Production of Vespa tropica Hyaluronidase by Pichia pastoris
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Reagents, and Medias
2.2. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
2.3. Gene Cloning via the Golden-Gate-Derived P. pastoris Cloning System (GoldenPiCS)
2.4. Screening of P. pastoris Production Using Enzymatic Glucose Release Method
2.5. Bioreactor Cultivation
2.6. Protein Purification
2.7. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.8. Analysis of Hyaluronidase Activity Assay
2.9. Molecular Docking
3. Results
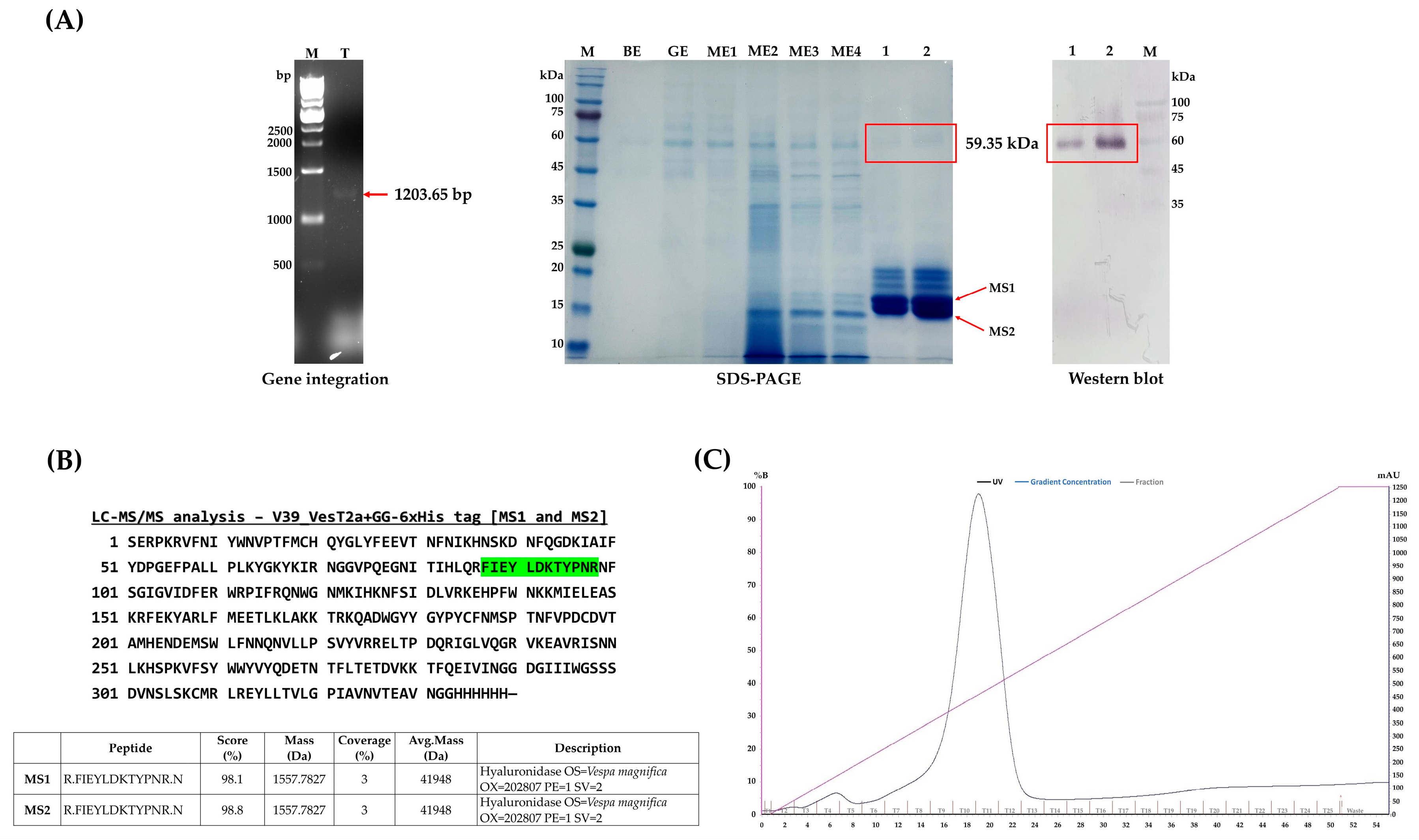
3.1. Construction of Recombinant VesT2a Plasmids and Small-Scaled Expression in P. pastoris
3.2. Upscaled Production, Detection, and Purification of Vest T2a Produced by P. pastoris
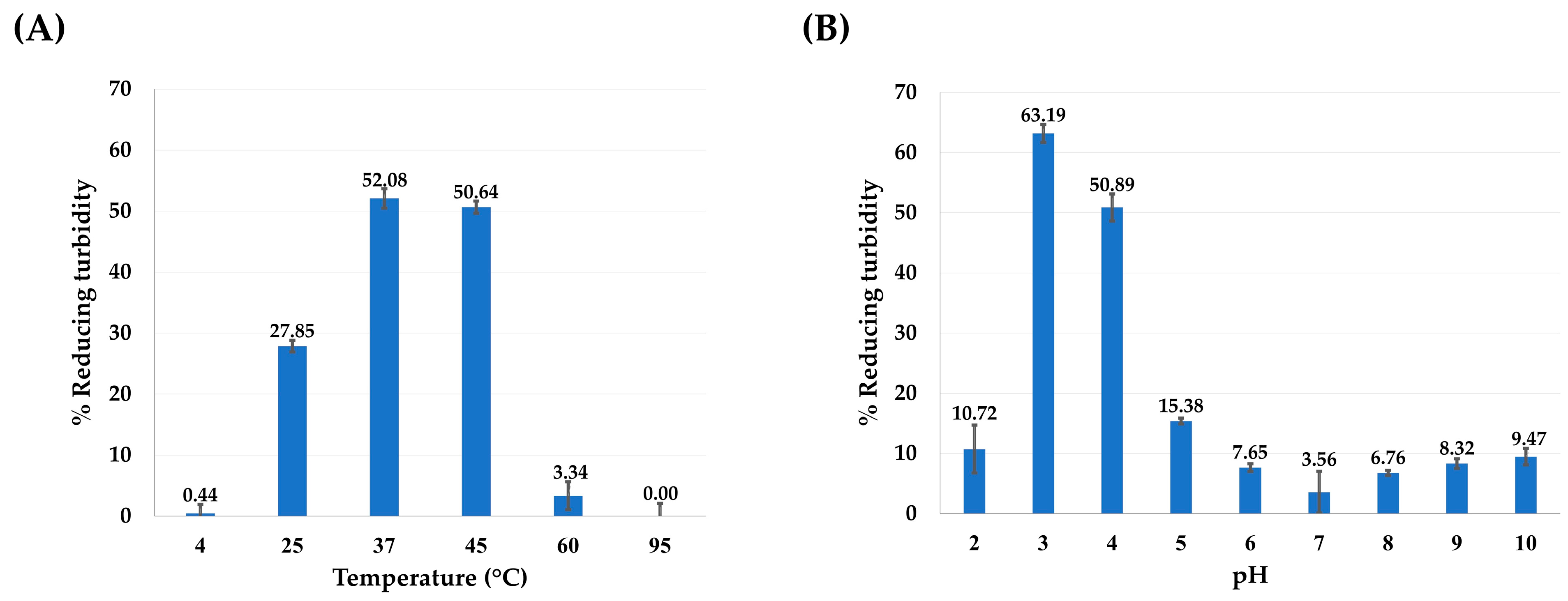
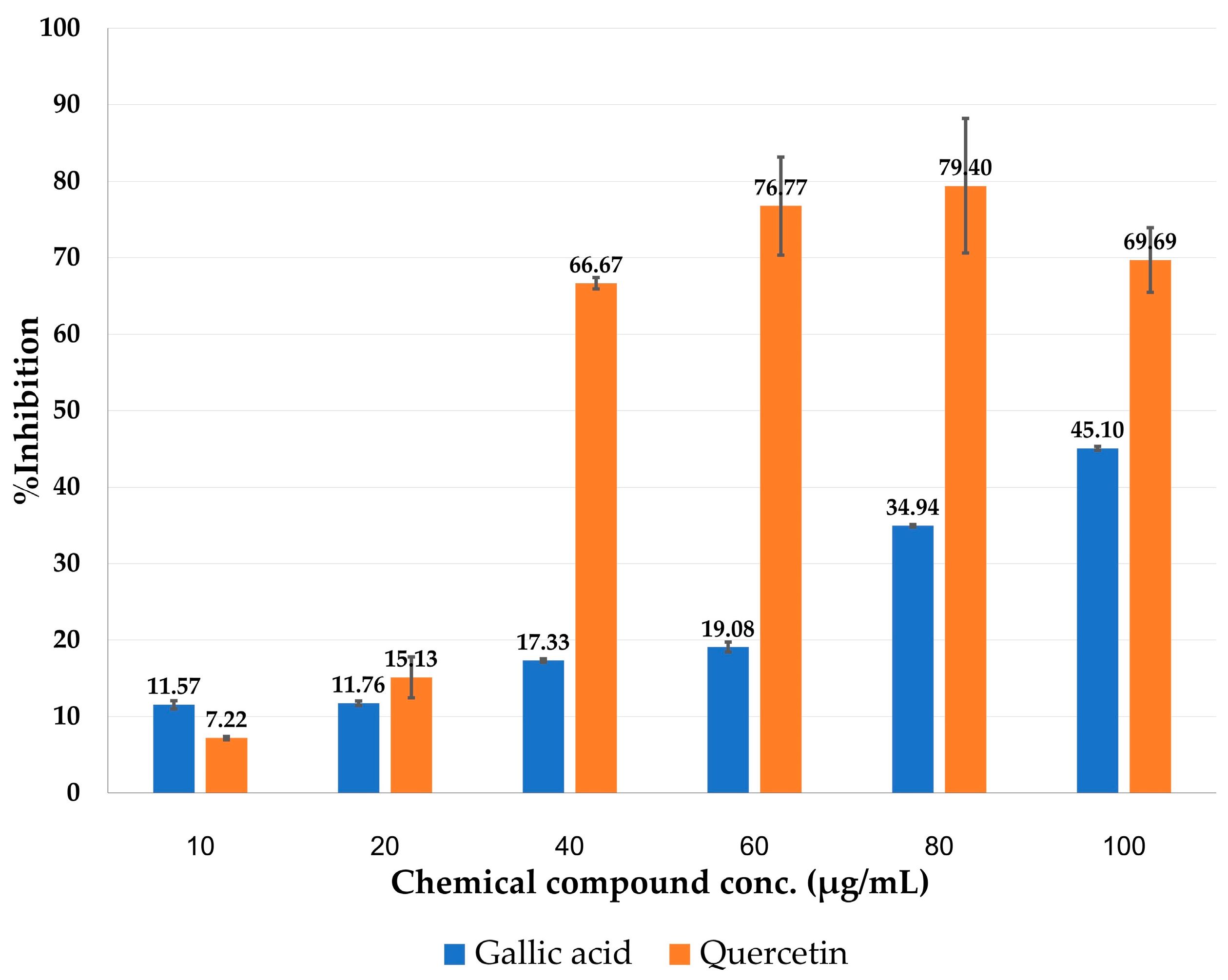
3.3. Hyaluronidase Activity Assay and Molecular Docking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Girish, K.S.; Kemparaju, K. The Magic Glue Hyaluronan and Its Eraser Hyaluronidase: A Biological Overview. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 1921–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimek, M.; Lemr, K.; Hermannová, M.; Havlíček, V. Analysis of Hyaluronan and Its Derivatives Using Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Techniques. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 117014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-safory, N.S.; Fazary, A.E.; Lee, C. Hyaluronidases, a Group of Glycosidases: Current and Future Perspectives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Kumar, V.; Bhatt, D.N.; Irfan, M.; Datta, A. N-Acetylglucosamine Sensing and Metabolic Engineering for Attenuating Human and Plant Pathogens. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, C.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Two Novel Functions of Hyaluronidase from Streptococcus Agalactiae Are Enhanced Intracellular Survival and Inhibition of Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2615–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, G.J.; Derrickson, B. Principles of Anatomy & Physiology, 14th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Seol, D.W.; Joo, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Song, B.S.; Sim, B.W.; Kim, S.U.; Park, S.; Wee, G.; Kim, E. Sperm Hyaluronidase Is Critical to Mammals’ Fertilization for Its Ability to Disperse Cumulus-Oocyte Complex Layer. Asian J. Androl. 2022, 24, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, E.; Hazarika, R.; Singh, P.; Yasir, M.; Shrivastava, R. A Biological Overview of Hyaluronidase: A Venom Enzyme and Its Inhibition with Plants Materials. In Proceedings of the Materials Today: Proceedings; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 5, pp. 6406–6412. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlrab, J.; Wohlrab, D.; Wohlrab, L.; Wohlrab, C.; Wohlrab, A. Use of Hyaluronidase for Pharmacokinetic Increase in Bioavailability of Intracutaneously Applied Substances. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 27, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H. Hyaluronidase: An Overview of Its Properties, Applications, and Side Effects. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2020, 47, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumurthy, K.; Kaliyamoorthy, K.; Kandasamy, K.; Ponnuvel, M.; Viyakarn, V.; Chavanich, S.; Dufossé, L. Antioxidant and Anti-Breast Cancer Properties of Hyaluronidase from Marine Staphylococcus Aureus (CASMTK1). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Kundu, A.; Hageman, M.; Lou, H.; Boisvert, D. Monoclonal Antibody and Protein Therapeutic Formulations for Subcutaneous Delivery: High-Concentration, Low-Volume vs. Low-Concentration, High-Volume. MAbs 2023, 15, 2285277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duco, M.R.; Murdock, J.L.; Reeves, D.J. Trastuzumab/Hyaluronidase-Oysk: A New Option for Patients With HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Ann. Pharmacother. 2020, 54, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordon, K.C.F.; Wiezel, G.A.; Amorim, F.G.; Arantes, E.C. Arthropod Venom Hyaluronidases: Biochemical Properties and Potential Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Gao, R.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Isolation and Characterization of a Hyaluronidase from the Venom of Chinese Red Scorpion Buthus Martensi. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 148, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhren, B.A.; Schrumpf, H.; Hoff, N.P.; Bölke, E.; Hilton, S.; Gerber, P.A. Hyaluronidase: From Clinical Applications to Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2016, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalczyk, M.; Humeniuk, E.; Adamczuk, G.; Korga-Plewko, A. Hyaluronic Acid as a Modern Approach in Anticancer Therapy-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungsa, P.; Incamnoi, P.; Sukprasert, S.; Uawonggul, N.; Klaynongsruang, S.; Daduang, J.; Patramanon, R.; Roytrakul, S.; Daduang, S. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Two Wasps Venom, Vespa Tropica and Vespa Affinis. Toxicon 2016, 119, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungsa, P.; Incamnoi, P.; Sukprasert, S.; Uawonggul, N.; Klaynongsruang, S.; Daduang, J.; Patramanon, R.; Roytrakul, S.; Daduang, S. Cloning, Structural Modelling and Characterization of VesT2s, a Wasp Venom Hyaluronidase (HAase) from Vespa Tropica. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo Jacomini, D.L.; Gomes Moreira, S.M.; Campos Pereira, F.D.; Zollner, R.D.L.; Brochetto Braga, M.R. Reactivity of IgE to the Allergen Hyaluronidase from Polybia Paulista (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) Venom. Toxicon 2014, 82, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungsa, P.; Janpan, P.; Saengkun, Y.; Jangpromma, N.; Klaynongsruang, S.; Patramanon, R.; Uawonggul, N.; Daduang, J.; Daduang, S. Heterologous Expression and Mutagenesis of Recombinant Vespa Affinis Hyaluronidase Protein (RVesA2). J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, G.D.; Emmerstorfer-Augustin, A.; Biundo, A.; Pisano, I.; Coccetti, P.; Mapelli, V.; Camattari, A. Industrial Production of Proteins with Pichia Pastoris—Komagataella Phaffii. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei, M.; Rezaee, S.A.; Farsiani, H. Pichia Pastoris: A Highly Successful Expression System for Optimal Synthesis of Heterologous Proteins. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5867–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, D.A.; Gasser, B.; Zanghellini, J.; Steiger, M.G.; Mattanovich, D. Metabolic Engineering of Pichia Pastoris. Metab. Eng. 2018, 50, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ata, Ö.; Ergün, B.G.; Fickers, P.; Heistinger, L.; Mattanovich, D.; Rebnegger, C.; Gasser, B. What Makes Komagataella Phaffii Non-Conventional? FEMS Yeast Res. 2021, 21, foab059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidijala, L.; Uthoff, S.; Kampen, S.J.; Steinbüchel, A.; Verhaert, R.M.D. Presence of Protein Production Enhancers Results in Significantly Higher Methanol-Induced Protein Production in Pichia Pastoris. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Hirz, M.; Pichler, H.; Schwab, H. Protein Expression in Pichia Pastoris: Recent Achievements and Perspectives for Heterologous Protein Production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5301–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cai, P.; Yao, L.; Zhou, Y.J. Genetic Tools for Metabolic Engineering of Pichia Pastoris. Eng. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzhans, J.P.; Wibberg, D.; Winkler, A.; Luttermann, T.; Kalinowski, J.; Friehs, K. Integration Event Induced Changes in Recombinant Protein Productivity in Pichia Pastoris Discovered by Whole Genome Sequencing and Derived Vector Optimization. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschmanová, H.; Weninger, A.; Knejzlík, Z.; Melzoch, K.; Kovar, K. Engineering of the Unfolded Protein Response Pathway in Pichia Pastoris: Enhancing Production of Secreted Recombinant Proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4397–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoman, B.; Grünwald-Gruber, C.; Schmelzer, B.; Zavec, D.; Gasser, B.; Altmann, F.; Mattanovich, D. The Degree and Length of O-Glycosylation of Recombinant Proteins Produced in Pichia Pastoris Depends on the Nature of the Protein and the Process Type. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 16, e2000266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitinger, S.; Boroviak, T.; Laschober, G.T.; Fehrer, C.; Müllegger, J.; Lindner, H.; Lepperdinger, G. High-Yield Recombinant Expression of the Extremophile Enzyme, Bee Hyaluronidase in Pichia Pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 57, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, F.G.; Boldrini-França, J.; de Castro Figueiredo Bordon, K.; Cardoso, I.A.; De Pauw, E.; Quinton, L.; Kashima, S.; Arantes, E.C. Heterologous Expression of RTsHyal-1: The First Recombinant Hyaluronidase of Scorpion Venom Produced in Pichia Pastoris System. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3145–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced Production of Leech Hyaluronidase by Optimizing Secretion and Cultivation in Pichia Pastoris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prielhofer, R.; Barrero, J.J.; Steuer, S.; Gassler, T.; Zahrl, R.; Baumann, K.; Sauer, M.; Mattanovich, D.; Gasser, B.; Marx, H. GoldenPiCS: A Golden Gate-Derived Modular Cloning System for Applied Synthetic Biology in the Yeast Pichia Pastoris. BMC Syst. Biol. 2017, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavec, D.; Gasser, B.; Mattanovich, D. Characterization of Methanol Utilization Negative Pichia Pastoris for Secreted Protein Production: New Cultivation Strategies for Current and Future Applications. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębalski, J.; Graczyk, F.; Załuski, D. Paving the Way towards Effective Plant-Based Inhibitors of Hyaluronidase and Tyrosinase: A Critical Review on a Structure–Activity Relationship. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 1120–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo Jacomini, D.L.; Campos Pereira, F.D.; Aparecido dos Santos Pinto, J.R.; dos Santos, L.D.; da Silva Neto, A.J.; Giratto, D.T.; Palma, M.S.; de Lima Zollner, R.; Brochetto Braga, M.R. Hyaluronidase from the Venom of the Social Wasp Polybia Paulista (Hymenoptera, Vespidae): Cloning, Structural Modeling, Purification, and Immunological Analysis. Toxicon 2013, 64, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković-Housley, Z.; Miglierini, G.; Soldatova, L.; Rizkallah, P.J.; Müller, U.; Schirmer, T. Crystal Structure of Hyaluronidase, a Major Allergen of Bee Venom. Structure 2000, 8, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, S.; Schrumpf, H.; Buhren, B.A.; Bölke, E.; Gerber, P.A. Hyaluronidase Injection for the Treatment of Eyelid Edema: A Retrospective Analysis of 20 Patients. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2014, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heistinger, L.; Gasser, B.; Mattanovich, D. Microbe Profile: Komagataella Phaffii: A Methanol Devouring Biotech Yeast Formerly Known as Pichia Pastoris. Microbiology 2020, 166, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Fang, H. Current Advances of Pichia Pastoris as Cell Factories for Production of Recombinant Proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1059777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Lu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Y. The α-Mating Factor Secretion Signals and Endogenous Signal Peptides for Recombinant Protein Secretion in Komagataella Phaffii. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2022, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaoglan, M.; Yildiz, H.; Inan, M. Screening of Signal Sequences for Extracellular Production of Aspergillus Niger Xylanase in Pichia Pastoris. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 92, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bharadwaj, A.G.; Casper, A.; Barkley, J.; Barycki, J.J.; Simpson, M.A. Hyaluronidase Activity of Human Hyal1 Requires Active Site Acidic and Tyrosine Residues. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9433–9442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterham, H.R.; Digan, M.E.; Koutz, P.J.; Lair, S.V.; Cregg, J.M.; Bernardi, A. Isolation of the Pichia Pastoris Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene and Regulation and Use of Its Promoter. Gene 1997, 186, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, G.; Ahmad, A.; Zhang, Z. Bioprocess Engineering Aspects of Heterologous Protein Production in Pichia Pastoris: A Review. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 64, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Hsiung, H.A.; Hong, K.L.; Huang, C.T. Enhancing the Efficiency of the Pichia Pastoris AOX1 Promoter via the Synthetic Positive Feedback Circuit of Transcription Factor Mxr1. BMC Biotechnol. 2018, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Tu, T.; Huai, Q.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Shi, Z.; Ding, J. Enhancing Monellin Production by Pichia Pastoris at Low Cell Induction Concentration via Effectively Regulating Methanol Metabolism Patterns and Energy Utilization Efficiency. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anane, E.; van Rensburg, E.; Görgens, J.F. Comparison of Constitutive and Inducible β-Fructofuranosidase Production by Recombinant Pichia Pastoris in Fed-Batch Culture Using Defined and Semi-Defined Media. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 22, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Lin, J.C.; Chieng, L.L.; Lee, C.K.; Hsu, T.A. Combined Use of GAP and AOX1 Promoter to Enhance the Expression of Human Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor in Pichia Pastoris. In Proceedings of the Enzyme and Microbial Technology; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 33, pp. 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Huang, S.; Kaleem, I.; Li, C. N-Glycosylation Enhances Functional and Structural Stability of Recombinant β-Glucuronidase Expressed in Pichia Pastoris. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 164, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagar, V.K.; Babbal; Mohanty, S.; Khasa, Y.P. Effect of N-Glycosylation on Secretion, Stability, and Biological Activity of Recombinant Human Interleukin-3 (HIL-3) in Pichia Pastoris. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, F.; Han, S. Reinforcement Strategies of Chassis Cell Secretory Pathway for Improving Heterologous Protein Production. Microbe 2024, 3, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Tsumura, H.; Komeda, T.; Mori, E.; Motoki, K.; Kataoka, S.; Chiba, Y.; Jigami, Y. Antibody Expression in Protease-Deficient Strains of the Methylotrophic Yeast Ogataea Minuta. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007, 7, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenormand, H.; Deschrevel, B.; Vincent, J.C. PH Effects on the Hyaluronan Hydrolysis Catalysed by Hyaluronidase in the Presence of Proteins: Part I. Dual Aspect of the PH-Dependence. Matrix Biol. 2010, 29, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaighofer, A.; Ablasser, S.; Lux, L.; Kopp, J.; Herwig, C.; Spadiut, O.; Lendl, B.; Slouka, C. Production of Active Recombinant Hyaluronidase Inclusion Bodies from Apis Mellifera in e. Coli Bl21(De3) and Characterization by Ft-Ir Spectroscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofinger, E.S.A.; Spickenreither, M.; Oschmann, J.; Bernhardt, G.; Rudolph, R.; Buschauer, A. Recombinant Human Hyaluronidase Hyal-1: Insect Cells versus Escherichia Coli as Expression System and Identification of Low Molecular Weight Inhibitors. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, G.H. Evaluation of Antioxidant and Inhibitory Activities for Different Subclasses Flavonoids on Enzymes for Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, H212–H217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| F_VesT2a | GATCGGTCTCGTCAGAAAGGCCCAAAAGAGTGTTTAACATTTACTG | VesT2a gene |
