alshihri, A.; Rajappa, R.; Wang, L.; Kurisawa, M.; Spector, M. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Stimulated Migration of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into an Injectable Gelatin-Hydroxyphenyl Propionic Acid Matrix. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.C.; Rokkappanavar, S.; Toh, W.S.; Wang, L.-S.; Kurisawa, M.; Spector, M. Chemotactic recruitment of adult neural progenitor cells into multifunctional hydrogels providing sustained SDF-1alpha release and compatible structural support. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, M. Musculoskeletal connective tissue cells with muscle: Expression of muscle actin in and contraction of fibroblasts, chondrocytes, and osteoblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 2001, 9, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizman, I.; Holland, W.S.; Yang, C.; Bates, D. alphaSMA Expression in Large Colonies of Colony-Forming Units-Fibroblast as an Early Predictor of Bone Marrow MSC Expandability. Cell Med. 2016, 8, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchiano, A.; De Marchis, F.; Turchetti, E.; Guglielmi, M.; Denaro, A.; Palumbo, R.; Scoccianti, M.; Capogrossi, M. The chemotactic and mitogenic effects of platelet-derived growth factor-BB on rat aorta smooth muscle cells are inhibited by basic fibroblast growth factor. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 16, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, D.; Aguzzi, M.S.; Ragone, G.; Russo, K.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Facchiano, A. Heterodimerization of FGF-receptor 1 and PDGF-receptor-alpha: A novel mechanism underlying the inhibitory effect of PDGF-BB on FGF-2 in human cells. Blood 2006, 107, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, H.; Montaseri, A.; Mojaddadi, A.; Zonouzi, H.R.M.; Karimiyan, N.; Arami, S. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Differentiation of Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts in the Presence of Three-Dimensional Scaffold. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 24, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakudo, N.; Morimoto, N.; Ogawa, T.; Hihara, M.; Notodihardjo, P.V.; Matsui, M.; Tabata, Y.; Kusumoto, K. Angiogenic effect of platelet-rich plasma combined with gelatin hydrogel granules injected into murine subcutis. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 11, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Tabata, Y. Enhanced angiogenesis by multiple release of platelet-rich plasma contents and basic fibroblast growth factor from gelatin hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Ueda, M.; Naiki, T.; Nagasaka, T. Tissue-engineered injectable bone regeneration for osseointegrated dental implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 15, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, G.; Petralia, S.; Fabbi, C.; Forte, S.; Franco, D.; Guglielmino, S.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Traina, F.; Conoci, S. Au, Pd and maghemite nanofunctionalized hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone regeneration. Regen. Biomater. 2020, 7, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nadra, M.; Niu, W.; Kurisawa, M.; Rousson, D.; Spector, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma Lysate-Incorporating Gelatin Hydrogel as a Scaffold for Bone Reconstruction. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100513
Nadra M, Niu W, Kurisawa M, Rousson D, Spector M. Platelet-Rich Plasma Lysate-Incorporating Gelatin Hydrogel as a Scaffold for Bone Reconstruction. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(10):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100513
Chicago/Turabian StyleNadra, Meral, Wanting Niu, Motoichi Kurisawa, Dominique Rousson, and Myron Spector. 2022. "Platelet-Rich Plasma Lysate-Incorporating Gelatin Hydrogel as a Scaffold for Bone Reconstruction" Bioengineering 9, no. 10: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100513
APA StyleNadra, M., Niu, W., Kurisawa, M., Rousson, D., & Spector, M. (2022). Platelet-Rich Plasma Lysate-Incorporating Gelatin Hydrogel as a Scaffold for Bone Reconstruction. Bioengineering, 9(10), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100513