miRNA Profiles of Canine Intestinal Carcinomas, Lymphomas and Enteritis Analysed by Digital Droplet PCR from FFPE Material
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Samples
2.2. miRNA Analysis
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
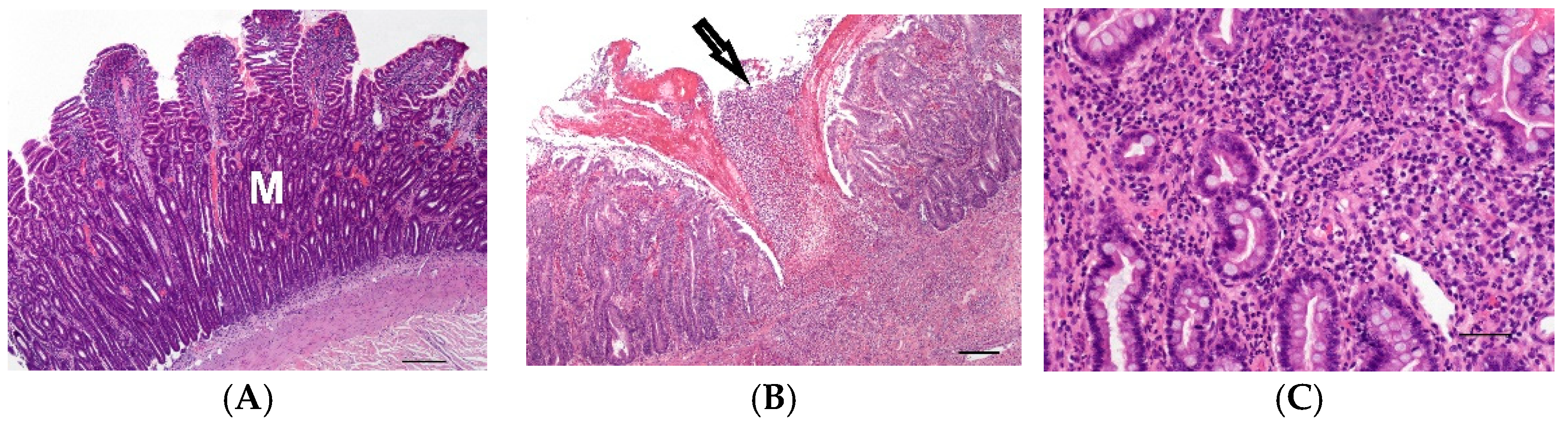
3.1. Pathological Characterisation of the Intestinal Findings
3.1.1. Control Cases (Groups 1S and 1L)
3.1.2. Enteritis Cases (Groups 2S-a, 2S-b and 2L)
3.1.3. Lymphoma Cases (Groups 3S and 3L)
3.1.4. Carcinoma Cases (Groups 4S and 4L)
3.2. miRNA Levels and Correlation between the Groups
3.3. Comparison of miRNA Levels between the Groups (1–4)
3.3.1. Small Intestine vs. Large Intestine (Controls, Carcinoma, Lymphoma)
3.3.2. Inflammation vs. Controls or Tumour
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Crow, S.E. Tumors of the Alimentary Tract. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1985, 15, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, M.D. Alimentary neoplasia in geriatric dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 42, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Löhr, C.V.; Kiupel, M. Tumors of the Alimentary Tract. In Tumors in Domestic Animals; Meuten, D.J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 499–601. ISBN 9781119181200. [Google Scholar]
- Gaschen, L. Ultrasonography of small intestinal inflammatory and neoplastic diseases in dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfanti, U.; Bertazzolo, W.; Bottero, E.; Lorenzi, D.d.; Marconato, L.; Masserdotti, C.; Zatelli, A.; Zini, E. Diagnostic value of cytologic examination of gastrointestinal tract tumors in dogs and cats: 83 cases (2001–2004). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 229, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleis, S.E. Cancer screening tests for small animals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2014, 44, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibuk, J.; Flory, A.; Kruglyak, K.M.; Leibman, N.; Nahama, A.; Dharajiya, N.; van den Boom, D.; Jensen, T.J.; Friedman, J.S.; Shen, M.R.; et al. Horizons in Veterinary Precision Oncology: Fundamentals of Cancer Genomics and Applications of Liquid Biopsy for the Detection, Characterization, and Management of Cancer in Dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 664718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, D.L.; Cave, N.J.; Gedye, K.R.; Bridges, J.P. Investigation of cell-free DNA in canine plasma and its relation to disease. Vet. Q. 2016, 36, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, A.; Kruglyak, K.M.; Tynan, J.A.; McLennan, L.M.; Rafalko, J.M.; Fiaux, P.C.; Hernandez, G.E.; Marass, F.; Nakashe, P.; Ruiz-Perez, C.A.; et al. Clinical validation of a next-generation sequencing-based multi-cancer early detection “liquid biopsy” blood test in over 1000 dogs using an independent testing set: The CANcer Detection in Dogs (CANDiD) study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heishima, K.; Ichikawa, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Iwasaki, R.; Sakai, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Hoshino, Y.; Okamura, Y.; Murakami, M.; et al. Circulating microRNA-214 and -126 as potential biomarkers for canine neoplastic disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev. Biol. 2007, 302, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, N.; Rana, S.; Espinosa-Diez, C.; Anand, S. MicroRNAs in Cancer: Challenges and opportunities in early detection, disease monitoring, and therapeutic agents. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2017, 5, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohel, M.M.H. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in cancer diagnosis. Life Sci. 2020, 248, 117473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joos, D.; Leipig-Rudolph, M.; Weber, K. Tumour-specific microRNA expression pattern in canine intestinal T-cell-lymphomas. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, M.; Ye, M. Upregulation of MicroRNA 18b Contributes to the Development of Colorectal Cancer by Inhibiting CDKN2B. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, e00391-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngby, J.G.; Gòdia, M.; Brogaard, L.; Kristensen, A.T.; Fredholm, M.; Skancke, E.; Morris, J.; Dupont, N.; Salavati Schmitz, S.; Argyle, D.; et al. Association of fecal and serum microRNA profiles with gastrointestinal cancer and chronic inflammatory enteropathy in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, A.O.; Pardali, D.; Adamama-Moraitou, K.K.; Gazouli, M.; Dovas, C.I.; Legaki, E.; Brellou, G.D.; Savvas, I.; Jergens, A.E.; Rallis, T.S.; et al. Colonic mucosal and serum expression of microRNAs in canine large intestinal inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikitis, V.L.; White, I.; Mori, M.; Potter, A.; Bhattcharyya, A.; Hamilton, S.R.; Buckmeier, J.; Lance, P.; Thompson, P. Differential expression of microRNA-320a, -145, and -192 along the continuum of normal mucosa to high-grade dysplastic adenomas of the colorectum. Am. J. Surg. 2014, 207, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaoka, T.; Saito, Y.; Shimamoto, Y.; Muramatsu, T.; Kimura, M.; Kanai, Y.; Saito, H. Cluster microRNAs miR-194 and miR-215 suppress the tumorigenicity of intestinal tumor organoids. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parvaee, P.; Sarmadian, H.; Khansarinejad, B.; Amini, M.; Mondanizadeh, M. Plasma Level of MicroRNAs, MiR-107, MiR-194 and MiR-210 as Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosis Intestinal-Type Gastric Cancer in Human. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Ren, L.-L.; Zheng, P.; Zheng, H.-M.; Yu, Y.-N.; Wang, J.-L.; Lin, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-X.; Ge, Z.-Z.; Chen, X.-Y.; et al. miR-194 as a predictor for adenoma recurrence in patients with advanced colorectal adenoma after polypectomy. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heishima, K.; Mori, T.; Ichikawa, Y.; Sakai, H.; Kuranaga, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Okamura, Y.; Masuzawa, M.; Sugito, N.; et al. MicroRNA-214 and MicroRNA-126 Are Potential Biomarkers for Malignant Endothelial Proliferative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 25377–25391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamstock, D.A.; Ehrhart, E.J.; Getzy, D.M.; Bacon, N.J.; Rassnick, K.M.; Moroff, S.D.; Liu, S.M.; Straw, R.C.; McKnight, C.A.; Amorim, R.L.; et al. Recommended guidelines for submission, trimming, margin evaluation, and reporting of tumor biopsy specimens in veterinary surgical pathology. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeis-Mikroskopische Technik; Mulisch, M.; Welsch, U. (Eds.) 19. Aufl. 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9783642551901. [Google Scholar]
