Simple Summary
Captive animals in zoos, particularly non-human primates (NHPs), are in close contact with humans, raising concerns about the transmission of zoonotic diseases. NHPs, being phylogenetically similar to humans, are susceptible to infections by various species of Entamoeba (Entamoeba spp.). The aim of this study was to investigate the prevalence of Entamoeba spp. in captive NHPs in Chinese zoos. We collected fecal samples from 14 NHP species in five regions of China and examined them for six Entamoeba species. The results show that three asymptomatic Entamoeba species capable of infecting humans, Entamoeba coli, E. dispar, and E. polecki, were prevalent among NHPs. This indicates a potential zoonotic risk and underscores the need to strengthen control measures for asymptomatic parasites in zoos to prevent cross-infection between humans and animals.
Abstract
The genus Entamoeba infects both humans and NHPs. In zoos, visitors feeding significantly increases the frequency of human-to-NHP contact, thereby raising the risk of zoonotic transmission. In this study, six Entamoeba species were investigated and analyzed in the fecal samples of 14 NHP species from zoos in Beijing, Guiyang, Shijiazhuang, Tangshan, and Xingtai in China. A total of 19 out of 84 primate fecal samples tested positive for Entamoeba spp. by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Among these, 14 samples contained mono-detections of E. coli (7/84), E. dispar (4/84), and E. polecki (3/84). Five samples were found to have mixed detections with two or three species, suggesting the potential for zoonotic transmission; however, no pathogenic E. histolytica, E. moshkovskii, or E. nuttalli were detected. This study provides new insights into parasitic detections in NHPs in Chinese zoos and offers valuable background information for the prevention and control of zoonotic parasitic diseases.
1. Introduction
Entamoeba spp. are present in humans, NHPs, and various other vertebrate and invertebrate species around the world [1]. At least seven species have been identified as parasitizing the human gut, including E. coli, E. dispar, E. histolytica, E. hartmanni, E. moshkovskii, E. polecki, and E. Bangladeshi [2,3]. The global molecular prevalence of Entamoeba spp. infections in humans is 3.55% (3817/107,396), and amebiasis, caused by E. histolytica, is the second most common parasitic disease-related cause of death worldwide, resulting in about 67,900 deaths per year [4,5,6]. Although the age-standardized disability-adjusted life years rate of Entamoeba spp. infection-associated diseases presented significantly declining trends, it has remained a heavy burden among the age group of <5 years and the low sociodemographic index regions from 1990 to 2019 [7], raising concerns about potential zoonotic transmission.
Due to space constraints and close contact with humans, the lifestyle of zoo animals differs significantly from that of their wild counterparts. In captivity, animals are more frequently exposed to feces and fecal-contaminated food and water, which increases the risk of disease in captive animals and poses a potential threat to animal caretakers and visitors. Entamoeba spp. are frequently reported as protozoa parasites in captive NHPs [8,9], and there are six main species of intestinal Entamoeba spp. to which NHPs are susceptible, including E. chattoni, E. coli, E. dispar, E. hartmanni, E. nuttalli, and E. polecki [6]. Few molecular epidemiological studies of NHPs have been published, with most conducted in Asia, Europe, Africa, and North America [4]. It has been shown that NHPs can be experimentally infected with E. histolytica cysts of human origin without developing invasive disease [7]. Some studies suggest that lemurs in both the wild and in zoo settings may be infected with E. histolytica, resulting in diarrhea symptoms [8,9]. The relationship between the pathogenicity of Entamoeba spp. in NHPs and zoonotic diseases still needs to be further explored.
The morphological similarity among Entamoeba spp. in the intestine makes it challenging to differentiate them using microscopy alone, particularly between E. histolytica, E. moshkovskii, and E. dispar [10]. Therefore, various molecular techniques, including PCR, nested PCR, real-time PCR, multiplex PCR, and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), have been widely used in epidemiologic investigations because of their high sensitivity and specificity [11,12]. The small subunit ribosomal RNA (SSU rRNA) gene is a multicopy gene that is relatively easy to amplify from fecal samples, providing sufficient resolution to distinguish between Entamoeba spp. Evidence for the genetic diversity of Entamoeba spp. in NHPs is primarily based on SSU rRNA gene analyses, differential diagnosis by PCR, and characterization of the SSU rRNA gene [13].
