Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Arteriovenous Fistula Creation Simulation Training in a Lifelike Flow Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
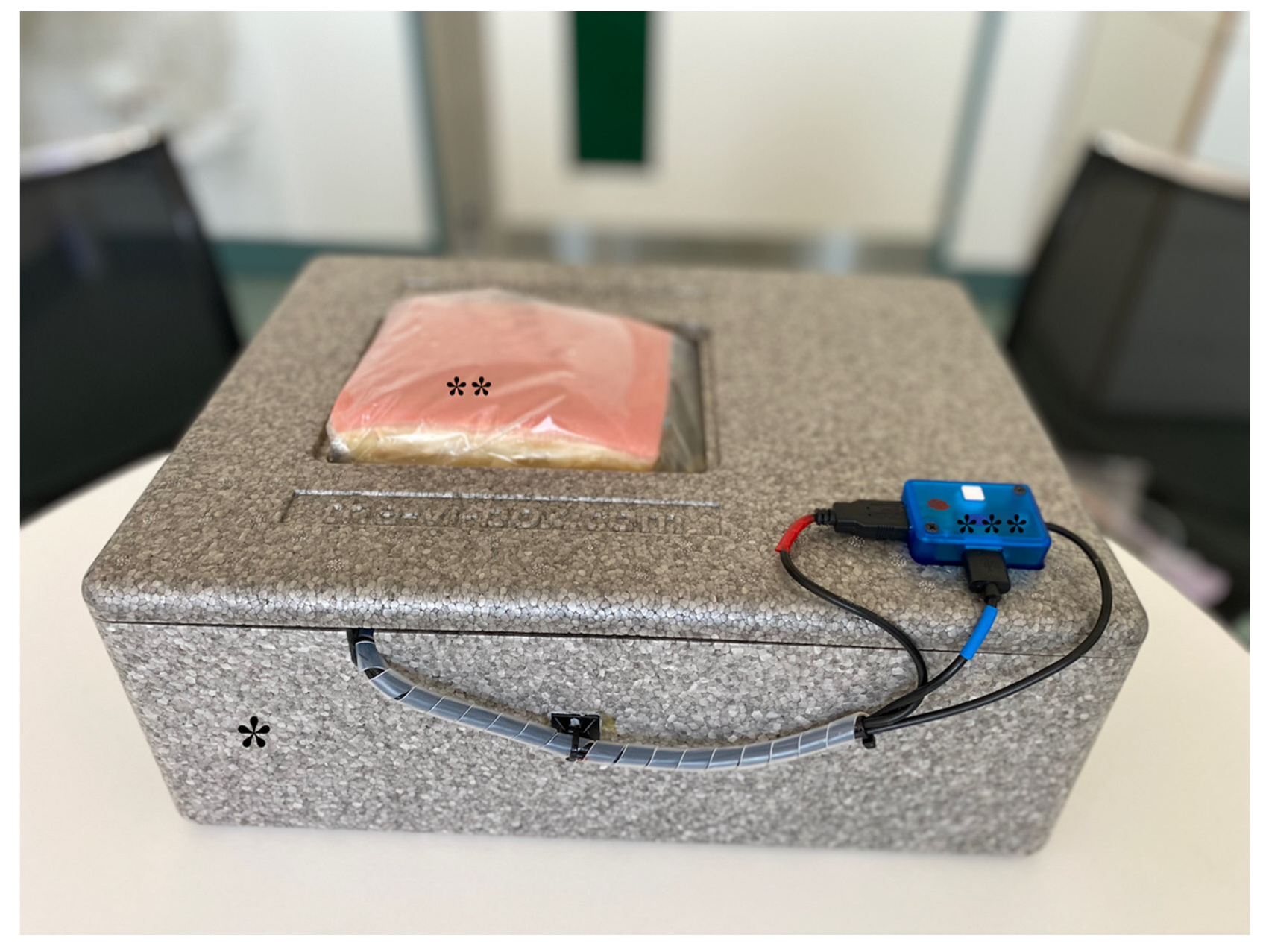
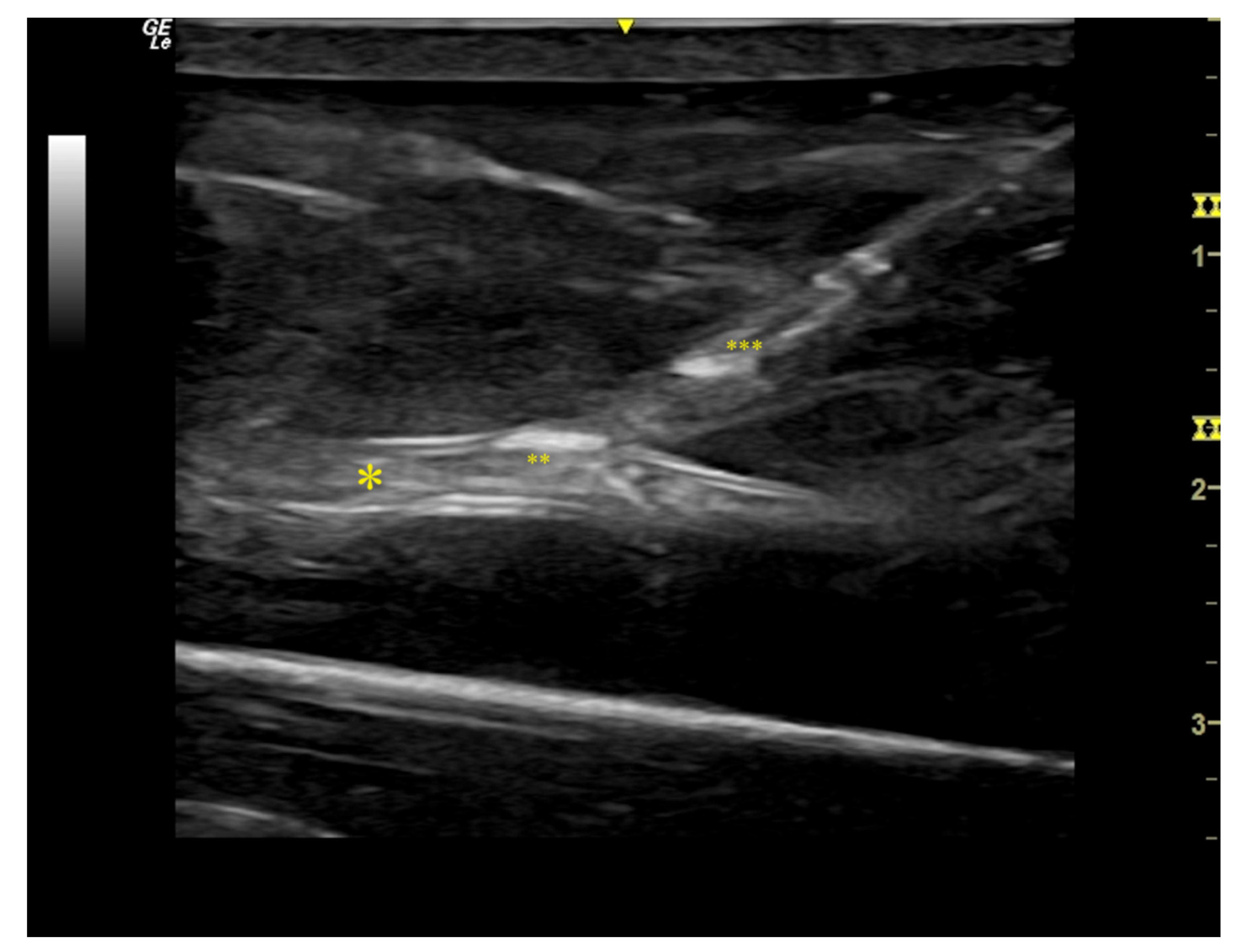
2.1. Flow Model Development
2.2. Study Design and Intervention
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
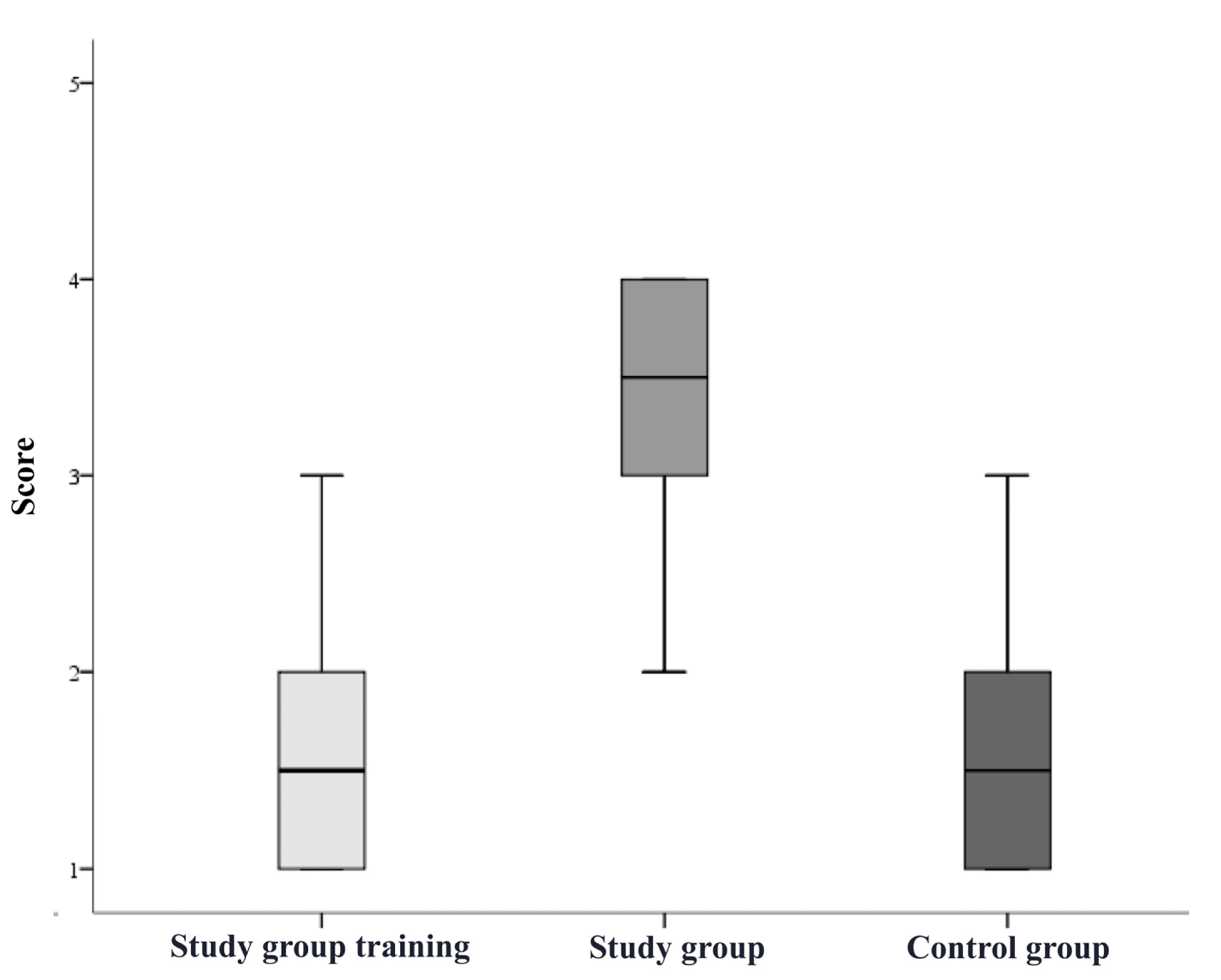
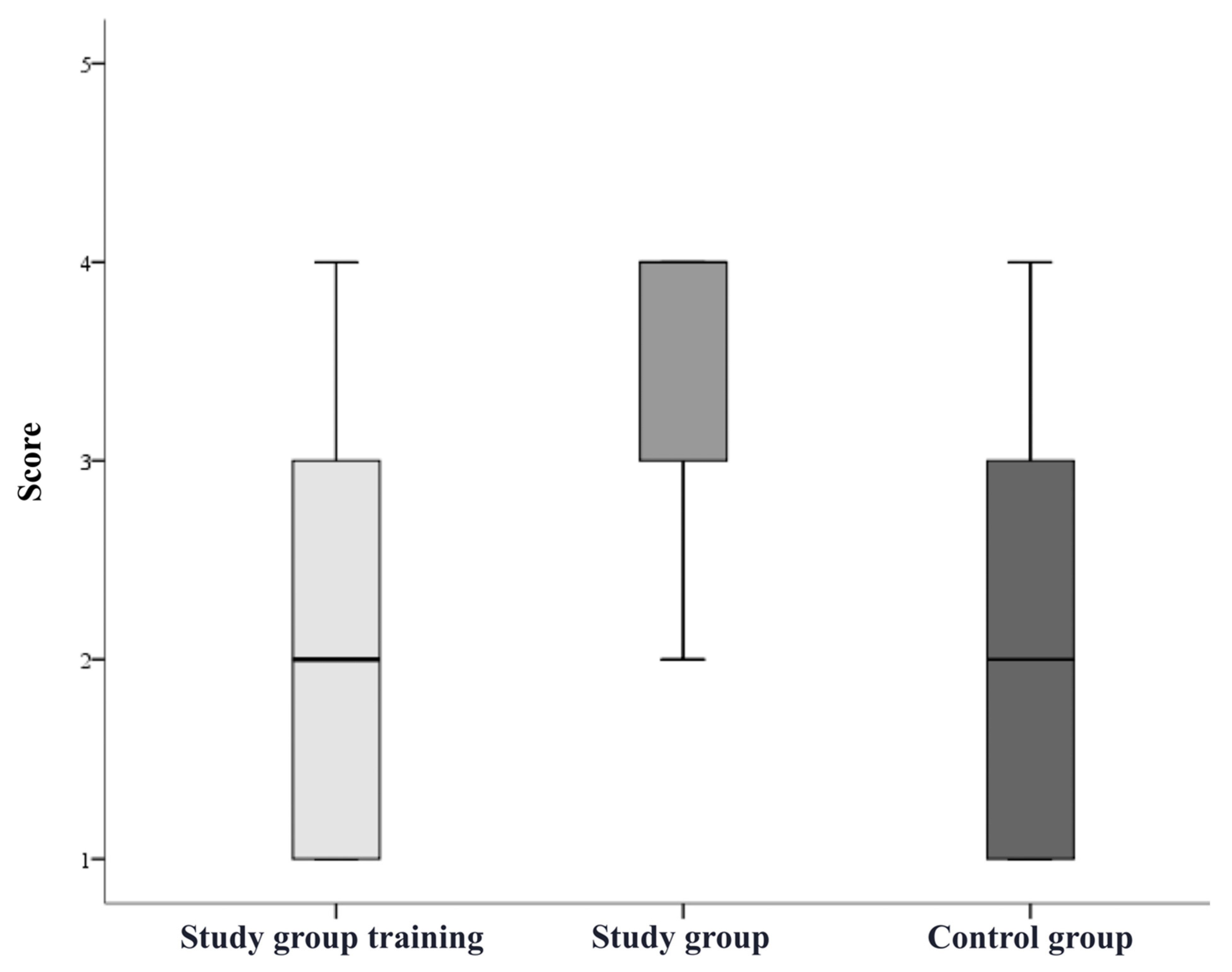
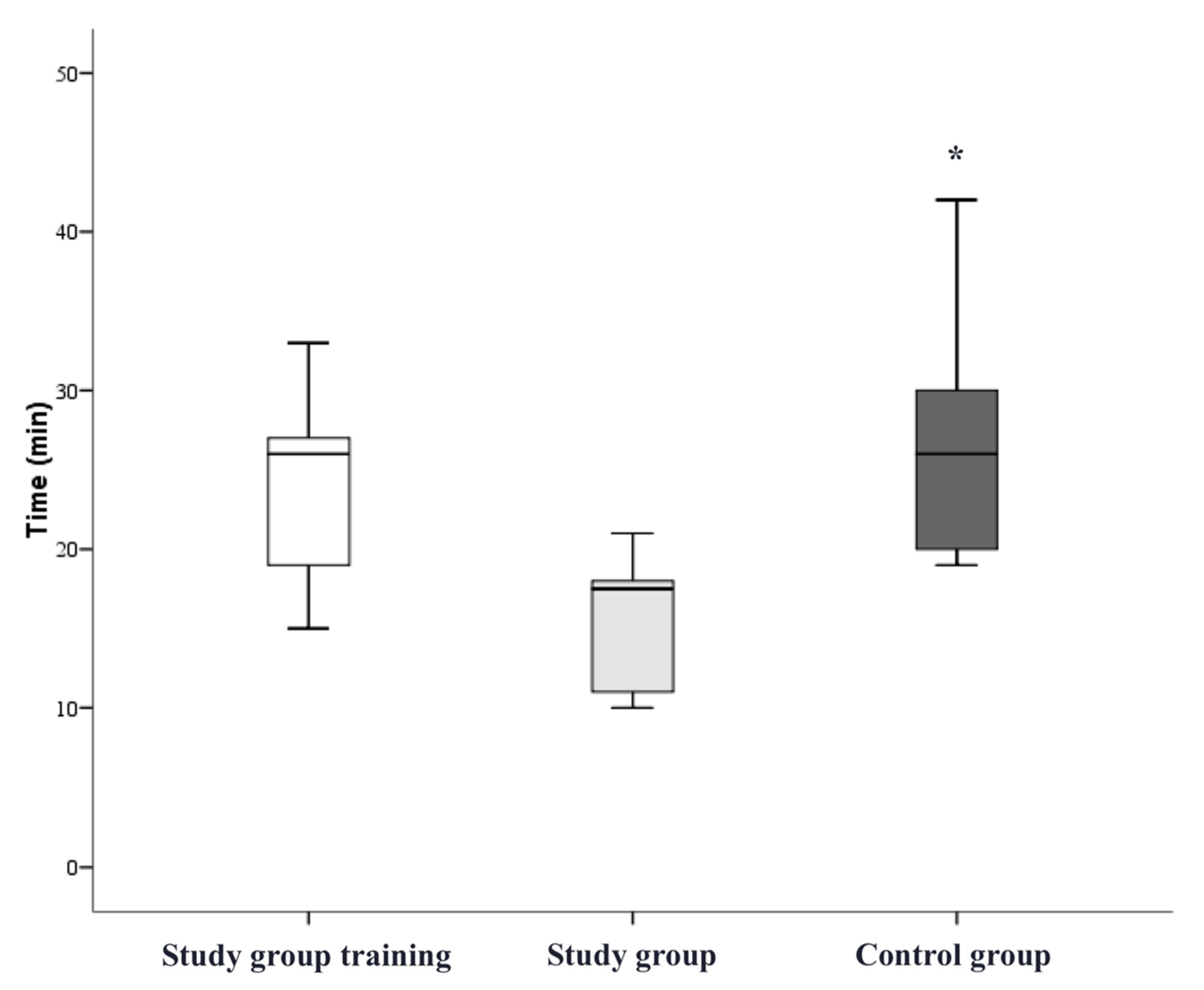
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mallios, A.; Beathard, G.A.; Jennings, W.C. Early cannulation of percutaneously created arteriovenous hemodialysis fistulae. J. Vasc. Access 2019, 21, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallios, A.; Bourquelot, P.; Franco, G.; Hebibi, H.; Fonkoua, H.; Allouache, M.; Costanzo, A.; Blic, R.; Harika, G.; Boura, B.; et al. Midterm results of percutaneous arteriovenous fistula creation with the Ellipsys Vascular Access System, technical recommendations, and an algorithm for maintenance. