Molecular Survey of Rickettsia raoultii in Ticks Infesting Livestock from Pakistan with Notes on Pathogen Distribution in Palearctic and Oriental Regions
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
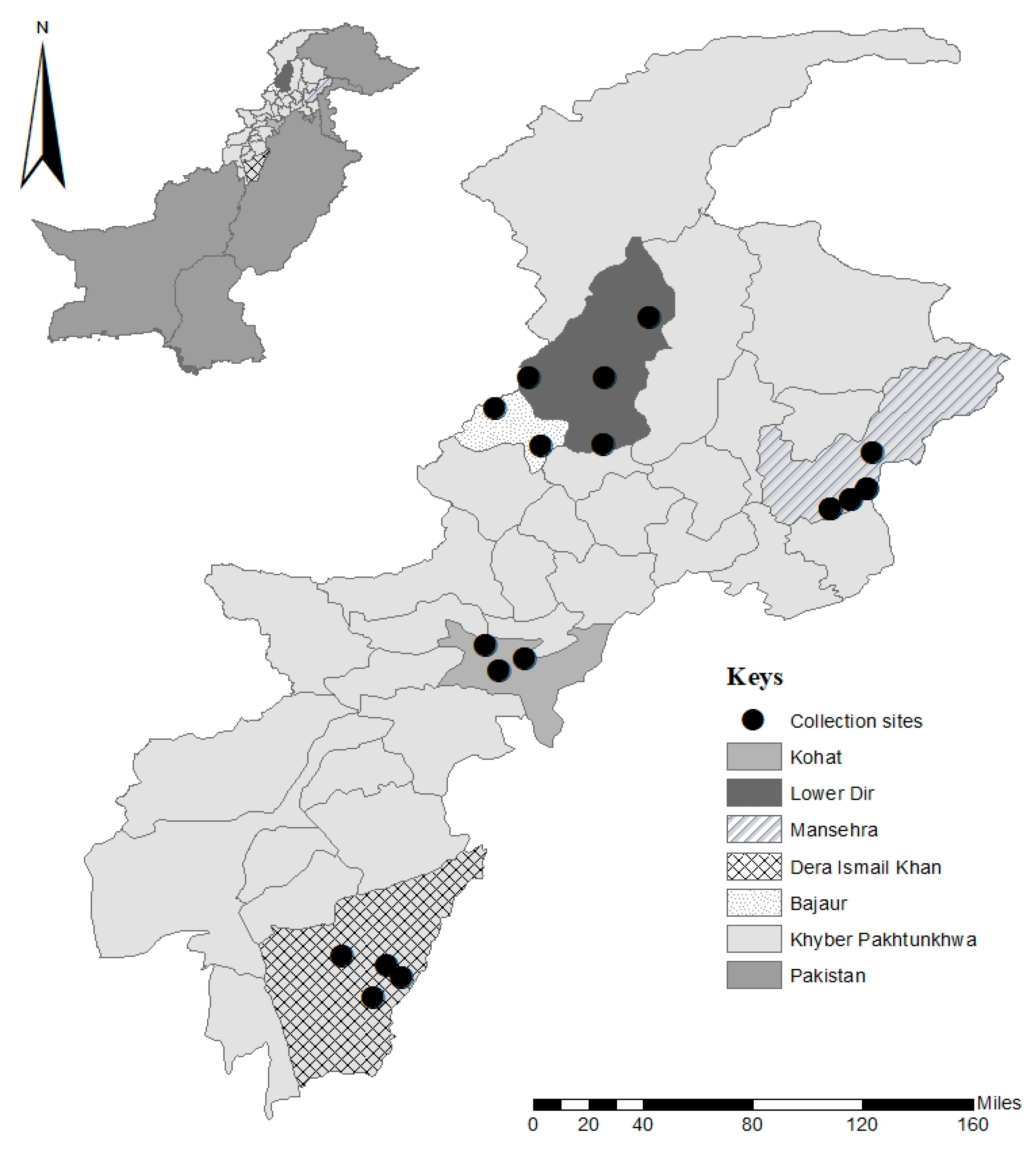
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Ticks Collection and Identification
2.4. Molecular Screening of Rickettsia spp.
2.5. Sequences and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.6. Literature Search and Selection Criteria
3. Results
3.1. Ticks and Hosts
3.2. Molecular Screening of Rickettsia spp.
3.3. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Latrofa, M.S.; Annoscia, G.; Giannelli, A.; Parisi, A.; Otranto, D. Morphological and genetic diversity of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato from the New and Old Worlds. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parola, P.; Paddock, C.D.; Socolovschi, C.; Labruna, M.B.; Mediannikov, O.; Kernif, T.; Abdad, M.Y.; Stenos, J.; Bitam, I.; Fournier, P.E.; et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: A geographic approach. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 657–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente, J.; Antunes, S.; Bonnet, S.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Domingos, A.G.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Johnson, N.; Kocan, K.M.; Mansfield, K.L.; Nijhof, A.M.; et al. Tick-pathogen interactions and vector competence: Identification of molecular drivers for tick-borne diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, H.R.; Pilgrim, J.; Wybouw, N.; Parker, J.; Pirro, S.; Hunter-Barnett, S.; Campbell, P.M.; Blow, F.; Darby, A.C.; Hurst, G.D.; et al. Genomic diversity across the Rickettsia and ‘Candidatus Megaira’genera and proposal of genus status for the Torix group. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, L.L.; Robinson, M.; Liang, Y.F.; Shih, C.M. First detection and molecular identification of Rickettsia massiliae, a human pathogen, in Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks collected from Southern Taiwan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, 0010917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parola, P.; Paddock, C.D.; Raoult, D. Tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: Emerging diseases challenging old concepts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 719–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, P.E.; Raoult, D. Current knowledge on phylogeny and taxonomy of Rickettsia spp. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1166, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merhej, V.; Angelakis, E.; Socolovschi, C.; Raoult, D. Genotyping, evolution and epidemiological findings of Rickettsia species. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 25, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elelu, N.; Ola-Fadunsin, S.D.; Bankole, A.A.; Raji, M.A.; Ogo, N.I.; Cutler, S.J. Prevalence of tick infestation and molecular characterization of spotted fever Rickettsia massiliae in Rhipicephalus species parasitizing domestic small ruminants in north-central Nigeria. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, 0263843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Tian, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, H.; Han, J.; Guo, W.; Li, K. High diversity of Rickettsia spp.; Anaplasma spp.; and Ehrlichia spp. in ticks from Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Front. Microbiol 2022, 13, 1008110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, Y.Q.; Chen, J.J.; Teng, A.Y.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Hay, S.I.; Fang, L.Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W. Mapping the global distribution of spotted fever group rickettsiae: A systematic review with modelling analysis. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 5, e5–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydkina, E.; Roux, V.; Rudakov, N.; Gafarova, M.; Tarasevich, I.; Raoult, D. New Rickettsiae in ticks collected in territories of the former Soviet Union. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediannikov, O.; Matsumoto, K.; Samoylenko, I.; Drancourt, M.; Roux, V.; Rydkina, E.; Davoust, B.; Tarasevich, I.; Brouqui, P.; Fournier, P.E. Rickettsia raoultii sp. novel, a spotted fever group Rickettsia associated with Dermacentor ticks in Europe and Russia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. 2008, 58, 1635–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Špitalská, E.; Štefanidesová, K.; Kocianová, E.; Boldiš, V. Rickettsia slovaca and Rickettsia raoultii in Dermacentor marginatus and Dermacentor reticulatus ticks from Slovak Republic. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 57, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.C.; Liu, G.Y.; Shen, H.; Xie, J.R.; Luo, J.; Tian, M.Y. First report on the occurrence of Rickettsia slovaca and Rickettsia raoultii in Dermacentor silvarum in China. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.P.; Mu, L.M.; Xu, J.; Jiang, S.H.; Wang, A.D.; Chen, C.F.; Guo, G.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, Y.Z. Rickettsia raoultii in Haemaphysalis erinacei from marbled polecats, China–Kazakhstan border. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Fu, W.; Ju, W.; Yang, L.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Hu, M.X.; Wen, J.; et al. Diversity of spotted fever group Rickettsia infection in hard ticks from Suifenhe, Chinese–Russian border. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, G.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, W.; Xiao, R.; Hazihan, W.; Hornok, S.; Wang, Y. Molecular evidence of Rickettsia raoultii, “Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae” and a novel Babesia genotype in marbled polecats (Vormela peregusna) at the China-Kazakhstan border. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, S.; Tan, W.; Hornok, S.; Yuan, W.; Mi, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hazihan, W.; et al. Rickettsiae in red fox (Vulpes vulpes), marbled polecat (Vormela peregusna) and their ticks in northwestern China. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisu, V.; Foxi, C.; Masala, G. First molecular detection of the human pathogen Rickettsia raoultii and other spotted fever group rickettsiae in Ixodid ticks from wild and domestic mammals. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3421–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, M.; Jiang, M.; Yan, B.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, W.; Wang, B.; Hornok, S.; Wang, Y. Rickettsia raoultii and Rickettsia sibirica in ticks from the long-tailed ground squirrel near the China–Kazakhstan border. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 77, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, M.; Seo, J.W.; Kim, D.Y.; Panchali, M.J.L.; Yun, N.R.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, D.M. First report of the molecular detection of human pathogen Rickettsia raoultii in ticks from the Republic of Korea. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomar, A.M.; Premchand-Branker, S.; Alberdi, P.; Belova, O.A.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Kahl, O.; Bell-Sakyi, L. Isolation of known and potentially pathogenic tick-borne microorganisms from European ixodid ticks using tick cell lines. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibáñez, S.; Portillo, A.; Palomar, A.M.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Romero, L.; Oteo, J.A. Isolation and maintenance of Rickettsia raoultii in a Rhipicephalus sanguineus tick cell line. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güvendi, M.; Can, H.; Köseoğlu, A.E.; Alak, S.E.; Kandemir, Ç.; Taşkın, T.; Sürgeç, E.; Demir, S.; Döşkaya, A.D.; Karakavuk, M. Investigation of the genetic diversity and flea-borne pathogens in Ctenocephalides felis samples collected from goats in İzmir and Şanlıurfa provinces of Turkey. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 90, 101896. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, S.T.; Mokhtar, A.S.; Low, K.C.; Mohd Zain, S.N.; Jeffery, J.; Abdul Aziz, N.; Kho, K.L. Identification of rickettsiae from wild rats and cat fleas in Malaysia. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2014, 28, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Shu, P.Y.; Mu, J.J.; Wang, H.C. High prevalence of Rickettsia spp. infections in small mammals in Taiwan. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kho, K.L.; Koh, F.X.; Singh, H.K.L.; Zan, H.A.M.; Kukreja, A.; Ponnampalavanar, S.; Tay, S.T. Case report: Spotted fever group rickettsioses and murine typhus in a Malaysian teaching hospital. Am. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 95, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, P.H.; Huang, Y.; Du, J.; Cui, N.; Yang, Z.D.; Tang, F.; Fu, F.X.; Li, X.M.; Cui, X.M.; et al. Isolation and identification of Rickettsia raoultii in human cases: A surveillance study in 3 medical centers in China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatta, R.; Sazmand, A.; Nguyen, V.L.; Nemati, F.; Ayaz, M.M.; Bahiraei, Z.; Zafari, S.; Giannico, A.; Greco, G.; Dantas-Torres, F.; et al. Vector-borne pathogens in dogs of different regions of Iran and Pakistan. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 4219–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, E.; Pulcini, C.; Waton, J.; Imbert, P.; Socolovschi, C.; Edouard, S.; Dellamonica, P.; Raoult, D. Scalp eschar and neck lymphadenopathy caused by Bartonella henselae after tick bite. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xie, S.; Zhao, S.; Tan, W.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Y. A case with neurological abnormalities caused by Rickettsia raoultii in northwestern China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igolkina, Y.; Krasnova, E.; Rar, V.; Savelieva, M.; Epikhina, T.; Tikunov, A.; Khokhlova, N.; Provorova, V.; Tikunova, N. Detection of causative agents of tick-borne rickettsioses in Western Siberia, Russia: Identification of Rickettsia raoultii and Rickettsia sibirica DNA in clinical samples. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 199-e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switaj, K.; Chmielewski, T.; Borkowski, P.; Tylewska-Wierzbanowska, S.; Olszynska-Krowicka, M. Spotted fever rickettsiosis caused by Rickettsia raoultii—Case report. Prz. Epidemiol. 2012, 66, 347–350. [Google Scholar]
- Parola, P.; Rovery, C.; Rolain, J.M.; Brouqui, P.; Davoust, B.; Raoult, D. Rickettsia slovaca and R. raoultii in tick-borne rickettsioses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekeyova, Z.; Subramanian, G.; Mediannikov, O.; Diaz, M.Q.; Nyitray, A.; Blaskovicova, H.; Raoult, D. Evaluation of clinical specimens for Rickettsia, Bartonella, Borrelia, Coxiella, Anaplasma, Franciscella and Diplorickettsia positivity using serological and molecular biology methods. FEMS Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 64, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, S.; Budachetri, K.; Mukherjee, N.; Williams, J.; Kausar, A.; Hassan, M.J.; Adamson, S.; Dowd, S.E.; Apanskevich, D.; Arijo, A.; et al. A study of ticks and tick-borne livestock pathogens in Pakistan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, 0005681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Shehla, S.; Alouffi, A.; Kashif Obaid, M.; Zeb Khan, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Numan, M.; Aiman, O.; Alam, S.; Ullah, S. Molecular survey and genetic characterization of Anaplasma marginale in ticks collected from livestock hosts in Pakistan. Animals 2022, 12, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shehla, S.; Zahid, H.; Ullah, F.; Zeb, I.; Ahmed, H.; Da Silva Vaz, I., Jr.; Tanaka, T. Molecular survey and spatial distribution of Rickettsia spp. in ticks infesting free-ranging wild animals in Pakistan (2017–2021). Pathogens 2022, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiman, O.; Ullah, S.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Nijhof, A.M.; Ali, A. First report of Nosomma monstrosum ticks infesting Asian water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) in Pakistan. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numan, M.; Islam, N.; Adnan, M.; Zaman Safi, S.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Labruna, M.B.; Ali, A. First genetic report of Ixodes kashmiricus and associated Rickettsia sp. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.M.; Khan, M.; Alouffi, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Numan, M.; Ullah, S.; Obaid, M.K.; Islam, Z.U.; Ahmed, H.