- Day, M.J.; Bilzer, T.; Mansell, J.; Wilcock, B.; Hall, E.J.; Jergens, A.; Minami, T.; Willard, M.; Washabau, R. Histopathological standards for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal inflammation in endoscopic biopsy samples from the dog and cat: A report from the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Gastrointestinal Standardization Group. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 138 (Suppl. 1), S1–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, K.W.; Cullen, J.M.; Dubielzig, R.R. Histological Classification of Tumors of the Alimentary System of Domestic Animals; Armed Forces Institute of Pathology: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2003; ISBN 9781881041863. [Google Scholar]
- Valli, V.E.; Jacobs, R.; Parodi, A.L.; Vernau, W.; Moore, P.F. Histological Classification of Hematopoietic Tumors of Domestic Animals; Armed Forces Institute of Pathology: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; ISBN 9781881041757. [Google Scholar]
- Laprovitera, N.; Grzes, M.; Porcellini, E.; Ferracin, M. Cancer Site-Specific Multiple microRNA Quantification by Droplet Digital PCR. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filetti, V.; Loreto, C.; Falzone, L.; Lombardo, C.; Cannizzaro, E.; Castorina, S.; Ledda, C.; Rapisarda, V. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Three microRNAs in Environmental Asbestiform Fibers-Associated Malignant Mesothelioma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, A.; Törner, K.; Jordan, A.; Lorenz, M.; Schwittlick, U.; Conrad, D.; Steiger, K.; Schusser, B.; Aupperle-Lellbach, H. Pathological Findings in Gastrointestinal Neoplasms and Polyps in 860 Cats and a Pilot Study on miRNA Analyses. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortarino, M.; Gioia, G.; Gelain, M.E.; Albonico, F.; Roccabianca, P.; Ferri, E.; Comazzi, S. Identification of suitable endogenous controls and differentially expressed microRNAs in canine fresh-frozen and FFPE lymphoma samples. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, K.R.M.; Canavez, J.M.S.; Reis, S.T.; Tomiyama, A.H.; Piantino, C.B.; Sañudo, A.; Camara-Lopes, L.H.; Srougi, M. miRNA analysis of prostate cancer by quantitative real time PCR: Comparison between formalin-fixed paraffin embedded and fresh-frozen tissue. Urol. Oncol. 2011, 29, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtechova, Z.; Zavadil, J.; Klozar, J.; Grega, M.; Tachezy, R. Comparison of the miRNA expression profiles in fresh frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tonsillar tumors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malnar, M.; Režen, T. Factors affecting RNA quantification from tissue long-term stored in formalin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2019, 96, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, G.; Bovio, E.; Rena, O.; Rrapaj, E.; Mercalli, F.; Veggiani, C.; Paganotti, A.; Andorno, S.; Boldorini, R. Prognostic impact of a 3-MicroRNA signature in cytological samples of small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016, 124, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; da Silva, A.M.; Calin, G.; Pantel, K. Data Normalization Strategies for MicroRNA Quantification. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forero, D.A.; González-Giraldo, Y.; Castro-Vega, L.J.; Barreto, G.E. qPCR-based methods for expression analysis of miRNAs. Biotechniques 2019, 67, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landais, S.; Landry, S.; Legault, P.; Rassart, E. Oncogenic potential of the miR-106-363 cluster and its implication in human T-cell leukemia. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5699–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuu, C.; Utheim, T.P.; Sehic, A. The Three Paralogous MicroRNA Clusters in Development and Disease, miR-17-92, miR-106a-363, and miR-106b-25. Scientifica 2016, 2016, 1379643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Iijima, T.; Wakaume, R.; Takahashi, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakano, D.; Nakayama, Y.; Mori, T.; Horiguchi, S.; Miyaki, M. Underexpression of miR-126 and miR-20b in hereditary and nonhereditary colorectal tumors. Oncology 2014, 87, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuu, C.; Jevnaker, A.