In this study, we used PCR to amplify SSU rRNA gene loci from six Entamoeba species, including E. coli, E. dispar, E. histolytica, E. moshkovskii, E. nuttalli, and E. polecki, to explore Entamoeba spp. and their zoonotic potential in 14 species of NHPs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection
Samples were collected on the basis of whether the animals could come into direct or indirect contact with people, taking into account factors such as visitor feeding, fecal disposal, and enclosures. A total of 84 fecal samples were randomly collected from NHPs in Beijing (n = 34), Guiyang (n = 10), Shijiazhuang (n = 18), Tangshan (n = 9), and Xingtai (n = 13) in China from September 2020 to November 2021. The NHP species included in this study were Ateles fusciceps (brown-headed spider monkeys, n = 1), Colobus polykomos (king colobus, n = 6), Erythrocebus patas (patas monkey, n = 3), Lemur catta (ring-tailed lemur, n = 21), Macaca leonina (pig-tailed macaques, n = 2), Macaca mulatta (rhesus macaque, n = 10), Mandrillus sphinx (mandrills, n = 9), Nomascus annamensis (northern yellow-cheeked crested gibbon, n = 10), Pan troglodytes (chimpanzees, n = 9), Papio hamadryas (baboon, n = 2), Rhinopithecus roxellana (golden snub-nosed monkeys, n = 5), Saimiri sciureus (squirrel monkeys, n = 3), Sapajus apella (capuchin monkeys, n = 1), and Trachypithecus francoisi (Francois’ langur, n = 2), totaling 14 species of NHPs (Table 1). All fecal samples were stored independently at −20 °C for subsequent testing.

Table 1.
The distribution of NHPs across 5 studied zoos.
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction
TIANamp Stool DNA Kit (Tigen, Beijing, China) was used for fecal samples genomic DNA extraction. According to the instructions, 200 mg of fecal sample was used for genomic DNA extraction, and finally, DNA was eluted with 50 mL elution buffer. The extracted DNA samples were stored at −20 °C for reserve.
2.3. PCR Amplification
Eighty-four collected fecal DNA samples from NHPs were tested by PCR for Entamoeba spp. (E. nuttalli [14], E. coli [14], E. polecki [14], E. dispar [15], E. histolytica [15], and E. moshkovskii [15]). The amplification targets were SSU rRNA gene locus sequences. The upstream primer of E. dispar, E. histolytica, and E. moshkovskii was Enta F, while downstream primers differed. The primer sequences are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Species-specific primers used in diagnostic PCR for Entamoeba spp.
2.4. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
Positive PCR products were sequenced (Ruiboxingke Company, Beijing, China) and compared with published/reference sequences in GenBank to determine the sample species/genotype using the BLAST tool (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) and Clustal X 2.13 software.
The reference sequences downloaded from GenBank and the SSU rRNA gene locus sequences obtained in this study were used to construct an evolutionary tree based on the neighbor-joining (NJ) method, and the Tamura–Nei model using Mega11.0.13 software and bootstrap analysis with 1000 replicates were performed.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Results were processed into contingency tables according to factors such as location, species, and detection status. Since the proportion of cells with an expected count of fewer than 5 is >20%, we chose Fisher’s exact test for statistical analysis using SPSS 26.0 software, as well as the 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of detection rates. A statistical significance level of p < 0.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference.
3. Results
3.1. Occurrence of Entamoeba spp.
In this study, we used six species-specific primers to detect Entamoeba spp. in the fecal samples of 14 NHP species from five local zoos. A total of 19 out of 84 fecal samples tested positive, for an overall positive rate of 22.6% (95% CI: 15.0–32.7%). Only 3 species of Entamoeba spp. were detected: E. coli, E. dispar, and E. polecki. Among them, E. coli had the highest positivity rate of 14.3% (12/84, 95% CI: 8.4–23.3%), followed by E. dispar at 8.3% (7/84, 95% CI: 4.1–16.2%), and E. polecki at 7.1% (6/84, 95% CI: 3.3–14.7%), E. histolytica, E. moshkovskii, and E. nuttalli were not detected. Additionally, co-detection results indicate that 1 sample (1.2%, 95% CI: 0.2–6.4%) was concurrently detected by three Entamoeba spp., 2 samples (2.4%, 95% CI: 0.7–8.3%) and 2 samples (2.4%, 95% CI: 0.7–8.3%) were simultaneously detected by E. coli + E. polecki and E. coli + E. dispar, while no simples for E. polecki + E. dispar were detected (Table 3).