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Phylogenetic Position of Haemaphysalis kashmirensis and Haemaphysalis cornupunctata, with Notes on Rickettsia spp. Genes 2023, 14, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Obaid, M.K.; Almutairi, M.; Alouffi, A.; Numan, M.; Ullah, S.; Rehman, G.; Islam, Z.U.; Khan, S.B.; Tanaka, T. Molecular Detection of Coxiella spp. in Ticks (Ixodidae and Argasidae) Infesting Domestic and Wild Animals: With Notes on the Epidemiology of Tick-borne Coxiella burnetii in Asia. Front. Microbiol 2023, 14, 1229950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaid, M.K.; Almutairi, M.M.; Alouffi, A.; Safi, S.Z.; Tanaka, T.; Ali, A. Assessment of cypermethrin and amitraz resistance and molecular profiling of voltage-gated sodium channel and octopamine tyramine genes of Rhipicephalus microplus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1176013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Islam, N.; Khan, A.; Islam, Z.U.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Labruna, M.B.; Ali, A. New records of Amblyomma gervaisi from Pakistan, with detection of a reptile-associated Borrelia sp. Ticks. Tick. Borne. Dis. 2022, 13, 102047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Zahid, H.; Zeb, I.; Tufail, M.; Khan, S.; Haroon, M.; Bilal, M.; Hussain, M.; Alouffi, A.S.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; et al. Risk factors associated with tick infestations on equids in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, with notes on Rickettsia massiliae detection. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Numan, M.; Khan, M.; Aiman, O.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Labruna, M.B. and Nijhof, A.M. Ornithodoros (Pavlovskyella) ticks associated with a Rickettsia sp. in Pakistan. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogstraal, H.; Varma, M.G.R. Haemaphysalis cornupunctata sp. n. and H. kashmirensis sp. n. from Kashmir, with Notes on H. sundrai Sharif and H. sewelli Sharif of India and Pakistan (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). J. Parasitol. 1962, 48, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogstraal, H.; Trapido, H. Redescription of the type materials of Haemaphysalis (Kaiseriana) bispinosa Neumann (India), H. (K.) neumanni Dönitz (Japan), H. (K.) lagrangei Larrousse (Vietnam), and H. (K.) yeni Toumanoff (Vietnam) (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). J. Parasitol. 1966, 52, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogstraal, H.; Trapido, H.; Kohls, G.M. Studies on southeast Asian Haemaphysalis ticks (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). Speciation in the H. (Kaiseriana) obesa group: H. semermis Neumann, H. obesa Larrousse, H. roubaudi Toumanoff, H. montgomeryi Nuttall, and H. hirsuta sp. n. J. Parasitol. 1966, 52, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.B.; Keirans, J.E.; Horak, I.G. The Genus Rhipicephalus (Acari, Ixodidae): A Guide to the Brown Ticks of the World; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Apanaskevich, D.A.; Schuster, A.L.; Horak, I.G. The genus Hyalomma: VII. Redescription of all parasitic stages of H. (Euhyalomma) dromedarii and H. (E.) schulzei (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (No. Ed. 2); Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Long Island, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Labruna, M.B.; Whitworth, T.; Horta, M.C.; Bouyer, D.H.; McBride, J.W.; Pinter, A.; Popov, V.; Gennari, S.M.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsia species infecting Amblyomma cooperi ticks from an area in the state of Sao Paulo, Brazil, where Brazilian spotted fever is endemic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnery, R.L.; Spruill, C.L.; Plikaytis, B. Genotypic identification of rickettsiae and estimation of intraspecies sequence divergence for portions of two rickettsial genes. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, V.; Raoult, D. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Rickettsia using the gene encoding the outer-membrane protein rompB (ompB). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.; Biosciences, I.; Carlsbad, C.J.G.B.B. BioEdit: An important software for molecular biology. GERF Bull. Biosci. 2011, 2, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar]
- Sarih, M.; Socolovschi, C.; Boudebouch, N.; Hassar, M.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks, Morocco. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez, S.; Portillo, A.; Santibáñez, P.; Palomar, A.M.; Oteo, J.A. Usefulness of rickettsial PCR assays for the molecular diagnosis of human rickettsioses. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2013, 31, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, M.; Sakata, A.; Takano, A.; Kawabata, H.; Fujita, H.; Une, Y.; Goka, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Ando, S. Detection of Rickettsia and Ehrlichia spp. in ticks associated with exotic reptiles and amphibians imported into Japan. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0133700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargili, A.; Palomar, A.M.; Midilli, K.; Portillo, A.; Kar, S.; Oteo, J.A. Rickettsia species in ticks removed from humans in Istanbul, Turkey. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milhano, N.; de Carvalho, I.L.; Alves, A.S.; Arroube, S.; Soares, J.; Rodriguez, P.; Carolino, M.; Núncio, M.S.; Piesman, J.; de Sousa, R. Co-infections of Rickettsia slovaca and Rickettsia helvetica with Borrelia lusitaniae in ticks collected in a Safari Park, Portugal. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2010, 1, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Földvári, G.; Rigó, K.; Lakos, A. Transmission of Rickettsia slovaca and Rickettsia raoultii by male Dermacentor marginatus and Dermacentor reticulatus ticks to humans. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 76, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, A.; Ibarra, V.; Santibáñez, S.; Pérez-Martínez, L.; Blanco, J.R.; Oteo, J.A. Genetic characterisation of ompA, ompB and gltA genes from Candidatus Rickettsia rioja. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; You, B.J.; Liu, E.; Apte, A.; Yarina, T.R.; Myers, T.E.; Lee, J.S.; Francesconi, S.C.; O’Guinn, M.L.; Tsertsvadze, N.; et al. Development of three quantitative real-time PCR assays for the detection of Rickettsia raoultii, Rickettsia slovaca, and Rickettsia aeschlimannii and their validation with ticks from the country of Georgia and the Republic of Azerbaijan. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reye, A.L.; Stegniy, V.; Mishaeva, N.P.; Velhin, S.; Hübschen, J.M.; Ignatyev, G.; Muller, C.P. Prevalence of tick-borne pathogens in Ixodes ricinus and Dermacentor reticulatus ticks from different geographical locations in Belarus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 54476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doornbos, K.; Sumrandee, C.; Ruang–Areerate, T.; Baimai, V.; Trinachartvanit, W.; Ahantarig, A. Rickettsia sp. closely related to Rickettsia raoultii (Rickettsiales: Rickettsiaceae) in an Amblyomma helvolum (Acarina: Ixodidae) tick from a Varanus salvator (Squamata: Varanidae) in Thailand. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.G.; Kwon, O.D.; Kwak, D. High prevalence of Rickettsia raoultii and associated pathogens in canine ticks, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiegala, A.; Oltersdorf, C.; Silaghi, C.; Kiefer, D.; Kiefer, M.; Woll, D.; Pfeffer, M. Rickettsia spp. in small mammals and their parasitizing ectoparasites from Saxony, Germany. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud 2016, 5, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, I.; Venclíková, K.; Blažejová, H.; Betášová, L.; Mendel, J.; Hubálek, Z.; Parola, P. First report of Rickettsia raoultii and Rickettsia helvetica in Dermacentor reticulatus ticks from the Czech Republic. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 1222–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, M.; Popescu, C.P.; Florescu, S.A.; Ceausu, E.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P.; Socolovschi, C. Rickettsia massiliae infection and SENLAT syndrome in Romania. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Špitalská, E.; Boldišová, E.; Palkovičová, K.; Sekeyová, Z.; Škultéty, L. Case studies of rickettsiosis, anaplasmosis and Q fever in Slovak population from 2011 to 2020. Biologia 2021, 77, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, S.; Docters van Leeuwen, A.; Rigó, K.; Jablonszky, M.; Majoros, G.; Sprong, H.; Földvári, G. Prevalence and diversity of human pathogenic rickettsiae in urban versus rural habitats, Hungary. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 68, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, N.; Zheng, Y.C.; Ma, L.; Huo, Q.B.; Ni, X.B.; Jiang, B.G.; Chu, Y.L.; Jiang, R.R.; Jiang, J.F.; Cao, W.C. Human infections with Rickettsia raoultii, China. Emerging Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wächter, M.; Wölfel, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Dobler, G.; Kohn, B.; Moritz, A.; Pachnicke, S.; Silaghi, C. Serological differentiation of antibodies against Rickettsia helvetica, R. raoultii, R. slovaca, R. monacensis and R. felis in dogs from Germany by a micro-immunofluorescent antibody test. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speck, S.; Derschum, H.; Damdindorj, T.; Dashdavaa, O.; Jiang, J.; Kaysser, P.; Jigjav, B.; Nyamdorj, E.; Baatar, U.; Munkhbat, E.; et al. Rickettsia raoultii, the predominant Rickettsia found in Mongolian Dermacentor nuttalli. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.J.; Vongphayloth, K.; Vongsouvath, M.; Grandadam, M.; Brey, P.T.; Newton, P.N.; Sutherland, I.W.; Dittrich, S. Large-scale survey for tickborne bacteria, Khammouan Province, Laos. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Cerro, A.; Oleaga, A.; Somoano, A.; Barandika, J.F.; García-Pérez, A.L.; Espí, A. Molecular identification of tick-borne pathogens (Rickettsia spp.; Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, Coxiella burnetii and piroplasms) in questing and feeding hard ticks from North-Western Spain. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, K.L.; Koh, F.X.; Hasan, L.I.M.; Wong, L.P.; Kisomi, M.G.; Bulgiba, A.; Nizam, Q.N.H.; Tay, S.T. Rickettsial seropositivity in the indigenous community and animal farm workers, and vector surveillance in Peninsular Malaysia. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.G.; Kwon, O.D.; Kwak, D. Molecular detection of Rickettsia raoultii, Rickettsia tamurae, and associated pathogens from ticks parasitizing water deer (Hydropotes inermis argyropus) in South Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.O.; Marga, G.; Banu, T.; Dobler, G.; Chitimia-Dobler, L. Tick-borne pathogens in tick species infesting humans in Sibiu County, central Romania. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionita, M.; Silaghi, C.; Mitrea, I.L.; Edouard, S.; Parola, P.; Pfister, K. Molecular detection of Rickettsia conorii and other zoonotic spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks, Romania. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stańczak, J.; Biernat, B.; Racewicz, M.; Zalewska, M.; Matyjasek, A. Prevalence of different Rickettsia spp. in Ixodes ricinus and Dermacentor reticulatus ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in north-eastern Poland. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, N.; Obiegala, A.; Pfeffer, M.; Lonc, E.; Kiewra, D. Detection of selected pathogens in ticks collected from cats and dogs in the Wrocław Agglomeration, South-West Poland. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didyk, Y.M.; Blaňárová, L.; Pogrebnyak, S.; Akimov, I.; Pet’ko, B.; Víchová, B. Emergence of tick-borne pathogens (Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Ricketsia raoultii and Babesia microti) in the Kyiv urban parks, Ukraine. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumpertz, M.; Sevestre, J.; Luciani, L.; Houhamdi, L.; Fournier, P.E.; Parola, P. Bacterial Agents Detected in 418 Ticks Removed from Humans during 2014–2021, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraga-Fernández, A.; Chaligiannis, Ι.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Papa, A.; Sotiraki, S.; de La Fuente, J.; Fernández de Mera, I.G. Molecular identification of spotted fever group Rickettsia in ticks collected from dogs and small ruminants in Greece. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 78, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dib, L.; Lafri, I.; Boucheikhchoukh, M.; Dendani, Z.; Bitam, I.; Benakhla, A. Seasonal distribution of Rickettsia spp. in ticks in northeast Algeria. New Microbes New Infect. 