Comparison of Detomidine or Romifidine in Combination with Morphine for Standing Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Horses
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
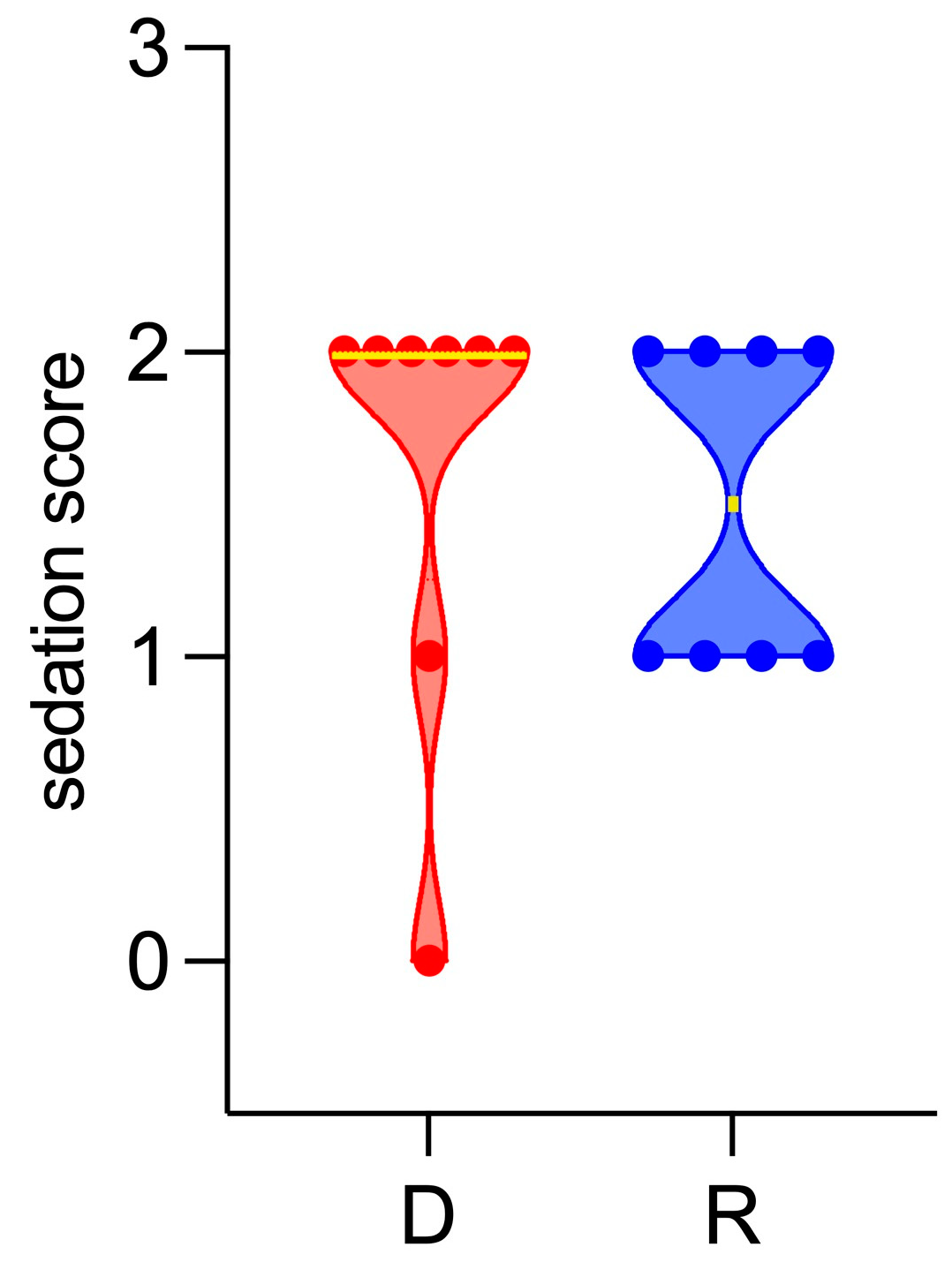
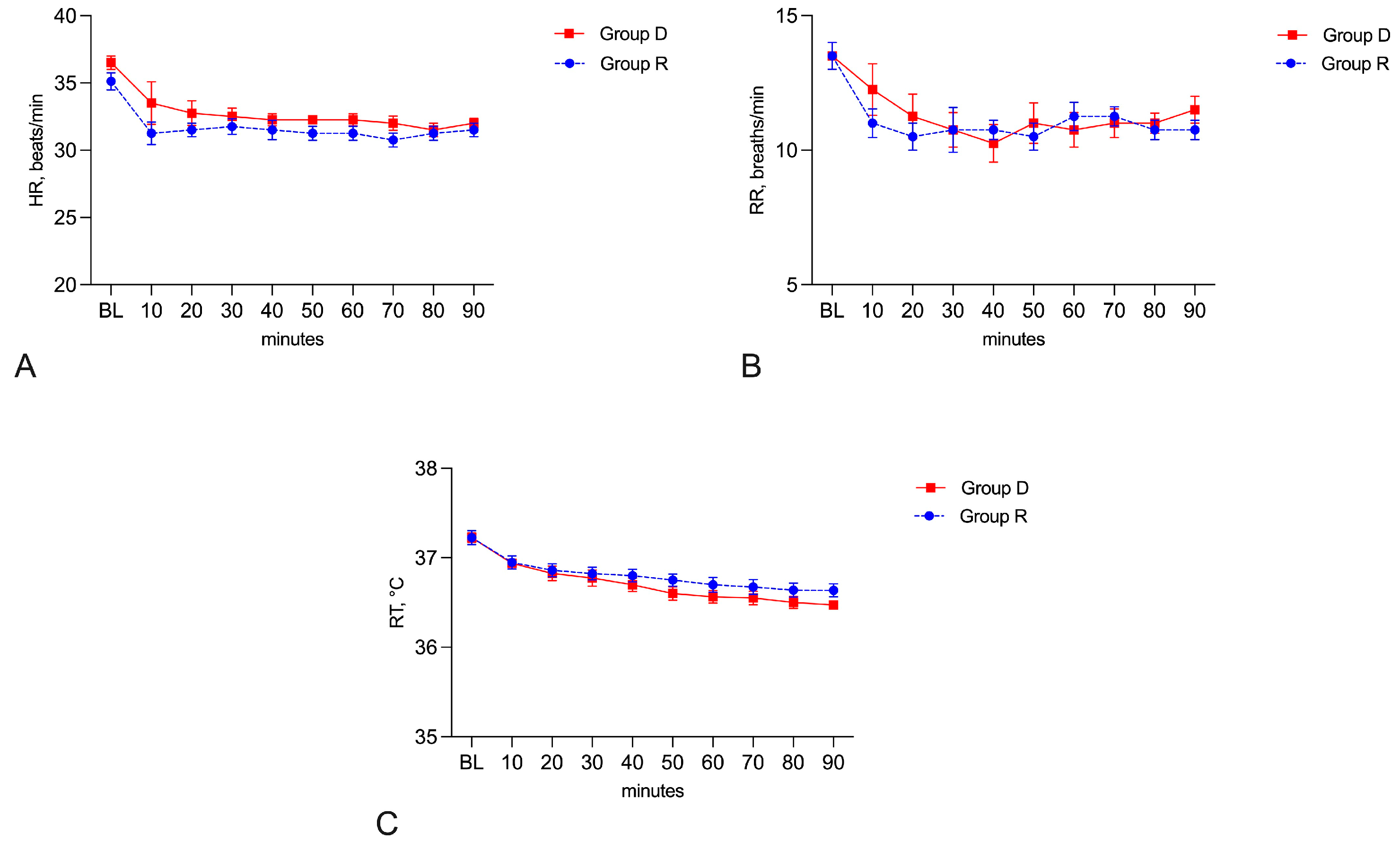
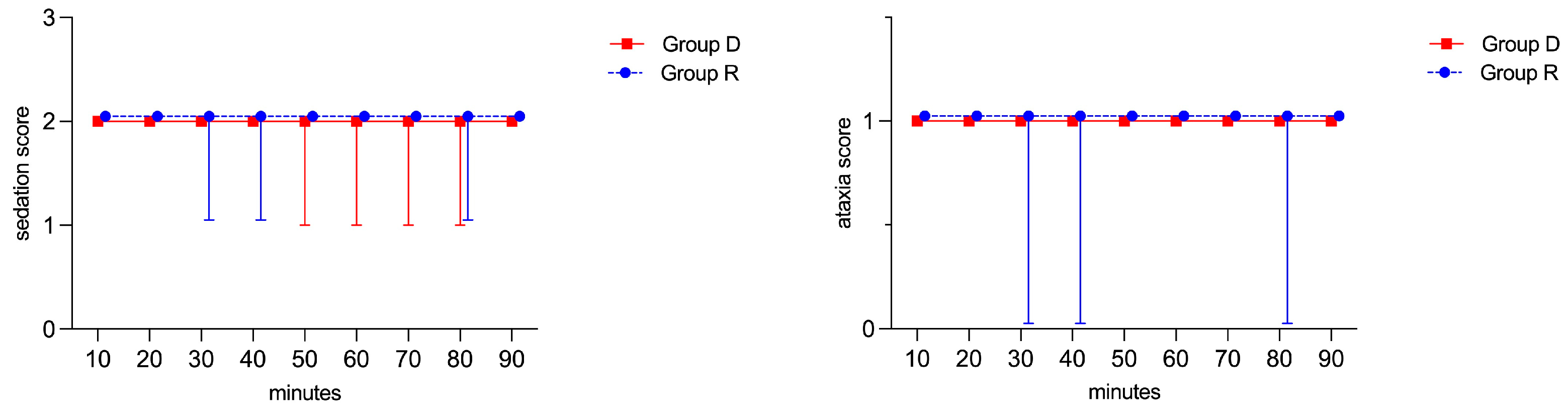
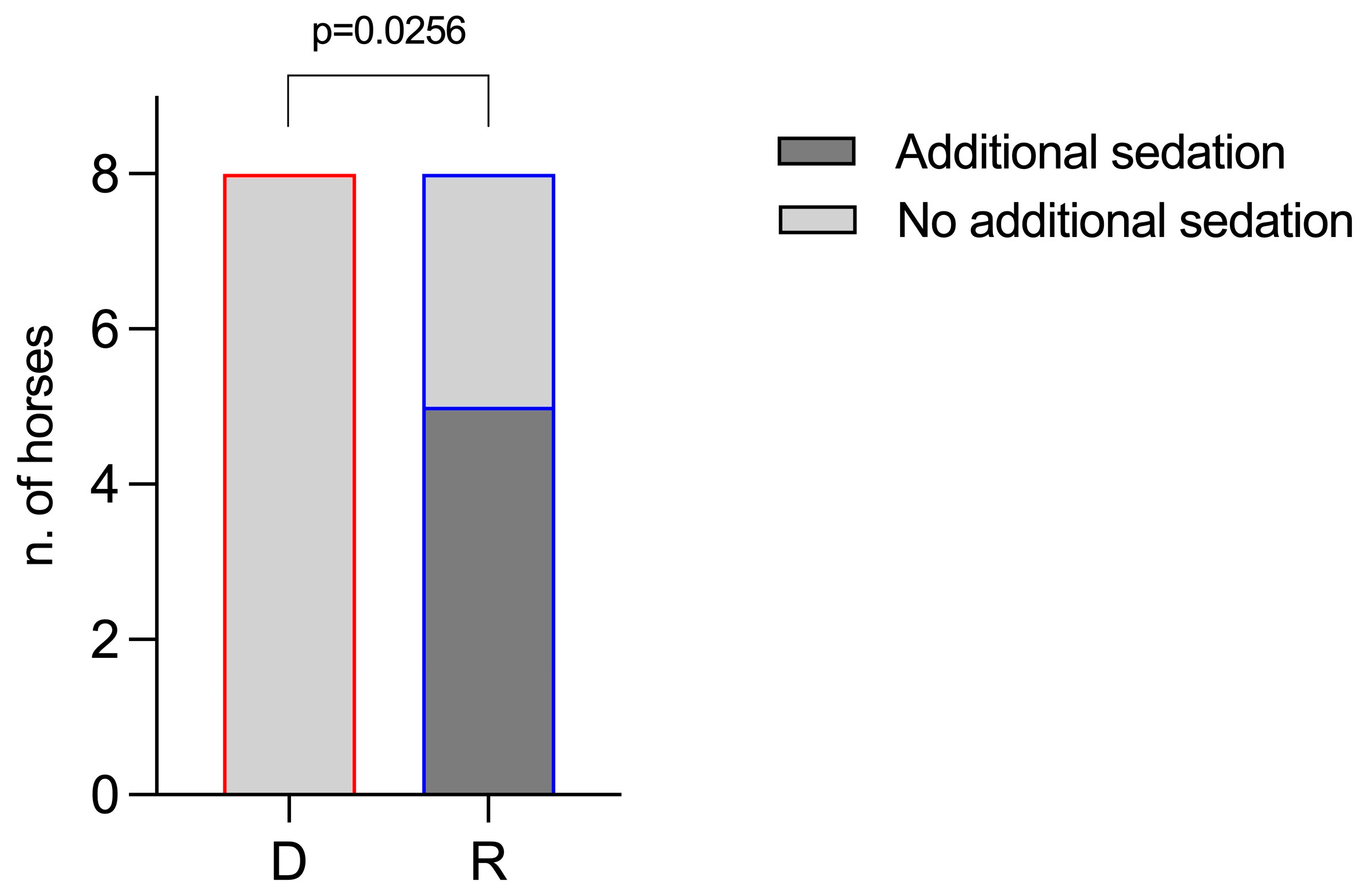
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaskólska, M.; Adamiak, Z.; Zhalniarovich, P.; Holak, P.; Przyborowska, P. Magnetic resonance protocols in equine lameness examination, used sequences, and interpretation. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 16, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.M.; Aceto, H.; Manzi, T.; Davidson, E.J. Incidence and risk factors for complications associated with equine general anaesthesia for elective magnetic resonance imaging. Equine Vet. J. 2023. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, E.G.; Werpy, N.M. New Concepts in Standing Advanced Diagnostic Equine Imaging. Vet. Clin. Equine 2014, 30, 239–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigani, A.; Garcia-Pereira, F.L. Anesthesia and Analgesia for Standing Equine Surgery. Vet. Clin. Equine 2013, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou, J.; Leece, E. Sedation and analgesia in the standing horse 1. Drugs used for sedation and systemic analgesia. Practice 2012, 34, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A. How to Maximize Standing Chemical Restraint. In Proceedings of the 59th American Association of Equine Practitioners Convention, Nashville, TN, USA, 7–11 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, J.J.; MacFarlane, P.D.; Love, E.J.; Tremaine, H.; Taylor, P.M.; Murrell, J.C. Preliminary investigation comparing a detomidine continuous rate infusion combined with either morphine or buprenorphine for standing sedation in horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2016, 43, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.M.; Hopster, K.; Bienert-Zeit, A.; Rohn, K.; Kästner, S.B.R. Effect of butorphanol, midazolam or ketamine on romifidine based sedation in horses during standing cheek tooth removal. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troya-Portillo, L.; López-Sanromán, J.; Villalba-Orero, M.; Santiago-Llorente, I. Cardiorespiratory, Sedative and Antinociceptive Effects of a Medetomidine Constant Rate Infusion with Morphine, Ketamine or Both. Animals 2021, 11, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, D.W.; Lashnits, K.J.; Wegner, K. Managing severe hoof pain in a horse using multimodal analgesia and a modified composite pain score. Equine Vet. Ed. 2009, 21, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, A.M.; Valverde, A.; Desrochers, A.; Nykamp, S.; Boure, L.P. Behavioural and cardiorespiratory effects of a constant rate infusion of medetomidine and morphine for sedation during standing laparoscopy in horses. Equine Vet. J. 2009, 41, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clutton, R.E. Opioid analgesia in horses. Vet. Clin. North Am. Equine Pract. 2010, 26, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, V.J.; Bass, L.; King, M.R. Evaluation of the effects of commonly used α2-adrenergic receptor agonists alone and in combination with butorphanol tartrate on objective measurements of lameness in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 80, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozalo-Marcilla, M.; de Oliveira, A.R.; Fonseca, M.W.; Possebon, F.S.; Pelligand, L.; Taylor, P.M.; Luna, S.P.L. Sedative and antinociceptive effects of different detomidine constant rate infusions, with or without methadone in standing horses. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, S.P.; Moorman, V.J.; Hendrickson, D.A.; Mama, K.R. Comparison of sedation quality and safety of detomidine and romifidine as a continuous rate infusion for standing elective laparoscopic ovariectomy in mares. Vet. Surg. 2021, 50, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, D.; Turchi, P.; Jöchle, W. Sedative and analgesic effects of detomidine and romifidine