Estimating Internal Migration in Contemporary Mexico and its Relevance in Gridded Population Distributions
Abstract
:1. Summary
2. Data Description
Underlying Source Data
3. Methods
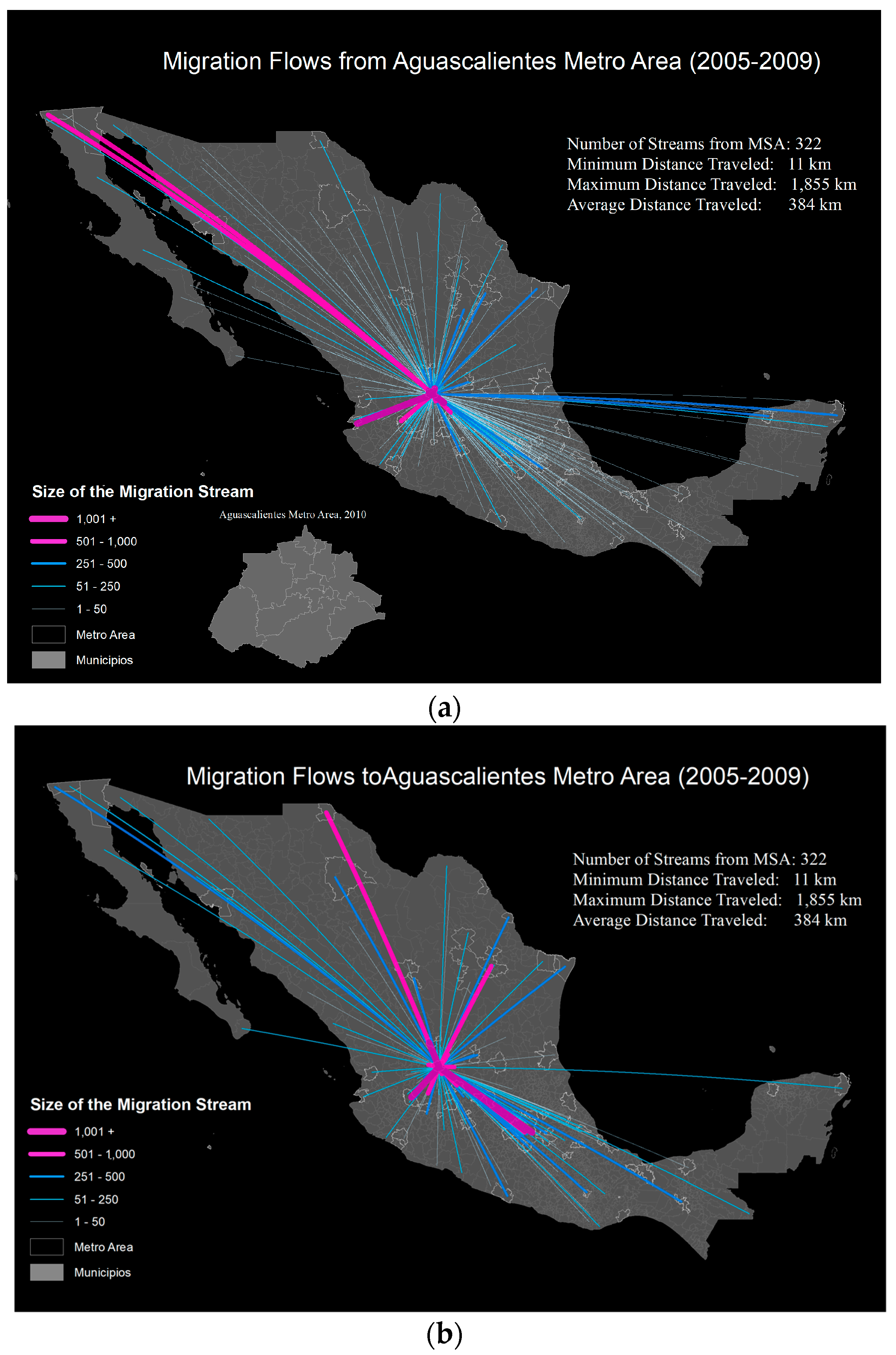
4. Data Outputs
4.1. Data Limitations
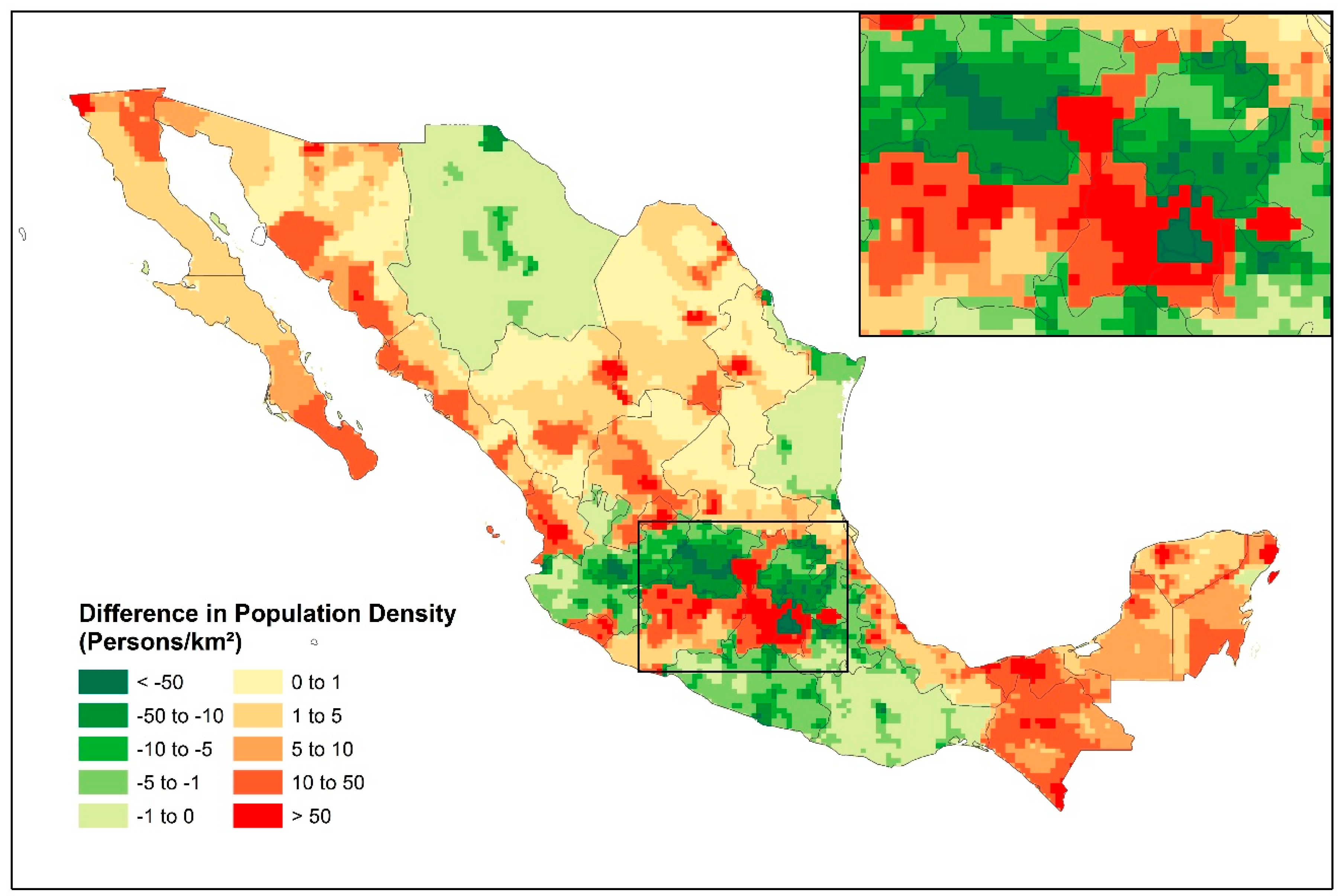
4.2. Data Format and Applications to Gridded Population Products
Notes: Map Produced Using ArcGIS
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Stata Code Used to Create Total and Sex-Specific Intermunicipal and Interstate Origin-Destination Matrices from IPUMS International Publicly-Available Data
References
- Jones, B.; O’Neill, B.C.; McDaniel, L.; McGinnis, S.; Mearns, L.O.; Tebaldi, C. Future population exposure to US heat extremes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatem, A.J. WorldPop, open data for spatial demography. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggles, S.; Alexander, J.T.; Genadek, K.; Goeken, R.; Schroeder, M.B.; Sobek, M. Integrated Public Use Microdata Series: Version 5.0 [Machine-Readable Database]; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggles, S.; Manson, S.M.; Kugler, T.A.; Haynes, D.A., II; Van Riper, D.C.; Bakhtsiyarava, M. IPUMS Terra: Integrated Data on Population and Environment: Version 2 [Dataset]; IPUMS: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.; Charles-Edwards, E.; Kupiszewska, D.; Kupiszewski, M.; Stillwell, J.; Zhu, Y. Internal migration data around the world: Assessing contemporary practice. Popul. Space Place 2015, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEGI. Síntesis metodológica del XII Censo General de Población y Vivienda. 2000. Available online: http://internet.contenidos.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/Productos/prod_serv/contenidos/espanol/bvinegi/productos/metodologias/est/702825000014.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2018).