2019, 27, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeester, T.R.; van der Lei, P.B.; Van Leeuwen, A.D.; Sprong, H.; van Wieren, S.E. New foci of Haemaphysalis punctata and Dermacentor reticulatus in the Netherlands. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Guo, S.; Ding, C.; Cao, M.; Kawabata, H.; Sato, K.; Ando, S.; Fujita, H.; Kawamori, F.; Su, H.; et al. Spotted fever group rickettsiae in Inner Mongolia, China, 2015–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potkonjak, A.; Gutiérrez, R.; Savić, S.; Vračar, V.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Jurišić, A.; Kleinerman, G.; Rojas, A.; Petrović, A.; Baneth, G.; et al. Molecular detection of emerging tick-borne pathogens in Vojvodina, Serbia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duscher, G.G.; Hodžić, A.; Weiler, M.; Vaux, A.G.; Rudolf, I.; Sixl, W.; Medlock, J.M.; Versteirt, V.; Hubálek, Z. First report of Rickettsia raoultii in field collected Dermacentor reticulatus ticks from Austria. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turebekov, N.; Abdiyeva, K.; Yegemberdiyeva, R.; Dmitrovsky, A.; Yeraliyeva, L.; Shapiyeva, Z.; Amirbekov, A.; Oradova, A.; Kachiyeva, Z.; Ziyadina, L.; et al. Prevalence of Rickettsia species in ticks including identification of unknown species in two regions in Kazakhstan. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igolkina, Y.; Rar, V.; Vysochina, N.; Ivanov, L.; Tikunov, A.; Pukhovskaya, N.; Epikhina, T.; Golovljova, I.; Tikunova, N. Genetic variability of Rickettsia spp. in Dermacentor and Haemaphysalis ticks from the Russian Far East. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Kiewra, D.; Czułowska, A.; Robak, A.; Bajer, A. Update on prevalence of Babesia canis and Rickettsia spp. in adult and juvenile Dermacentor reticulatus ticks in the area of Poland (2016–2018). Sci. Rep 2022, 12, 5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, S.; Erkunt Alak, S.; Köseoğlu, A.E.; Ün, C.; Nalçacı, M.; Can, H. Molecular investigation of Rickettsia spp. and Francisella tularensis in ticks from three provinces of Turkey. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 81, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimisha, M.; Devassy, J.K.; Pradeep, R.K.; Pakideery, V.; Sruthi, M.K.; Pious, A.; Kurbet, P.S.; Amrutha, B.M.; Chandrasekhar, L.; Deepa, C.K.; et al. Ticks and accompanying pathogens of domestic and wild animals of Kerala, South India. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 79, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, A.; Latifian, M.; Esmaeili, S.; Naddaf, S.R.; Mostafavi, E. Molecular surveillance for Rickettsia spp. and Bartonella spp. in ticks from Northern Iran. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, 0278579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lernout, T.; De Regge, N.; Tersago, K.; Fonville, M.; Suin, V.; Sprong, H. Prevalence of pathogens in ticks collected from humans through citizen science in Belgium. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klitgaard, K.; Chriél, M.; Isbrand, A.; Jensen, T.K.; Bødker, R. Identification of Dermacentor reticulatus ticks carrying Rickettsia raoultii on migrating jackal, Denmark. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuck, H.M.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Król, N.; Kacza, J.; Pfeffer, M. Collection of immature Dermacentor reticulatus (Fabricius, 1794) ticks from vegetation and detection of Rickettsia raoultii in them. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgroi, G.; Iatta, R.; Lia, R.P.; D’Alessio, N.; Manoj, R.R.S.; Veneziano, V.; Otranto, D. Spotted fever group rickettsiae in Dermacentor marginatus from wild boars in Italy. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Y.; Xie, S.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Y. A tick bite patient with fever and meningitis co-infected with Rickettsia raoultii and Tacheng tick virus 1: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, T.; Matei, I.A.; Novac, C.Ș.; Kalmár, Z.; Borșan, S.D.; Panait, L.C.; Gherman, C.M.; Ionică, A.M.; Papuc, I.; Mihalca, A.D. Spotted Fever Group Rickettsia spp. Diversity in Ticks and the First Report of Rickettsia hoogstraalii in Romania. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Ren, Q.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, J.; Xie, G.; Du, L.; Guo, W.P. Human pathogens in ticks removed from humans in Hebei, China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallan, K.; Ayyavu, V.; Ayyanar, E.; Thirupathi, B.; Gupta, B.; Devaraju, P.; Kumar, A.; Rajaiah, P. Molecular Evidence of Rickettsia conorii subsp. raoultii and Rickettsia felis in Haemaphysalis intermedia Ticks in Sirumalai, Eastern Ghats, Tamil Nadu, South India. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczwarska, J.; Pawełczyk, A.; Dunaj-Małyszko, J.; Polaczyk, J.; Welc-Falęciak, R. Rickettsia species in Dermacentor reticulatus ticks feeding on human skin and clinical manifestations of tick-borne infections after tick bite. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Q.; Gu, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Han, H.J.; Yu, X.J. Molecular detection of Rickettsia, Anaplasma, and Bartonella in ticks from free-ranging sheep in Gansu Province, China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakov, A.V.; Chekanova, T.A.; Petremgvdlishvili, K.; Timonin, A.V.; Valdokhina, A.V.; Shirokostup, S.V.; Lukyanenko, N.V.; Akimkin, V.G. High Prevalence of Rickettsia raoultii Found in Dermacentor Ticks Collected in Barnaul, Altai Krai, Western Siberia. Pathogens 2023, 12, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkahia, H.; Selmi, R.; Zamiti, S.; Daaloul-Jedidi, M.; Messadi, L.; Ben Said, M. Zoonotic Rickettsia species in Small ruminant ticks from Tunisia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 676896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyiche, T.E.; Răileanu, C.; Tauchmann, O.; Fischer, S.; Vasić, A.; Schäfer, M.; Biu, A.A.; Ogo, N.I.; Thekisoe, O.; Silaghi, C. Prevalence and molecular characterization of ticks and tick-borne pathogens of one-humped camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Nigeria. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Khan, M.; Alouffi, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Ullah, S.; Numan, M.; Islam, N.; Khan, Z.; Aiman, O.; Zaman Safi, S.