Preparation of Polyvinylidene Fluoride–Gold Nanoparticles Electrospinning Nanofiber Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
2.2. Preparation of Fiber Membranes
2.3. Characterizations
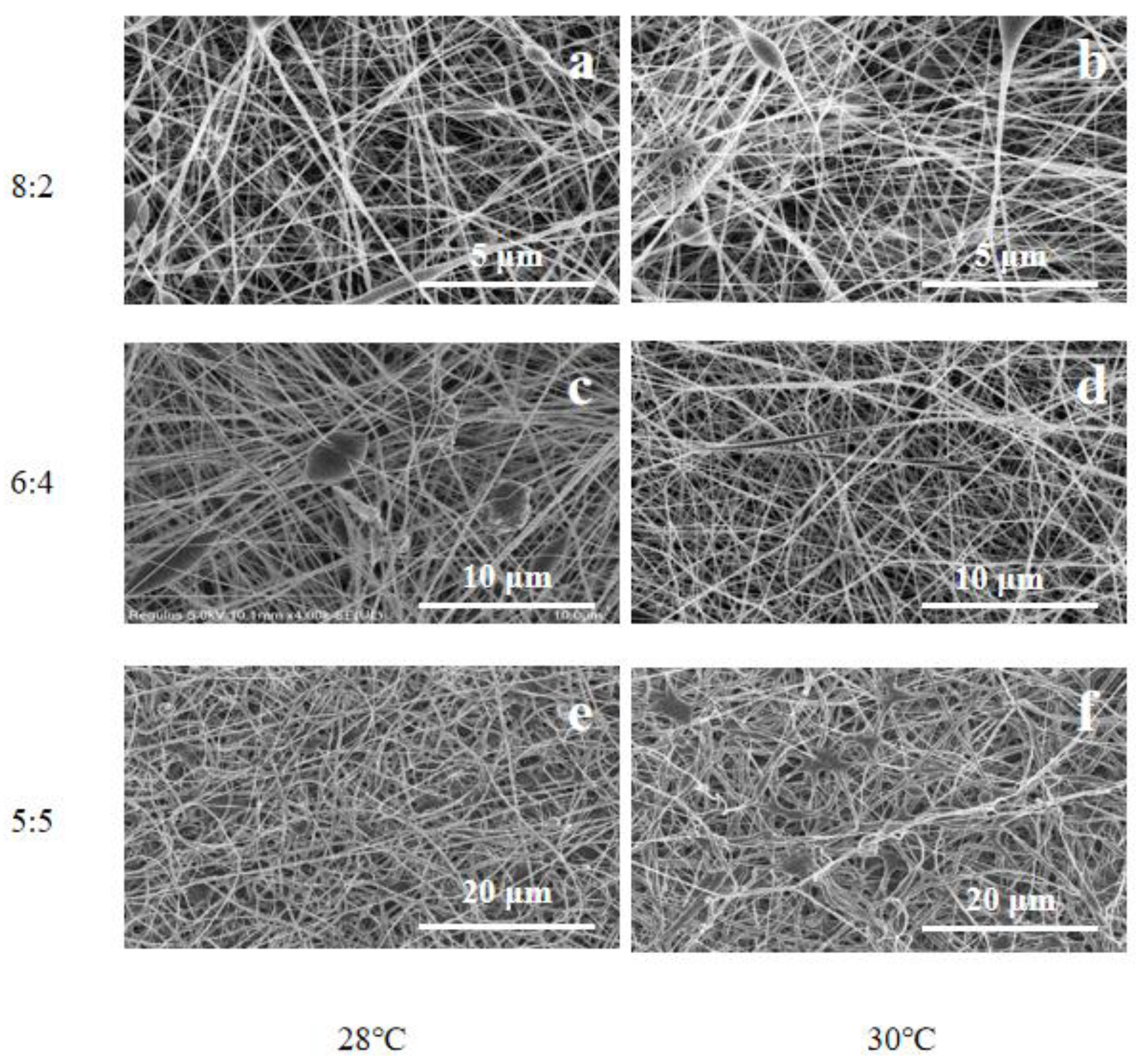
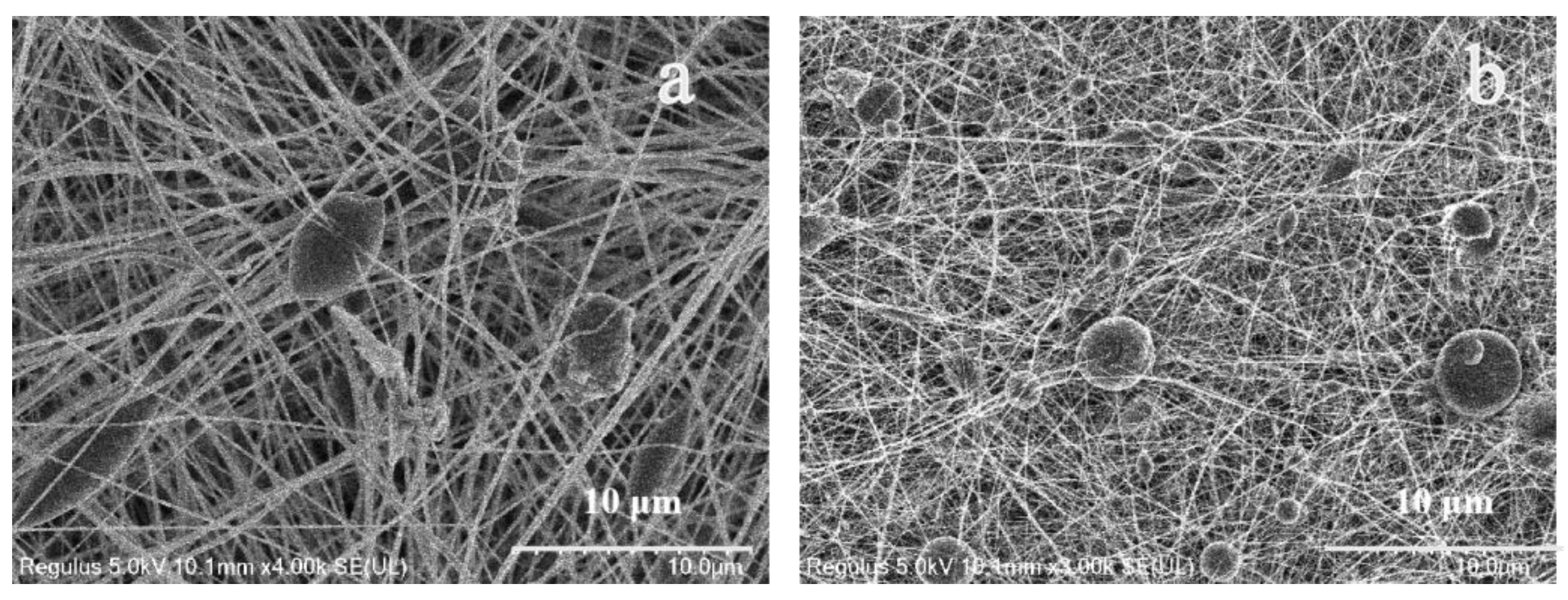
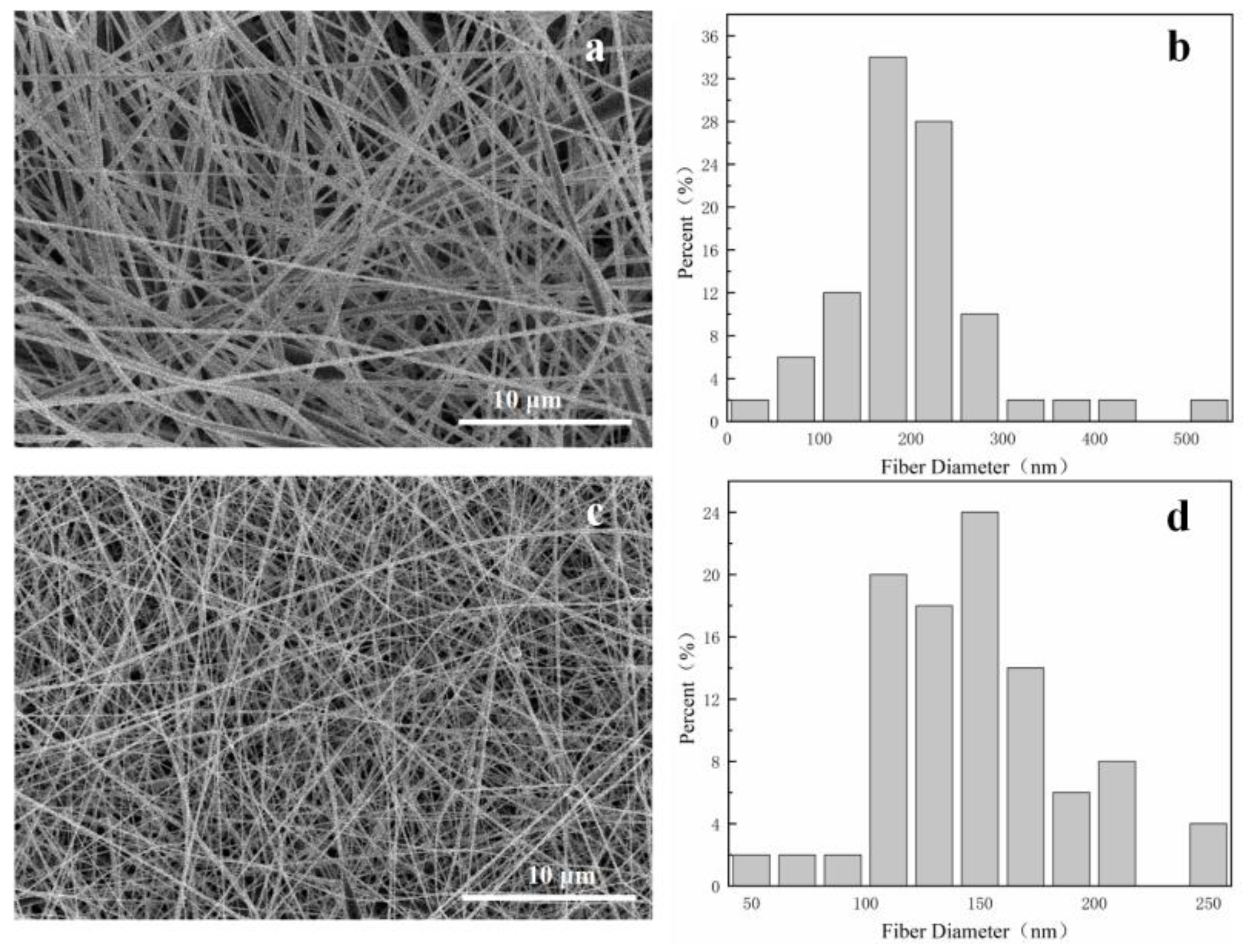
2.3.1. SEM
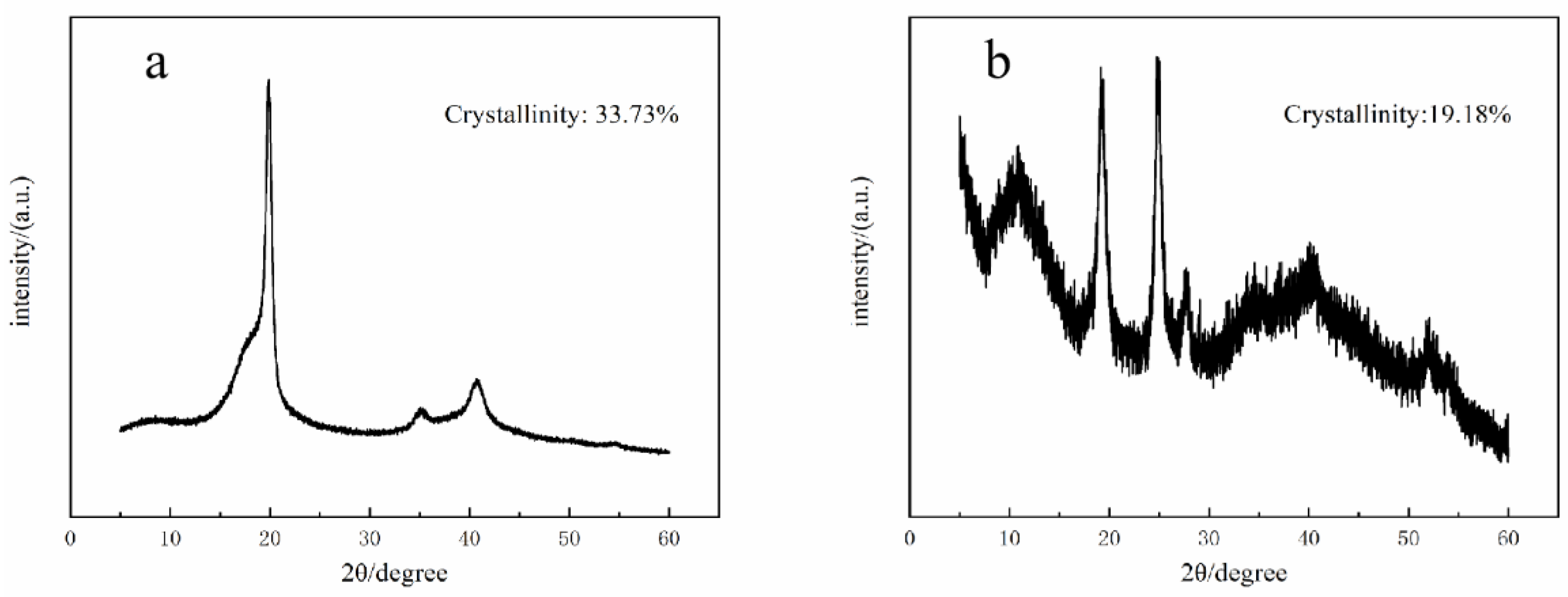
2.3.2. XRD
2.3.3. XPS
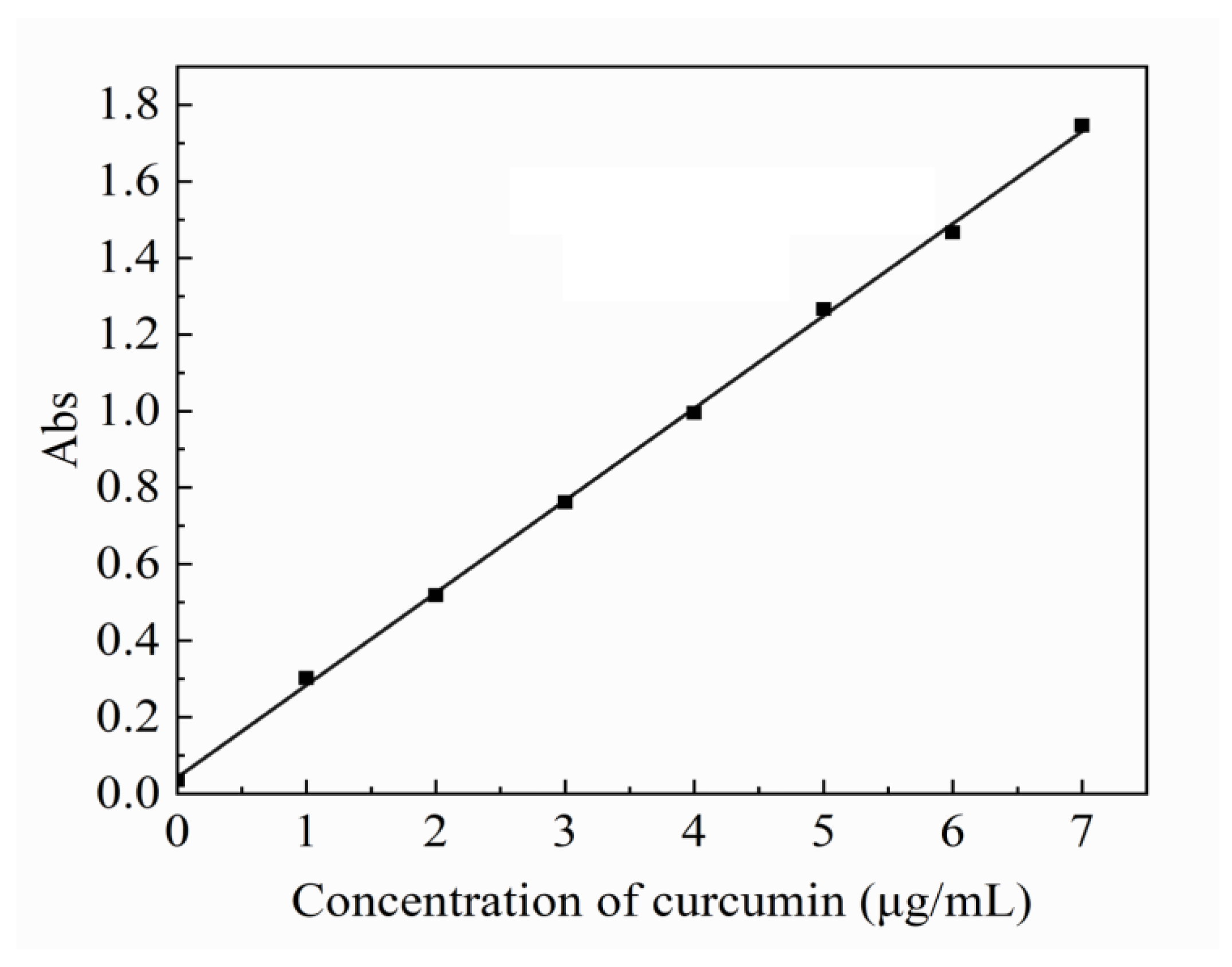
2.4. In Vitro Release Behavior of Model Drug Curcumin
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of Fiber Membranes
3.2. XRD
3.3. XPS
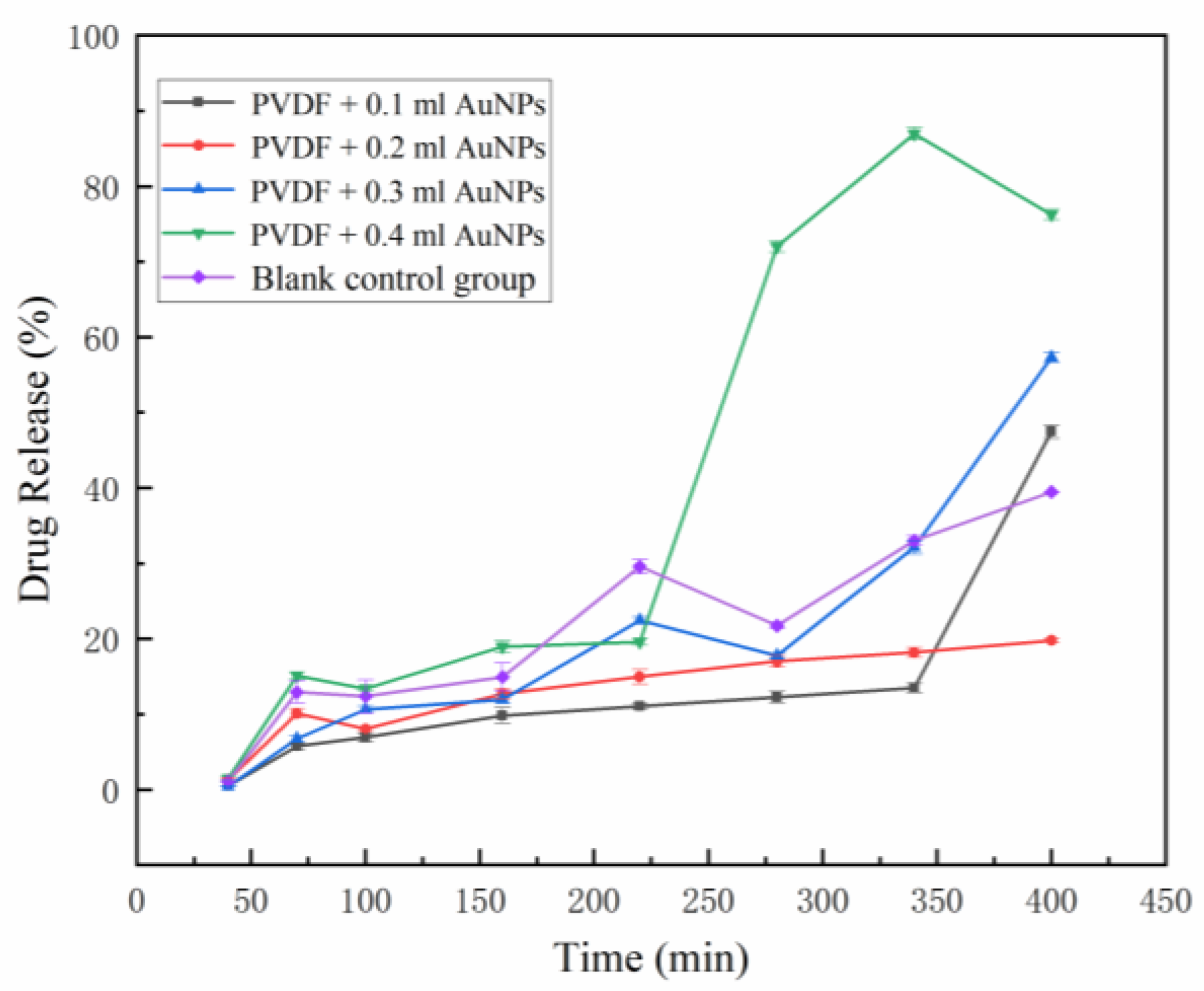
3.4. In Vitro Release of Model Drugs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daly, W.; Yao, L.; Zeugolis, D.; Windebank, A.; Pandit, A. A biomaterials approach to peripheral nerve regeneration: Bridging the peripheral nerve gap and enhancing functional recovery. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Liu, S.-Y.; Pi, W.; Zhang, P.-X. Cortical plasticity and nerve regeneration after peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, H.; Rasul, A.; Iqbal, J.; Ahmad, N.; Imran, A.; Malik, S.A.; Ijaz, F.; Akram, R.; Maqbool, J.; Sajid, F.; et al. Dietary biomolecules as promising regenerative agents for peripheral nerve injury: An emerging nutraceutical-based therapeutic approach. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srihagulang, C.; Vongsfak, J.; Vaniyapong, T.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Potential roles of vagus nerve stimulation on traumatic brain injury: Evidence from in vivo and clinical studies. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 347, 113887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijntjes, J.; Borchert, A.; van Alfen, N. Nerve ultrasound in traumatic and iatrogenic peripheral nerve injury. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-C.; Du, W.-Q.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Yu, S.-X.; Lu, F.-Z.; Ding, H.-M.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Ren, C.; Geng, D.-Q. Mesenchymal stem cell treatment for peripheral nerve injury: A narrative review. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.; Eisenberg, H.M.; Jia, X. Advances and future applications of augmented peripheral nerve regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, C.-F.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Han, S.; Wei, P.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Kou, Y.-H.; Jiang, B.-G. Chitin scaffold combined with autologous small nerve repairs sciatic nerve defects. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, R.P.; Cicha, I.; Alexiou, C. Iron oxide nanoparticles in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaderinejad, P.; Najmoddin, N.; Bagher, Z.; Saeed, M.; Karimi, S.; Simorgh, S.; Pezeshki-Modaress, M. An injectable anisotropic alginate hydrogel containing oriented fibers for nerve tissue engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 130465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Shi, W.; Kong, Y.; Kuss, M.; Duan, B. Anisotropic scaffolds for peripheral nerve and spinal cord regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4141–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J.-H.; Shi, L.-Y.; Huang, M.-Y.; Huang, L.-J.; Lin, Z.-J.; Lin, Q.-Y.; Lai, B.-Q.; Ma, Y.-H.; et al. An nt-3-releasing bioscaffold supports the formation of trkc-modified neural stem cell-derived neural network tissue with efficacy in repairing spinal cord injury. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3766–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.J.; Chan, C.Y.; Rastogi, A.; Grant, A.M.; White, C.M.; Bette, N.; Schaub, N.J.; Corey, J.M. Combining electrospun nanofibers with cell-encapsulating hydrogel fibers for neural tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 1625–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Weng, T.; Li, Q.; Jin, R.; You, C.; Wu, P.; Shao, J.; Xia, S.; Yang, M.; Han, C.; et al. Applications of poly(caprolactone)-based nanofibre electrospun scaffolds in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 16, 414–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Zhou, L.-P.; Pi, W.; Zhang, P.-X. Polymer scaffolds for biomedical applications in peripheral nerve reconstruction. Molecules 2021, 26, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Kim, C.S.; Park, C.H. Harnessing nanotopography of electrospun nanofibrous nerve guide conduits (ngcs) for neural tissue engineering. In Cutting-Edge Enabling Technologies for Regenerative Medicine; Chun, H.J., Park, C.H., Kwon, I.K., Khang, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1078, pp. 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo, V.; Clements, B.A.; Guarino, V.; Bushman, J.; Kohn, J.; Ambrosio, L. A comparison of the performance of mono- and bi-component electrospun conduits in a rat sciatic model. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8970–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, W.; Li, S.; Shi, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Huang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, G.