Characterization of the CBM50 Gene Family in Tilletia horrida and Identification of the Putative Effector Gene ThCBM50_1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Analysis of Physicochemical Properties Analysis of ThCBM50 Family Genes
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Analysis of Gene Structure, Protein Motifs, and Protein Structure
2.4. Promoter Cis-Acting Regulatory Element Analysis
2.5. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.6. Yeast Secretion Assay Involving TTC
2.7. Transient Expression Assays
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of ThCBM50 Gene Family
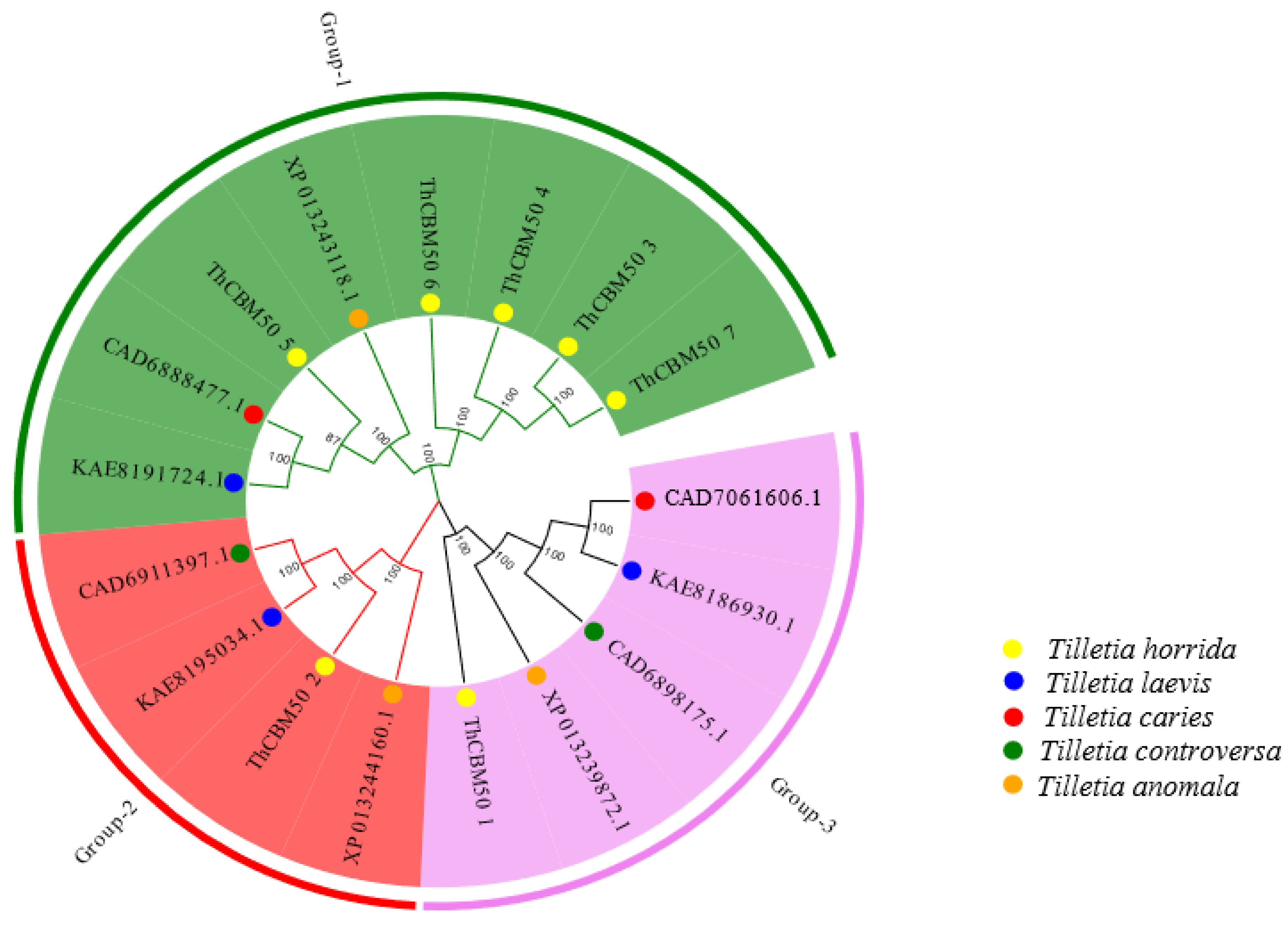
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of ThCBM50 Proteins
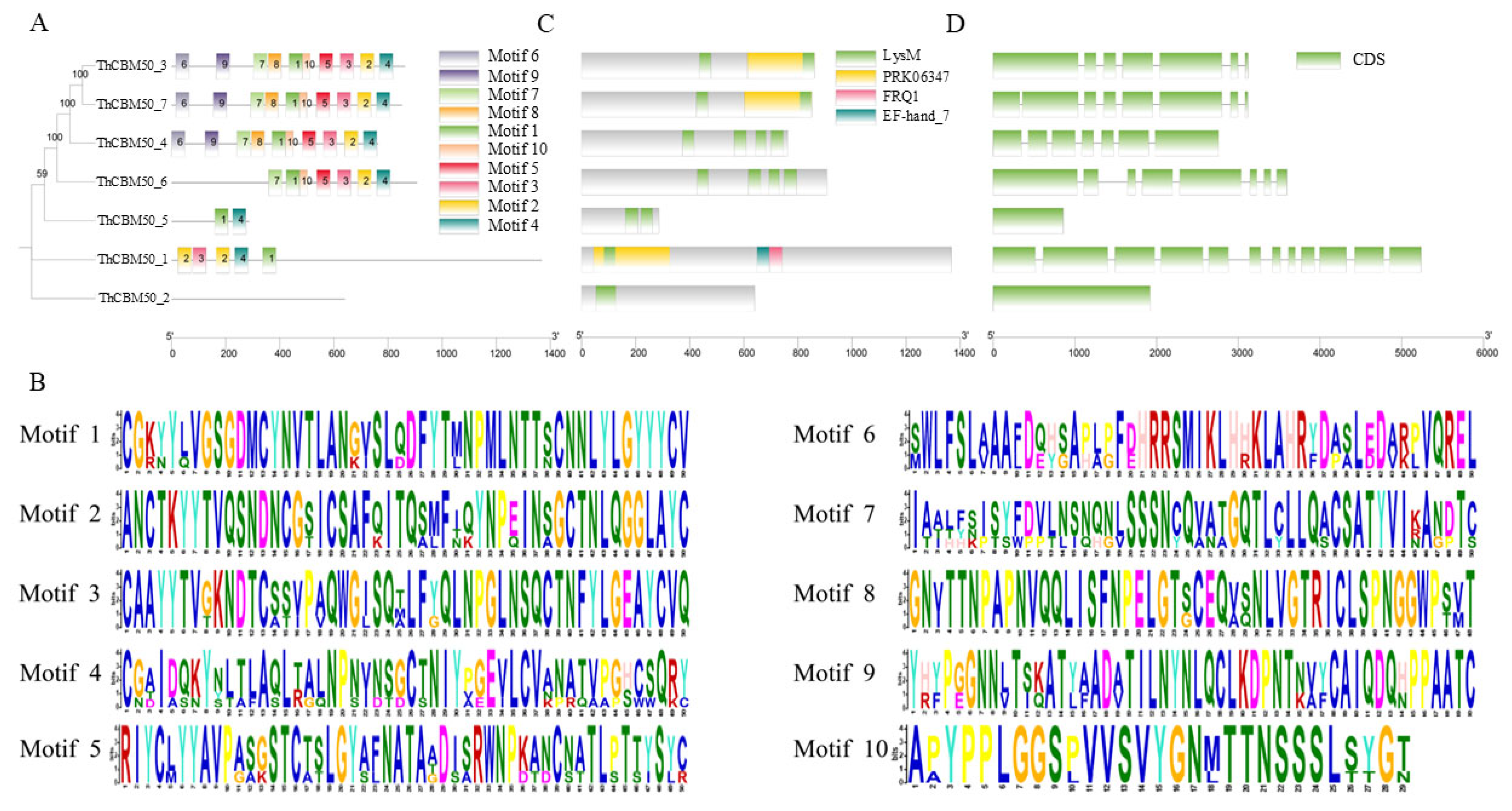
3.3. Conserved Motifs and Gene Structure Analysis of ThCBM50 Proteins
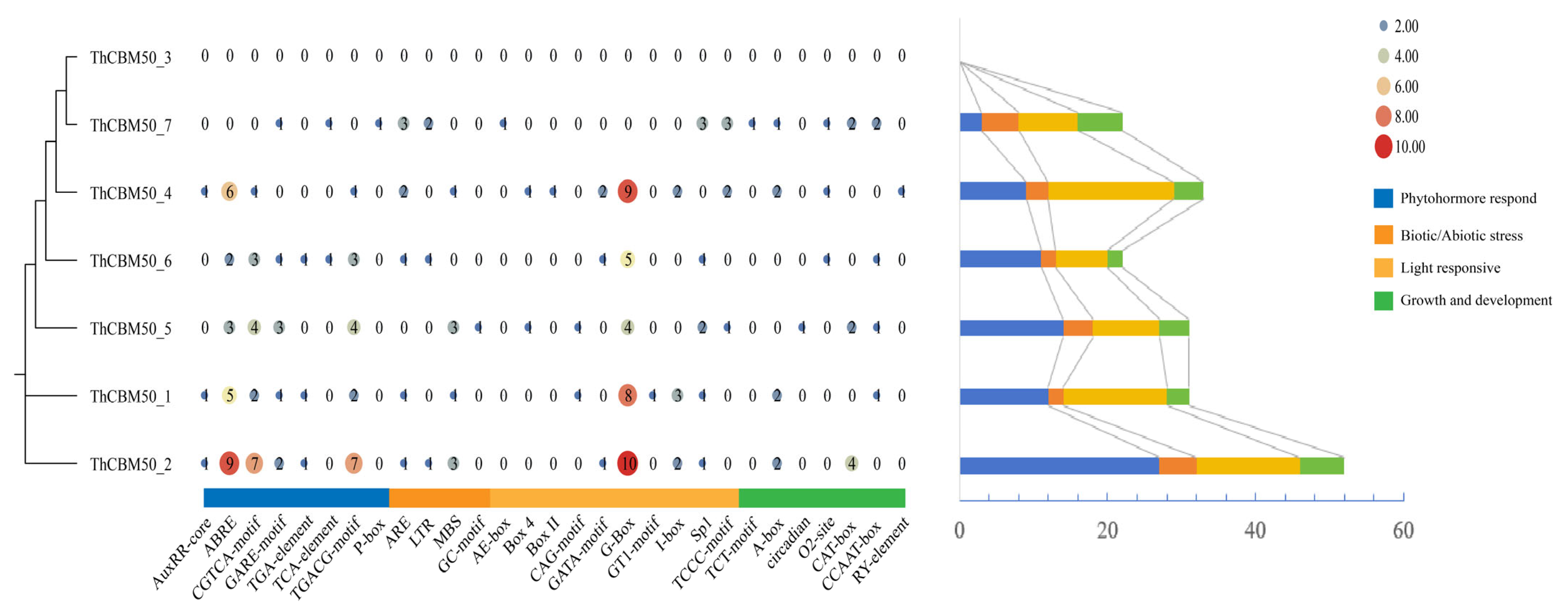
3.4. The Promoter Cis-Acting Element Analysis of the ThCBM50 Genes
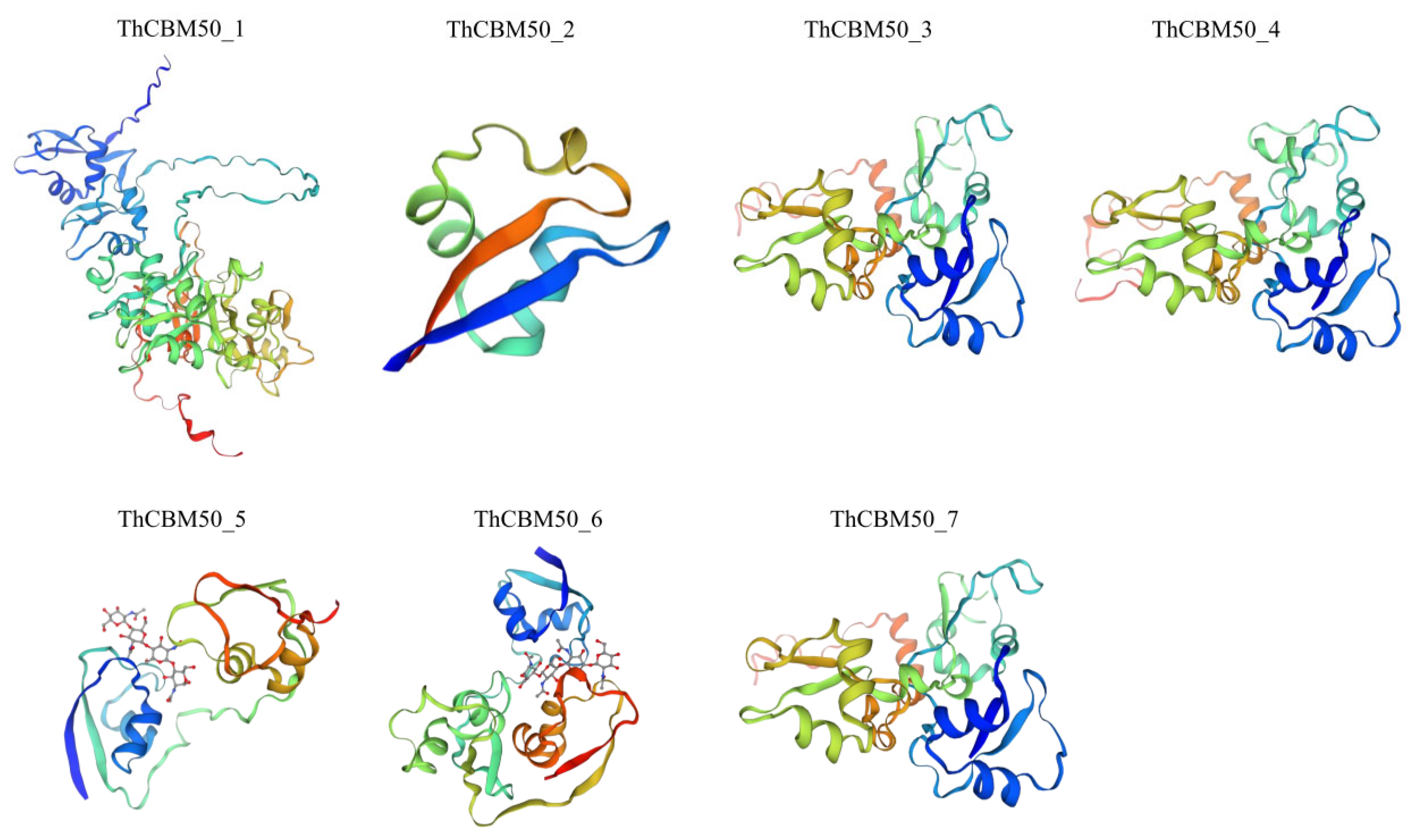
3.5. Protein Structure Analysis of the ThCBM50 Genes
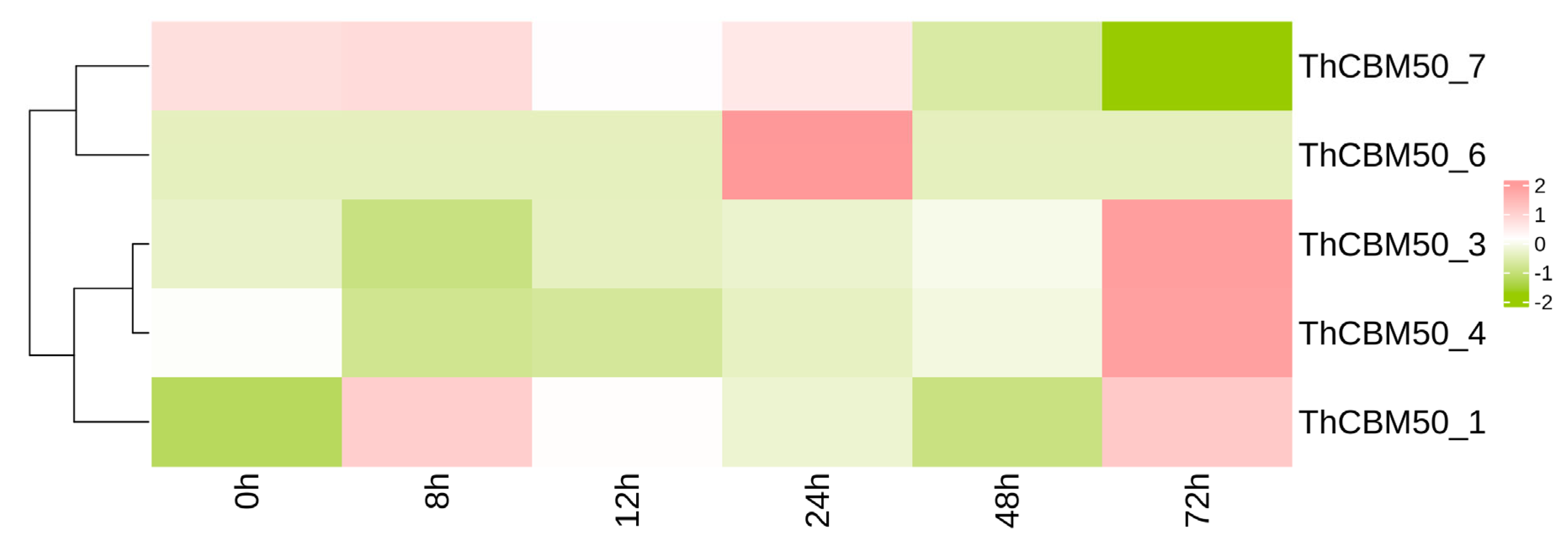
3.6. ThCBM50 Gene Response During T. horrida Infection in Rice
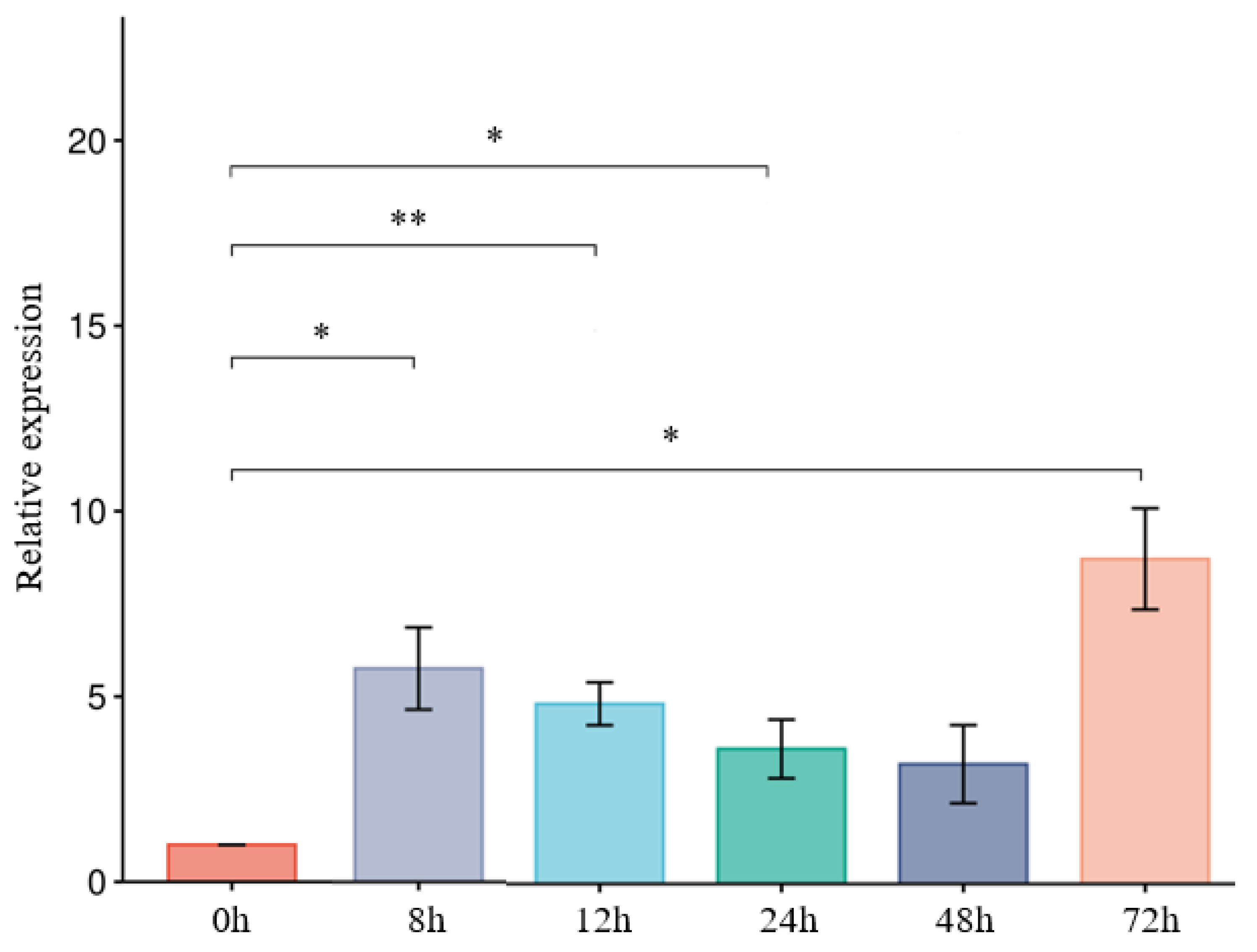
3.7. ThCBM50_1 Is Upregulated During T. horrida Infection
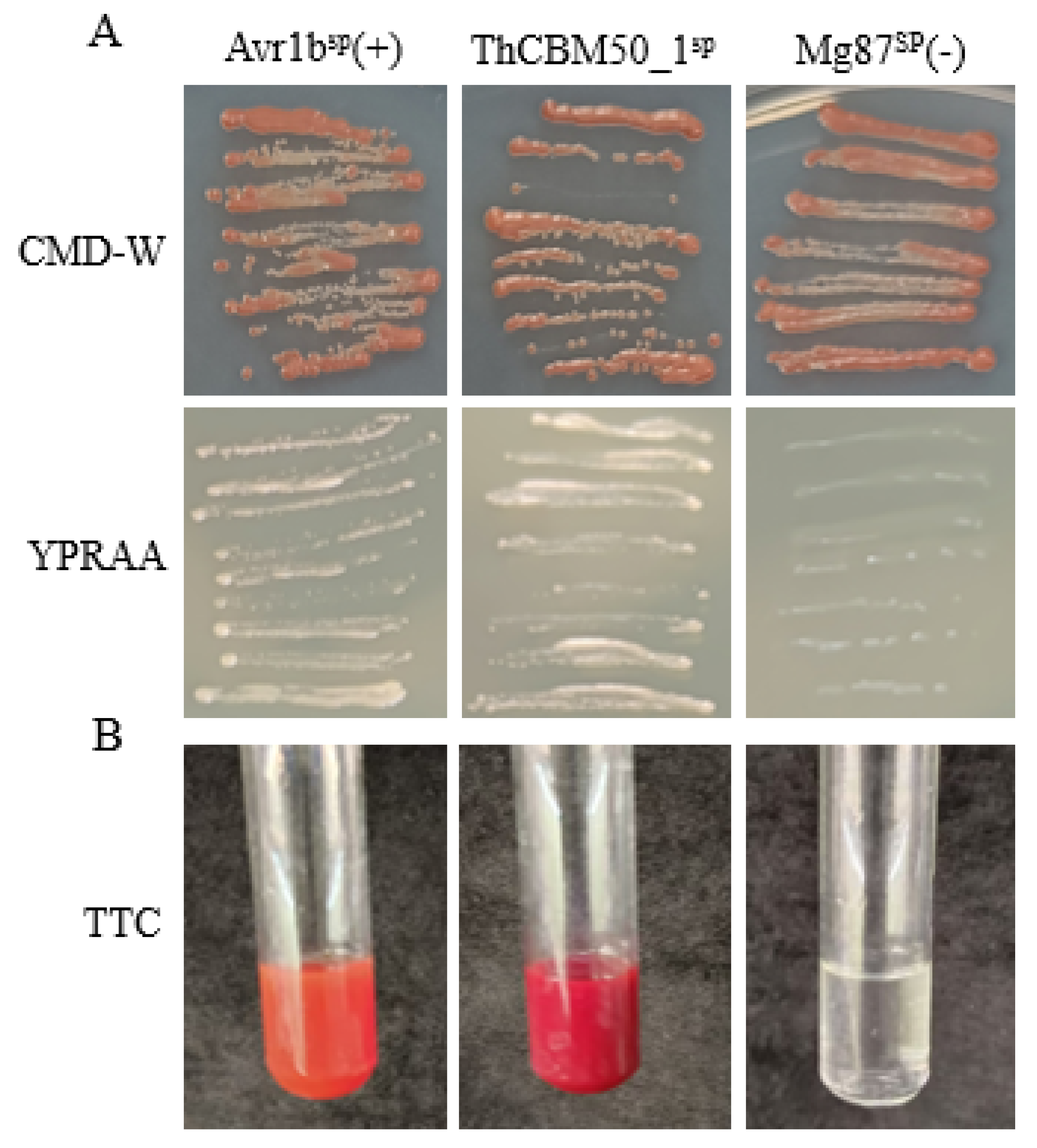
3.8. ThCBM50_1 Is Secreted Protein
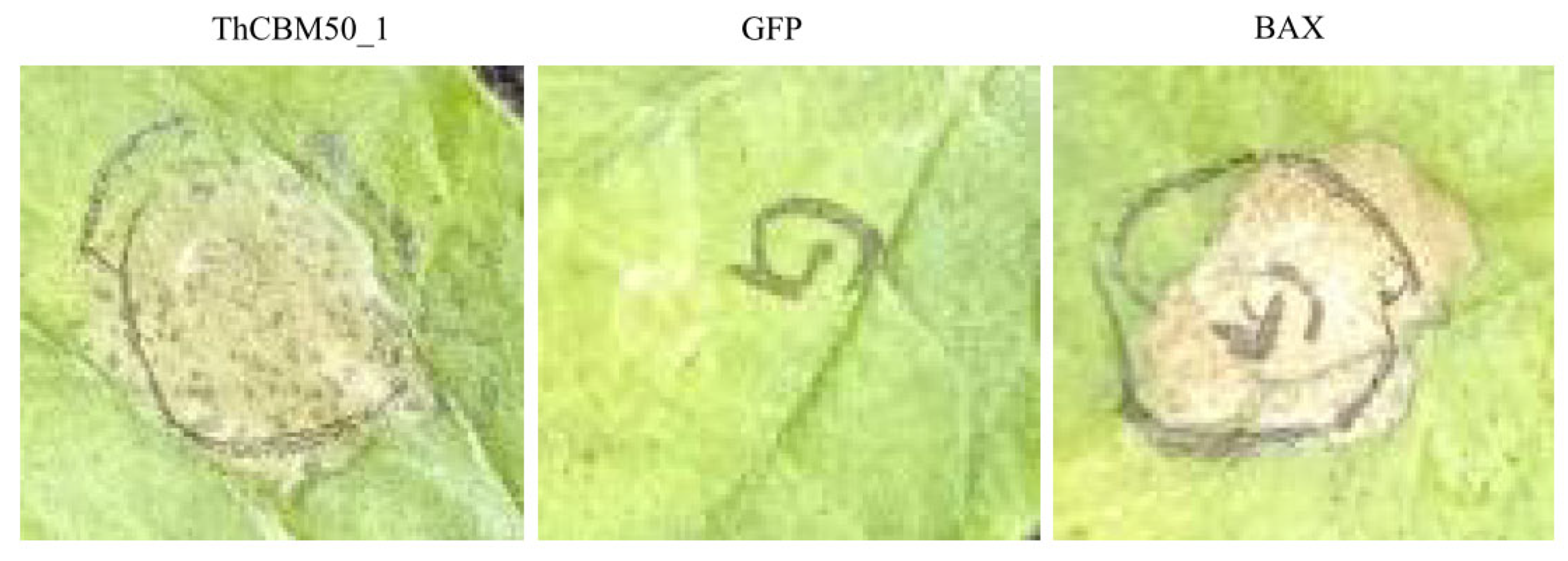
3.9. ThCBM50_1 Induces Cell Death in N. benthamiana
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, J. Comparative analysis of fungal genomes reveals different plant cell wall degrading capacity in fungi. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarel, B.; Coutinho, P.; Rancurel, C.; Bernard, T.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): An expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombard, V.; Golaconda, R.