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Ticks and Molecular Survey of Anaplasma marginale, with Notes on Their Phylogeny. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uspensky, I. Preliminary observations on specific adaptations of exophilic ixodid ticks to forests or open country habitats. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2002, 28, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, K.; Ali, A.; Villagra, C.A.; Bazai, Z.A.; Iqbal, A.; Sajid, M.S. Hyalomma anatolicum resistance against ivermectin and fipronil is associated with indiscriminate use of acaricides in south-western Balochistan, Pakistan. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamani, J.; Baneth, G.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Harrus, S. Molecular detection of Rickettsia aeschlimannii in Hyalomma spp. ticks from camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Nigeria, West Africa. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2015, 29, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Robbins, R.G. Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae) Parasitizing Humans; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 230. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Khan, M.A.; Zahid, H.; Yaseen, P.M.; Khan, M.Q.; Nawab, J.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ateeq, M.; Khan, S.; Ibrahim, M. Seasonal dynamics, record of ticks infesting humans, wild and domestic animals and molecular phylogeny of Rhipicephalus microplus in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, V.; Rydkγna, E.; Eremeeva, M.; Raoult, D. Citrate synthase gene comparison, a new tool for phylogenetic analysis, and its application for the rickettsiae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1997, 47, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmi, M.; Martello, E.; Bertolotti, L.; Bisanzio, D.; Tomassone, L. Rickettsia slovaca and Rickettsia raoultii in Dermacentor marginatus ticks collected on wild boars in Tuscany, Italy. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 1490–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Primer | Sequence | Amplicon Size | PCR Condition | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gltA | CS-78 | GCAAGTATCGGTGAGGATGTAAT | 401 bp | 95 °C 3 min, 40× (95 °C 15 s, 48 °C 30 s, 72°C 30 s), 72 °C 7 min | [54] |
| CS-323 | GCTTCCTTAAAATTCAATAAATCAGGAT | ||||
| ompA | Rrl9O.70 | ATGGCGAATATTTCTCCAAAA | 532 bp | 95 °C 3 min, 35× (95 °C 20 s, 48 °C 30 s, 63 °C 2 min), 72 °C 7 min | [55] |
| Rrl9O.602 | AGTGCAGCATTCGCTCCCCCT | ||||
| ompB | 120-M59 | CCGCAGGGTTGGTAACTGC | 862 bp | 95 °C 3 min, 40× (95 °C 30 s, 50 °C 30 s, 68 °C 90 s), 68 °C 7 min | [56] |
| 120-807 | CCTTTTAGATTACCGCCTAA |
| Country/Year of Study | Rickettsia raoultii | Tick Species/Source | Hosts/Sources | Identification Method (Serologically/Molecularly) | Genetic Marker (s) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morocco/2002–2006 | R. raoultii | Dermacentor marginatus | Livestock, dogs, and vegetation | Molecularly | gltA, ompA | [60] |
| France/2002–2007 | R. raoultii | Blood | Humans | Serologically and molecularly (sequencing) | ompA | [35] |
| Dermacentor spp. | ||||||
| Spain/2003–2008 | R. raoultii | Body fluids and biopsies | Humans | Molecularly (sequencing) | gltA and ompB | [61] |
| Japan/2004–2009 | R. raoultii | Amblyomma sparsum | Snakes, tortoises, lizards, and frogs imported from Zambia | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA | [62] |
| Slovakia/2004–2010 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Vegetation, horses, sheep, | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA, ompA and sca4 | [14] |
| Dermacentor reticulatus | Goats, and dogs | |||||
| Turkey/2006 | R. raoultii | Hyalomma marginatum | Humans | Molecularly (sequencing) | ompA | [63] |
| De. marginatus | ||||||
| Portugal/2006–2009 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Vegetation | Molecularly | gltA, ompA | [64] |
| Taiwan/2006–2010 | R. raoultii–like | liver, spleen, and kidney | Bandicota indica | Molecularly (sequencing) | ompB and gltA | [27] |
| Mus musculus | ||||||
| Hungary/2006–2010 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Humans | Molecularly (sequencing) | gltA, ompA, and16S rRNA | [65] |
| De. reticulatus | ||||||
| Spain | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Humans | Molecularly | gltA, ompA | [66] |
| Blood | ||||||
| Georgia/2008–2009 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Livestock, rodents | Molecularly | ompB | [67] |
| Malaysia/2008–2011 | R. raoultii–like | kidney, liver, spleen and heart | Wild rats | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA | [26] |
| Belarus/2009 | R. raoultii | Ixodes ricinus | Cows and vegetation | Molecularly and phylogenetically | ompA | [68] |
| De. reticulatus | ||||||
| Thailand/2009 | R. raoultii–like | Amblyomma helvolum | Lizard | Molecularly and phylogenetically | 16S rRNA, gltA, and ompA | [69] |
| Korea/2010–2015 | R. raoultii | Haemaphysalis longicornis | Dogs | Molecularly and phylogenetically | 16S rRNA | [70] |
| Germany/2010–2011 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Myodes glareolus | Molecularly | gltA | [71] |
| Ix. ricinus | ||||||
| Fleas | ||||||
| Czech Republic/2010–2011 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Vegetation | Molecularly | gltA | [72] |
| Romania/2011–2012 | R. raoultii | Blood | Humans | Serologically | – | [73] |
| Slovakia/2011–2020 | R. raoultii | Blood | Humans | Serologically | – | [74] |
| Molecularly | gltA, 23S rRNA, and ompB | |||||
| Hungary/2011–2012 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Vegetation | Molecularly | gltA | [75] |
| China/2012 | R. raoultii | Dermacentor silvarum | Humans | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA and ompA | [76] |
| Blood | ||||||
| Germany | R. raoultii | Blood | Dogs | Serologically | [77] | |
| Mongolia | R. raoultii | Dermacentor nuttalli | Vegetation | Molecularly and phylogenetically | ompB, gltA | [78] |
| Laos/2012–2014, | R. raoultii | Amblyomma testudinarium | Molecularly and phylogenetically | ompA, gltA, ompB, and 17–kDa | [79] | |
| Haemaphysalis | ||||||
| Spain/2012–2019 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Cantabrian brown bear | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA, ompA | [80] |