Table 3.
Occurrence of Entamoeba spp. in NHPs of 5 study zoos.
3.2. Geographic Distribution of Entamoeba spp.
Table 4 summarizes the prevalence of Entamoeba spp. identified among NHPs across the 5 study locations. Positive samples were detected only in fecal samples from Beijing, Guiyang, and Shijiazhuang zoos. The highest positivity rate was observed in Shijiazhuang Zoo at 33.3% (6/18), followed by Beijing Zoo at 29.4% (10/34) and Guiyang Zoo at 30% (3/10). The prevalence of Entamoeba spp. varied significantly among zoos (p < 0.01). In the Beijing Zoo, three Entamoeba species were identified, with E. coli showing the highest positivity rate at 26.5% (9/34), followed by E. dispar at 11.8% (4/34), and E. polecki at 5.9% (2/34). There were also cases of mixed detections: one case involving E. coli and E. polecki, two cases involving E. coli and E. dispar, and one case involving all three Entamoeba spp. In Shijiazhuang Zoo, E. coli and E. polecki were detected with positivity rates of 16.7% (3/18) and 22.2% (4/18), respectively, including one case of mixed detection with both species. In Guiyang Zoo, only E. dispar detections were found, with a positivity rate of 30% (3/10).

Table 4.
Prevalence of Entamoeba spp. identified among NHPs across 5 study zoos.
3.3. Distribution Patterns of Detections Among Species and Molecular Characterization
Prevalence of Entamoeba spp. identified among NHPs according to host species is summarized in Table 5. Out of the 14 NHPs, seven were detected by Entamoeba spp., including Colobus polykomos, Erythrocebus patas, Lemur catta, Mandrillus sphinx, Nomascus annamensis, Pan troglodytes, and Papio hamadryas. The highest prevalence was observed in Colobus polykomos at 83.3% (5/6). Colobus polykomos also had the highest rate of E. coli detection at 66.7 (4/6). The highest rate of E. dispar detection was found in Erythrocebus patas at 66.7 (2/3), while Mandrillus sphinx had the highest rate of E. polecki detection at 44.4 (4/9). The prevalence of Entamoeba spp. detections varied significantly among different NHP species (p < 0.01). Prevalence of Entamoeba spp. identified among NHPs according to zoos and host species is summarized in Table 6; Fisher’s exact test results show that the prevalence of Entamoeba spp. in Beijing Zoo and Shijiazhuang Zoo was significantly different among NHPs (p < 0.01) but not in Guizhou Zoo NHPs (p > 0.01). The constructed phenetic tree (Figure 1) illustrates the assignment of Entamoeba spp. within hosts, demonstrating that the affinities of Entamoeba spp. were similar among the same species of NHPs. Mandrillus sphinx had the highest rates of mixed detections, including one case of E. coli and E. polecki (M. sphinx 68, Beijing), one case of E. coli and E. dispar (M. sphinx 72, Beijing), and one case of mixed detection by all three Entamoeba spp. (M. sphinx 73, Beijing). In addition, a mixed detection of E. coli and E. dispar was found in Papio hamadryas (P. hamadryas 60, Beijing), and a mixed detection of E. coli and E. polecki was found in Pan troglodytes (P. troglodytes 33, Shijiazhuang).

Table 5.
Prevalence of Entamoeba spp. identified among NHPs according to host species.

Table 6.
Prevalence of Entamoeba spp. identified among NHPs according to zoos and host species.
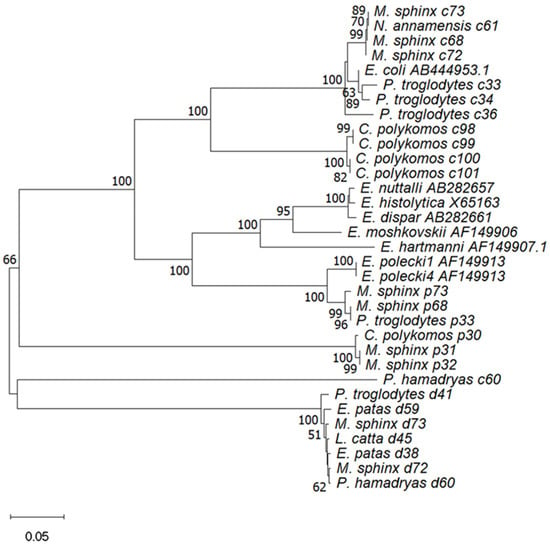
Figure 1.