| R_VesT2a | GATCGGTCTCCAAGCCTATTAGTGATGGTGGTGGTGATGTCCAC | VesT2a gene |
| F_SDM | GGCGTGATAGACTTCGAAAGATGGC | Gene mutation ** |
| R_SDM | ACGCCATCTTTCGAAGTCTATCACG | Gene mutation ** |
| F_BB1 | CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC | Sequencing |
| R_BB1 | GTAAAACGACGGCCAGTT | Sequencing |
| F_AOX1 | CTTTCATAATTGCGACTGGTTC | Sequencing |
| F_GAP | ACCAGAATCGAATATAAA | Sequencing |
| R_BB3 | CGAGCGTCCCAAAACC | Sequencing |
| 5′AOX1 | GACTGGTTCCAATTGACAAGC | Gene integration |
| 3′AOX1 | GCAAATGGCATTCTGACATCC | Gene integration |
| Plasmid DNA Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| eBB1_Fs-23 | Empty vector of backbone 1 (eBB1) |
| BB1_12_pGAP | Constitutive promoter |
| BB1_12_pAOX1 | Inducible promoter |
| BB1_34_ScCYC1tt | Terminator |
| edBB3aZ_Fs-14 | Empty vector of direct backbone 3 (edBB3) |
| Construction | Promoter | Terminator | Protein Conc. (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VesT2a + GG-6xHis tag | PGAP | ScCYC1tt | 8.91 |
| VesT2a + GG-6xHis tag | PAOX1 | ScCYC1tt | 19.23 (2.16-folds) |
| Crude Venom | VesT2a (E. coli) | VesT2a (P. pastoris) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific activity (U/mg) | 89.25 ± 4.15 | 28.46 ± 0.71 | 4238.37 ± 135.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janpan, P.; Schmelzer, B.; Klamrak, A.; Tastub, P.; Upathanpreecha, T.; Rahman, S.S.; Nabnueangsap, J.; Saengkun, Y.; Rungsa, P.; Mattanovich, D.; et al. Production of Vespa tropica Hyaluronidase by Pichia pastoris. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120854
Janpan P, Schmelzer B, Klamrak A, Tastub P, Upathanpreecha T, Rahman SS, Nabnueangsap J, Saengkun Y, Rungsa P, Mattanovich D, et al. Production of Vespa tropica Hyaluronidase by Pichia pastoris. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(12):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120854
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanpan, Piyapon, Bernhard Schmelzer, Anuwatchakij Klamrak, Patthana Tastub, Tewa Upathanpreecha, Shaikh Shahinur Rahman, Jaran Nabnueangsap, Yutthakan Saengkun, Prapenpuksiri Rungsa, Diethard Mattanovich, and et al. 2024. "Production of Vespa tropica Hyaluronidase by Pichia pastoris" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 12: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120854
APA StyleJanpan, P., Schmelzer, B., Klamrak, A., Tastub, P., Upathanpreecha, T., Rahman, S. S., Nabnueangsap, J., Saengkun, Y., Rungsa, P., Mattanovich, D., & Daduang, S. (2024). Production of Vespa tropica Hyaluronidase by Pichia pastoris. Journal of Fungi, 10(12), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120854