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahverdyan, R.; Beathard, G.; Mushtaq, N.; Litchfield, T.F.; Nelson, P.R.; Jennings, W.C. Comparison of Outcomes of Percutaneous Arteriovenous Fistulae Creation by Ellipsys and WavelinQ Devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kwon, E.J.; Min, J.J. Simulation-based training using a vessel phantom effectively improved first attempt success and dynamic needle-tip positioning ability for ultrasound-guided radial artery cannulation in real patients: An assessor-blinded randomized controlled study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taher, F.; Plimon, M.; Isaak, A.; Falkensammer, J.; Pablik, E.; Walter, C.; Kliewer, M.; Assadian, A. Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Arterial Puncture and Closure Device Training in a Pulsatile Model. J. Surg. Educ. 2020, 77, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickham, P.P. Human Experimentation. Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki. Br. Med. J. 1964, 2, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, G.; Mallios, A.; Bourquelot, P.; Hebibi, H.; Jennings, W.; Boura, B. Feasibility for arteriovenous fistula creation with Ellipsys®. J. Vasc. Access 2020, 21, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaak, A.; Mallios, A.; Gürke, L.; Wolff, T. Teleproctoring in Vascular Surgery to Defy COVID-19 Travel Restrictions. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020, 60, 623–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raft, J.; Dupanloup, D.; Clerc-Urmès, I.; Baumann, C.; Richebé, P.; Bouaziz, H. Training novice in ultrasound-guided venipuncture: A randomized controlled trial comparing out-of-plane needle-guided versus free-hand ultrasound techniques on a simulator. J. Vasc. Access 2020, 22, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramonell, R.P.; Coleman, C.; Binder, A.; Creel-Bulos, C.; Wiepking, M.D.; Stentz, M.J.; Daniels, L.M. Pilot Study of a Novel Gelatin-based Model for Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Cannula Insertion Simulation. ATS Sch. 2021, 2, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, A.E.; Rose, J.S.; Vance, C.W.; Andrada-Brown, E.; Kuppermann, N. Ultrasound-Assisted Peripheral Venous Access in Young Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial and Pilot Feasibility Study. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 9, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Alvarez, J.M.; Perez-Quevedo, O.; Naya-Esteban, J.; Ramirez-Lorenzo, T.; Lopez-Manteola, S.A.; Lorenzo-Villegas, D.L. Evaluation of Training in Pediatric Ultrasound-guided Vascular Cannulation Using a Model. J. Med. Ultrasound 2021, 29, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.U.; Joo, Y.H.; Chang, I.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.C.; Jung, J.Y.; Park, J.W.; Kwak, Y.H. Novel Simulation Model That Realizes Arterial and Venous Blood Flow for Ultrasound-Guided Central Venous Catheter Insertion in Children. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2021, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Choi, S.; Kim, H. Evaluation of a simplified augmented reality device for ultrasound-guided vascular access in a vascular phantom. J. Clin. Anesth. 2014, 26, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshad-Amacker, N.A.; Bay, T.; Rosskopf, A.B.; Spirig, J.M.; Wanivenhaus, F.; Pfirrmann, C.W.A.; Farshad, M. Ultrasound-guided interventions with augmented reality in situ visualisation: A proof-of-mechanism phantom study. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2020, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Plishker, W.; Matisoff, A.; Sharma, K.; Shekhar, R. HoloUS: Augmented reality visualization of live ultrasound images using HoloLens for ultrasound-guided procedures. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 17, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facharzt für Gefässchirurgie 2015. Available online: https://www.siwf.ch/weiterbildung/facharzttitel-und-schwerpunkte/gefaesschirurgie.cfm (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Teodoro-Vite, S.; Pérez-Lomelí, J.S.; Domínguez-Velasco, C.F.; Hernández-Valencia, A.F.; Capurso-García, M.A.; Padilla-Castañeda, M.A. A High-Fidelity Hybrid Virtual Reality Simulator of Aneurysm Clipping Repair With Brain Sylvian Fissure Exploration for Vascular Neurosurgery Training. Simul. Healthc. 