Phenetic relationships of Entamoeba spp. Numbers on the branches are percent bootstrapping values from 1000 replicates, only bootstrap values > 50 are indicated. The accession numbers utilized for the identification of Entamoeba spp. were AB444953 (E. coli), AB282661 (E. dispar), AF149907 (E. hartmanni), X65163 (E. histolytica), AF149906 (E. moshkoskii), AB282657 (E. nuttalli), AF149913 (E. polecki-like variant 1), and AF149912 (E. polecki-like variant 4).
4. Discussion
China is relatively rich in primate resources and is currently a major producer and primary supplier of NHPs in the international market [16]. Entamoeba spp. are among the most common intestinal parasites in NHPs [17], capable of spreading rapidly and causing widespread infections because of their direct monoxenous life cycle, a short prepatent period, and various transmissible morphological forms [18,19,20,21,22]. Despite this, there have been relatively few studies on the infection rates and species distribution of Entamoeba spp. in the intestines of NHPs in China.
In this study, SSU rRNA gene locus sequences of six Entamoeba spp. include E. coli, E. dispar, E. histolytica, E. moshkovskii, E. nuttalli, and E. polecki. Among these, E. coli, E. dispar, and E. polecki are known to infect both humans and NHPs [23,24,25,26]. Our findings revealed these three species were present among the NHPs studied, with E. coli having the highest prevalence (26.5%) among the five zoos, followed by E. dispar (11.8%). These results are consistent with those reported by Dos Santos Zanetti et al., who detected Entamoeba spp. in human and animal samples from Brazil [27]. In addition, we observed instances of co-detections, including cases where E. coli was found alongside two other Entamoeba spp. Such mixed detections, particularly involving E. coli and E. dispar, are commonly reported in global studies [14,28,29,30,31,32]. While E. histolytica and E. moshkovskii are more frequently detected in humans, these two species were not identified in our study. Entamoeba histolytica is pathogenic and can cause amoebiasis in humans [2,8], but its occurrence in NHPs is rare, with reports limited to a few countries, including China [33,34], Belgium [32], the Netherlands [35], Singapore [36], and the Philippines [37,38]. Recent evidence suggests that what has been previously identified as E. histolytica in NHPs is usually a distinct species, E. nuttalli [13]. Entamoeba nuttalli appears to be prevalent among NHPs and is often associated with sympatric carriage [39]. Feng et al. [30] and Yu et al. [40] reported the presence of E. nuttalli in NHPs from the Guangxi, Guiyang, and Sichuan regions of southwest China; however, our experimental results do not detect this species, possibly due to its host-specific distribution to NHPs [41] or regional variability.
The infection rate of wild NHPs Entamoeba spp. seems to be higher than that of captive ones, e.g., Wild Macaca mulatta (89.96%, Taihang Mountain area, China) [42] and Pan troglodytes (79%, savanna woodland, Tanzania) [14] had significantly higher positive detection rates of Entamoeba spp. than captive NHPs, such as in the Zoological Garden in Belgium (44%) [8] and in Nanjing, China (49.17%) [43]. Our Entamoeba spp. detection rate (22.6%) was lower than that of the above studies but higher than that of European zoo NHPs (8.8%) [44] and Ibadan in Nigeria [45]. This may be due to the fact that captive breeding and management in zoos hinder the spread of Entamoeba spp. However, rapid urbanization in recent years has led to the construction of zoos with concrete enclosures or floors, potentially facilitating the accumulation of feces in the animals’ living environments. This may increase the risk of cross-contamination of parasites among groups of animals through the fecal–oral route of transmission. In addition, Entamoeba spp. were detected in rats that were either free-living sympatric [46] or used as food for captive animals [47] in zoos, contaminated water, food, contact with shared keepers, or the introduction of infected new animals could further exacerbate this risk [21], these factors raise concerns regarding the health of captive animals in zoos and the risk of zoonotic diseases. Our previous studies have demonstrated that animals in the zoos of Beijing, Guiyang, Shijiazhuang, Tangshan, and Xingtai are affected by a variety of intestinal protozoan infections, including Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Blastocystis spp. [48]. In this study, Entamoeba spp. were detected in NHPs from Beijing, Guiyang, and Shijiazhuang zoos. The results show significant differences in the prevalence of Entamoeba spp. in different zoos (Table 1); this may be related to factors such as regional prevalence, lifestyle of NHPs, and zoo management. Unfortunately, our study did not capture the relevant information. Entamoeba spp. prevalence differs significantly among NHPs (Table 5) and NHPs in Beijing Zoo and Shijiazhuang Zoo (Table 6), with mixed detections observed in Beijing (four cases) and Shijiazhuang (one case) zoos. Phylogenetic analyses showed that phenetic relationships of Entamoeba spp. were similar within the same NHPs (Figure 1); this suggests the potential for cross-infection of NHPs in the same environment. In zoos, symptomatic animals typically attract the attention of caretakers, whereas all three Entamoeba spp. identified in this study were asymptomatic and detectable in the human gut. This indicates that asymptomatic Entamoeba spp. are likely prevalent in NHPs and may be zoonotic, underscoring the need for molecular detection methods and preventive measures to reduce the risk of zoonotic diseases.