| Malaysia/2012–2013 | R. raoultii–like | Haemaphysalis bispinosa | Cattle, sheep | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA, ompA and ompB | [81] |
| Haemaphysalis spp. | Chicken, Dogs | |||||
| Rhipicephalus microplus | Cattle | |||||
| Rhipicephalus sanguineus | Dogs | |||||
| Malaysia/2013 | R. raoultii–like | Blood | Human | Molecularly | gltA, ompB | [28] |
| Korea/2013–2017 | R. raoultii | Ixodes nipponensis | Korean water deer | Molecularly and phylogenetically | 16S rRNA and gltA | [82] |
| Ha. longicornis | ||||||
| Romania/2013–2014 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Humans | Molecularly (sequencing) | 23S rRNA | [83] |
| Romania/2013 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Dogs | Molecularly (sequencing) | ompB | [84] |
| Poland/2013 | R. raoultii | Ix. ricinus | Vegetation | Molecularly and phylogenetically | ompA, 16S rRNA, | [85] |
| De. reticulatus | ||||||
| Poland/2013–2014 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Dogs and cats | Molecularly | gltA | [86] |
| Ukraine/2013–2014 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Vegetation | Molecularly | sca4, | [87] |
| France/2014–2021 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Humans | Molecularly | gltA | [88] |
| Greece/2014 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Goats | Molecularly and phylogenetically | Atp, gltA, DnaA and DnaK | [89] |
| China–Russian border/2014 | R. raoultii | Ixodes persulcatus | Vegetation | Molecularly (sequencing) | gltA, ompA | [17] |
| Algeria/2014 | R. raoultii | Ix. ricinus | Cattle | Molecularly | [90] | |
| Netherlands/2014 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Vegetation | Molecularly | gltA | [91] |
| Mongolia/2015–2016 | R. raoultii | Blood | Human | Molecularly and phylogenetically | 16S rRNA, gltA, and ompA | [92] |
| Hyalomma asiaticum | Sheep, cattle, camels, dogs | |||||
| De. nuttalli | ||||||
| Serbia | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Dogs | Molecularly | ompA | [93] |
| Austria/2015 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Vegetation | Molecularly | ompA, gltA | [94] |
| China/2015–2016 | R. raoultii | Serum and blood | Human | Serologically and molecularly | rrs, gltA, ompA, ompB, and sca4 | [29] |
| Kazakhstan/2015 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Vegetation | Molecularly and phylogenetically | ompB, ompA, 23S–5S | [95] |
| De. reticulatus | ||||||
| Hy. asiaticum | ||||||
| Russia | R. raoultii | De. silvarum | Vegetation | Molecularly and phylogenetically | 16S, ompA, ompB, sca4 | [96] |
| Haemaphysalis japonica | ||||||
| Haemaphysalis concinna | ||||||
| Russia (Siberia)/2016 | R. raoultii | Blood | Human | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA | [33] |
| Cerebrospinal fluid | ||||||
| Poland/2016–2018 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Vegetation | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA | [97] |
| Turkey/2016–2019 | R. raoultii | Hyalomma aegyptium | Tortoise | Molecularly (sequencing) | gltA | [98] |
| India | R. raoultii–like | Ha. bispinosa | Goats | Molecularly and phylogenetically | htrA, gltA | [99] |
| Iran/2017–2018 | R. raoultii | Hy. marginatum | Sheep | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA | [100] |
| China/2017 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Humans | Serologically and molecularly (phylogenetically) | 17—kDa, gltA, sca1, sca4, ompA, and ompB | [32] |
| Blood | ||||||
| Belgium/2017 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Humans | Molecularly | gltA | [101] |
| China–Kazakhstan border/2017 | R. raoultii | De. nuttalli | Long–tailed ground squirrel | Molecularly and phylogenetically | 17–kDa, sca1, sca4, gltA, ompA and ompB | [21] |
| De. silvarum | ||||||
| Denmark/2017 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Jackal | Molecularly and phylogenetically | ompA, gltA, ompB | [102] |
| Korea/2018 | R. raoultii | Ha. longicornis | Human | Molecularly and phylogenetically | ompA | [22] |
| Pakistan/2018–2019 | R. raoultii–like | Blood | Dogs | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA | [30] |
| Iran/2018–2019 | R. raoultii | Blood | Dogs | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA, ompA | [30] |
| Turkey/2018–2020 | R. raoultii | Ctenocephalides felis | Goats | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA | [25] |
| Germany/2018–2019 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Vegetation | Molecularly | ompB | [103] |
| China/2018–2019 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Red foxes | Molecularly and phylogenetically | 17–kDa, gltA, ompA, sca1 | [19] |
| heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney | ||||||
| Ixodes canisuga | Marbled polecat | |||||
| Italy/2019 | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Wild boars | Molecularly and phylogenetically | ompA | [104] |
| China/2019 | R. raoultii | Blood | Human | Molecularly and phylogenetically | ompA and sca1 | [105] |
| Romania | R. raoultii | De. marginatus | Dogs | Molecularly (sequencing) | gltA, 17–kDa | [106] |
| Ix. ricinus | ||||||
| Rhipicephalus rossicus | ||||||
| Haemaphysalis punctata | Vegetation | |||||
| China/2019–2020 | R. raoultii | Ix. persulcatus | Human | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA and ompA | [107] |
| De. silvarum | ||||||
| Ha. concinna | ||||||
| India/2020 | R. raoultii | Haemaphysalis intermedia | Cows, goats, and dogs | Molecularly and phylogenetically | 16s rRNA, gltA, ompA, and ompB | [108] |
| Poland/2021–2022 | R. raoultii | De. reticulatus | Humans | Molecularly (sequencing) | gltA and ompB | [109] |
| China/2021–2022 | R. raoultii | De. silvarum | Sheep | Molecularly and phylogenetically | rrs, gltA, ompA, and ompB | [110] |
| Siberia/2022 | R. raoultii | Dermacentor spp. | Vegetation | Molecularly and phylogenetically | gltA, ompA, ompB, htrA, and 16S rRNA | [111] |
| District | Host | Tick Species | Nymph (%) | Female (%) | Male (%) | Total (%) | Subjected for Molecular Analysis (N, F) | Detection of Rickettsia raoultii | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Examined | Infested | gltA | ompA | ompB | |||||||
| Kohat | Camels | 20 | 14 | Hyalomma dromedarii | 7 (41.2) | 6 (35.3) | 4 (23.5) | 17 (3.0) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ |
| Hyalomma isaaci | 15 (45.5) | 12 (36.4) | 6 (18.2) | 33 (5.8) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Hyalomma turanicum | 20 (60.6) | 9 (27.3) | 4 (12.1) | 33 (5.8) | 2,2 | 1N, 1F | 1N, 1F | 1N, 1F | ||||
| Sheep | 19 | 12 | Hy. turanicum | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 6 (1.1) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | |
| Hy. isaaci | 2 (40.0) | 2 (40.0) | 1 (20.0) | 5 (0.9) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Hyalomma anatolicum | 3 (50.0) | 2 (33.3) | 1 (16.7) | 6 (1.1) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Goats | 16 | 14 | Hy. isaaci | 3 (42.9) | 2 (28.6) | 2 (28.6) | 7 (1.2) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | |
| Rhipicephalus turanicus | 9 (60.0) | 4 (26.7) | 2 (13.3) | 15 (2.7) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Rhipicephalus microplus | 5 (41.7) | 4 (33.3) | 3 (25.0) | 12 (2.1) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Total | 55 | 40 (72.7%) | 66N | 43F | 25M | 134 (23.8%) | 18N, 18F | 1N, 1F | ||||
| D.I Khan | Camels | 18 | 12 | Hy. dromedarii | 8 (44.4) | 6 (33.3) | 4 (22.2) | 18 (3.9) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ |
| Sheep | 16 | 9 | Hy. anatolicum | 11 (47.8) | 8 (34.8) | 4 (17.4) | 23 (4.1) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | |
| Hy. turanicum | 4 (44.4) | 3 (33.3) | 2 (22.2) | 9 (1.6) | 2,2 | 1N, 1F | 1N, 1F | 1N, 1F | ||||
| Rh. turanicus | 12 (48.0) | 9 (36.0) | 4 (16.0) | 25 (4.4) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides | 7 (46.7) | 5 (33.3) | 3 (20.0) | 15 (2.7) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Goats | 14 | 9 | Hy. anatolicum | 7 (53.8) | 4 (30.8) | 2 (15.4) | 13 (2.3) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | |
| Rh. turanicus | 14 (58.3) | 6 (25.0) | 4 (16.7) | 24 (4.2) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Rh. microplus | 4 (40.0) | 3 (30.0) | 3 (30.0) | 10 (1.8) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Total | 48 | 30 (62.5%) | 67N | 44F | 26M | 137 (24.3%) | 16N, 16F | 1N, 1F | ||||
| Lower Dir | Camels | 21 | 14 | Hy. dromedarii | 5 (50.0) | 3 (30.0) | 2 (20.0) | 10 (1.8) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ |
| Sheep | 15 | 8 | Haemaphysaliscornupunctata | 8 (57.1) | 4 (28.6) | 2 (14.3) | 14 (2.5) | 2,2 | 1N | 1N | 1N | |
| Haemaphysalis sulcata | 20 (58.8) | 6 (17.6) | 8 (23.5) | 34 (6.0) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Rh. microplus | 5 (45.5) | 4 (36.4) | 2 (18.2) | 11 (1.9) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Goats | 13 | 6 | Ha. cornupunctata | 5 (55.6) | 2 (22.2) | 2 (22.2) | 9 (1.6) | 2,2 | 1N | 1N | 1N | |
| Rh. haemaphysaloides | 8 (66.7) | 2 (16.7) | 2 (16.7) | 12 (2.1) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Total | 49 | 28 (57.1%) | 51N | 21F | 18M | 90 (16.0%) | 12N, 12F | 2N | ||||
| Bajaur | Camels | 17 | 11 | Hy. dromedarii | 7 (50.0) | 4 (28.6) | 3 (21.4) | 14 (2.5) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ |
| Sheep | 17 | 9 | Haemaphysalis bispinosa | 7 (46.7) | 5 (33.3) | 3 (20.0) | 15 (2.7) | 2,2 | 1N | 1N | 1N | |
| Haemaphysalis sulcata | 10 (52.6) | 6 (31.6) | 3 (15.8) | 19 (3.4) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Ha. cornupunctata | 5 (38.5) | 5 (38.5) | 3 (23.1) | 13 (2.3) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Goats | 16 | 8 | Ha. bispinosa | 9 (60.0) | 4 (26.7) | 2 (13.3) | 15 (2.7) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | |
| Rh. microplus | 5 (41.7) | 4 (33.3) | 3 (25.0) | 12 (2.1) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Ha. cornupunctata | 8 (61.5) | 3 (23.1) | 2 (15.4) | 13 (2.3) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Total | 50 | 28 (56.0%) | 51N | 31F | 19M | 101 (17.9%) | 14N, 14F | 1N | ||||
| Mansehra | Camels | 23 | 13 | Hy. dromedarii | 6 (46.2) | 4 (30.8) | 2 (15.4) | 13 (2.3) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ |
| Sheep | 18 | 10 | Rh. haemaphysaloides | 5 (50.0) | 3 (30.0) | 2 (20.0) | 10 (1.8) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | |
| Ha. bispinosa | 4 (50.0) | 2 (25.0) | 2 (25.0) | 8 (1.4) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Haemaphysalis montgomeryi | 15 (55.6) | 9 (33.3) | 3 (11.1) | 27 (4.8) | 2,2 | 1N | 1N | 1N | ||||
| Goats | 18 | 12 | Ha. sulcata | 8 (47.1) | 6 (35.3) | 3 (17.7) | 17 (3.0) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | |
| Rh. microplus | 5 (50.0) | 3 (30.0) | 2 (20.0) | 10 (1.8) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Ha. montgomeryi | 9 (52.9) | 5 (29.4) | 3 (17.7) | 17 (3.0) | 2,2 | ─ | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Total | 59 | 35 (59.3%) | 52N | 32F | 18M | 102 (18.1%) | 14N, 14F | 1N | ||||
| Overall total | 261 | 161 (61.7%) | 287N (50.9%) | 171F (30.3%) | 106M(18.8%) | 564 | 74N (25.8%), 74F (43.3%) | 6N (2.1%), 2F (3.5%) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shehla, S.; Almutairi, M.M.; Alouffi, A.; Tanaka, T.; Chang, S.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Ali, A. Molecular Survey of Rickettsia raoultii in Ticks Infesting Livestock from Pakistan with Notes on Pathogen Distribution in Palearctic and Oriental Regions. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10110636
Shehla S, Almutairi MM, Alouffi A, Tanaka T, Chang S-C, Chen C-C, Ali A. Molecular Survey of Rickettsia raoultii in Ticks Infesting Livestock from Pakistan with Notes on Pathogen Distribution in Palearctic and Oriental Regions. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(11):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10110636
Chicago/Turabian StyleShehla, Shehla, Mashal M. Almutairi, Abdulaziz Alouffi, Tetsuya Tanaka, Shun-Chung Chang, Chien-Chin Chen, and Abid Ali. 2023. "Molecular Survey of Rickettsia raoultii in Ticks Infesting Livestock from Pakistan with Notes on Pathogen Distribution in Palearctic and Oriental Regions" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 11: 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10110636
APA StyleShehla, S., Almutairi, M. M., Alouffi, A., Tanaka, T., Chang, S.-C., Chen, C.-C., & Ali, A. (2023). Molecular Survey of Rickettsia raoultii in Ticks Infesting Livestock from Pakistan with Notes on Pathogen Distribution in Palearctic and Oriental Regions. Veterinary Sciences, 10(11), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10110636