-L. Application and effectiveness evaluation of electrostatic spinning plga-silk fibroin-collagen nerve conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 9413–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Shen, Y.; Khan, A.U.R.; Aldalbahi, A.; Fetz, A.E.; Bowlin, G.L.; El-Newehy, M.; et al. Electrospinning nanofiber scaffolds for soft and hard tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Mo, X.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, G. 3d printing electrospinning fiber-reinforced decellularized extracellular matrix for cartilage regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.S.S.; Chakrapani, V.Y. Electrospun 3d scaffolds for tissue regeneration. In Cutting-Edge Enabling Technologies for Regenerative Medicine; Chun, H.J., Park, C.H., Kwon, I.K., Khang, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 1078, pp. 29–47. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Ren, S.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, W.; Xu, Y. Biodegradable engineered fiber scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning for periodontal tissue regeneration. J. Biomater. Appl. 2021, 36, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Kang, S.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Wan, F.; Williams, G.R.; Bligh, S.-W.A. Combination of structure-performance and shape-performance relationships for better biphasic release in electrospun janus fibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 596, 120203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of cyclodextrin functional nanofibers for drug delivery applications. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farokhi, M.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Reis, R.L.; Ramakrishna, S.; Kundu, S.C. Functionalized silk fibroin nanofibers as drug carriers: Advantages and challenges. J. Control Release 2020, 321, 324–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Pan, H.; Ji, D.; Li, Y.; Duan, H.; Pan, W. Curcumin-loaded sandwich-like nanofibrous membrane prepared by electrospinning technology as wound dressing for accelerate wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 127, 112245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Lee, W.-H.; Gao, Z.; Qin, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, T.; Gao, Y. Wound dressing from polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan electrospun fiber membrane loaded with oh-cath30 nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 232, 115786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, K.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, Y.; Bligh, S.W.A.; Williams, G.R. Electrospun janus nanofibers loaded with a drug and inorganic nanoparticles as an effective antibacterial wound dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 111, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeckson, T.A.; Neo, Y.P.; Sisinthy, S.P.; Gorain, B. Delivery of therapeutics from layer-by-layer electrospun nanofiber matrix for wound healing: An update. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 635–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, R.; Vaghi, F.; Erba, E.; Romanelli, A.; Gelmi, M.L.; Clerici, F. Peptide grafting strategies before and after electrospinning of nanofibers. Acta Biomater. 2021, 122, 82–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gade, H.; Bokka, S.; Chase, G.G. Polarization treatments of electrospun pvdf fiber mats. Polymer 2021, 212, 123152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Shao, M.; Yang, F.; Shao, C.; Chen, C. Preparation and properties of antibacterial pvdf composite thin films. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 160, 110803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Lye, S.W.; Miao, J. Holistic investigation of the electrospinning parameters for high percentage of beta- phase in pvdf nanofibers. Polymer 2021, 214, 123366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Lim, J.Y.; Hong, S.M.; Lee, J.; Ha, J.; Choi, H.J.; Seo, Y. Enhanced piezoelectric properties of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride)/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites due to high beta-phase formation in poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11791–11799. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liao, C.; Tjong, S.C. Electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride-based fibrous scaffolds with piezoelectric characteristics for bone and neural tissue engineering. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lins, L.C.; Wianny, F.; Livi, S.; Dehay, C.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Gerard, J.-F. Effect of polyvinylidene fluoride electrospun fiber orientation on neural stem cell differentiation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B-Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 2376–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiue, A.; Chen, J.-H.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chang, S.-M.; Hwa, K.-Y.; Chin, K.-Y.; Leggett, G. Synthesis and cytotoxic analysis of thiolated xylose derivatives decorated on gold nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 28, e00549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaswal, R.; Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, B.K.; Kumar, D.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Nanographene enfolded aunps sophisticatedly synchronized polycaprolactone based electrospun nanofibre scaffold for peripheral nerve regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 116, 111213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Q. Curcumin accelerates the repair of sciatic nerve injury in rats through reducing schwann cells apoptosis and promoting myelinization. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moattari, M.; Moattari, F.; Kouchesfahani, H.M.; Kaka, G.; Sadraie, S.H.; Naghdi, M.; Mansouri, K. Curcumin and biodegradable membrane promote nerve regeneration and functional recovery after sciatic nerve transection in adult rats. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2018, 81, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahromi, H.K.; Farzin, A.; Hasanzadeh, E.; Barough, S.E.; Mahmoodi, N.; Najafabadi, M.R.H.; Farahani, M.S.; Mansoori, K.; Shirian, S.; Ai, J. Enhanced sciatic nerve regeneration by poly-l-lactic acid/multi-wall carbon nanotube neural guidance conduit containing schwann cells and curcumin encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles in rat. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 109, 110564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, K.; Luhrs, C.C.; Perez-Luna, V.H. Controlled and reversible aggregation of biotinylated gold nanoparticles with streptavidin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 15631–15639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from uv-vis spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Vazquez, E.F.; Rojas-Chavez, H.; Hernandez-Rodriguez, Y.M.; Morales-Bautista, J.; Cigarroa-Mayorga, O.E. The role of aunps on the photocatalytic degradation enhancement in moo3-based heterostructures. Mater. Lett. 2021, 290, 129464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhasani, M.M.; Azimi, S.; Fashandi, H. Enhanced ferroelectric properties of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers by adjusting processing parameters. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61277–61283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, X.; Wu, S.; Shen, W.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ao, F.; Ning, Y.; Mao, Y.; Chen, Z. Preparation of Polyvinylidene Fluoride–Gold Nanoparticles Electrospinning Nanofiber Membranes. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040130
Ge X, Wu S, Shen W, Chen L, Zheng Y, Ao F, Ning Y, Mao Y, Chen Z. Preparation of Polyvinylidene Fluoride–Gold Nanoparticles Electrospinning Nanofiber Membranes. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(4):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040130
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Xuemei, Shang Wu, Wen Shen, Lijuan Chen, Yan Zheng, Fen Ao, Yuanlan Ning, Yueyang Mao, and Zhong Chen. 2022. "Preparation of Polyvinylidene Fluoride–Gold Nanoparticles Electrospinning Nanofiber Membranes" Bioengineering 9, no. 4: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040130
APA StyleGe, X., Wu, S., Shen, W., Chen, L., Zheng, Y., Ao, F., Ning, Y., Mao, Y., & Chen, Z. (2022). Preparation of Polyvinylidene Fluoride–Gold Nanoparticles Electrospinning Nanofiber Membranes. Bioengineering, 9(4), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040130