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.; Henrissat, B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D490–D495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, H.; Knox, J.; Boraston, A. Advances in understanding the molecular basis of plant cell wall polysaccharide recognition by carbohydrate-binding modules. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freelove, A.C.J.; Bolam, D.N.; White, P.; Hazlewood, G.P.; Gilbert, H.J. A Novel Carbohydrate-binding Protein Is a Component of the Plant Cell Wall-degrading Complex of Piromyces equi. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43010–43017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, N.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Short, D.P.G.; Li, L.; Guo, W.; et al. Verticillium dahliae manipulates plant immunity by glycoside hydrolase 12 proteins in conjunction with carbohydrate-binding module 1. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1914–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, N.; Duan, W.; Pi, L.; Shen, D.; Dou, D. Phytophthora capsici CBM1-containing protein CBP3 is an apoplastic effector with plant immunity-inducing activity. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1358–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buist, G.; Steen, A.; Kok, J.; Kuipers, O. LysM, a widely distributed protein motif for binding to (peptido) glycans. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.; Kombrink, A.; Motteram, J.; Loza-Reyes, E.; Lucas, J.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Thomma, B.P.H.J.; Rudd, J.J. Analysis of two in planta expressed LysM effector homologues from the fungus Mycosphaerella graminicola reveals novel functional properties and varying contributions to virulence on wheat. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentlak, T.A.; Kombrink, A.; Shinya, T.; Ryder, L.S.; Otomo, I.; Saitoh, H.; Terauchi, R.; Nishizawa, Y.; Shibuya, N.; Thomma, B.P.; et al. Effector-mediated suppression of chitin-triggered immunity by Magnaporthe oryzae is necessary for rice blast disease. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, R.; van Esse, H.P.; Kombrink, A.; Shinya, T.; Desaki, Y.; Bours, R.; van der Krol, S.; Shibuya, N.; Joosten, M.H.A.J.; Thomma, B.P.H.J. Conserved fungal LysM effector Ecp6 prevents chitintriggered immunity in plants. Science 2010, 329, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kombrink, A.; Rovenich, H.; Shi, X.; Rojas, E.; Van, D.; Domazakis, E.; de Jonge, R.; Valkenburg, D.J.; Sánchez-Vallet, A.; Seidl, M.F.; et al. Verticillium dahliae LysM effectors differentially contribute to virulence on plant hosts. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, K.; Masood, S.; Faqir, M.; Saima, H. Rice bran: A novel functional ingredient. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 807–816. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Wu, C.; Shi, X. Estimating the amino acid composition in milled rice by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Field Crop Res. 2002, 75, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Asitk, B. Kernel smut disease of rice: Current status and future challenges. Envrion. Ecol. 2003, 21, 336–351. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Xue, Y.; Jian, Y.; Ei, P.; Zhang, A.; Li, Y.; Gu, C.; Zang, H.; Gao, T. Simple and rapid detection of Tilletia horrida causing rice kernel smut in rice seeds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33258. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y. On Ustilago virens Cooke and a new species of Tilletia parasitic on rice plant. Shokubutsugaku Zasshi 1896, 10, en16–en20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Pan, L.; Wang, N.; Ai, P.; Yin, D.; Li, S.; Deng, Q.; Zhu, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. The pathogenic mechanisms of Tilletia horrida as revealed by comparative and functional genomics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Shu, X.; Niu, X.; Yi, X.; Zheng, A. Transcriptome analysis and whole genome re-sequencing provide insights on rice kernel smut (Tilletia horrida) pathogenicity. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 102, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfand, J.; LeFevre, G.; Luthy, R. Metabolization and degradation kinetics of the urban-use pesticide fipronil by white rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2016, 18, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajthaml, T. Biodegradation of endocrine-disrupting compounds by ligninolytic fungi: Mechanisms involved in the degradation. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4822–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.; Appel, R.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the expasy server. Proteom. Protoc. Handb. 2005, 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. SOPMA: Significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Bioinformatics 1995, 11, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriventseva, E.; Fleischmann, W.; Zdobnov, E.; Apweiler, R. CluSTr: A database of clusters of SWISS-PROT+TrEMBL proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, K.A.; Collins-Racie, L.A.; Colbert, M.; Duckett, M.; Golden-Fleet, M.; Kelleher, K.; Kriz, R.; LaVallie, E.R.; Merberg, D.; Spaulding, V.; et al. A genetic selection for isolating cDNAs encoding secreted proteins. Gene 1997, 198, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Yin, D.; Liang, J.; Xiang, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Zheng, A.; Li, P.; Wang, A. Tilletia horrida glycoside hydrolase family 128 protein, designated ThGhd_7, modulates plant immunity by blocking reactive oxygen species production. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 2459–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Xu, H.; Wu, B.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. The Phytophthora effector Avh94 manipulates host jasmonic acid signaling to promote infection. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Situ, J.; Xie, L.; Xi, P.; Yang, B.; Kong, G.; Jiang, Z. Peronophythora litchii RXLR effector P. litchii avirulence homolog 202 destabilizes a host ethylene biosynthesis enzyme. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 756–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Lin, R.; Zhang, D.; Qin, P.; Xu, L.; Ai, P.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. The evolution and pathogenic mechanisms of the rice sheath blight pathogen. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.A.; Talbot, N.J.; Ebbole, D.J.; Farman, M.L.; Mitchell, T.K.; Orbach, M.J.; Thon, M.; Kulkarni, R.; Xu, J.R.; Pan, H.; et al. The genome sequence of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Nature 2005, 434, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Rose, J. A yeast secretion trap assay for identification of secreted proteins from eukaryotic phytopathogens and their plant hosts. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 835, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.; Yin, D.; Liang, J.; Xu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Xiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, C.; Li, P.; Zheng, A.; et al. ThSCSP_12: Novel effector in Tilletia horrida that induces cell death and defense responses in non-host plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, J.; Xiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Han, X.; Jiao, C.; Zheng, A.; et al. Functional analyses of a small secreted cysteine-rich protein ThSCSP_14 in Tilletia horrida. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesei, G.; Trolle, A.I.; Jonsson, N.; Betz, J.; Knudsen, F.E.; Pesce, F.; Johansson, K.E.; Lindorff-Larsen, K. Conformational ensembles of the human intrinsically disordered proteome. Nature 2024, 626, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holehouse, A.; Kragelund, B. The molecular basis for cellular function of intrinsically disordered protein regions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidl-Seiboth, V.; Zach, S.; Frischmann, A.; Spadiut, O.; Dietzsch, C.; Herwig, C.; Ruth, C.; Rodler, A.; Jungbauer, A.; Kubicek, C.P. Spore germination of Trichoderma atroviride is inhibited by its LysM protein TAL6. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.; Ballester, A.R.; Raphael, G.; Feigenberg, O.; Liu, Y.; Norelli, J.; Gonzalez-Candelas, L.; Ma, J.; Dardick, C.; Wisniewski, M.; et al. Identification and characterization of LysM effectors in Penicillium expansum. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, W.; Mehrabi, R.; Van, D.; Stergiopoulos, I. Fungal effector proteins: Past, present and future. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 735–747. [Google Scholar]
- De, J.; Thomma, B. Fungal LysM effectors: Extinguishers of host immunity? Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Garvey, K.; Saedi, M.; Ito, J. Nucleotide sequence of Bacillus phage phi 29 genes 14 and 15: Homology of gene 15 with other phage lysozymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986, 14, 10001–10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukamolova, G.V.; Murzin, A.G.; Salina, E.G.; Demina, G.R.; Kell, D.B.; Kaprelyants, A.S.; Young, M. Muralytic activity of Micrococcus luteus Rpf and its relationship to physiological activity in promoting bacterial growth and resuscitation. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, M.; Vélëz, H.; Broberg, M.; Jensen, D.; Karlsson, M. LysM Proteins Regulate Fungal Development and Contribute to Hyphal Protection and Biocontrol Traits in Clonostachys rosea. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcapinar, G.; Kappel, L.; Sezerman, O.; Seidl-Seiboth, V. Molecular diversity of LysM carbohydrate binding motifs in fungi. Curr. Genet. 2015, 61, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Li, X.; Yin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, J.; Lu, J. A candidate RxLR effector from Plasmopara viticola can elicit immune responses in Nicotiana benthamiana. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Hu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Hou, X.; Xu, Q.; Han, C.; Wang, Q. A conserved glycoside hydrolase family 7 cellobiohydrolase PsGH7a of Phytophthora sojae is required for full virulence on soybean. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Yamamoto, N.; Yang, G.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, A. A small secreted protein, RsMf8HN, in Rhizoctonia solani triggers plant immune response, which interacts with rice OsHIPP28. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Proposed Gene Name | Gene ID | Protein Length (aa) | Mw (kDa) | Instability Index | pI | GRAVH | Predicted Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ThCBM50_1 | smut_1650 | 1368 | 145.57 | 41.69 | 6.24 | −0.25 | extracellular |
