Caenorhabditis elegans Infrared-Based Motility Assay Identified New Hits for Nematicide Drug Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. C. elegans, Strains, and Culture Methods
2.3. Assessment of C. elegans Motility Using WMicrotracker ONE
2.4. Pharmacodynamic Function
2.5. Screening of Compound Libraries
2.6. In Vivo Toxicity on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Larvae
2.7. Ethics Statement
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caffrey, C.R. Parasitic Helminths: Targets, Screens, Drugs and Vaccines; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J. The Drugs We Have and the Drugs We Need Against Major Helminth Infections. In Advances in Parasitology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 73, pp. 197–230. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helminth-infections (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- Lo, N.C.; Addiss, D.G.; Hotez, P.J.; King, C.H.; Stothard, J.R.; Evans, D.S.; Colley, D.G.; Lin, W.; Coulibaly, J.T.; Bustinduy, A.L.; et al. A Call to Strengthen the Global Strategy against Schistosomiasis and Soil-Transmitted Helminthiasis: The Time Is Now. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e64–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Lymphatic Filariasis. Available online: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lymphatic-filariasis (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- WHO. Onchocerciasis. Available online: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/onchocerciasis (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- Charlier, J.; van der Voort, M.; Kenyon, F.; Skuce, P.; Vercruysse, J. Chasing Helminths and Their Economic Impact on Farmed Ruminants. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, D.L.; Hunt, P.W.; Le Jambre, L.F. Haemonchus Contortus: The Then and Now, and Where to from Here? Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, Z.; Laurenson, Y.C.S.M.; Forbes, A.B.; Kyriazakis, I. Modelling the Consequences of Targeted Selective Treatment Strategies on Performance and Emergence of Anthelmintic Resistance amongst Grazing Calves. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2016, 6, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, T. Ivermectin 20 Years on: Maturation of a Wonder Drug. Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramünke, S.; Melville, L.; Rinaldi, L.; Hertzberg, H.; de Waal, T.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Cringoli, G.; Mavrot, F.; Skuce, P.; Krücken, J.; et al. Benzimidazole Resistance Survey for Haemonchus, Teladorsagia and Trichostrongylus in Three European Countries Using Pyrosequencing Including the Development of New Assays for Trichostrongylus. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2016, 6, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I.A.; Leathwick, D.M. Anthelmintic Resistance in Nematode Parasites of Cattle: A Global Issue? Trends Parasitol. 2011, 27, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, W.C. Lessons from the History of Ivermectin and Other Antiparasitic Agents. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2016, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotez, P.J.; Brindley, P.J.; Bethony, J.M.; King, C.H.; Pearce, E.J.; Jacobson, J. Helminth Infections: The Great Neglected Tropical Diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.R.; Luciani, G.M.; Musso, G.; Bagg, R.; Yeo, M.; Zhang, Y.; Rajendran, L.; Glavin, J.; Hunter, R.; Redman, E.; et al. Caenorhabditis Elegans Is a Useful Model for Anthelmintic Discovery. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, J. Is Caenorhabditis Elegans the Magic Bullet for Anthelminthic Drug Discovery? Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 455–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotze, A.C.; Hunt, P.W.; Skuce, P.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Martin, R.J.; Sager, H.; Krücken, J.; Hodgkinson, J.; Lespine, A.; Jex, A.R.; et al. Recent Advances in Candidate-Gene and Whole-Genome Approaches to the Discovery of Anthelmintic Resistance Markers and the Description of Drug/Receptor Interactions. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2014, 4, 164–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaxter, M. Nematodes: The Worm and Its Relatives. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Helminth Genomes Consortium. Comparative Genomics of the Major Parasitic Worms. Nat. Genet. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden-Dye, L.; Walker, R.J. Anthelmintic Drugs and Nematicides: Studies in Caenorhabditis Elegans. WormBook 2014, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.E.; Davey, M.W. A Rapid Colorimetric Assay for the Quantitation of the Viability of Free-Living Larvae of Nematodes in Vitro. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.R.; Mendes, T.A.O.; Bueno, L.L.; De Araújo, J.V.; Bartholomeu, D.C.; Fujiwara, R.T. A New Methodology for Evaluation of Nematode Viability. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, M.D.; Mathew, N.D.; Miller, A.; Simpson, M.; Au, V.; Garland, S.; Gestin, M.; Edgley, M.L.; Flibotte, S.; Balgi, A.; et al. Using C. Elegans Forward and Reverse Genetics to Identify New Compounds with Anthelmintic Activity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckingham, S.D.; Partridge, F.A.; Sattelle, D.B. Automated, High-Throughput, Motility Analysis in Caenorhabditis Elegans and Parasitic Nematodes: Applications in the Search for New Anthelmintics. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2014, 4, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, S.; Jiao, Y.; Jabbar, A.; McGee, S.L.; Laleu, B.; Willis, P.; Wells, T.N.C.; Gasser, R.B. Screening of the ‘Pathogen Box’ Identifies an Approved Pesticide with Major Anthelmintic Activity against the Barber’s Pole Worm. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2016, 6, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, E.; Varela, J.; Birriel, E.; Serna, E.; Torres, S.; Yaluff, G.; de Bilbao, N.V.; Aguirre-López, B.; Cabrera, N.; Díaz Mazariegos, S.; et al. Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Trypanosoma Cruzi Triosephosphate Isomerase with Concomitant Inhibition of Cruzipain: Inhibition of Parasite Growth through Multitarget Activity. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Varela, J.; Márquez, P.; Gabay, M.; Arias Rivas, C.E.; Cuchilla, K.; Echeverría, G.A.; Piro, O.E.; Chorilli, M.; Leal, S.M.; et al. Optimization of Antitrypanosomatid Agents: Identification of Nonmutagenic Drug Candidates with in Vivo Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3984–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Martínez, J.; Varela, J.; Birriel, E.; Cruces, E.; Gabay, M.; Leal, S.M.; Escobar, P.; Aguirre-López, B.; Cabrera, N.; et al. Development of Bis-Thiazoles as Inhibitors of Triosephosphate Isomerase from Trypanosoma Cruzi. Identification of New Non-Mutagenic Agents That Are Active in Vivo. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 100, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerecetto, H.; González, M. Anti-T. Cruzi Agents: Our Experience in the Evaluation of More than Five Hundred Compounds. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1355–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Perdomo, C.; Coronel, C.; Aguilera, E.; Varela, J.; Aparicio, G.; Zolessi, F.; Cabrera, N.; Vega, C.; Rolón, M.; et al. Multi-Anti-Parasitic Activity of Arylidene Ketones and Thiazolidene Hydrazines against Trypanosoma Cruzi and Leishmania spp. Molecules 2017, 22, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, S. The Genetics of Caenorhabditis Elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simonetta, S.H.; Golombek, D.A. An Automated Tracking System for Caenorhabditis Elegans Locomotor Behavior and Circadian Studies Application. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 161, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drwal, M.N.; Banerjee, P.; Dunkel, M.; Wettig, M.R.; Preissner, R. ProTox: A Web Server for the in Silico Prediction of Rodent Oral Toxicity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W53–W58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, G.; Varela, J.; Cruces, E.; Fernández, M.; Gabay, M.; Leal, S.M.; Escobar, P.; Sanabria, L.; Serna, E.; Torres, S.; et al. Identification of a new amide-containing thiazole as a drug candidate for treatment of Chagas’ disease. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Chemolibrary Code | Structure | Motility (%) at 25–50 µm |
|---|---|---|
| 796 |  | 7 |
| 694 |  | 64 |
| 795 |  | 0 |
| 808 | 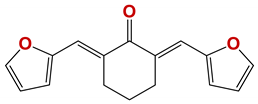 | 53 |
| 804 |  | 63 |
| 798 | 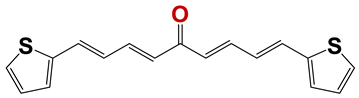 | 63 |
| 809 |  | 55 |
| 1282 | 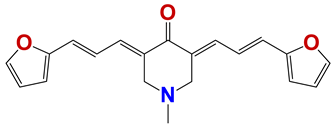 | 62 |
| 1245 | 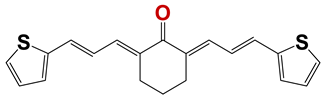 | 23 |
| 262 |  | 59 |
| 145 | 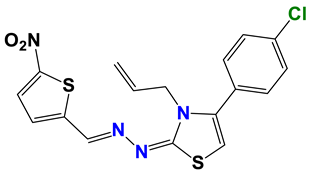 | 60 |
| 313 | 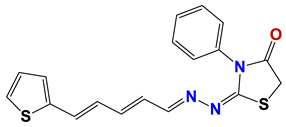 | 63 |
| 314 |  | 60 |
| 1364 | 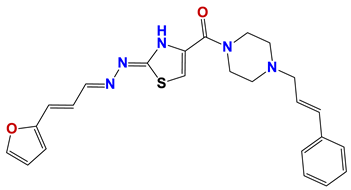 | 61 |
| 1381 |  | 2 |
| 1140 |  | 23 |
| 782 | 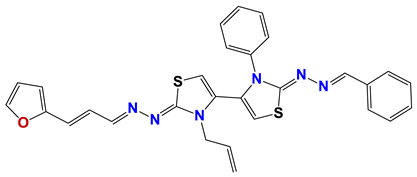 | 61 |
| 724 |  | 63 |
| 731 | 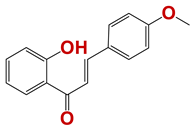 | 8 |
| 813 |  | 50 |
| 1384 | 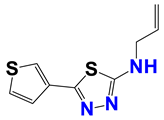 | 55 |
| 568 | 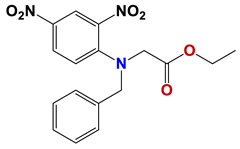 | 58 |
| 1367 |  | 63 |
| 1219 | 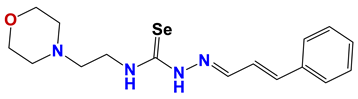 | 62 |
| 1377 | 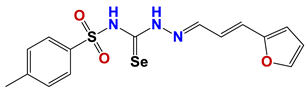 | 45 |
| 1278 |  | 60 |
| 1287 |  | 61 |
| 1272 | 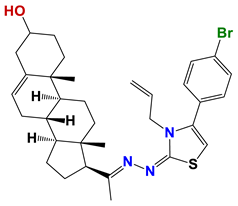 | 55 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Risi, G.; Aguilera, E.; Ladós, E.; Suárez, G.; Carrera, I.; Álvarez, G.; Salinas, G. Caenorhabditis elegans Infrared-Based Motility Assay Identified New Hits for Nematicide Drug Development. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6010029
Risi G, Aguilera E, Ladós E, Suárez G, Carrera I, Álvarez G, Salinas G. Caenorhabditis elegans Infrared-Based Motility Assay Identified New Hits for Nematicide Drug Development. Veterinary Sciences. 2019; 6(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleRisi, Gastón, Elena Aguilera, Enrique Ladós, Gonzalo Suárez, Inés Carrera, Guzmán Álvarez, and Gustavo Salinas. 2019. "Caenorhabditis elegans Infrared-Based Motility Assay Identified New Hits for Nematicide Drug Development" Veterinary Sciences 6, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6010029
APA StyleRisi, G., Aguilera, E., Ladós, E., Suárez, G., Carrera, I., Álvarez, G., & Salinas, G. (2019). Caenorhabditis elegans Infrared-Based Motility Assay Identified New Hits for Nematicide Drug Development. Veterinary Sciences, 6(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6010029