2020, 16, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonn, L.; Edmond, J.J.; Marco, J.; Kearney, P.P.; Gallagher, A.G. Virtual Reality Simulation Training in a High-fidelity Procedure Suite: Operator Appraisal. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 1361–1366.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarez, C.E.; Bertani, R.; Batista, D.M.L.; Lovato, R.; Perret, C.; Abi-Aad, K.R.; Oliveira, M.M.; Cannizzaro, B.; Costa, P.H.V.; da Silveira, R.L.; et al. Superficial Temporal Artery-Middle Cerebral Artery Bypass Ex Vivo Hybrid Simulator: Face, Content, Construct, and Concurrent Validity. World Neurosurg. 2020, 142, e378–e384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Burg, B.L.B.; Hörer, T.M.; Eefting, D.; van Dongen, T.T.C.F.; Hamming, J.F.; DuBose, J.J.; Bowyer, M.; Hoencamp, R. Vascular access training for REBOA placement: A feasibility study in a live tissue-simulator hybrid porcine model. J. R. Army Med. Corps 2019, 165, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, H.-H.; Schmidli, J.; Schumacher, H.; Gürke, L.; Klemm, K.; Duschek, N.; Meile, T.; Assadian, A. Rationale, scope, and 20-year experience of vascular surgical training with lifelike pulsatile flow models. J. Vasc. Surg. 2013, 57, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]



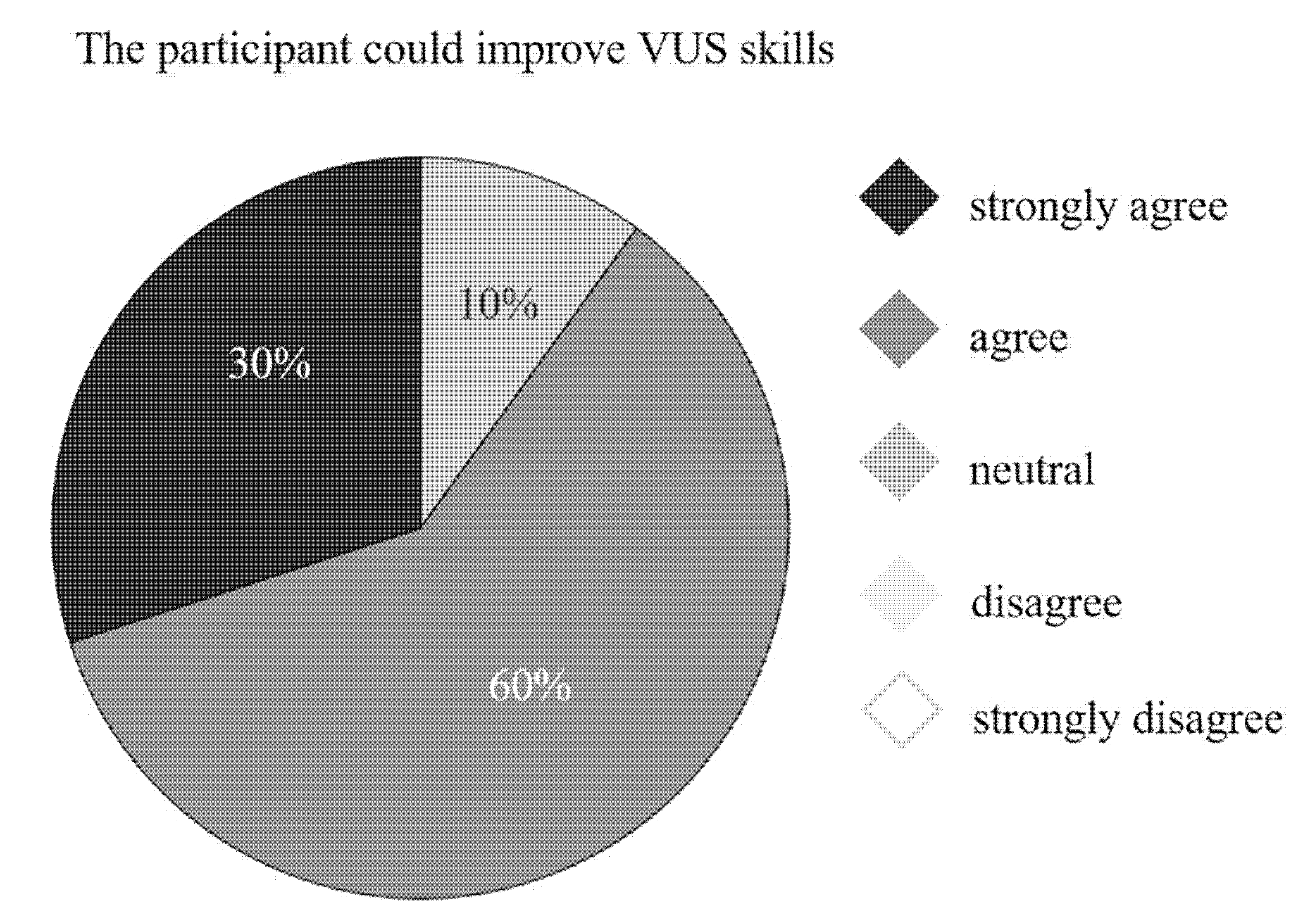
| VUS Skills | VUS-Guided Puncture | Endovascular Device Handling | Ellipsys Catheter® Handling | pAVF Dilatation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task type | Correct identification of DCV and PRA, diameter and distance measurement | Successful puncture of PRA through DCV | VUS-guided guide-wire advancement and sheath insertion | Correct placement of Ellipsys® catheter | Correct application of PTA balloon |
| Study group simulation training, n = 10 | 80% | 10% | 20% | 0% | 20% |
| Study group after simulation training, n = 10 | 90% | 80% | 50% | 80% | 80% |
| Control group, n = 10 | 90% | 20% | 20% | 30% | 50% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isaak, A.; Wolff, T.; Zdoroveac, A.; Taher, F.; Gürke, L.; Richarz, S.; Akifi, S. Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Arteriovenous Fistula Creation Simulation Training in a Lifelike Flow Model. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110659
Isaak A, Wolff T, Zdoroveac A, Taher F, Gürke L, Richarz S, Akifi S. Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Arteriovenous Fistula Creation Simulation Training in a Lifelike Flow Model. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(11):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110659
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsaak, Andrej, Thomas Wolff, Andrei Zdoroveac, Fadi Taher, Lorenz Gürke, Sabine Richarz, and Shuaib Akifi. 2022. "Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Arteriovenous Fistula Creation Simulation Training in a Lifelike Flow Model" Bioengineering 9, no. 11: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110659
APA StyleIsaak, A., Wolff, T., Zdoroveac, A., Taher, F., Gürke, L., Richarz, S., & Akifi, S. (2022). Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Arteriovenous Fistula Creation Simulation Training in a Lifelike Flow Model. Bioengineering, 9(11), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110659