Due to the social nature of most NHPs studied, collecting individual fecal samples posed challenges. Consequently, our study lacked analyses correlating Entamoeba spp. detections with variables such as sex, age, and symptoms. Among the 14 NHPs investigated, Entamoeba spp. were detected in only 7, primarily those whose natural habitats are in Africa and Southeast Asia. Colobus polykomos exhibited the highest detection rate (83.3%), predominantly with E. coli (4/6, 66.7%) and E. polecki (1/6, 16.7%). This aligns with the findings of Roland Yao Wa Kouassi et al. in Taï National Park, Côte d’Ivoire [49], suggesting the importance of Colobus polykomos in preventing detections of Entamoeba spp. Mandrillus sphinx exhibited the highest rates of mixed detections (3/9, 33.3%); mixed detections appear to be common in Mandrillus sphinx and have been recorded in both semi-free-range [50] and wild [51] environments. Pan troglodytes, one of the closest evolutionary relatives of humans [52], can be infected with E. histolytica and have zoonotic potential [53]. Our experimental results show that Pan troglodytes can be detected with E. coil (3/9, 33.3%), E. dispar (1/9, 11.1%), and E. polecki (1/9, 11.1%), with a total detection rate of 44.4% (4/9), with one case of mixed detection of E. coil and E. polecki. These three Entamoeba species seem to be frequently detected in Pan troglodytes [54,55,56]. Our study further confirms that mixed Entamoeba spp. detections occur in captive Mandrillus sphinx, and the transmission dynamics in this species warrant further investigation.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the prevalence of Entamoeba spp. in 14 specials of NHPs across five zoos in China. Our findings indicate that the asymptomatic presence of three Entamoeba spp. of E. coli, E. dispar, and E. polecki was significantly prevalent among NHPs in those zoos, with a potential risk for cross-contamination. This raises concerns about the increased risk of zoonotic transmission to both humans and other animals. It is crucial to recognize and address asymptomatic parasitic infections in herd animals within zoo environments and implement effective measures to prevent the spread of these parasites.
Author Contributions
J.L. and Q.L. were responsible for the study’s conception; D.A. and T.J. were involved in the sample collection and detection; D.A., J.Z. and S.Y. performed the analysis of results; S.Y. and J.L. were involved in the drafting and revision of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32273029).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by China Agricultural University Laboratory Animal Welfare and Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection Committee, code: AW71211202-2-1.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from animals owner.
Data Availability Statement
The sequences that support the findings of this study are openly available in the GenBank database at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/ (accessed on 3 June 2024).