in horses. Vet. Rec. 1995, 136, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainionpää, M.H.; Raekallio, M.R.; Pakkanen, S.A.; Ranta-Panula, V.; Rinne, V.M.; Scheinin, M.; Vainio, O.M. Plasma drug concentrations and clinical effects of a peripheral alpha-2-adrenoceptor antagonist, MK-467, in horses sedated with detomidine. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2013, 40, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.P.; Smith, J. Sedative and analgesic effects of romifidine in horses. Intern J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2005, 3, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrbach, H.; Korpivaara, T.; Schatzmann, U.; Spadavecchia, C. Comparison of the effects of the alpha-2 agonists detomidine, romifidine and xylazine on nociceptive withdrawal reflex and temporal summation in horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2009, 36, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vullo, C.; Carluccio, A.; Robbe, D.; Meligrana, M.; Petrucci, L.; Catone, G. Guaiphenesin-ketamine-xylazine infusion to maintain anesthesia in mules undergoing field castration. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauvliege, S.; Cuypers, C.; Michielsen, A.; Gasthuys, F.; Gozalo-Marcilla, M. How to score sedation and adjust the administration rate of sedatives in horses: A literature review and introduction of the Ghent Sedation Algorithm. Vet. Anaest. Analg. 2019, 46, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozalo-Marcilla, M.; Luna, S.P.; Gasthuys, F.; Pollaris, E.; Vlaminck, L.; Martens, A.; Haspeslagh, M.; Schauvliege, S. Clinical applicability of detomidine and methadone constant rate infusions for surgery in standing horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2019, 46, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallman, I.; Tapio, H.; Raekallio, M.; Karikoski, N. Effect of constant rate infusion of detomidine with and without vatinoxan on blood glucose and insulin concentrations in horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2023, 51, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evrard, L.; Joostens, Z.; Vandersmissen, M.; Audigié, F.; Busoni, V. Comparison between ultrasonographic and standing magnetic resonance imaging findings in the podotrochlear apparatus of horses with foot pain. Front Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 675180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto-Hardman, B.D.; Steffey, E.P.; Weiner, D.; McKemie, D.S.; Kass, P.; Knych, H.K. Pharmacokinetics and selected pharmacodynamics of morphine and its active metabolites in horses after intravenous administration of four doses. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 42, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knych, H.K.; Steffey, E.P.; McKemie, D.S. Preliminary pharmacokinetics of morphine and its major metabolites following intravenous administration of four doses to horses. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 37, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, E.J.; Taylor, P.M.; Murrell, J.; Whay, H.R. Effects of acepromazine, butorphanol and buprenorphine on thermal and mechanical nociceptive thresholds in horses. Equine Vet. J. 2012, 44, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poller, C.; Hopster, K.; Rohn, K.; Kästner, S.B. Nociceptive thermal threshold testing in horses-effect of neuroleptic sedation and neuroleptanalgesia at different stimulation sites. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combie, J.; Shults, T.; Nugent, E.C.; Dougherty, J.; Tobin, T. Pharmacology of narcotic analgesics in the horse: Selective blockade of narcotic-induced locomotor activity. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1981, 42, 716–721. [Google Scholar]
- Kohn, C.W.; Muir, W.W. 3rd. Selected aspects of the clinical pharmacology of visceral analgesics and gut motility modifying drugs in the horse. J. Vet. Intern Med. 1988, 2, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, A.M.; Keating, S.C.; Lascola, K.M.; Schaeffer, D.J.; Clark-Price, S.C. Cardiopulmonary effects and recovery characteristics of horses anesthetized with xylazine-ketamine with midazolam or propofol. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2018, 45, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringer, S.K.; Portier, K.P.; Fourel, I.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R. Development of a xylazine constant rate infusion with or without butorphanol for standing sedation of horses. Vet. Anaest. Analg. 2012, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringer, S.K.; Portier, K.G.; Fourel, I.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R. Development of a romifidine constant rate infusion with or without butorphanol for standing sedation of horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2012, 39, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Scores | Definition of Scoring |
|---|---|
| Poor: 0 | (Fully responsive to environment, lips apposed, no lowering of the head, no drooping of the ears) |
| Mild: 1 | (Still responsive to environment, slight separation of the lower lip, slight lowering of the head, slight drooping of the ears) |
| Good: 2 | (No response to environment, separation of the lower lip, lowering of the head, drooping of the ears) |
| Heavy: 3 | (No response to environment, extreme lip separation, pronounced loss of postural tone and ataxia, pronounced separation of the ears tips) |
| Scores | Definition of Scoring |
|---|---|
| Depth of Sedation | |
| Score 0: | (No sedation. Animal is alert with normal posture and response to environment/contact with assessor. Normal objection to intervention. Ears responsive to surroundings and moving). |
| Score 1: | (Mild sedation. May or may not lean on head support; relaxed facial muscles. Reduced responses to background activity in the room. Ears partially responsive to surroundings. Light or no ptosis of the ears). |
| Score 2: | (Good sedation. Leans on head support. No response to background activity in the room. Pendulous lower lip. Ears mildly responsive to surroundings. Moderate ear ptosis. Eyelids partially closed). |