-M.; Bryne, M.; Osmundsen, H. An investigation into anti-proliferative effects of microRNAs encoded by the miR-106a-363 cluster on human carcinoma cells and keratinocytes using microarray profiling of miRNA transcriptomes. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids--the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, H.; Yuan, D.; Tang, Q.; Chen, L.; Pang, X.; Leng, W.; Bi, F. Plasma miR-122 and miR-192 as potential novel biomarkers for the early detection of distant metastasis of gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, C.; Buchner, A.; Pohla, H. Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of miR-192 in Different Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8851035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Gopalan, V.; Wahab, R.; Lu, C.-T.; Smith, R.A.; Lam, A.K.-Y. Deregulation of miR-126 expression in colorectal cancer pathogenesis and its clinical significance. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 339, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, X.; An, P.; Quan, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, S.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Luo, H. MicroRNA-126 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer cells by targeting CXCR4 via the AKT and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, N.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, X. Expression of miR-126 suppresses migration and invasion of colon cancer cells by targeting CXCR4. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 381, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yuan, W.; Luo, W.; Nie, K.; Wu, X.; Meng, X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, X. miR-126 downregulates CXCL12 expression in intestinal epithelial cells to suppress the recruitment and function of macrophages and tumorigenesis in a murine model of colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 3465–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, J.A.; Robinson, K.R.; Bullington, A.-C.M.; Schmiedt, J.M. Identification of serum microRNAs with differential expression between dogs with splenic masses and healthy dogs with histologically normal spleens. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2021, 82, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, K.K.L.; Wood, G.A.; Keller, S.M.; Mutsaers, A.J.; Wood, R.D. MicroRNA profiling in canine multicentric lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Group | Breed | Age (Years) | Sex |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1S: controls small intestine (n = 10) | 4 Terrier, 2 mix, 1 Dachshund, 1 French Bulldog, 1 Pug, 1 Rhodesian Ridgeback | 2–15 | 3 m, 4 mc, 3 fn |
| Group 1L: controls large intestine (n = 7) | 2 Labrador, 1 Akita, 1 Hovawart, 1 mix, 1 Munsterlander, 1 Terrier | 4–10 | 3 m, 1 f, 3 fn |
| Group 2S-a: enteritis (lymphoplasmacytic) of the small intestine (n = 6) | 2 mix, 1 Beagle, 1 French Bulldog, 1 Magyar Vizsla, 1 Rottweiler | 2–10 | 3 m, 1 mc, 2 fn |
| Group 2S-b: enteritis (transmural) of the small intestine (n = 7) | 2 Shepherd, 1 Labrador, 1 mix, 1 Rhodesian Ridgeback, 1 Shar Pei, 1 Terrier | 1–11 | 3 m, 2 mc, 2 f |
| Group 2L: enteritis (mixed) of the large intestine (n = 5) | 2 Shepherd, 1 Labrador, 1 mix, 1 Rottweiler | 1–5 | 2 f, 3 fn |