Acknowledgments
We extend our heartfelt thanks to Changsheng Zhang of the National Natural History Museum of China and Lei Ma of Hebei Normal University for their contributions in providing the experimental materials essential to this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Stensvold, C.R.; Lebbad, M.; Victory, E.L.; Verweij, J.J.; Tannich, E.; Alfellani, M.; Legarraga, P.; Clark, C.G. Increased sampling reveals novel lineages of Entamoeba: Consequences of genetic diversity and host specificity for taxonomy and molecular detection. Protist 2011, 162, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngobeni, R.; Samie, A.; Moonah, S.; Watanabe, K.; Petri, W.A., Jr.; Gilchrist, C. Entamoeba Species in South Africa: Correlations With the Host Microbiome, Parasite Burdens, and First Description of Entamoeba bangladeshi Outside of Asia. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royer, T.L.; Gilchrist, C.; Kabir, M.; Arju, T.; Ralston, K.S.; Haque, R.; Clark, C.G.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Entamoeba bangladeshi nov. sp., Bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1543–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. Molecular epidemiology, evolution, and phylogeny of Entamoeba spp. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 104018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, A.; Yanagawa, Y.; Shimogawara, R.; Yagita, K.; Gatanaga, H.; Watanabe, K. Amebiasis as a sexually transmitted infection: A re-emerging health problem in developed countries. Glob. Health Med. 2023, 5, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Naghavi, M.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; Coates, M.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, L.; Ge, M.; Yu, M.; Sun, Y.; Shen, L. Global burden and trends of the Entamoeba infection-associated diseases from 1990 to 2019: An observational trend study. Acta Trop. 2023, 240, 106866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levecke, B.; Dorny, P.; Geurden, T.; Vercammen, F.; Vercruysse, J. Gastrointestinal protozoa in non-human primates of four zoological gardens in Belgium. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munene, E.; Otsyula, M.; Mbaabu, D.A.; Mutahi, W.T.; Muriuki, S.M.; Muchemi, G.M. Helminth and protozoan gastrointestinal tract parasites in captive and wild-trapped African non-human primates. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 78, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Broucke, S.; Verschueren, J.; Van Esbroeck, M.; Bottieau, E.; Van den Ende, J. Clinical and microscopic predictors of Entamoeba histolytica intestinal infection in travelers and migrants diagnosed with Entamoeba histolytica/dispar infection. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, J.; Ghosh, S.K.; Singha, B.; Paul, J. Molecular Epidemiology of Amoebiasis: A Cross-Sectional Study among North East Indian Population. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khunger, S.; Mewara, A.; Kaur, U.; Duseja, A.; Ray, P.; Kalra, N.; Sharma, N.; Sehgal, R. Real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification (real-time LAMP) assay for rapid diagnosis of amoebic liver abscess. Trop. Med. Int. Health TM IH 2024, 29, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Regan, C.S.; Clark, C.G. Novel Entamoeba Findings in Nonhuman Primates. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirků-Pomajbíková, K.; Čepička, I.; Kalousová, B.; Jirků, M.; Stewart, F.; Levecke, B.; Modrý, D.; Piel, A.K.; Petrželková, K.J. Molecular identification of Entamoeba species in savanna woodland chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii). Parasitology 2016, 143, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, Z.; Petmitr, S.; Mungthin, M.; Leelayoova, S.; Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr, P. Differential detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar, and Entamoeba moshkovskii by a single-round PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3196–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Pang, W.; Hu, X.T.; Li, J.L.; Yao, Y.G.; Zheng, Y.T. Experimental primates and non-human primate (NHP) models of human diseases in China: Current status and progress. Dong wu xue yan jiu = Zool. Res. 2014, 35, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrut, X.; Diffo, J.L.; Somo, R.M.; Bilong Bilong, C.F.; Delaporte, E.; LeBreton, M.; Gonzalez, J.P. Prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites in primate bushmeat and pets in Cameroon. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 175, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graczyk, T.K.; Grimes, B.H.; Knight, R.; Da Silva, A.J.; Pieniazek, N.J.; Veal, D.A. Detection of Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia carried by synanthropic flies by combined fluorescent in situ hybridization and a monoclonal antibody. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.B.; Altizer, S.; Poss, M.; Cunningham, A.A.; Nunn, C.L. Patterns of host specificity and transmission among parasites of wild primates. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.V.; Cacciò, S.M.; Tait, A.; McLauchlin, J.; Thompson, R.C. Tools for investigating the environmental transmission of Cryptosporidium and Giardia infections in humans. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrilli, F.; Prisco, C.; Friedrich, K.G.; Di Cerbo, P.; Di Cave, D.; De Liberato, C. Giardia duodenalis assemblages and Entamoeba species infecting non-human primates in an Italian zoological garden: Zoonotic potential and management traits. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morf, L.; Singh, U. Entamoeba histolytica: A snapshot of current research and methods for genetic analysis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Jung, B.K.; Cho, J.; Kim, D.G.; Song, H.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, S.; Htoon, T.T.; Tin, H.H.; Chai, J.Y. Prevalence of Intestinal Protozoans among Schoolchildren in Suburban Areas near Yangon, Myanmar. Korean J. Parasitol. 2016, 54, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, L.; Morán, P.; Valadez, A.; Gómez, A.; González, E.; Hernández, E.; Partida, O.; Nieves, M.; Gudiño, M.; Magaña, U.; et al. Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar infection in Mexican school children: Genotyping and phylogenetic relationship. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimer, M.; Zenebe, Y.; Mulu, W.; Abera, B.; Saugar, J.M. Molecular prevalence of Entamoeba histolytica/dispar infection among patients attending four health centres in north-west Ethiopia. Trop. Dr. 2016, 47, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshyar, H.; Rostamkhani, P.; Rezaeian, M. An Annotated Checklist of the Human and Animal Entamoeba (Amoebida: Endamoebidae) Species—A Review Article. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2015, 10, 146–156. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos Zanetti, A.; Malheiros, A.F.; de Matos, T.A.; Dos Santos, C.; Battaglini, P.F.; Moreira, L.M.; Lemos, L.M.S.; Castrillon, S.K.I.; da Costa Boamorte Cortela, D.; Ignotti, E.; et al. Diversity, geographical distribution, and prevalence of Entamoeba spp. in Brazil: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasite 2021, 28, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Li, J.; Qi, M.; Wang, R.; Yu, F.; Jian, F.; Ning, C.; Zhang, L. Prevalence, molecular epidemiology, and zoonotic potential of Entamoeba spp. in nonhuman primates in China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 54, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Yang, B.; Yang, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Liang, L.; Xu, Q.; Cheng, X.; Tachibana, H. High prevalence of Entamoeba infections in captive long-tailed macaques in China. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Cai, J.; Min, X.; Fu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Tachibana, H.; Cheng, X. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Entamoeba species infecting macaques in southwest China. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, H.; Cheng, X.J.; Kobayashi, S.; Fujita, Y.; Udono, T. Entamoeba dispar, but not E. histolytica, detected in a colony of chimpanzees in Japan. Parasitol. Res. 2000, 86, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levecke, B.; Dreesen, L.; Dorny, P.; Verweij, J.J.; Vercammen, F.; Casaert, S.; Vercruysse, J.; Geldhof, P. Molecular identification of Entamoeba spp. in captive nonhuman primates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2988–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Yang, G.Y.; Yu, X.M.; Cheng, A.C.; Bi, F.J. A case report: Entamoeba histolytica infections in the rhesus macaque, China. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.H.; Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, J.Q.; Yang, J.F.; Zou, F.C. Prevalence, molecular epidemiology and zoonotic risk of Entamoeba spp. from experimental macaques in Yunnan Province, southwestern China. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, J.J.; Vermeer, J.; Brienen, E.A.; Blotkamp, C.; Laeijendecker, D.; van Lieshout, L.; Polderman, A.M. Entamoeba histolytica infections in captive primates. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 90, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Y.; Chong, S.M.; Hsu, C.D.; Ahmad, A.A. Management of Entamoeba histolytica in the non-human primates at the Singapore Zoo. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 3595–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, W.L.; Yason, J.A.; Adao, D.E. Entamoeba histolytica and E. dispar infections in captive macaques (Macaca fascicularis) in the Philippines. Primates J. Primatol. 2010, 51, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beup, R.A.; Nicolas, G.G., Jr.; Rolando, V.P., Jr. Entamoeba histolytica Infection in the Philippines: A Review. Uttar Pradesh J. Zool. 2024, 45, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, H.; Yanagi, T.; Lama, C.; Pandey, K.; Feng, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Sherchand, J.B. Prevalence of Entamoeba nuttalli infection in wild rhesus macaques in Nepal and characterization of the parasite isolates. Parasitol. Int. 2013, 62, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Su, A.; Xie, M.