| Score 3: | (Marked sedation. Leans strongly on head support. No response to background activity in the room. Pendulous lower lip. Pronounced ear. Ptosis; minimal/no movement of ears. Eyelids partially or fully closed. Eye may be rotated; little to no movements of the eye). |
| Ataxia | |
| Score 0: | (Standing square; bearing equal weight on all four legs). |
| Score 1: | (One hind limb in resting position and/or slight swaying). |
| Score 2: | (Clear swaying or leaning: not maximally bearing weight on one of the four limbs). |
| Score 3: | (Very pronounced leaning: possibly not bearing weight on several limbs- and/or attempts to become recumbent). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vullo, C.; Gugliandolo, E.; Biondi, V.; Biffarella, M.; Catone, G.; Tambella, A.M. Comparison of Detomidine or Romifidine in Combination with Morphine for Standing Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Horses. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11030124
Vullo C, Gugliandolo E, Biondi V, Biffarella M, Catone G, Tambella AM. Comparison of Detomidine or Romifidine in Combination with Morphine for Standing Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Horses. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(3):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11030124
Chicago/Turabian StyleVullo, Cecilia, Enrico Gugliandolo, Vito Biondi, Marco Biffarella, Giuseppe Catone, and Adolfo Maria Tambella. 2024. "Comparison of Detomidine or Romifidine in Combination with Morphine for Standing Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Horses" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 3: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11030124
APA StyleVullo, C., Gugliandolo, E., Biondi, V., Biffarella, M., Catone, G., & Tambella, A. M. (2024). Comparison of Detomidine or Romifidine in Combination with Morphine for Standing Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Horses. Veterinary Sciences, 11(3), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11030124