- INEGI. Censo de Población y Vivienda 2010: Diseño de la Muestra Censal. 2010. Available online: http://internet.contenidos.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/Productos/prod_serv/contenidos/espanol/bvinegi/productos/metodologias/est/dis_muestra_cpv2010.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2018).
- Sorichetta, A.; Bird, T.J.; Ruktanonchai, N.W.; Zu Erbach-Schoenberg, E.; Pezzulo, C.; Tejedor, N.; Waldock, I.; Sadler, J.D.; Garcia, A.J.; Seda, L.; et al. Mapping internal connectivity through human migration in malaria endemic countries. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez Campuzano, E.; Santos Cerquera, C. Tendencias recientes de la migración interna en México. Pap. Población 2013, 19, 53–88. [Google Scholar]
- The Image Project: Comparing Internal Migration Around the Globe: Project Framework. Available online: https://imageproject.com.au/framework/ (accessed on 29 March 2019).
- Censo General de Población y Vivienda 2000: Conjunto de datos: Población de 5 y más años. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/sistemas/olap/proyectos/bd/censos/cpv2000/p5.asp?s=est&c=10262&proy=cpv00_p5 (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- Censo General de Población y Vivienda 2010. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/sistemas/olap/proyectos/bd/censos/cpv2010/p3mas.asp?s=est&c=27781&proy=cpv10_p3mas (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- Sobrino, J. Patrones de dispersión intrametropolitana en México. Estud. Demog. Urbanos 2007, 22, 583–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riosmena, F.; Balk, D. Internal Migration and other Mobility in Contemporary Mexico: Understanding Their Dynamics and Drivers Using Alternative Flow Typologies. 2019, Unpublished manuscript. 2019; Unpublished manuscript. [Google Scholar]
- Hauer, M. Migration induced by sea-level rise could reshape the US population landscape. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaud, K.K.; de Sherbinin, A.; Jones, B.; Bergmann, J.; Clement, V.; Ober, K.; Schewe, J.; Adamo, S.; McCusker, B.; Heuser, S.; et al. Groundswell: Preparing for Internal Climate Migration; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B.; O’Neill, B.C. Historically grounded spatial population projections for the continental United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; O’Neill, B.C. Spatially explicit global population scenarios consistent with the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 084003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proyecciones de la Población de México y de las Entidades Federativas, 2016–2050. Available online: https://datos.gob.mx/busca/dataset/proyecciones-de-la-poblacion-de-mexico-y-de-las-entidades-federativas-2016-2050 (accessed on 20 January 2019).

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, B.; Riosmena, F.; Simon, D.H.; Balk, D. Estimating Internal Migration in Contemporary Mexico and its Relevance in Gridded Population Distributions. Data 2019, 4, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/data4020050
Jones B, Riosmena F, Simon DH, Balk D. Estimating Internal Migration in Contemporary Mexico and its Relevance in Gridded Population Distributions. Data. 2019; 4(2):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/data4020050
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Bryan, Fernando Riosmena, Daniel H. Simon, and Deborah Balk. 2019. "Estimating Internal Migration in Contemporary Mexico and its Relevance in Gridded Population Distributions" Data 4, no. 2: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/data4020050
APA StyleJones, B., Riosmena, F., Simon, D. H., & Balk, D. (2019). Estimating Internal Migration in Contemporary Mexico and its Relevance in Gridded Population Distributions. Data, 4(2), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/data4020050