| Group 3S T-cell lymphoma of the small intestine (n = 15) | 3 mix, 2 Labrador, 2 Terrier, 1 Cocker Spaniel, 1 French Bulldog, 1 Havanese, 1 Magyar Vizsla, 1 pug, 1 Schnauzer, 1 Shepherd, 1 Shih Tzu | 7–12 | 7 m, 3 mc, 3 f, 2 fc |
| Group 3L: B-cell lymphoma of the large intestine (n = 12) | 3 mix, 2 Terrier,1 Bulldog, 1 Dachshund, 1 Husky, 1 Lhasa Apso, 1 Munsterlander, 1 Pointer, 1 Wolfhound | 1–12 | 6 m, 5 f, 1 fn |
| Group 4S: carcinoma of the small intestine (n = 14) | 4 mix, 4 Terrier, 1 Dachshund, 1 Gordon Setter, 1 Kooikerhondje, 1 Pointer, 1 Poodle, 1 pug | 7–15 | 5 m, 4 mc, 1 f, 3 fn, 11 unknown |
| Group 4L: carcinoma of the large intestine (n = 13) | 5 mix, 2 Pointer, 1 Border Collie, 1 Labrador, 1 Rhodesian Ridgeback, 1 Samojede, 1 Shepherd, 1 Terrier | 7–13 | 4 m, 6 mc, 3 fn |
| 1S vs. 2S-b | 1S vs. 4S | 1S vs. 2S-a | 1S vs. 3S | 2S-a vs. 2S-b | 2S-a vs. 4S | 2S-a vs. 3S | 2S-b vs. 4S | 2S-b vs. 3S | 3S vs. 4S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-18b | 1.000 | 0.5387 | 0.7863 | 0.3317 | 0.8303 | 0.1735 | 0.9070 | 0.3139 | 0.4381 | 0.0636 |
| miR-20b | 0.3539 | 0.4292 | 0.0040 ↓ | 0.0158 ↓ | 0.3531 | 0.0034 ↑ | 0.6685 | 0.2183 | 0.3976 | 0.0018 ↑ |
| miR-126 | 0.2617 | 0.0498 ↓ | 0.0262 ↓ | 0.0025 ↓ | 0.8303 | 0.5919 | 0.2276 | 0.9702 | 0.0907 | 0.0576 |
| miR-214 | 0.0927 | 0.6605 | 0.0927 | 0.0247 ↓ | 0.0124 ↑ | 0.1078 | 0.8457 | 0.1087 | 0.0024 ↓ | 0.0246 ↑ |
| miR-192 | 0.4642 | 0.5387 | 0.6255 | 0.0043 ↓ | 0.8303 | 0.9671 | 0.0072 ↓ | 0.9702 | 0.0074 ↓ | 0.0083 ↑ |
| miR-194 | 0.4068 | 0.0434 ↓ | 0.0448 ↓ | 0.0003 ↓ | 0.0538 | 0.4333 | 0.0391 ↓ | 0.2183 | 0.0006 ↓ | 0.0064 ↑ |
| 1L vs. 2L | 1L vs. 4L | 1L vs. 3L | 2L vs. 3L | 2L vs. 4L | 3L vs. 4L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-18b | 0.2556 | 0.0394 ↓ | 0.4220 | 0.8744 | 0.0180 ↓ | 0.0043 ↓ |
| miR-20b | 0.7453 | 0.4757 | 0.0832 | 0.4932 | 0.9215 | 0.3143 |
| miR-126 | 1.000 | 0.4281 | 0.0384 ↓ | 0.0651 | 0.4902 | 0.4303 |
| miR-214 | 0.6261 | 0.0813 | 0.0160 ↓ | 0.0512 | 0.2782 | 0.0866 |
| miR-192 | 0.0230 ↓ | 0.0034 ↓ | 0.0027 ↓ | 0.2684 | 1.000 | 0.1211 |
| miR-194 | 0.0740 | 0.0813 | 0.0035 ↓ | 0.2684 | 0.4304 | 0.0684 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kehl, A.; Valkai, M.; Van de Weyer, A.-L.; Brockmann, M.; Steiger, K.; Schusser, B.; Aupperle-Lellbach, H. miRNA Profiles of Canine Intestinal Carcinomas, Lymphomas and Enteritis Analysed by Digital Droplet PCR from FFPE Material. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020125
Kehl A, Valkai M, Van de Weyer A-L, Brockmann M, Steiger K, Schusser B, Aupperle-Lellbach H. miRNA Profiles of Canine Intestinal Carcinomas, Lymphomas and Enteritis Analysed by Digital Droplet PCR from FFPE Material. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(2):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020125
Chicago/Turabian StyleKehl, Alexandra, Mario Valkai, Anna-Lena Van de Weyer, Maria Brockmann, Katja Steiger, Benjamin Schusser, and Heike Aupperle-Lellbach. 2023. "miRNA Profiles of Canine Intestinal Carcinomas, Lymphomas and Enteritis Analysed by Digital Droplet PCR from FFPE Material" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 2: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020125
APA StyleKehl, A., Valkai, M., Van de Weyer, A.-L., Brockmann, M., Steiger, K., Schusser, B., & Aupperle-Lellbach, H. (2023). miRNA Profiles of Canine Intestinal Carcinomas, Lymphomas and Enteritis Analysed by Digital Droplet PCR from FFPE Material. Veterinary Sciences, 10(2), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020125