| ThCBM50_2 | smut_2305 | 640 | 65.17 | 52.16 | 10.27 | −0.756 | nucleus |
| ThCBM50_3 | smut_4126 | 862 | 90.05 | 44.15 | 6.93 | −0.064 | extracellular |
| ThCBM50_4 | smut_4802 | 763 | 80.01 | 37.02 | 6.84 | −0.112 | extracellular |
| ThCBM50_5 | smut_5680 | 286 | 30.81 | 47.12 | 8.6 | −0.466 | extracellular |
| ThCBM50_6 | smut_7273 | 907 | 98.33 | 57.2 | 8.87 | −0.398 | nucleus |
| ThCBM50_7 | smut_7501 | 851 | 89.09 | 43.18 | 7.23 | −0.072 | extracellular |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, T.; Xu, D.; Pan, L.; Zhai, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, A.; Yin, D.; Wang, A. Characterization of the CBM50 Gene Family in Tilletia horrida and Identification of the Putative Effector Gene ThCBM50_1. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120856
Xiang T, Xu D, Pan L, Zhai D, Zhang Y, Zheng A, Yin D, Wang A. Characterization of the CBM50 Gene Family in Tilletia horrida and Identification of the Putative Effector Gene ThCBM50_1. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(12):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120856
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Ting, Deze Xu, Linxiu Pan, Dongyu Zhai, Yu Zhang, Aiping Zheng, Desuo Yin, and Aijun Wang. 2024. "Characterization of the CBM50 Gene Family in Tilletia horrida and Identification of the Putative Effector Gene ThCBM50_1" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 12: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120856
APA StyleXiang, T., Xu, D., Pan, L., Zhai, D., Zhang, Y., Zheng, A., Yin, D., & Wang, A. (2024). Characterization of the CBM50 Gene Family in Tilletia horrida and Identification of the Putative Effector Gene ThCBM50_1. Journal of Fungi, 10(12), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120856