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, S.; Ni, Q.; Xiao, H.; Xu, H. Epidemiological investigation of Entamoeba in wild rhesus macaques in China: A novel ribosomal lineage and genetic differentiation of Entamoeba nuttalli. Int. J. Parasitol. 2024, 54, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, C.S.; Yon, L.; Hossain, M.; Elsheikha, H.M. Prevalence of Entamoeba species in captive primates in zoological gardens in the UK. PeerJ 2014, 2, e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, C.; Luo, J.; Lu, J.; He, H. Molecular Characterization of Entamoeba spp. in Wild Taihangshan Macaques (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis) in China. Acta Parasitol. 2019, 64, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bao, G.; Yue, M.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, W.; Gu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Lu, M. Prevalence and Molecular Identification of Entamoeba spp. in Non-human Primates in a Zoological Garden in Nanjing, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 906822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, P.C.; Martínez-Nevado, E.; González, A.; Abelló-Poveda, M.T.; Fernández-Bellon, H.; de la Riva-Fraga, M.; Marquet, B.; Guéry, J.P.; Knauf-Witzens, T.; Weigold, A.; et al. Intestinal Protists in Captive Non-human Primates and Their Handlers in Six European Zoological Gardens. Molecular Evidence of Zoonotic Transmission. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 819887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adetunji, V.E. Prevalence of gastro-intestinal parasites in primates and their keeper s from two zoological gardens in Ibadan, Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 12, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, P.C.; Dashti, A.; Bailo, B.; Muadica, A.S.; Maloney, J.G.; Santín, M.; Chicharro, C.; Migueláñez, S.; Nieto, F.J.; Cano-Terriza, D.; et al. Occurrence and Genetic Diversity of Protist Parasites in Captive Non-Human Primates, Zookeepers, and Free-Living Sympatric Rats in the Córdoba Zoo Conservation Centre, Southern Spain. Animals 2021, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagas, C.R.F.; Gonzalez, I.H.L.; Favoretto, S.M.; Ramos, P.L. Parasitological surveillance in a rat (Rattus norvegicus) colony in São Paulo Zoo animal house. Ann. Parasitol. 2017, 63, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, C.; Ma, L.; Jia, T.; Pei, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J. Epidemiology and Molecular Characterization of Zoonotic Gastrointestinal Protozoal Infection in Zoo Animals in China. Animals 2024, 14, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouassi, R.Y.; McGraw, S.W.; Yao, P.K.; Abou-Bacar, A.; Brunet, J.; Pesson, B.; Bonfoh, B.; N’Goran, E.K.; Candolfi, E. Diversity and prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites in seven non-human primates of the Taï National Park, Côte d’Ivoire. Parasite 2015, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setchell, J.M.; Bedjabaga, I.-B.; Goossens, B.; Reed, P.; Wickings, E.J.; Knapp, L.A. Parasite Prevalence, Abundance, and Diversity in a Semi-free-ranging Colony of Mandrillus sphinx. Int. J. Primatol. 2007, 28, 1345–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirotte, C.; Basset, D.; Willaume, E.; Makaba, F.; Kappeler, P.M.; Charpentier, M.J. Environmental and individual determinants of parasite richness across seasons in a free-ranging population of Mandrills (Mandrillus sphinx). Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2016, 159, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.F.; Barnes, P.; Monroe, I.G.; Rukundo, J.; Emery Thompson, M.; Rosati, A.G. Age-related physiological dysregulation progresses slowly in semi-free-ranging chimpanzees. Evol. Med. Public Health 2024, 12, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deere, J.R.; Parsons, M.B.; Lonsdorf, E.V.; Lipende, I.; Kamenya, S.; Collins, D.A.; Travis, D.A.; Gillespie, T.R. Entamoeba histolytica infection in humans, chimpanzees and baboons in the Greater Gombe Ecosystem, Tanzania. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köster, P.C.; Lapuente, J.; Dashti, A.; Bailo, B.; Muadica, A.S.; González-Barrio, D.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Ponce-Gordo, F.; Carmena, D. Enteric protists in wild western chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) and humans in Comoé National Park, Côte d’Ivoire. Primates J. Primatol. 2022, 63, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, P.C.; Lapuente, J.; Pizarro, A.; Prieto-Pérez, L.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Dashti, A.; Bailo, B.; Muadica, A.S.; González-Barrio, D.; Calero-Bernal, R.; et al. Presence and genetic diversity of enteric protists in captive and semi-captive non-human primates in côte d’Ivoire, Sierra Leone, and Peru. International journal for parasitology. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, P.C.; Renelies-Hamilton, J.; Dotras, L.; Llana, M.; Vinagre-Izquierdo, C.; Prakas, P.; Sneideris, D.; Dashti, A.; Bailo, B.; Lanza, M.; et al. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Intestinal and Blood Parasites in Wild Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) in Senegal. Animals 2021, 11, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).